Research Methods > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > WGU (C224) Research Foundations Questions and Answers Graded A (All)
WGU (C224) Research Foundations Questions and Answers Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
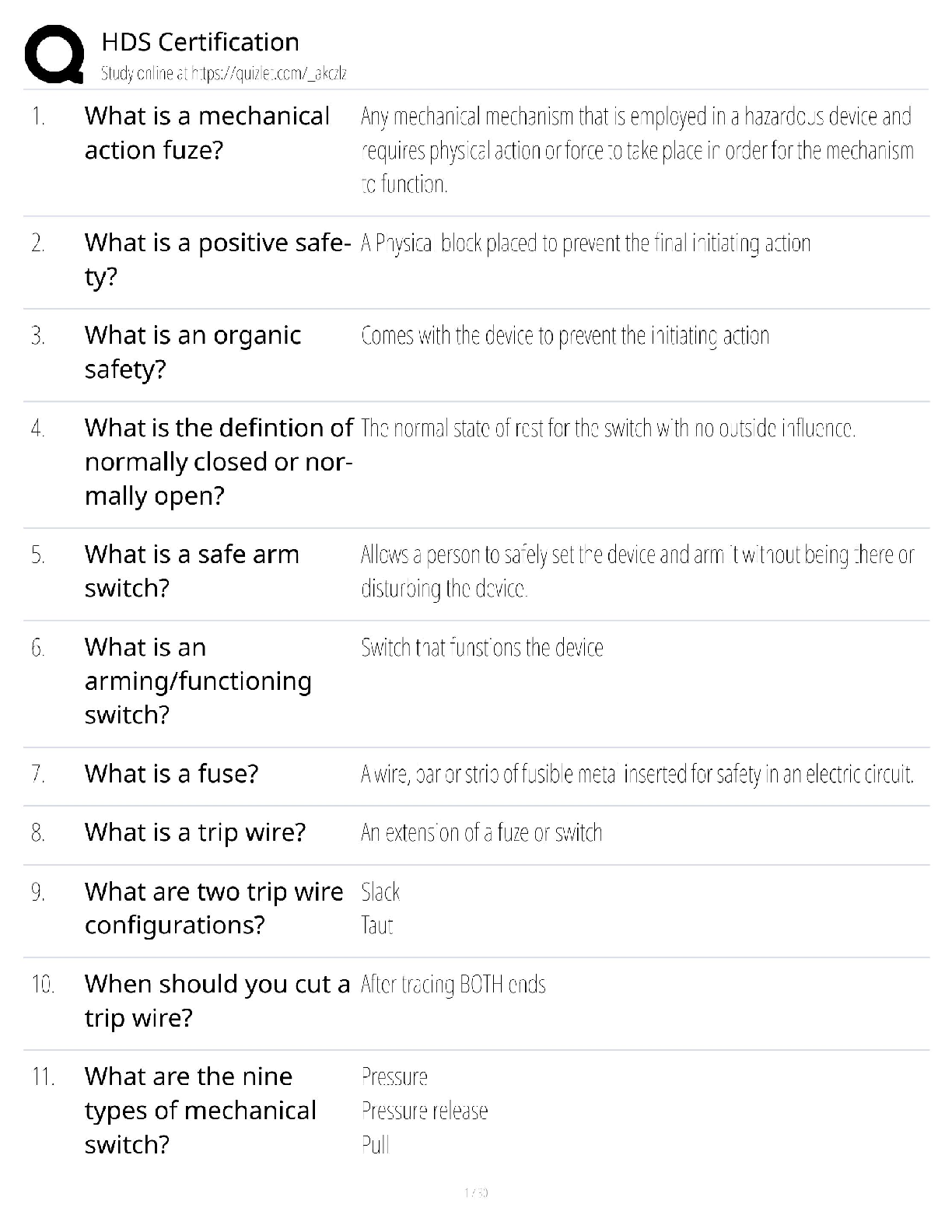
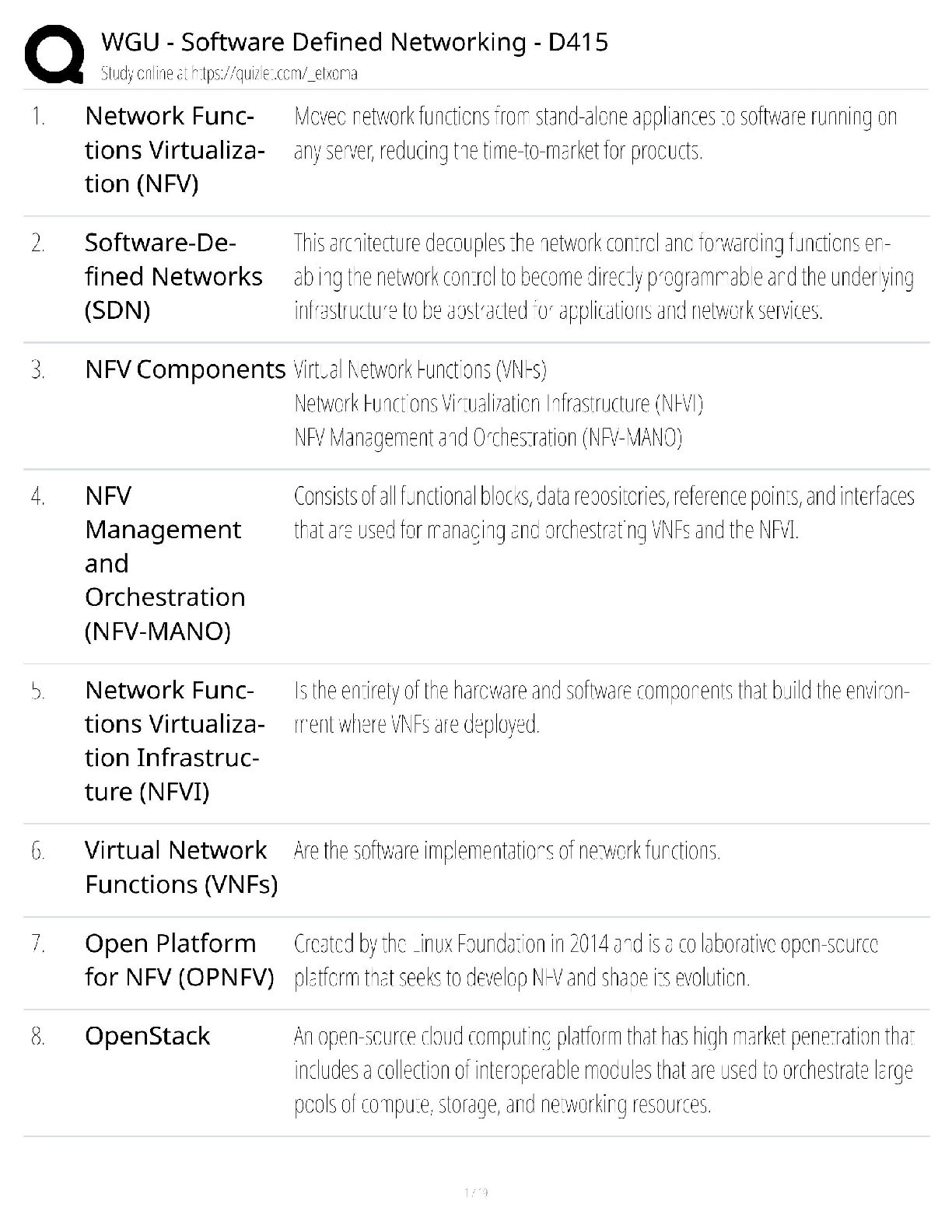
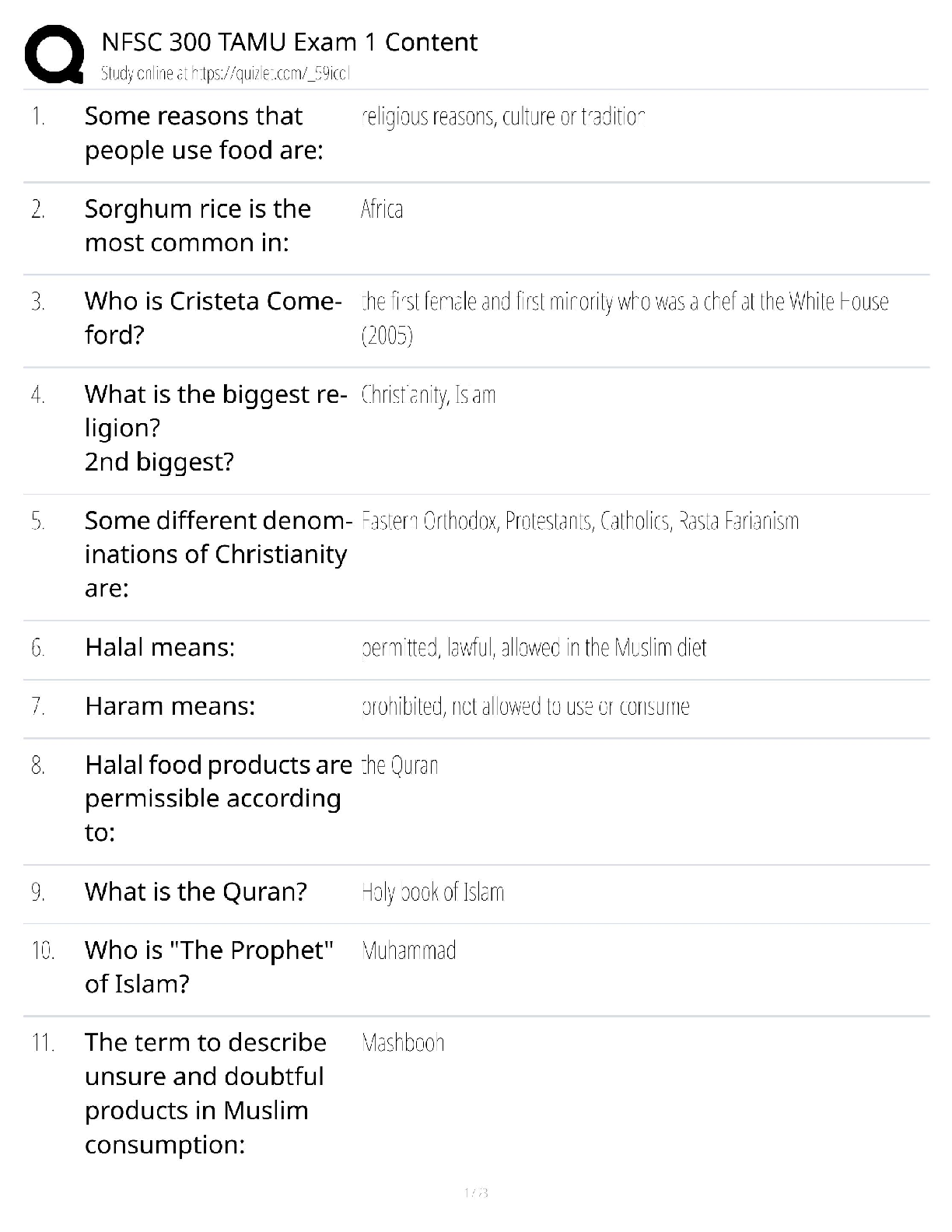
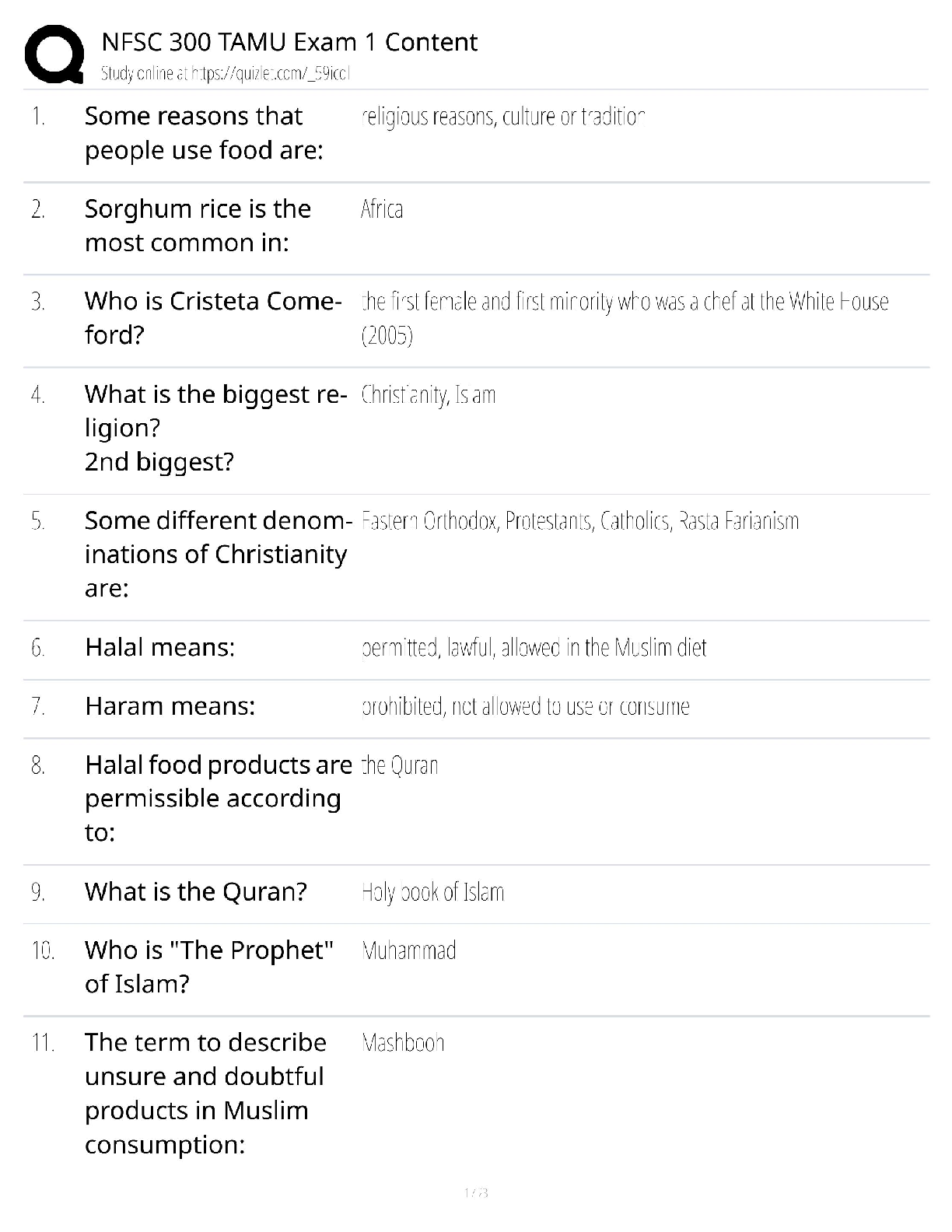
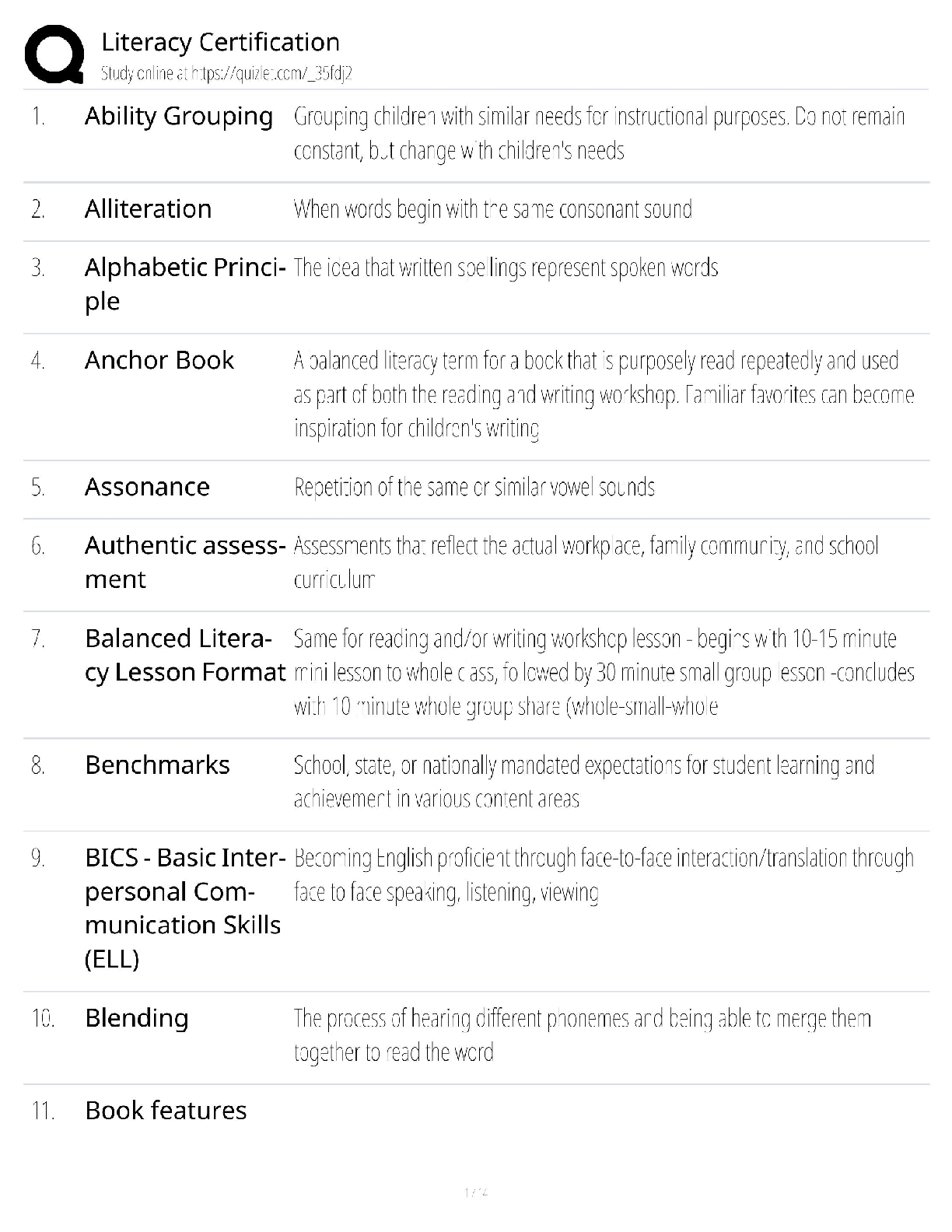
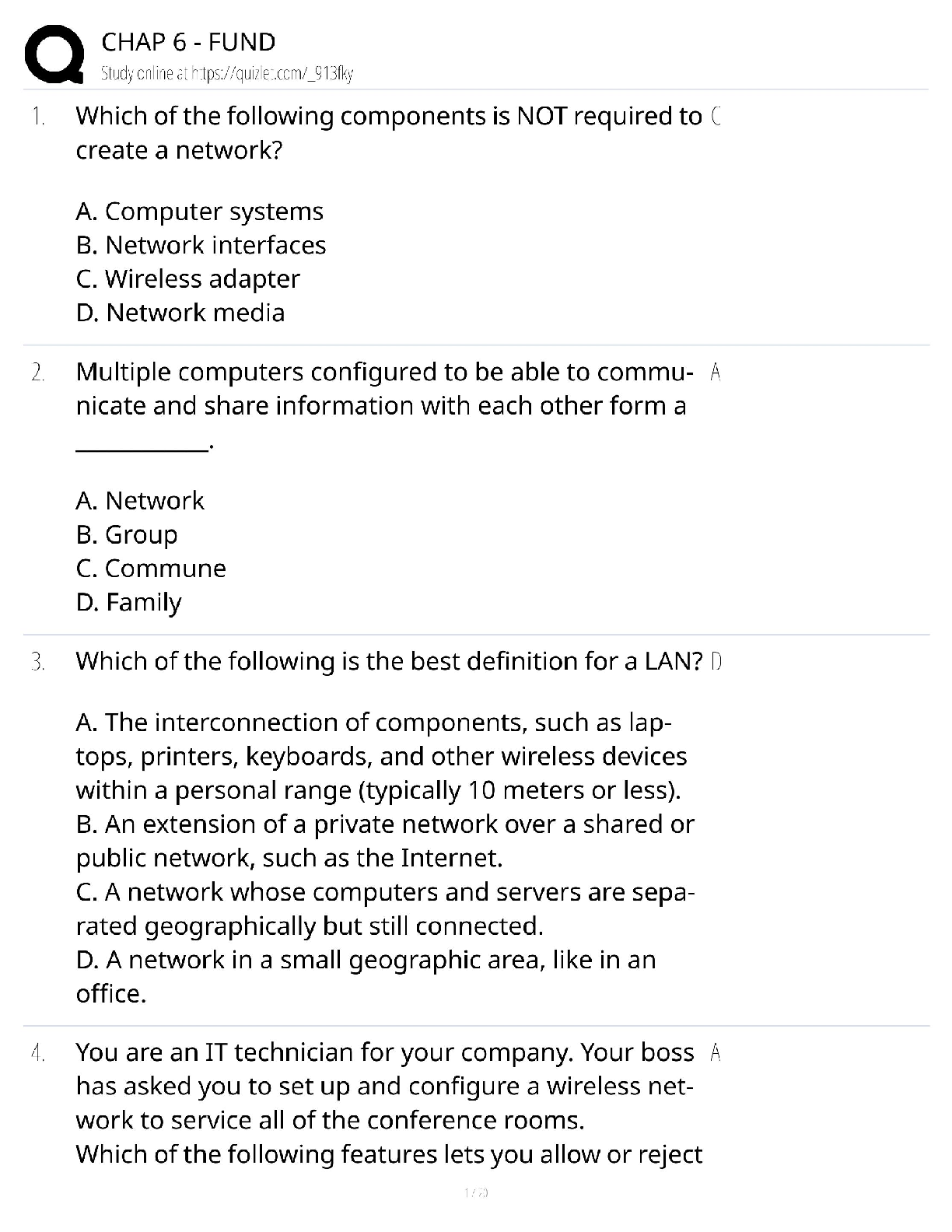
WGU (C224) Research Foundations Questions and Answers Graded A Non-Experimental Research Methods ✔✔Correlation and Casual Comparative Correlation research method ✔✔non-experimantal research ... method. A process to collect data to determine if a relationship exists between two or more quantitative variables, and to what degree. Correlation Coefficient ✔✔Strength and direction of a relationship between two variables. range of +1 to -1 Positive Correlation ✔✔r=+1 (points follow along a line) Negative Correlation ✔✔r=-1 (no correlation is a 0 and looks like a gun shot all over) Variable ✔✔a condition or characteristic that can take on different values or categories (such as age, GPA, gender, etc.) Descriptive Statistics ✔✔Goal is to describe, summarize, or make sense of a particular set of data. Inferential Statistics ✔✔where researchers use the laws of probability to make inferences about populations based on sample data. Strengths of Quantitative Research ✔✔-Testing and validating already constructed theories -Can generalize research findings when based on random samples -Determining nomothetic consumption (general scientific casual relationships) -Quick and cheapQualitative Research purpose ✔✔Collects text or imagery data to gain a deeper understanding of existing phenomena, gain insight on insider perspective. Exploration, discovery, understanding Quantitative Research Purpose ✔✔Collect numerical data. Purpose is to describe, predict, control, or explain. Narrow lens approach (top-down) Linguistic-relativity hypothesis ✔✔(assumptions of qualitative research) Intuits' local languages might allow them to see distinctions that you do not notice. Empathetic Understanding ✔✔(assumptions of qualitative research) I can appreciate where you're coming from. I have an interest in you Ontology (Qualitative Assumption) ✔✔(inherit understanding) Take on personal, mental, subjective, personal, constructed Epistemology (Qualitative Assumption) ✔✔(theory of knowledge) Everything is relative, varying standards, individual/group justification, social construction. Overall understanding of how knowledge is created. Criterion Based aka Purposive Sampling ✔✔selecting participants because they meet the criteria or purpose of the study. Phenomenology ✔✔Rich narrative allowing researcher to vicariously experience the phenomenon through the eyes of the participant. Purpose: Describing the individuals experience of the phenomena. Ethnography ✔✔Extensive physical description of the physical and social settings aimed at holistic understanding. Purpose: Describing cultural characteristics of a group of peopleNarrative Inquiry ✔✔including patterns, connections, and insights uncovered and carefully synthesized. Purpose: Describing people's lives/stories to add to our understanding. Chronological story Case Study ✔✔Rich, holistic narrative which triangulates data and places the case into a meaningful context Purpose: Addressing research questions through in-depth analysis. Environment based on a set of circumstances. Grounded Theory ✔✔Contains methodological description, then proposes and discusses the theory built during the research study. Purpose: Inductively generating a theory describing a phenomenon. Does this dynamic of people in this environment hold true to a theory that's related to it? Not manipulating data. Triangulation ✔✔Observations --> Interviews --> Questionnaires. Is everybody in sync with one another? It validates the story Major characteristics of qualitative research analysis ✔✔Unique Case Orientation, Inductive Analysis & Creative Synthesis, Holistic Perspective, Context Sensitivity, Voice Perspective & Reflectivity Voice, Perspective & Reflectivity ✔✔The qualitative analyst owns and is reflective about his or her own voice and perspective; a credible voice conveys authenticity and trustworthiness Context Sensitivity ✔✔Be sensitive to the environment around you. Research places findings in a context that is: social, historical, and temporal.Holistic Perspective ✔✔The whole phenomenon under study is understood as a complex system that is more than the sum of its parts. Inductive Analysis & Creative Synthesis ✔✔taking all the specific info and creating the big story. Looking for patterns, themes, and interrelationships to get the big picture Unique Case Orientation ✔✔Researcher assumes that each case is special and unique. The first level of analysis is being true to, respecting, and capturing the details of the individual cases being studies Qualitative Research Strengths ✔✔Responsive to local situations, conditions, stakeholders, needs and changes that occur during conduct study Is useful for determining idiographic causation Is useful for studying a limited number of cases in depth and describing complex phenomena Researcher can inductively generate a tentative but explanatory theory about a phenomenon Can conduct cross-case comparisons Mixed Method Research ✔✔Confirmatory and exploratory according to given situation. Purpose: combining quantitative and qualitative data collection and analysis elements in a research study. Description, understanding, explanation, prediction, influence, and integration. Mixed Method Rationales ✔✔Triangulation, Complementarity, Development, Initiation, Expansion Triangulation (Mixed Method Research Rational) ✔✔Seeks convergence, correspondence, and corroboration of results from different methods Complementarity (Mixed Method Research Rational) ✔✔Seeks elaboration, enhancement, illustration, and clarification of the results from one method with the results from the other method. Enhancement and clarificationDevelopment (Mixed Method Research Rational) ✔✔Seeks to use the results from one method to develop or inform the other method, where development is broadly construed to include sampling and implementation as well as measurement decisions. More details. Initiation (Mixed Method Research Rational) ✔✔Seeks discovery of paradox and questions, new perspectives and new frameworks, and the recasting of questions or results from one method with questions or results from the other method. Looking at both sides. Expansion (Mixed Method Research Rational) ✔✔Seeks to extend the breadth and range of inquiry by using different methods for different inquiry components. Marry two researches to get the whole picture. Warranted Assertibility ✔✔when you have good evidence about your research claim Assumptions of Mixed Method Research ✔✔Incompatibility thesis, Compatibility thesis, pragmatism, ontology, epistemology Incompatibility thesis ✔✔(assumption of mixed method research) either-or position claiming mixing is not possible or allowable Compatibility thesis ✔✔(assumption of mixed method research) Quantitative and qualitative approaches can be used together in a single research study as long as researchers respect assumptions of each Pragmatism ✔✔(assumption of mixed method research) want to be objective and look at the outcome, we also have to have a sense of ethics of what research is doing to the individual.Ontology (assumptions of mixed method research) ✔✔(Nature of reality/truth) Pluralism, appreciation of objective, subjective, intersubjective realities and their interrelations Epistemology (assumptions of mixed method research) ✔✔(theory of knowledge) Pragmatism, pragmatism justification (what works for who in specific contexts), mixture of universal (e.g. always be ethical and community-specific needs-based standards) Time Orientation Criterion ✔✔Are quantitative and qualitative data collected concurrently (same time) or sequentially (one after another)? Sample Relationship Criterion ✔✔is the sample consisting of the same participants for both phases, or are different individuals needed for a later phase of research? Mixed Method Criterion ✔✔Time orientation criterion and sample relationship criterion Identical (sample relationship criterion) ✔✔same people participate in both phases Parallel (sample relationship criterion) ✔✔samples for quantitative and qualitative components are different but drawn from same population Nested (sample relationship criterion) ✔✔Participants selected for one phase represent a subject of participants selected for another phase Multi-level (sample relationship criterion) ✔✔Using qualitative and quantitative samples obtained from different levels of population under study. Different people form different areas of different populations. Types of Validity in Mixed Method Research ✔✔Inside-outside, conversion, sample integration, paradigmatic/philosophical, sequential, sociopolitical, commensurability approximation, weakness minimization, multipleInside-Outside Validity ✔✔the degree to which the researcher accurately understand, uses, and presents the participants' subjective insider (emic) views and researchers objective outsider (etic) view Conversion Validity ✔✔The degree to which quantitizing or qualitizing yields high-quality metainferences Sample Integration Validity ✔✔the degree to which a mixed researcher makes appropriate conclusions, generalizations, and meta-inferences from mixed samples Paradigmatic/Philosophical Validity ✔✔the degree to which the mixed researcher clearly explains his or her philosophical beliefs about research Sequential Validity ✔✔the degree to which a mixed researcher appropriately addresses and/or builds on findings from earlier qualitative and quantitative phases. Sociopolitical Validity ✔✔the degree a mixed researcher addresses the interests, value and viewpoints of multiple stake-holders in a research process Commensurability Approximation Validity ✔✔the degree to which meta-inferences made in a mixed research study reflect a mixed worldview Weakness Minimization Validity ✔✔the degree researcher combines qualitative and quantitative approaches with non-overlapping weaknesses Multiple Validity ✔✔the extent to which all the pertinent validities are addressed and resolved successfully Types of Analysis in Mixed Method Research ✔✔Mono-analysis and multi-analysisMixed Method Strengths ✔✔Gives a big comprehensive picture of what's going on A research can use the strengths of an additional method to overcome the weaknesses in another method Can provide stronger evidence for conclusion through convergence and corroboration of findings (triangulation) Action Research ✔✔Applied mix of exploratory and confirmatory How did John Dewey influence action research? ✔✔Dewey in 1896 was the earliest advocate for S-O-R (Stimulus-Organism-Response) psychology. He inserted the thinking and acting organism (O) into the observed stimulus response relationship. Dewey believed that the thinking human organism is always embedded in and part of a dynamic, local, and complex ecology. According to his transactional theory, we are not separate from, but rather are part of, our environments. Our environments affect us and we affect our environments, continuously. Dewey argued that humans are adaptive organisms, continuously trying to improve their world. Dewey believed that all humans were active participants in their environments, trying new approaches to find what works and to make their schools, communities, and society better. For Dewey, the scientific method was just another name for inquiry. Cycle of Action Research (PAOR) ✔✔Plan (look forward and prepare to act thoughtfully), Act (conduct your investigation), Observe (what is going on, what did the data say), and Reflect (what does this mean, what do you want to do next?) Four Types of Action Research ✔✔Participatory (PAR), Critical (CAR), Action Science (AS), Appreciative Inquiry (AI) Participatory (PAR) ✔✔interest multiple parties/stakeholders with an interest in research topicCritical (CAR) ✔✔emphasizes the political possibilities and empowerment of those with the little power in their communities and society. Need to do something and need to do it now. Action Science (AS) ✔✔focuses on research in learning organizations. Experimentation to understand change. Looking at the practicing process of experimentation. Does everything in the machine work? Can things improve? Appreciative Inquiry (AI) ✔✔focuses on finding the best in people and working together to achieve a jointly constructed and shared purpose, vision, and goal. Discovery, Dream, Design, and Destiny Action Research Strengths ✔✔Can be conducted by local practitioners Produces lifelong learners Empowers practitioners to contribute to knowledge Integrates theory and practice Limitations of Action Research ✔✔Often involves a small-scale study that produces limited and delimited amount of information and knowledge Produces small-scale results that are difficult to generalize to different larger contexts Does not lend itself to making strong statements and research validity criteria Research Problem ✔✔education issue/problem within the broad topic Research Purpose ✔✔A statement of intent/objective of the study Research Question ✔✔Qualitative - asks a question about some [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 25 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 29, 2022
Number of pages
25
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 29, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
127