Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BIO 2313 Exam 1A Questions and Answers; Latest solution Guide, A+ Work; University of Texas, San Ant (All)
BIO 2313 Exam 1A Questions and Answers; Latest solution Guide, A+ Work; University of Texas, San Antonio.
Document Content and Description Below
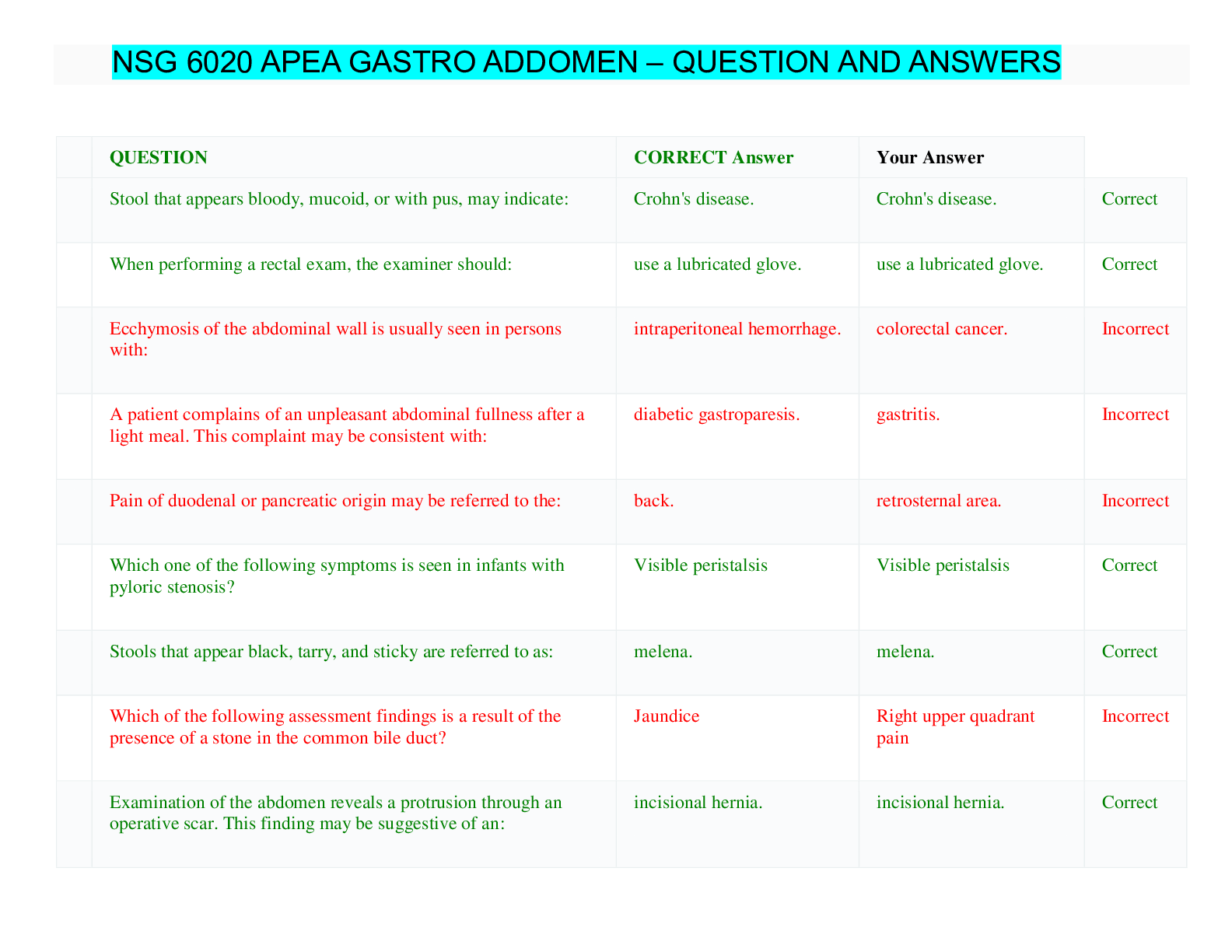
BIO 2313 Exam 1A Questions and Answers 1) Mendel performed many types of crosses, including those in which the same genotypes are crossed but the sexes of the parents are switched. These are known as ... A) replicate crosses. B) reciprocal crosses. C) test crosses. D) monohybrid crosses. E) dihybrid crosses. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 2) In peas, the round allele is dominant over the wrinkled allele. If a plant with round peas is crossed to a plant with wrinkled peas, all of the resulting plants have round peas. What is the genotype of the parents in this cross? A) RR × rr B) RR × Rr C) Rr × rr D) Rr × Rr E) rr × rr Skill: Application/Analysis 3) In peas, the yellow allele is dominant over the green allele. If a plant with yellow peas is crossed to a plant with green peas, the resulting plants are 50% yellow and 50% green. What are the genotypes of the parents in this cross? A) YY × yy B) YY × Yy C) Yy × yy D) Yy × Yy E) yy × yy Skill: Application/Analysis 4) Assuming independent assortment, what phenotypic ratio would you expect to see if an individual with the genotype RrGg is self-crossed? A) 1:3 B) 9:3:3:1 C) 1:2:1 D) 1:3:2:1 E) 3:1 Skill: Application/Analysis 5) Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in A) two unique daughter cells. B) four unique daughter cells. C) two identical daughter cells. D) three identical daughter cells. E) four identical daughter cells. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 6) During which stage or phase of the cell cycle does the cell replicate its chromosomes? A) M phase B) G1 C) G2 D) S E) G0 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 7) After which stage or phase of the cell cycle does the cell divide? A) M phase B) G1 C) G2 D) S E) G0 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 8) The separation of sister chromatids during anaphase I of mitosis is known as chromosome A) cytokinesis. B) karyokinesis. C) crossing over. D) synapsis. E) disjunction. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 9) Tumor suppressors are genes that A) promote advancement of the cell cycle. B) phosphorylate proteins involved in the cell cycle. C) block progression of the cell cycle. D) prevent apoptosis in normal cells. E) activate proto-oncogenes. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 10) A couple has four children. What is the probability that they would have four boys? A) 1/2 B) 1/4 C) 1/8 D) 1/16 E) 1/32 Skill: Application/Analysis 11) In peas, axial (A) flower position is dominant to terminal (a), tall (L) is dominant to short (l), and yellow (Y) is dominant to green (y). If a plant that is heterozygous for all three traits is allowed to self- fertilize, how many of the offspring would be dominant for all three traits? A) 3/64 B) 9/64 C) 27/64 D) 32/64 E) 64/64 Skill: Application/Analysis 12) In peas, axial (A) flower position is dominant to terminal (a), and tall (L) is dominant to short (l). If a plant that is heterozygous for both traits is allowed to self-fertilize, how many of the offspring would also be heterozygous for both traits? A) 9/16 B) 4/16 C) 3/16 D) 2/16 E) 1/16 Skill: Application/Analysis 13) The law of segregation states that the F2 progeny of F1 heterozygous plants will exhibit A) a 3:1 phenotypic ratio. B) a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio. C) a 1:2:1 genotypic ratio. D) a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio and 1:2:1 genotypic ratio. E) both a 3:1 phenotypic ratio and a 1:2:1 genotypic ratio. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 14) The law of independent assortment would predict that the F2 progeny of F1 heterozygous plants will exhibit a A) 3:1 phenotypic ratio. B) 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio. C) 1:2:1 genotypic ratio. D) 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio and 1:2:1 genotypic ratio. E) 3:1 phenotypic ratio and 1:2:1 genotypic ratio. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 15) Mutations that inhibit Rb gene expression will have what effect on cell proliferation? A) Cells will proliferate less, even if excess growth factors are present. B) Cells will proliferate less because growth factors are absent. C) Cells will proliferate more because growth factors are produced in excess. D) Cells will proliferate more, regardless of growth factor concentration. E) There will be no effect on cell proliferation; only apoptosis occurs. Skill: Application/Analysis 16) During meiosis I, when does homologous chromosome pairing and recombination occur? A) prophase I B) pro-metaphase I C) metaphase I D) anaphase I E) telophase I Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 17) The binding of nonsister chromatids by a synaptonemal complex draws the homologs into close contact so that what process can occur? A) cytokinesis B) karyokinesis C) independent assortment D) synapsis E) disjunction Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 18) If a trait is X-linked recessive, who would express the trait? A) homozygous dominant females and hemizygous recessive males B) heterozygous recessive females and hemizygous dominant males C) homozygous recessive females and hemizygous recessive males D) heterozygous dominant females and hemizygous dominant males E) the same proportions of females and males Skill: Application/Analysis 19) If a trait is X-linked dominant, who would express the trait? A) homozygous dominant females and hemizygous recessive males B) heterozygous recessive females and hemizygous dominant males C) homozygous recessive females and hemizygous recessive males D) heterozygous dominant females and hemizygous dominant males E) significantly more females than males Skill: Application/Analysis 20) What phenotypic ratio would you expect as a result of a test cross between a dihybrid organism and one that is homozygous recessive for alleles at two independent loci? A) 3:1 B) 1:2:1 C) 1:1:1:1 D) 9:3:3:1 E) 9:4:2:1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 21) How many possible gametes can be produced by a short plant with yellow, round peas with a heterozygous genotype (YyRrSs)? A) 3 B) 6 C) 8 D) 10 E) 12 Skill: Application/Analysis 22) A cross between a short pea plant and a tall pea plant results in a 1:1 genotypic and phenotypic ratio in the offspring. What are the genotypes of the parent plants? A) SS x ss B) ss x ss C) Ss × ss D) Ss x Ss E) SS x Ss Skill: Application/Analysis 23) What dosage compensation mechanism is employed by female placental mammals? A) synteny B) Y-inactivation C) X-inactivation D) X nondisjunction E) X chromosome crossing over Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 24) In a pea plant that is heterozygous for seed color, what proportion of gametes will carry the recessive allele? A) 1/4 B) 1/2 C) 3/4 D) all of the gametes E) none of the gametes 25) The appearance of traits expressed by genes in association with environmental influence is referred to as the organism's A) genome. B) karyotype. C) phenotype. D) genotype. E) prototype. 26) A cross of two heterozygous individuals produces 76 dominants and 24 recessives. What is the chi- square value for these results? 27) The gametes produced by human females may contain A) a single X chromosome. B) two X chromosomes. C) a single Y chromosome. D) either an X chromosome or a Y chromosome. E) two Y chromosomes. 28) An allele that is completely recessive A) will be expressed in a heterozygote. B) will be masked in a heterozygote. C) will be expressed in males. D) will be expressed in females. 29) Which mode of inheritance produces heterozygotes with phenotypes that differ from either homozygote but more closely resembles one homozygous phenotype than the other? A) complete dominance B) incomplete dominance C) codominance D) epistasis E) incomplete penetrance Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 30) Which mode of inheritance results in both alleles being detected equally in the heterozygous phenotype? A) complete dominance B) incomplete dominance C) codominance D) epistasis E) incomplete penetrance Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 31) Most combinations of different ABO alleles result in complete dominance of one allele. Which combination results in codominance? A) IAi B) IA I B C) IBi D) ii E) either IAi or IBi Skill: Application/Analysis 32) Gene interactions in which an allele of one gene modifies or prevents expression of alleles of another gene is known as A) complete dominance. B) incomplete dominance. C) codominance. D) epistasis. E) incomplete penetrance. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension Refer to the table to answer questions 33-34. 33) In the biosynthetic pathway for conversion from homoserine to methionine, you identify a Neurospora crassa double mutant Met1/Met2. This mutant will grow only if which supplement(s) are added to the minimal media? A) homoserine only B) cysteine only C) homocysteine only D) cystathionine and homocysteine E) methionine only Skill: Synthesis/Evaluation 34) Which step is catalyzed by the enzyme responsible for the Met 3 mutant? A) homoserine → cysteine B) cysteine → cystathionine C) cystathionine → homocysteine D) homocysteine → methionine E) methionine → homoserine Skill: Synthesis/Evaluation 35) Independent assortment predicts a 9:3:3:1 ratio with four different phenotypes in the F2 progeny. If the alleles are epistatic, what would you predict? A) more than four phenotypes B) fewer than four phenotypes C) heterozygotes with a novel phenotype between the dominant and recessive homozygotes D) 1/3 of the progeny with the dominant phenotypes and 2/3 recessive E) no change in the 9:3:3:1 ratio Skill: Application/Analysis 36) What genotypic ratio would you expect to see among the progeny of a monohybrid cross? A) 1:3 B) 9:3:3:1 C) 1:2:1 D) 1:3:2:1 E) 3:1 Skill: Application/Analysis 37) Humans have a gene, "T," that is involved in muscle formation of the tongue. Individuals with the one allele can roll their tongues, while individuals with the other allele cannot. If both parents can roll their tongues, but their child cannot, what can be said about the mode of inheritance? A) Tongue rolling is dominant. B) Tongue rolling is recessive. C) The parents were both homozygous, but the child was heterozygous. D) Tongue rolling is dominant, and both parents were heterozygous (Tt). E) Tongue rolling is recessive, and both parents were heterozygous (Tt). Skill: Synthesis/Evaluation 38) By convention, when the difference between the observed experimental outcomes and the expected outcome is less than 5 percent (< 0.05), the experimental results are considered to be A) within normal expected range. B) statistically significantly and different from the expected outcome. C) not significant. D) less than one standard deviation from the mean. E) equal to the mean. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 39) The statistical interpretation of a chi-square value is determined by identifying the A) mean. B) degrees of freedom. C) average. D) P value. E) joint probability. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension 40) The P value is a quantitative expression of the probability that the results of another experiment of the same size and structure will deviate as much or more from expected results by chance. The greater the difference between observed and expected results of an experiment, A) the lower the χ2 value and the lower the P value. B) the greater the χ2 value and the greater the P value. C) the greater the χ2 value and the lower the P value. D) the lower the χ2 value and the greater the P value. E) the greater the χ2 value; but the P value is unaffected. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 03, 2020
Number of pages
7
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 03, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
166