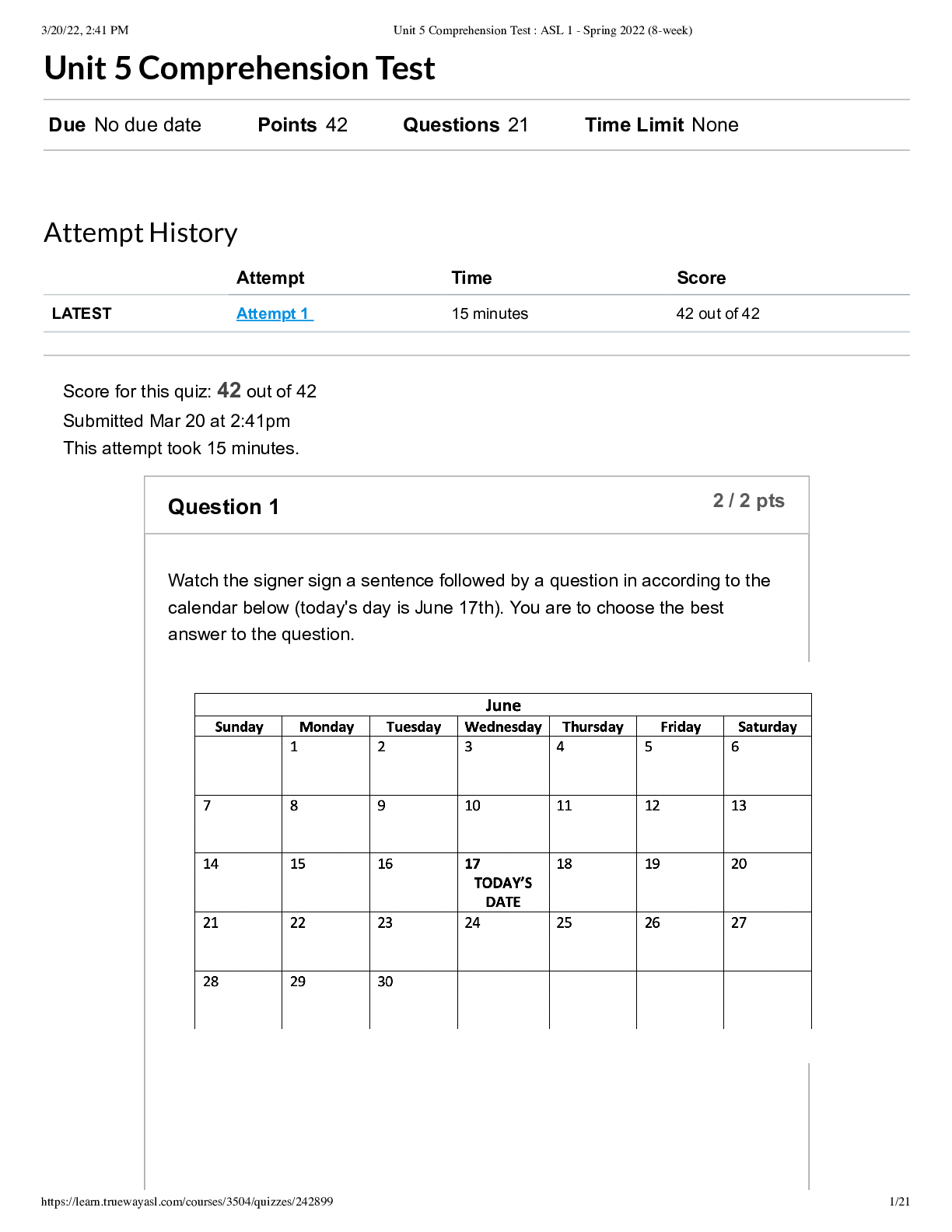
WGU C170 Objective Assessment With Complete Solution
$ 8

Digital Forensics in Cybersecurity Questions and correct Answers (Verified Answers) with Rationales 2025
$ 16

Cracking_SAT_2023_Prem_Online_Practice_Test_8
$ 9.5

HESI A2 Chemistry Questions with Answers and Explanations- NURSING ENTRANCE EXAM
$ 21.5

Instructor Solution Manual for A Student's Guide to the Navier-Stokes Equations. New 1st Edition. 2023 | Justin W. Garvin
$ 19

National University COM 103 Informative speech
$ 9
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 GCE, Mathematics Advanced PAPER 31: Statistics.
$ 11

TEST BANK/Solution Manual for Analytics, Data Science, & Artificial Intelligence: Systems for Decision Support 11 Edition ISBN 9780135172940, 0135172942 by Ramesh Sharda, Dursun Delen and Efraim Turban. All14 Chapters
$ 9

Medical Surgical Nursing 10th Edition Ignatavicius Workman Test Bank
$ 9.5
.png)
_aqa_a_level_physics_2021_paper_3_qp_all_components (1)
$ 10.5

AQA A-level PHYSICS 7408/1 Paper 1 Question Paper June 2020
$ 6

SOAP NOTE WEEK 8
$ 9

HESI Dental Hygiene / NBDHE Dental Hygienist (2025) – Exam Questions and All Correct Answers | 100% Solved and Guaranteed Success!!
$ 20.5

Actualtests NCLEX-RN - P1 National Council Licensure Examination
$ 11

eBook Deconstructing the Feminine 2nd Edition By Leticia Glocer Fiorini
$ 29

[eBook] [PDF] The Biochemical Guide to Toxins By Aebisher D., Bartusik-Aebisher D.
$ 29

BOC EXAM GUIDE WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 8.5

[eBook‑PDF] The Quick Guide to Prompt Engineering: Generative AI Tips and Tricks for ChatGPT, Bard, DALL·E, and Midjourney by Ian Khan ISBN13: 9781394243327
$ 9.5

eBook Auditing and Assurance Services 14th Edition By Alvin A. Arens , Randal J. Elder,Mark S. Beasley
$ 30

(LU) BUSI 304 Introduction to Health Policy - Latest Finals Review Q & S 2024
$ 11

Test Bank for Genetics Essentials, Concepts and Connections, 5e Benjamin Pierce (All Chapters download link is at the end of this file)
$ 7.5

eBook Number Theory Sailing on the Sea of Number Theory - Proceedings of the 4th China-Japan Seminar 1st Edition By Jianya Liu (Editor), Shigeru Kanemitsu
$ 30
.png)
WGU C961 Laws Questions and Answers Rated A
$ 5

215 Servsafe Exam 2022 Complete solution guide distinction level answers, updated fall 2022
$ 12

PSYC 110N Week 3 Discussion: Learning & Memory (Option 1)
$ 7.5
.png)
AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS 8300/3H Higher Tier Paper 3 Calculator Mark scheme June 2021 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 10

LETRS UNIT 2 Session 6 Check for Understanding
$ 5

A First Course in Abstract Algebra, 8th Edition By John Fraleigh, Neal Brand (eBook PDF)
$ 25

Medical Surgical: Kidney Disease
$ 13

NUR 198 Maternity exam 3 final Questions and Answers 100%Correct/Verified Latest Update 2022/2023
$ 5.5

[eBook] [PDF] Silicon, From Sand to Chips 2. Microelectronic Chips, Solar Cells, MEMS 1st Edition By Alain Vignes
$ 25
.png)
AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS 8300/2H Higher Tier Paper 2 Calculator Mark scheme June 2021 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 10

CIPP/E Certification from IAPP | 50 Questions with 100% Correct Answers | Updated & Verified
$ 6

ISYE 6501 Lecture Notes ISYE 6501 Midterm 2 with complete solution
$ 10

Introduction to Robotics Mechanics and Control 3rd Edition By John Craig (Solution Manual)
$ 20

The Reluctant Coroner
$ 4.5
.png)
WGU C207 Data Driven Decision Making Quizzes Already Graded A
$ 10
.png)
NR601 Final Exam Questions and answers. 100% Approved Pass Rate