HESI A2 V2 (Re-take)
$ 17

OCR GCSE Combined Science B Twenty First Century Science J260/01: Biology (Foundation Tier) General Certificate of Secondary Education Mark Scheme for June 2022
$ 5.5

[eBook] [PDF] Handbook of Water Harvesting and Conservation 1st Edition By Eslamian, Faezeh A._Eslamian, Sa
$ 30

ATI RN VATI COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR 2024/2025 FORM A
$ 8

AQA A-level CHEMISTRY 7405/1 Paper 1 Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Mark scheme June 2022 Version: 1.0 Final MS
$ 10

[eBook] [PDF] Radiographic Positioning and Related Anatomy 11th Edition By John Lampignano, Leslie Kendrick
$ 30

Case Notes Answers A POPULAR HR CHIEF BURNED TO DEATH PEOPLE MANAGEMENT DYNAMICS AT THE INDIAN SUBSIDIARY OF Suzuki Ltd
$ 45

FLORIDA FUNERAL LAWS AND RULES EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECTS
$ 6

Hesi_A2_Reading WITH ANSWERS
$ 13

Sterile Processing - Final Exam, IAHCSMM CENTRAL SUPPLY STUDY GUIDE, Sterile Processing Study Material for Certification Exam
$ 10

Kennesaw Mountain High SchoolSCIENCE 101Graphing Practice
$ 11

MGT 605 / MGT605 QUIZ 2 LATEST VERSION (VERIFIED ANSWERS GRADED A+)
$ 10.5

eBook [PDF] Gilbert Law Summaries on Torts 25th Edition By Marc A. Franklin, W. Jonathan Cardi, Michael D. Green
$ 30

Hesi rn exit exam 2025
$ 20
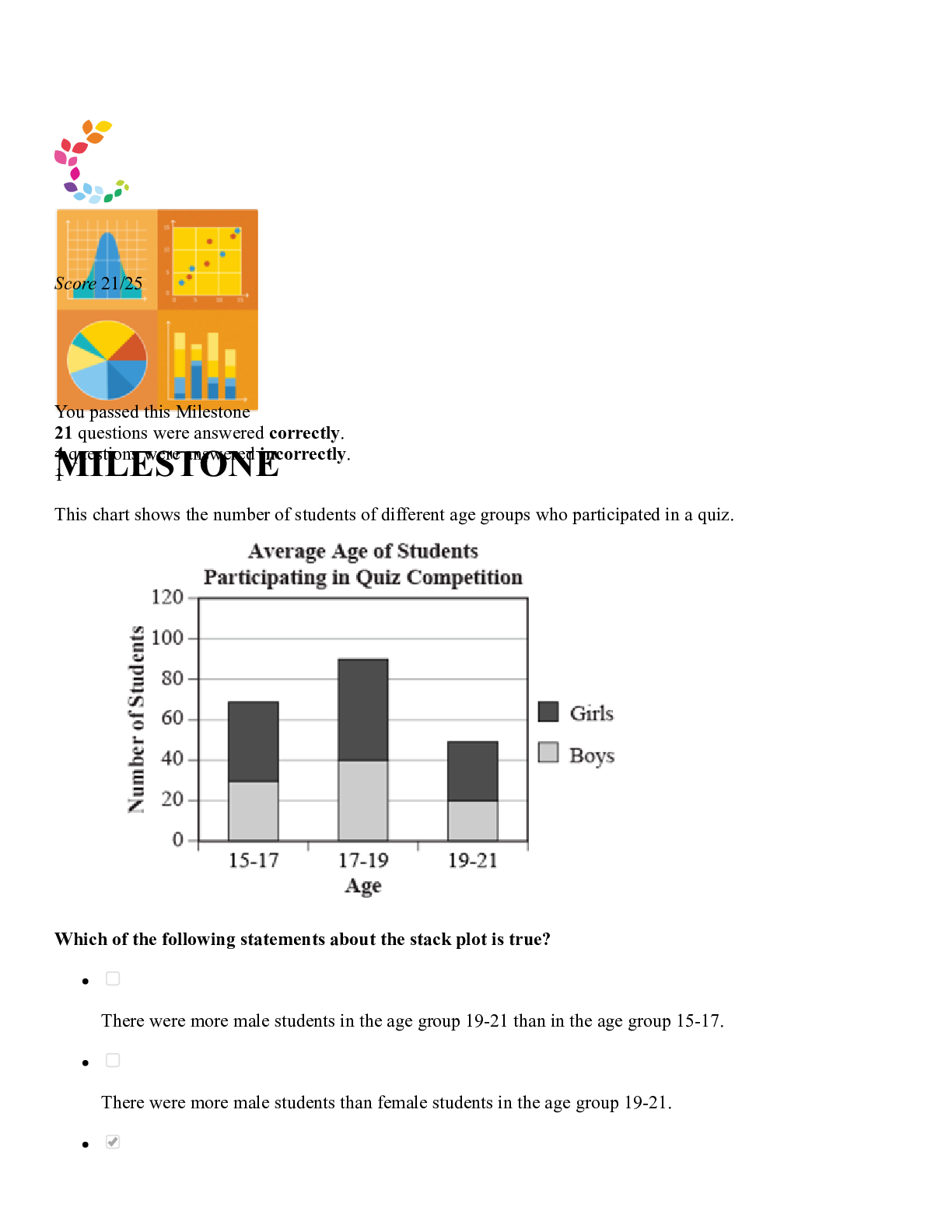
Sophia Statistics Final Milestone 2023
$ 10

PEDS ATI PROCTORED STUDY NOTES WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS
$ 15

Sophia College Algebra Unit 3 Milestone 3
$ 9
Rearfoot and forefoot procedures ABFAS certification material
$ 11

BEST REVIEW WGU C493 LEADERSHIP & PROFESSIONAL IMAGE_PASSED NO REVISIONS-PORTFOLIO
$ 23.5

Solution Manul For Survey of Operating Systems Release 2025 By Jane Holcombe and Charles Holcombe
$ 19
PHIL 1404 Final Exam | 50 Questions with 100% Correct Answers | University of the People
$ 15

MED-SURG PART A. The most frequently tested. 90 Questions and Answers. STUDY THIS TO SCORE AN A
$ 13

Pediatric Nursing Chapter 23 / Cardiac Disorders / 2025 NCLEX Update / Test Bank with Answers & Rationales
$ 13

eBook The Theory of Chinese Modernization 2025th Edition By Zhongmin Wu, YU Jianping, HE Jun
$ 30

D630 TASK 3 UPDATED STUDY GUIDE 2025
$ 15

MGT 498 Study Guide
$ 12.5

Avery's Neonatology Board Review: Certification and Clinical Refresher 1st Edition eBook Pdf file.
$ 29
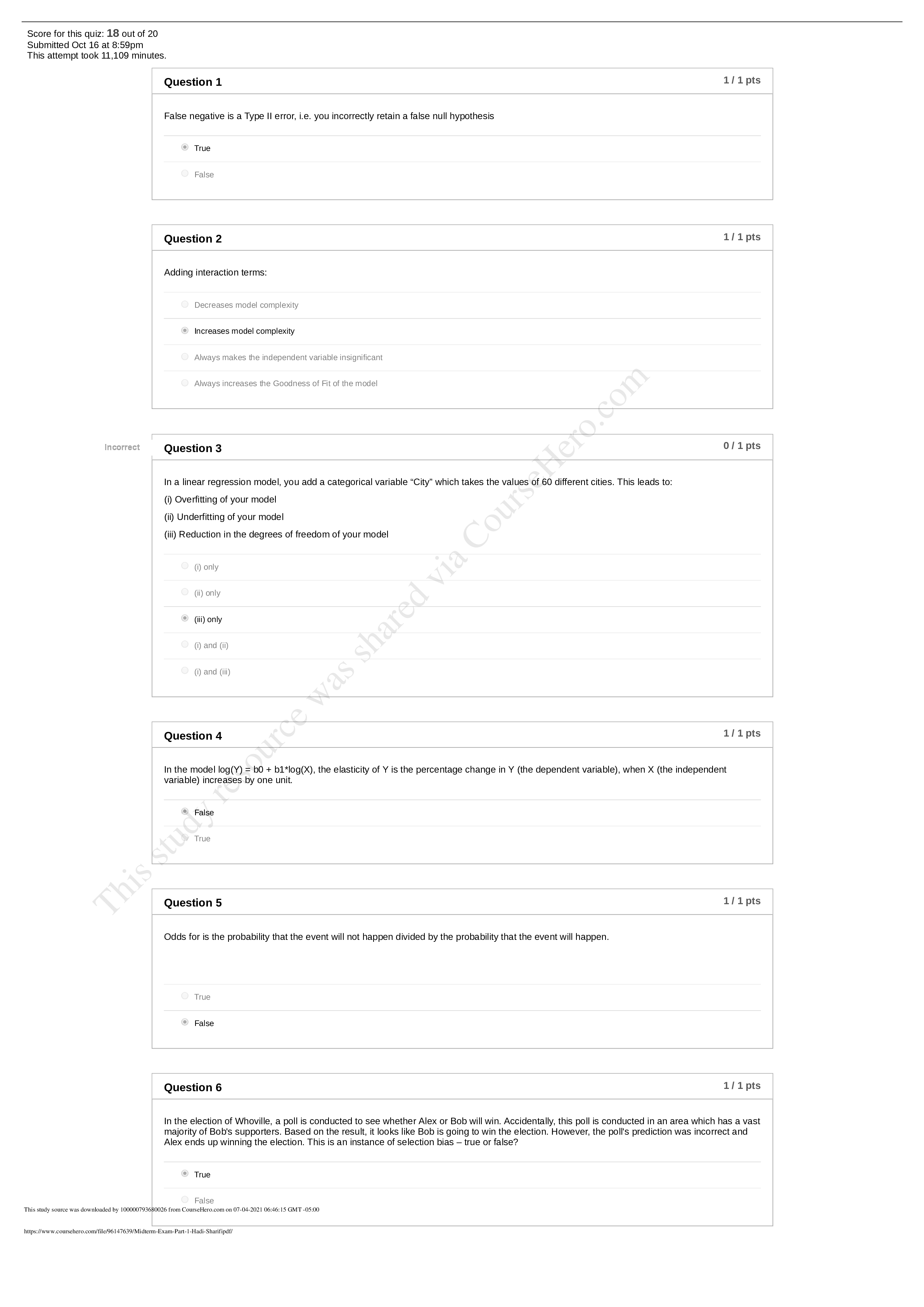
Georgia Institute Of Technology MGT 6203 Midterm Exam_ Part 1_ Hadi Sharifi
$ 9
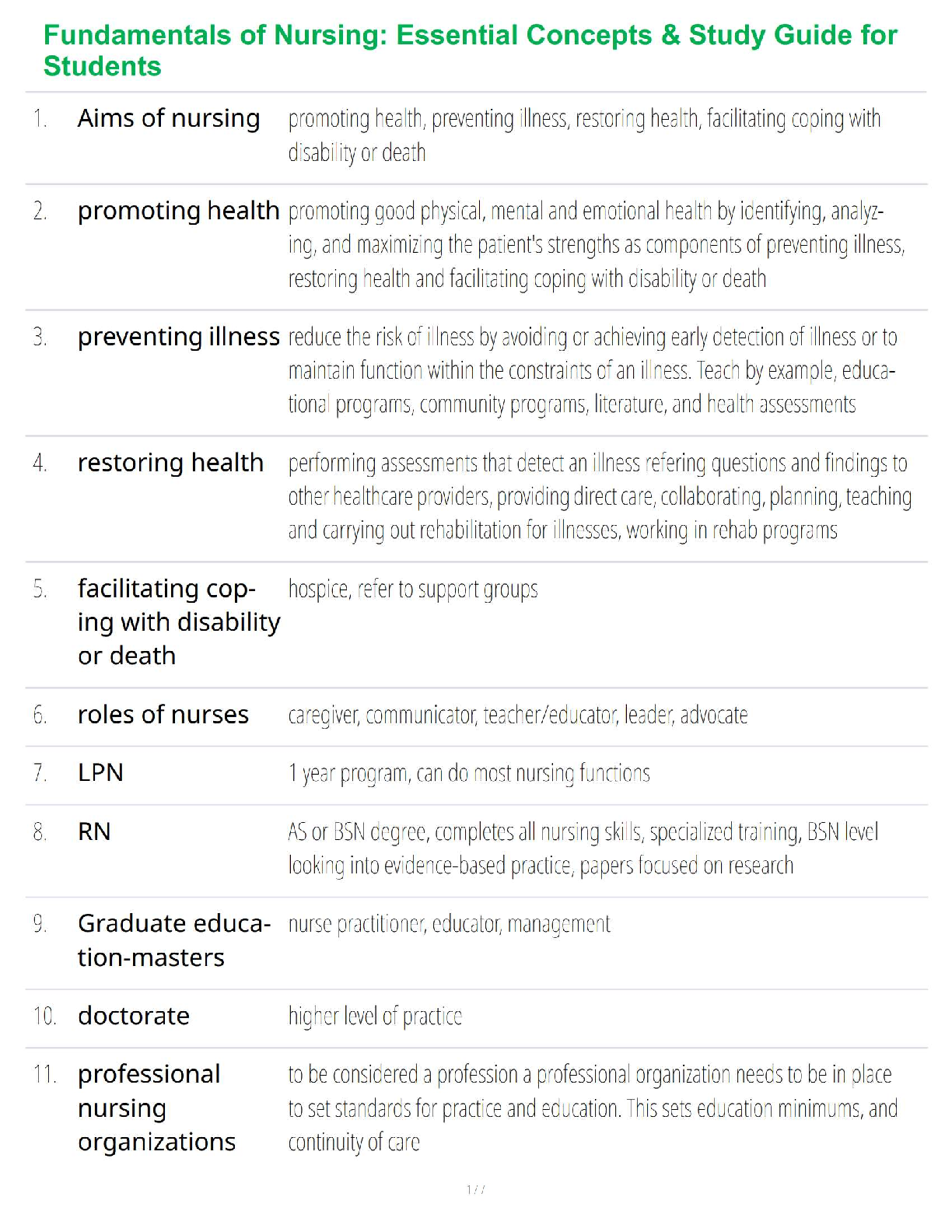
Fundamentals of Nursing: Essential Concepts & Study Guide for Students
$ 15

An Introduction to Management Science Quantitative Approach to Decision Making 12th Edition by Anderson, Sweeney, Williams | Chapters 1-21 | TEST BANK
$ 19

RN ATI PHARMACOLOGY form C 2019
$ 12

HSM 410 Week 3 Assignment: Healthcare Interview Paper (GRADED A)
$ 8
.png)
LETRS Module 2 test latest 2022 already passed
$ 6

Test Bank for Governmental and Nonprofit Accounting, 11th Edition by Freeman, McSwain [Includes Excel SpreadSheet Solutions]
$ 26

NR 304 Week 4 Musculoskeleton Review Questions with correct answers/NCLEX – Review Questions – Chapter 22 Assessment Performance
$ 10

AQA AS Accounting 7126 Analysis and evaluation of financial information Answers and Commentaries. 2021 Assessment Resources
$ 7

Georgia Adjuster Exam| 137 QUESTIONS| COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 6

ATI NCLEX UR 101 NCSBN_TEST BANK FOR THE NCLEX-RN&NCLEXPN.GRADED
$ 13.5

CIVICS EXAM 2022- PRACTICE TESTS 1 & 2 NEW 2022 EXAM STUDY GUIDE
$ 8.5

Summary 1ZM31 Multivariate Data Analysis by Hair 2- 2023
$ 6
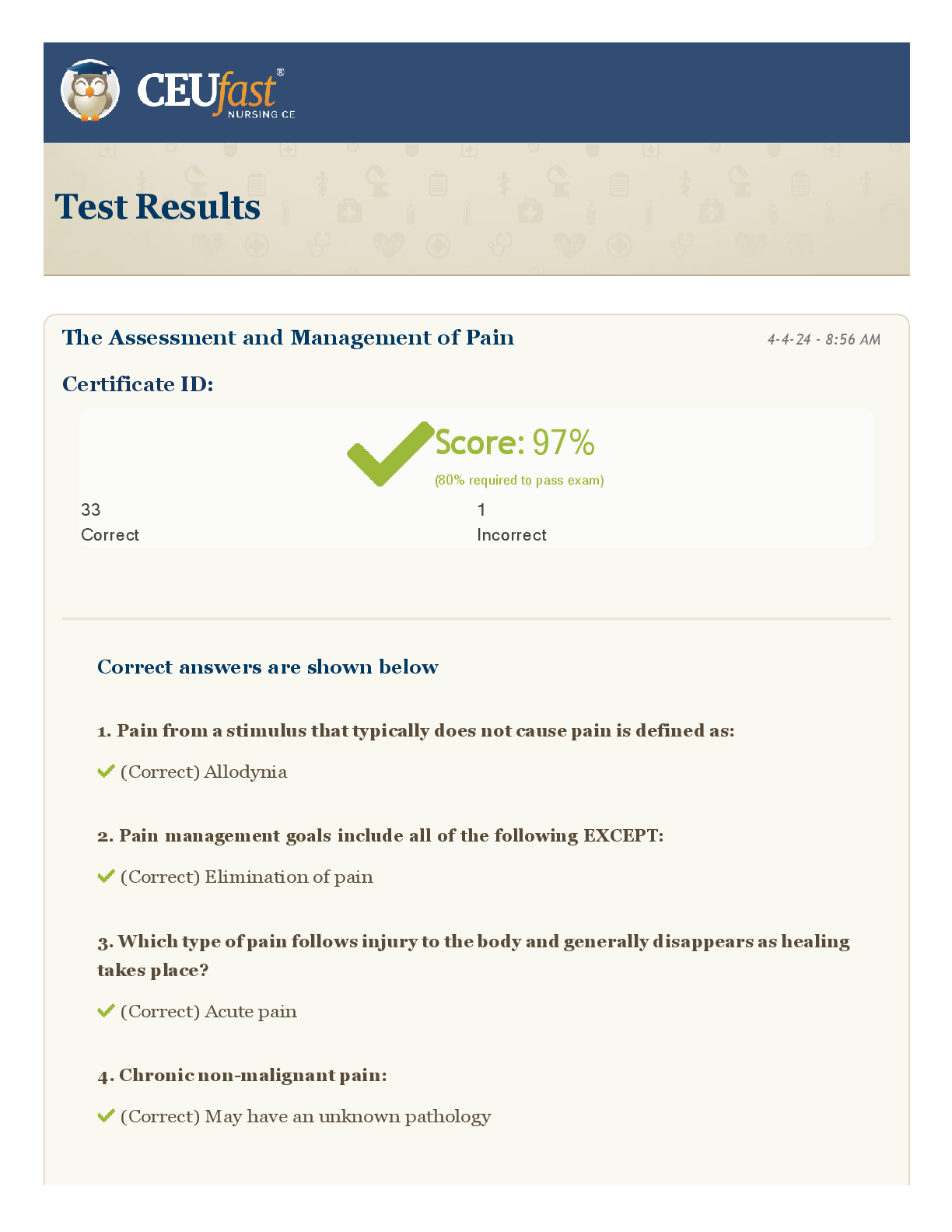
CEUFast - Test Results_ The Assessment and Management of Pain- New Generation
$ 19.5

MANAGEMENT 39205-CHAPTER 5: Sourcing Human Resources for Global Markets – Staffing, Recruitment and Selection-ALL ANSWERS CORRECT
$ 7

PMK-EE Warfighting and Readiness Exam for E4 Advancement 2023 (GRADED A) Questions and Answer Solutions
$ 9.5

EMT Final Exam Review study guide (Summary)
$ 15
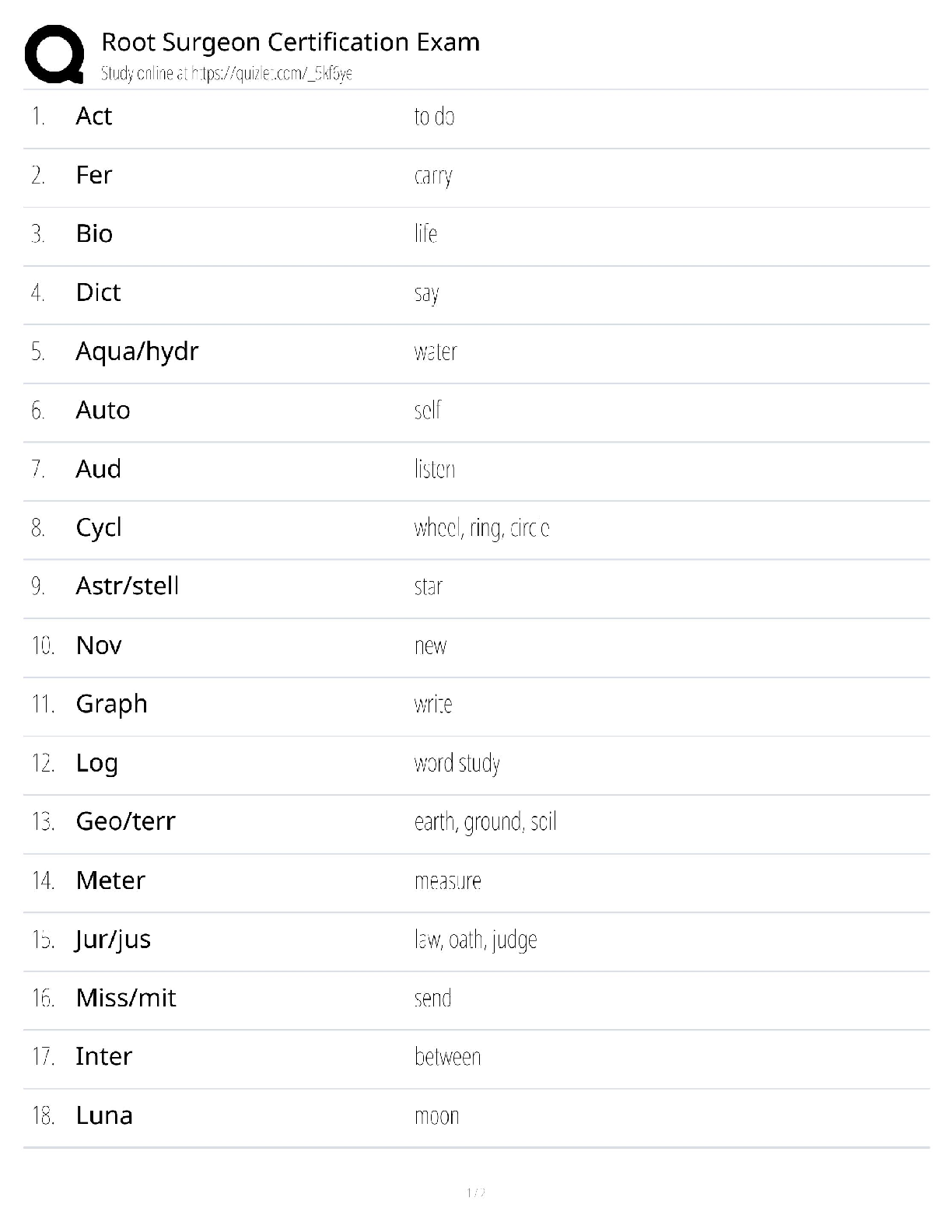
Root Surgeon Certification Exam / RSI Practice Test / 2025 Update / Score 100% Guide
$ 19

ATI_TEAS_6
$ 4

BIOS 251/BIOS251 Anatomy and Physiology I with Lab Week 2 Lab: Protein Denaturation (2022/2023) Chamberlain College of Nursing.
$ 15

WINDOWS Operating Systems
$ 3.5

NUR2212 Final Exam 2025 Complete Mastery Guide — Updated Concepts, Detailed Explanations & Guaranteed Learning Support
$ 8.6
.png)
PMP Class 2 Exam Questions and Answers
$ 3
PDF(eBook) Arthroplasty in Hand Surgery,M.D. Schindele,Stephan F.,Grey Giddins,Bellemre,Philippe,1e
$ 27

CITI Exam Modules 4-6 Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 10

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY FINAL PORTAGE LEARNING TEST EXAM 2025/2026 WITH COMPLETE STUDY QUESTIONS WITH CORRECT VERIFIED ANSWERS 100% GUARANTEED PASS | TOP RATED
$ 13

Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft® Excel®, 7e Anderson, Sweeney, Williams, Camm, Cochran, Fry, Ohlmann (Solution Manual)
$ 20

C773 ITWD 3110 User Interface Design - FA Review 2025 - WGU (Qns & Ans)
$ 12

ADVANCED PATHOPHYSIOLOGY EXAM 4 NEWEST 2025/2026 ACTUAL EXAM 300 QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS WITH RATIONALES
$ 35.5

SCI 228 Week 3 Quiz: Nutrition, Health, and Wellness with Lab (Jan 2020)
$ 12

CITI Module #3 Questions and Answers Latest Update 100% Correct
$ 15

Answer Key For Contemporary Linguistic Analysis An Introduction 9th Edition By William O'Grady Manoa, John Archibald
$ 20

Intermediate Patient Case Results | 6 pages
$ 9

CAPM Exam Study Guide.
$ 7.5
.png)
Strayer University BUS 325 Global Human Resource Management Quiz-REVIEWED BY EXPERTS 2021-GRADED A+
$ 15

University of Missouri MANAGEMENT 3920-CHAPTER 6: International Performance Management Q$A-ALL CORRECT-GRADED A
$ 8

CST Certification Surgical Specialties / General Surgery Guide / 2025 Update / Score 100%
$ 25

Criminal Procedure 1 CMP201-6/ Criminal Procedure 1 : CPR3701 CHAPTER 1 TO 11 CMP201-6 NOTES (University of South Africa)
$ 7.5

Sophia Milestone Unit 2.
$ 12

WGU C836 OA Study Guide (Overly Informative) Questions and Answers Rated A+
$ 15

Case Notes & Answer for OLEUM RESOURCES David Wood by Tom Hansen Jack Hansen
$ 15
.png)
ECIH Practice Assessment (NEW QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS ACTUAL EXAM TRIAL TEST 2022)
$ 9

eBook [PDF] The Oxford Handbook of the Law of Work By Guy Davidov, Brian Langille, Gillian Lester
$ 30

ASVAB Shop information Quiz (30 out 0f 30) Questions and Answer Elaborations
$ 9.5

AQA AS LEVEL MATHS JUNE 2022 PAPER 1 QUESTIONS PAPER
$ 10

I HUMAN CASE STUDY EVALUATION OF DYSPNEA IN A 60 YEARS OLD FEMALE PATIENT WITH SHORTNESS OF BREATH WEEK 7 OF NURS 6512 – ADVANCED HEALTH ASSESSMENT WALDEN UNIVERSITY FINAL DIAGNOSIS: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE INCLUDING SOAP NOTE, HPI, PE, DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
$ 27

iHuman Case Study: James Taylor – 39 Year-Old Male Presenting With Shortness of Breath NB all screenshots available but not well arranged.good luck | Chamberlain university instant pdf download
$ 32.5

Maternal-Newborn-Nursing-Handout
$ 20

eBook PDF Health Law Keyed to Courses Using 9th Edition By Aspen Publishing
$ 20

[eBook][PDF] Introduction to Statistical Methods for Financial Models, 1st Edition By Thomas A Severini
$ 14.5

Solubility Temperature SE Gizmo-CORRECT ANSWERS
$ 12
ESL Certification / Score 100% / 2025 Study Guide & Test Bank
$ 9

FNP 509 Bates’ Guide To Physical Examination and History Taking 13th Edition Bickley Test Bank 2024/25
$ 12.5

TestBank for Heizer Operations Management 9th Edition
$ 18

ati pn peds proctored exam questions and answers.pdf
$ 16

WNSF PII PERSONALLY IDENTIFIABLE INFORMATION (PII) QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 4

ACC 308 7-1 Final Project Submission
$ 7

MATHEMATICS PRACTICE QUESTIONS 2 & 3 NEW GENERATION 2025
$ 21
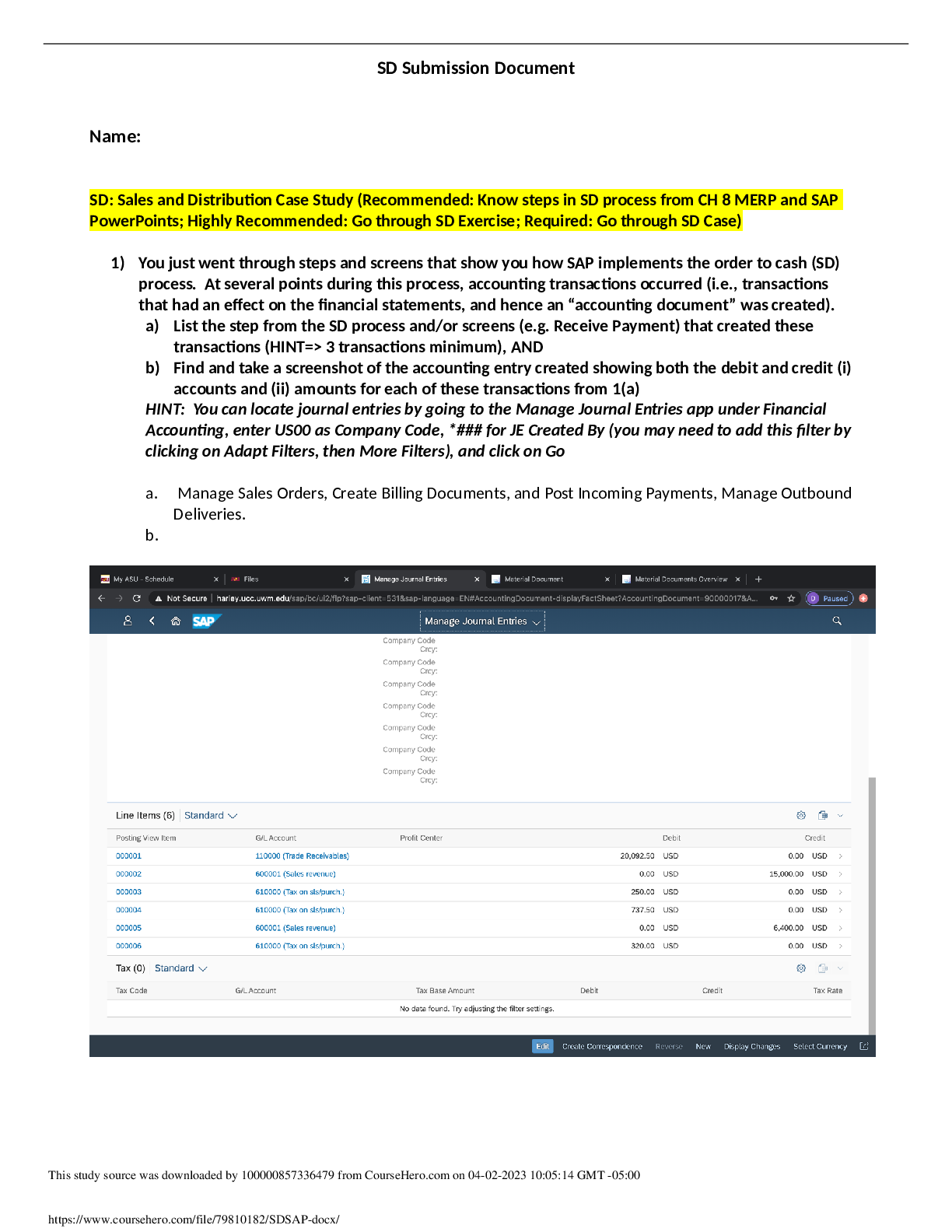
ACC 444 Enterprise Proc Analysis --Sales and Distribution Case Study (Recommended: Know steps in SD process from CH 8 MERP and SAP PowerPoints; Highly Recommended: Go through SD Exercise; Required: Go through SD Case)
$ 8.5

PMT 252 252 Module 2 Exam Results | Defense Acquisition University
$ 5

THE EMERGENCE OF INTERNATIONAL PROPERTY LAW
$ 2.5

2023 HESI EXIT RN EXAM V1-V7 160 TOTAL QUESTIONS EACH VOLUME