Psychology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Psych 101: Quiz 4 Latest Updated 2022 Already Passed. Rated A (All)
Psych 101: Quiz 4 Latest Updated 2022 Already Passed. Rated A
Document Content and Description Below
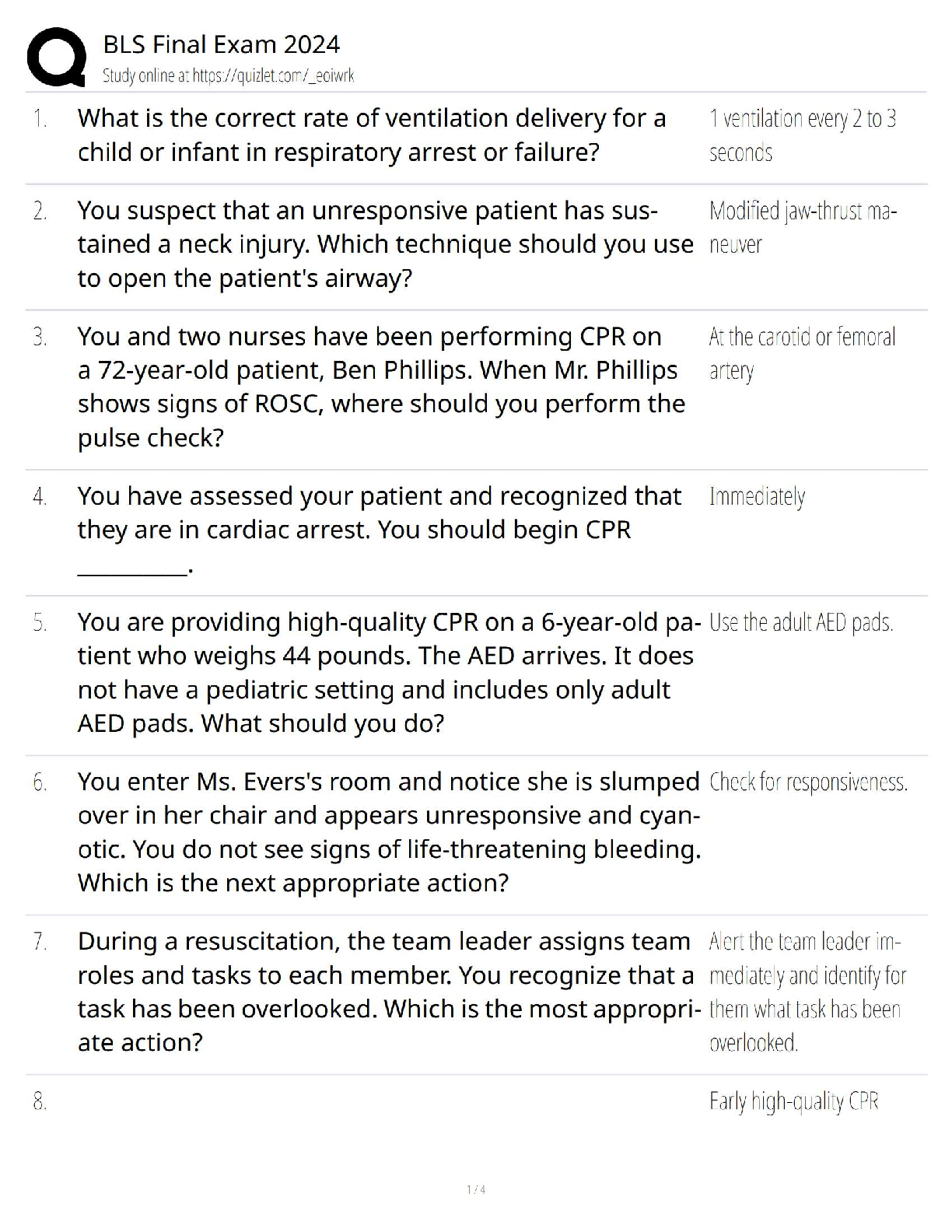
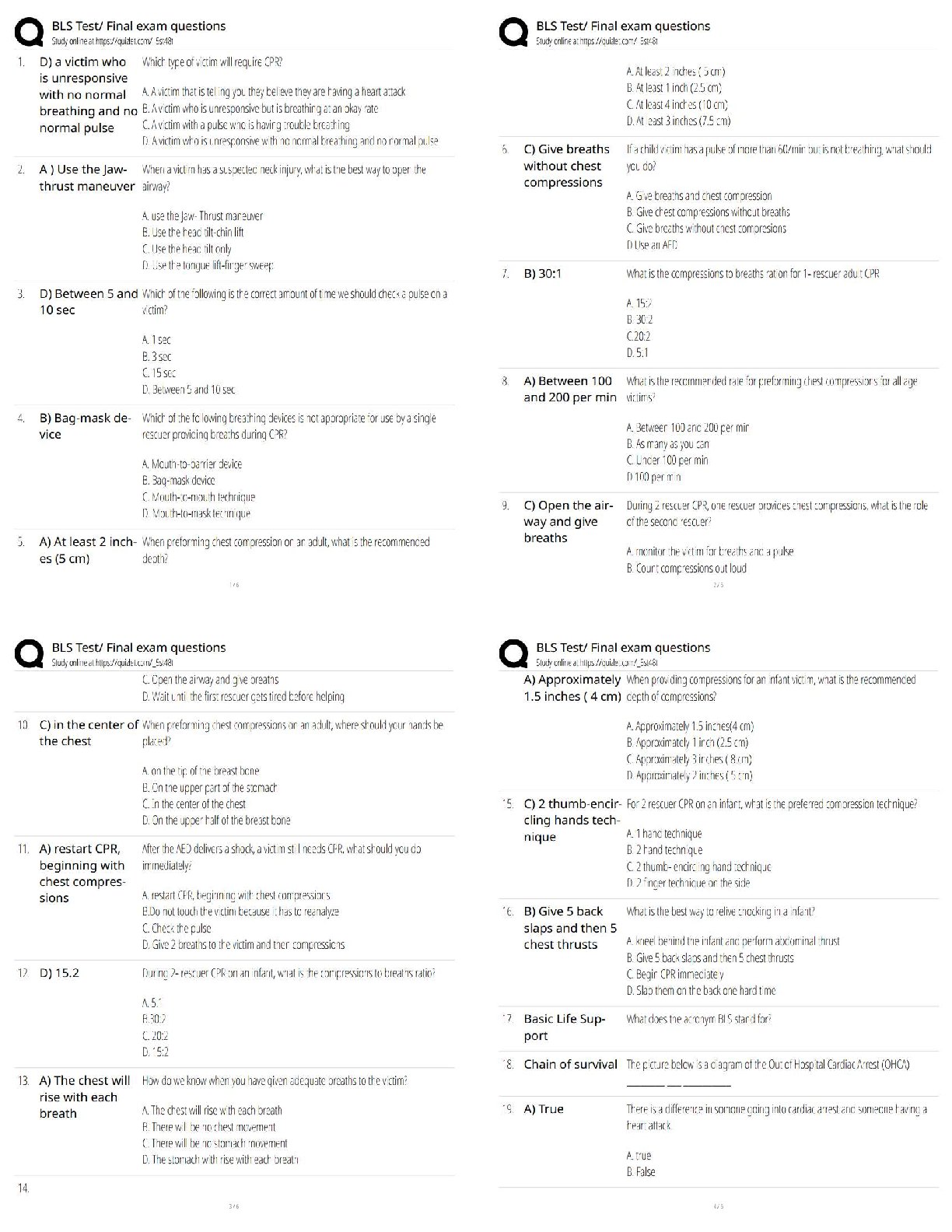
Psych 101: Quiz 4 Latest Updated 2022 Already Passed Social psychology ✔✔the branch of psychology concerned with the way individuals' thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by others ... Attributions ✔✔inferences that people draw about the causes of events, others' behavior, and their own behavior Internal attributions ✔✔ascribe the causes of behavior to personal dispositions, traits, abilities, and feelings External attributions ✔✔ascribe the causes of behavior to situational demands and environmental constraints Weiner's model of attributions for success and failure ✔✔assumes that people's explanations for success and failure emphasize internal vs. external causes and stable vs. unstable causes (four categories: internal-stable, internal-unstable, external stable, and external-unstable) Fundamental attribution error ✔✔observers' bias in favor of internal attributions rather than external attributions in explaining others' behavior; in general, actors favor external attributions for their behavior, while observers are more likely to explain the same behavior with internal attributions Self-serving bias ✔✔tendency to attribute one's successes to personal factors and one's failures to situational factors Individualism ✔✔putting personal goals ahead of group goals and defining one's identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group membershipCollectivism ✔✔putting group goals ahead of personal goals and defining one's identity in terms of the groups one belongs to Group ✔✔consists of two or more individuals who interact and are interdependent Bystander effect ✔✔people are less likely to provide needed help when they are in groups than when they are alone, caused by diffusion of responsibility Factors that contribute to reduced individual productivity in larger groups ✔✔reduced efficiency resulting from loss of coordination, social loafing Social loafing ✔✔the tendency to exert less effort when working on a group task , as compared with then they work by themselves, in which individual contributions cannot be identified Caused by diffusion of responsibility and because you think others will put in maximum effort Group polarization ✔✔when group discussion strengthens a group's dominant point of view and produces a shift toward a more extreme decision in that direction Groupthink ✔✔when members of a cohesive group emphasize concurrence at the expense of critical thinking in arriving at a decision; groups censors dissent at the pressure to conform increases and soon everyone begins to think alike Group cohesiveness ✔✔the strength of the liking relationships linking group members to each other and to the group itself Conformity ✔✔when people yield to real or imagined social pressures; key determinants are group size and group unanimityNormative influence ✔✔when people conform to social norms for fear of negative social consequences, about being liked Informational influence ✔✔when people look to others for guidance about how to behave in ambiguous situations, about being right Obedience ✔✔a form of compliance that occurs when people follow direct commands, usually from someone in a position of authority Social roles ✔✔widely shared expectations about how people in certain positions are supposed to behave Person perception ✔✔the process of forming impressions of others Stereotypes ✔✔widely held beliefs that people have certain characteristics because of their membership in a particular group Illusory correlation ✔✔when people estimate that they have encountered more confirmations of an association between social traits than they have actually seen Ingroup ✔✔a group that one belongs to and identifies with Outgroup ✔✔a group that one does not belong to or identify with Attitudes ✔✔positive or negative evaluations of objects of thought Explicit attitudes ✔✔attitudes one holds consciously and can readily describeImplicit attitudes ✔✔covert attitudes that are expressed in subtle automatic responses over which one has little conscious control Source ✔✔the person who sends a communication Receiver ✔✔the person to whom the message is sent Message ✔✔information transmitted by the source Channel ✔✔the medium through which the message is sent Mere exposure effect ✔✔the finding that repeated exposures to a stimulus promotes greater liking of the stimulus Cognitive dissonance ✔✔when related attitudes or beliefs are inconsistent, when they contradict each other Prejudice ✔✔a negative attitude held toward members of a group Discrimination ✔✔behaving differently, usually unfairly, toward the members of a group Interpersonal attraction ✔✔positive feelings toward another person Matching hypothesis ✔✔males and females of approximately equal physical attractiveness are likely to select each other as partners Reciprocity ✔✔liking those who show that they like usPassionate love ✔✔complete absorption in another that includes tender sexual feelings and the agony and ecstasy of intense emotion Companionate love ✔✔warm, trusting, tolerant affection for another whose life is deeply intertwined with one's own Darley & Batson's Good Samaritan Study ✔✔People were told they had to give a speech, on the walk there an emergency happened to a stranger Person variable: does religiosity affect likeliness to help? NO Situation variable: does being in a hurry affect likeliness to help? YES Variance in helping behavior ✔✔a person's previously helpful behavior is a weak predictor of their future likeliness to help Bystander Effect experiments ✔✔staged experiment where confederate has seizure over intercom, measured likeliness of participant to leave booth to help. As the number of bystanders increased, the likeliness to help decreased (environment, # of others, affects reaction) Mechanisms of Bystander Non-Intervention ✔✔Diffusion of responsibility, pluralistic ignorance Diffusion of responsibility ✔✔a person is less likely to take responsibility for action or inaction when others are present Pluralistic ignorance ✔✔misperception that results from observing people who are acting at variance with their private held beliefs, look to other people to disambiguate and understand Smoke-Filled Room Experiment ✔✔people fill out survey, smoke enters room, what is their reaction time? One person: react immediately because because the danger is only to the selfMultiple confederates, one person: doesn't react because the confederates don't react, Instituting Behavioral Change (effective method and examples) ✔✔to make successful changes, look to change the environment (Easy) rather than changing the disposition (hard) Ex. sleeping in: instead of convincing yourself of waking up, placing alarm clock far away is easier Ex. urinals: placing signs asking people to change their disposition has no effect, paining a fly as a target had a large effect Casual attribution ✔✔inappropriately implicating disposition rather than person perception ex. actors typecast in to particular roles, people expect actors to be like the [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (2)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

ALL PSYCHOLOGY EXAM QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS DOCUMENTS. LATEST 2022/2023. RATED A
ALL YOU NEED TO PASS THE PSYCHOLOGY 101. ACCURATE ANSWERS, 100% PRECISE AND EASY READING DOCUMENTS. RATED A
By bundleHub Solution guider 3 years ago
$40
75

ALL PSYCHOLOGY EXAM QUESTIONS WITH ACCURATE ANSWERS DOCUMENT. LATEST DOCUMENTS. GRADED A
ALL YOU NEED TO PASS ELL PSYCHOLOGY EXAMS, FOR MORE REACH ME AT WAMAESYMON@GMAIL. ALL PSYCHOLOGY EXAM QUESTIONS WITH ACCURATE ANSWERS DOCUMENT. LATEST DOCUMENTS. GRADED A
By bundleHub Solution guider 3 years ago
$42
39
Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 01, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
All
Seller

Reviews Received
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 01, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
169