Procurement > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > WGU C720 Operations and Supply Chain Management - Study Guide. Rated A (All)
WGU C720 Operations and Supply Chain Management - Study Guide. Rated A
Document Content and Description Below
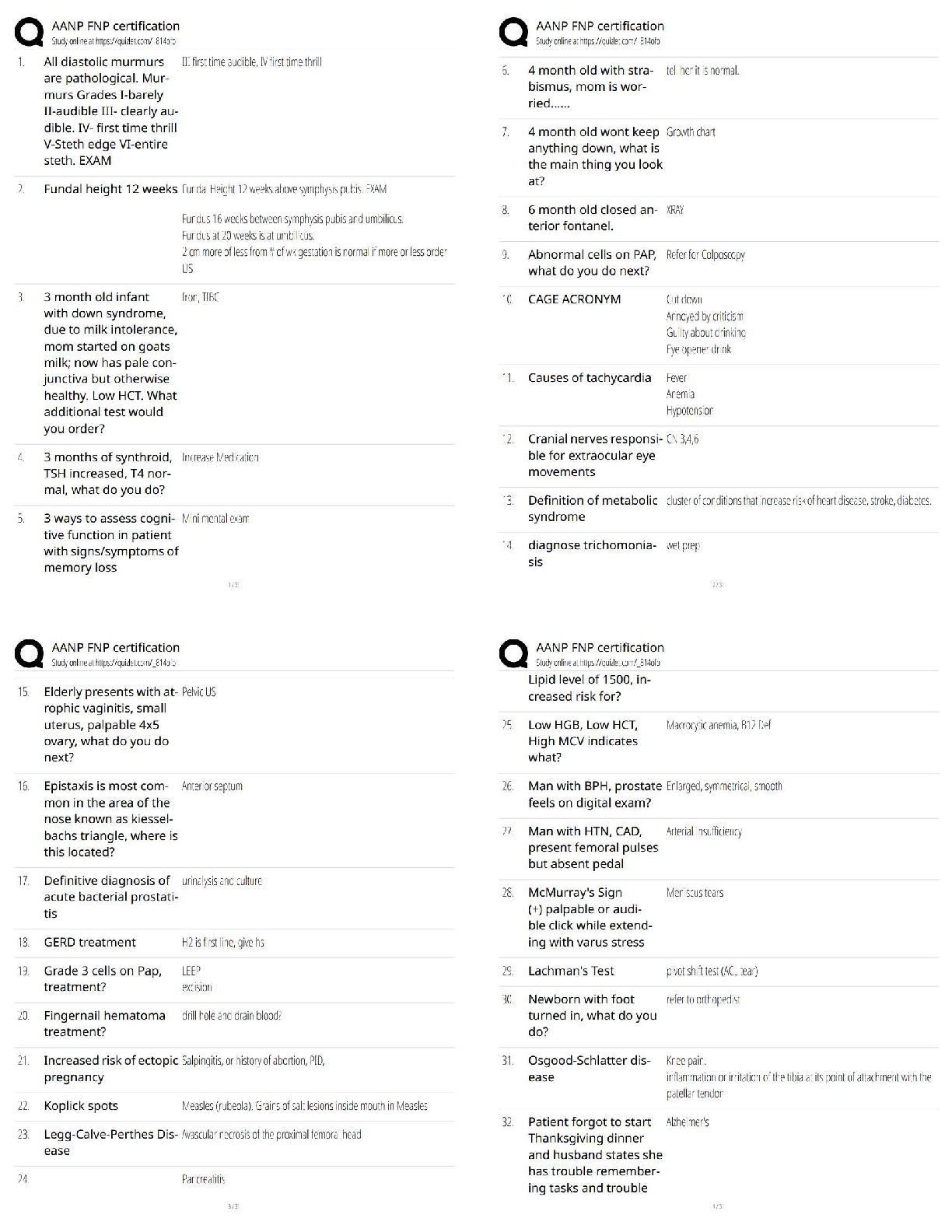
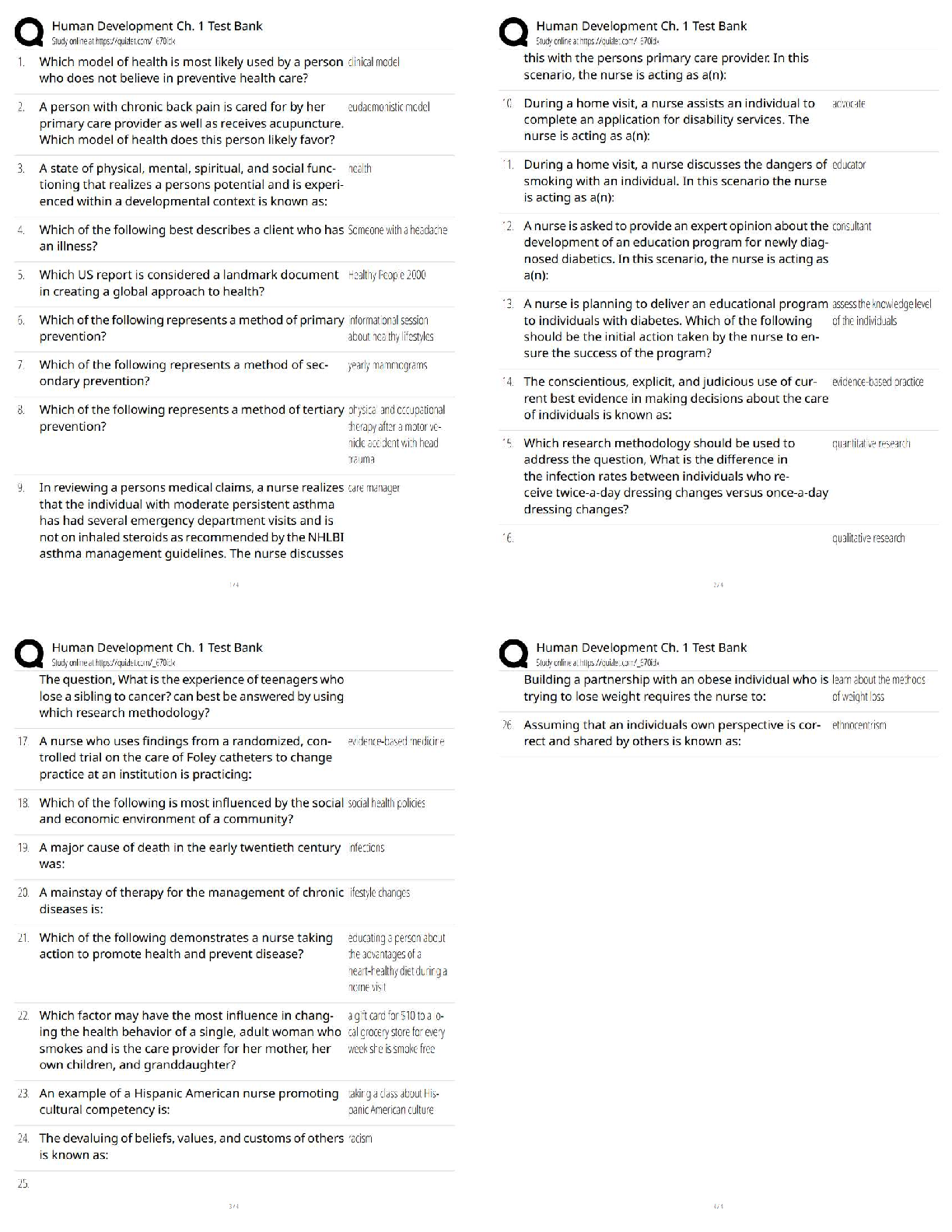
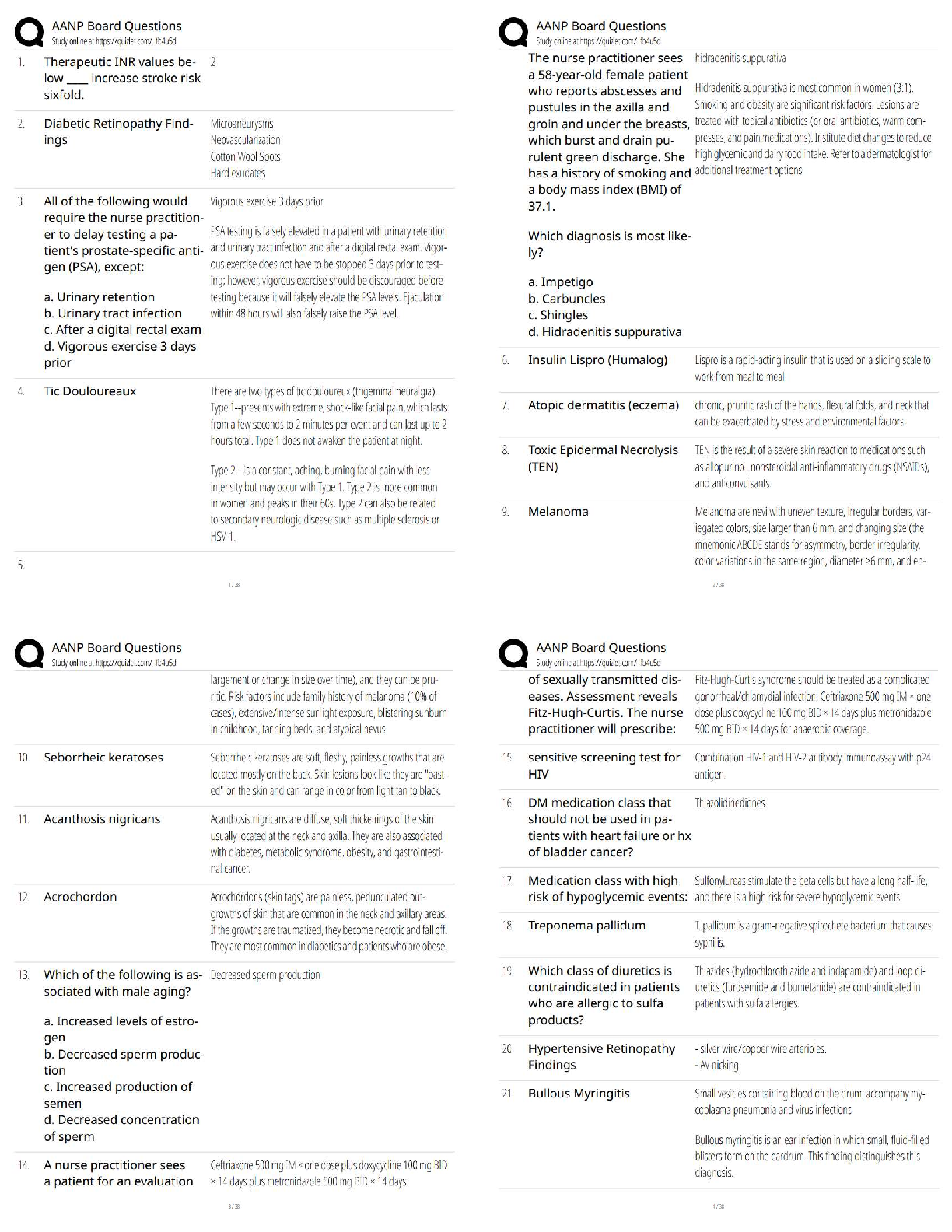
WGU C720 Operations and Supply Chain Management - Study Guide Teamwork ✔✔Teamwork in operations benefit the customer when coordinated decisions within an organization produce high quality produ ... cts that customers value. Teamwork can help make improvements to products. To remain competitive in the global marketplace, teamwork should be utilized to help solve quality and productivity problems. Product and process design ✔✔Product and process design are crucial and relate to both the design of goods and services. Product design ✔✔consideration of the characteristics, features, and performance of the product. Product technology ✔✔application of knowledge to improve the product. Process design ✔✔describes how a product will be made. Process technology ✔✔application of knowledge to improve a process. Common goals ✔✔Most organizations develop common goals during the budgeting and planning process, which are done annually. Most common type of organization ✔✔Many businesses are shifting to organization by process due to today's fast paced environment. Organizational structures ✔✔designed by process cross-functional lines. Cross-functionality ✔✔a unique feature important to any organization.Eliminating functional silos ✔✔allows teams to share knowledge and understanding of decisionmaking across the organization. Decentralizing decision ✔✔making leads to more cross-functional teams. Relative advantage ✔✔The difference between the lowest cost producer and the next-lowest cost producer. Ethics ✔✔A sense of what is right and wrong that guide behavior. Sustainability ✔✔Reflects the efforts organizations are expected to make to balance their interconnected obligations to economic viability, the societies in which they operate, and the natural environment - the "triple bottom line." Organizational focus points ✔✔Organizations need to focus on how a decision affects not just profitability, but also employees, the community, and the environment, in the long and short term. Competitive advantage ✔✔A capability that customers value that gives an organization an edge against its competition. VIRAL ✔✔VIRAL= Value to consumers, it should be Inimitable (not easily imitated), Rare, and an organization should have the Aptitude and Lifespan to earn appropriate returns on the advantage. SWOT Analysis ✔✔Assists in planning to achieve objectives. Strength, Weakness, Opportunity and Threat Key processes organizations must have: ✔✔Strategy development, product development, development of systems to produce services and goods, and order fulfillment to leverage impact.Systems development ✔✔Key to meeting strategic goals. Resources include: people, facilities, equipment, materials, and energy. Process redesign ✔✔Facilitates working toward a common goal in organizations. Productivity ✔✔A mathematical calculation. It is the ratio of the outputs achieved divided by the inputs consumed to achieve those outputs. Productivity Formula ✔✔Productivity = Output / Input. Change in productivity = (new productivity - old productivity) / old productivity. Labor Productivity Formula ✔✔Labor productivity = Quantity or value of units produced divided labor hours or labor cost. Quality ✔✔Determined by the customer and how the customer will use a product. Used to judge service quality: ✔✔Reliability- ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately. Responsiveness- willingness to help customers and provide prompt service. Assurance- knowledge and courtesy of employees and their ability to convey trust and confidence. Empathy- provision of caring, individualized attention to customers. Tangibles- appearance of physical facilities, equipment, personnel, and communication materials. Factors that determine quality for goods: ✔✔Performance- primary operating characteristic of a product Features- secondary characteristics that supplement the product's basic functioning. Reliability- length of time a product will function before it fails or the probability it will function for a stated period of time. Conformance- degree to which a product's design and operating characteristics match preestablished standards.Durability- ability of a product to function when subjected to hard and frequent use. Serviceability- speed, courtesy and competence of repair. Aesthetics- how a product looks, feels, sounds, tastes, or smells. Perceived quality- image, advertising, or brand name of a product. Failure costs ✔✔Can be internal to the organization (defects found before product reaches consumer) or external after reaching the customer (cost of warranty repair work, handling complaints, or replacing products). Failure costs can lead to: lost goodwill, legal liability if someone is injured/killed, and even loss of customers. Appraisal costs ✔✔Investment in measuring the quality and assessing customer satisfaction. Appraisal costs include: costs involved with customer satisfaction surveys, hiring individuals to inspect property at a hotel chain, or testing computers to ensure they will operate as intended. Prevention costs ✔✔Put a stop to the quality problem. Prevention costs include: activities such as employee training, quality control procedures or other activities designed to prevent product defects. Statistical process control (SPC) ✔✔The use of statistical methods to determine when a process that produces a good or service is getting close to producing an unacceptable level of defects. Walter Shewhart ✔✔Father of statistical quality control. Founding father of statistical process control. Developed the P-D-C-A (Plan Do Check Act) which came to be known as Shewhart Cycle, and also the Deming Wheel. However, Deming preferred to call it the Shewhart Cycle. Deming later revised it to P-D-S-A (Plan Do Study Analyze) because he felt "check" emphasized inspection over analysis. Deming's 14 points for transformation of management: ✔✔a. ✔✔1. Create constancy of purpose toward improvement of product and service. Aim to become competitive and to stay in business, and provide jobs. 2. Adopt the new philosophy. 3. Cease dependence and inspection to achieve quality. 4. End the practice of awarding business on the basis of price tag. 5. Improve constantly and forever the system of production and service. 6. Institute training on the job. 7. Institute leadership. 8. Drive out fear so everyone may work effectively for the company. 9. Break down barriers between department. 10. Eliminate slogans, exhortations, and targets for the workforce asking for zero defects and new levels of productivity. 11. Eliminate work standard on the factory floor. Substitute leadership. Eliminate management by objective. 12. Remove barriers robbing the hourly worker of his right to pride of workmanship. 13. Institute a vigorous program education and self-improvement. 14. Put everybody in the company to work to accomplish the transformation. Deming's basic premise: ✔✔Systems, not employees cause defects. Deming ✔✔Deming emphasized the importance of training employees to use tools of statistical process control. Joseph Juran ✔✔1950s began his "cost of quality" approach, which stressed the desirability of lowering costs associated with prevention. Juran also suggested the Pareto Principle (he named it after Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto). Pareto Principle is known as 80/20 Rule (80% of effects come from 20% of causes). Pareto Principle has become standard term to describe any situation where a relatively small percentage of factors are responsible for the substantial percentage of effect. Juran believed that product quality means "fitness for use" which gives the customer the best value. Emphasized management's responsibility for ensuring quality.Emphasized need for continuous improvement through 3 quality elements: planning, control, improvement. Quality planning ✔✔(Juran)- the development of products and services that appeal to the everchanging customer wants and needs. Quality Control ✔✔(Juran)- Inspection and control functions revolve around understanding the customer's perception of fitness of use. Quality improvement ✔✔(Juran)- The elimination of waste and errors is something that must be led by leadership of a firm. Crosby ✔✔Stated that all errors must be eliminated. Believed that failure costs were much higher than companies thought and creating a zero-error environment was key. "Do it right the first time" Taguchi ✔✔Quality must be designed into a product. Quality cannot be achieved through inspections after the good is made or the service is provided Robust design - designs that guarantee the highest quality product or procedure. regardless of variations perfecting of experiments to create higher quality products and processes Ishikawa ✔✔Developed a diagram to show cause and effect relationships. (Fishbone diagram). Teamwork is essential - quality circles. Quality with an external orientation feature focuses on customer needs rather than product characteristics. "Quality is the capacity to satisfy customers' needs." Quality with internal orientation focuses on the characteristics of the product/service. Quality circles and cycles (Include all employees, agree with Deming)teamwork is essential for quality leadership Quality function deployment ✔✔Transforming customer expectations into specific actions designed to meet those expectations. Total quality management (TQM) ✔✔An approach to quality management that originated in Japan and was adopted successfully by many companies throughout the world. Focus on the customer. Quality function development. Responsibility for quality. Team problem-solving. Employee training. Fact-based management. Whole business focused on quality vs. a quality control department Focus on the customer, quality function deployment, responsibility for quality, team problem solving, employee training, fact-based management. Voice of the customer (VOC) ✔✔Describes what customers want and that they like and do not like. Quality function deployment (QFD) ✔✔One method that can be used to make that transformation by relating customer needs and expectations to specific design characteristics through a series of grid or matrices. House of quality matrix (what vs. how - customer needs vs. design characteristics) helps a company evaluate trade-offs. Plan-do-check-act cycle ✔✔1)Plan—Before making any changes, be sure everything is documented and standardized. Use appropriate tools to identify problems or opportunities for improvement. Develop a plan to make changes. 2)Do—Implement the plan and document any changes made. 3)Check—Analyze the revised process to determine if goals have been achieved. 4)Act—If the goals have been achieved, then standardize and document the changes. Communicate the results to others that could benefit from similar changes. If the goals have not been achieved, determine why not, and proceed accordingly.Continuous improvement ✔✔Extremely important part of TQM. No matter how good a company is, it must always strive to do better. Bench marking ✔✔A process by which a company compares its performance to the performance of other companies. Benchmark does not define the best possible outcome; it only identifies what a company has achieved. Statistical process control (SPC) ✔✔The use of mathematical methods to determine when a process that produces a good or service is getting close to producing an unacceptable level of defects. Use: cause-and-effect diagrams, check sheets, control charts, histograms, Pareto charts, scatter diagrams, and flow or run charts. Determines the stability of a manufacturing process and reduce the number of product defects. Fishbone ✔✔(cause and effect) charts/diagrams-Ishikawa diagrams Show the impact of various inputs into the result of a process. (Help find root causes/bottlenecks in process) Check sheets ✔✔The means used to record data points in real-time at the site where the date is generated. C=Real Time Histogram ✔✔Demonstrates the frequency of data observations within a present range of values. Pareto chart ✔✔Represents data values in a descending order to visualize the most frequent occurrences. Control charts ✔✔Graphical depictions of process output where the raw data is plotted in realtime within upper and lower control limits. C=Real TimeRun charts ✔✔Another form of control chart for processes that might have common features, a common scale, or some form of central tendency. Scatter diagrams ✔✔Relationship between two variables. Only one can be influenced Six sigma ✔✔• Uses quantitative and qualitative techniques and tools. • Uses a project charter which includes all aspects of a project to ensure optimal success. • Six sigma = 6 standard deviations or....3.4 defects per 1 million units, or 99.99966% error free • 5 step (DMAIC) 1) Define - The Six Sigma expert uses a project charter to define a problem or improvement opportunity. Plan process to satisfy customer 2)Measure - Measuring current, or "as-is", process performance is accomplished with a process map of the activities performed at each step of the process. Each step is assessed to determine the ability to meet customer specification in a capability analysis. 3)Analyze - The main objective of the Analysis phase is to determine the root causes of variation in the process that result in failures or defects. (Use charts and other tools) 4)Improve 5)Control Employee empowerment ✔✔Involving employees in every step - from product design, to process design, and system design. As workforce becomes more highly skilled, decision-making and responsibility can be moved to individual contributors in frontline processes or lowest level in the organization. When errors occur, frontline employees often have the best perspective to solve the problem, and identify means to prevent defects and eliminate errors.Kaizen teams ✔✔Can make rapid changes using ideas from the people who are directly involved in the process. Kaizen - Japanese word for "change better" or continuous improvement. 5S process ✔✔Sort, Straighten, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain Problem statement ✔✔A concise verbal statement of the problem under study. Supply chain ✔✔The network of organizations that participate in producing goods or providing services. Encompasses all activities associated with the flow and transfer of goods and services from raw material extraction through use by final customer. Focal firm ✔✔Directs the flow of information. The better the focal firm is at moving information among participants, the better the supply chain will perform. Usually interacts with the final customer. Vertical integration ✔✔Owning multiple assets in a supply chain. Logistics ✔✔Involves managing the movement of materials, components and information from point to point in the supply chain. Reverse logistics ✔✔The returning of defective products to the manufacturer for repair or replacement. Also, includes efforts to reuse and recycle materials. Insourced ✔✔Goods/services are provided by the organization itself. Outsourced ✔✔Goods and services obtained from outside suppliers. Ca [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

WGU C720 Operations and Supply Chain Management BUNDLE – Questions and Answers, 100% ACCURATE. RATED A
COMPRISE OF EXAMINABLE QUESTIONS WITH ACCURATE ANSWERS, RATED A.
By bundleHub Solution guider 3 years ago
$20
21
Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 30, 2022
Number of pages
26
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 30, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
198