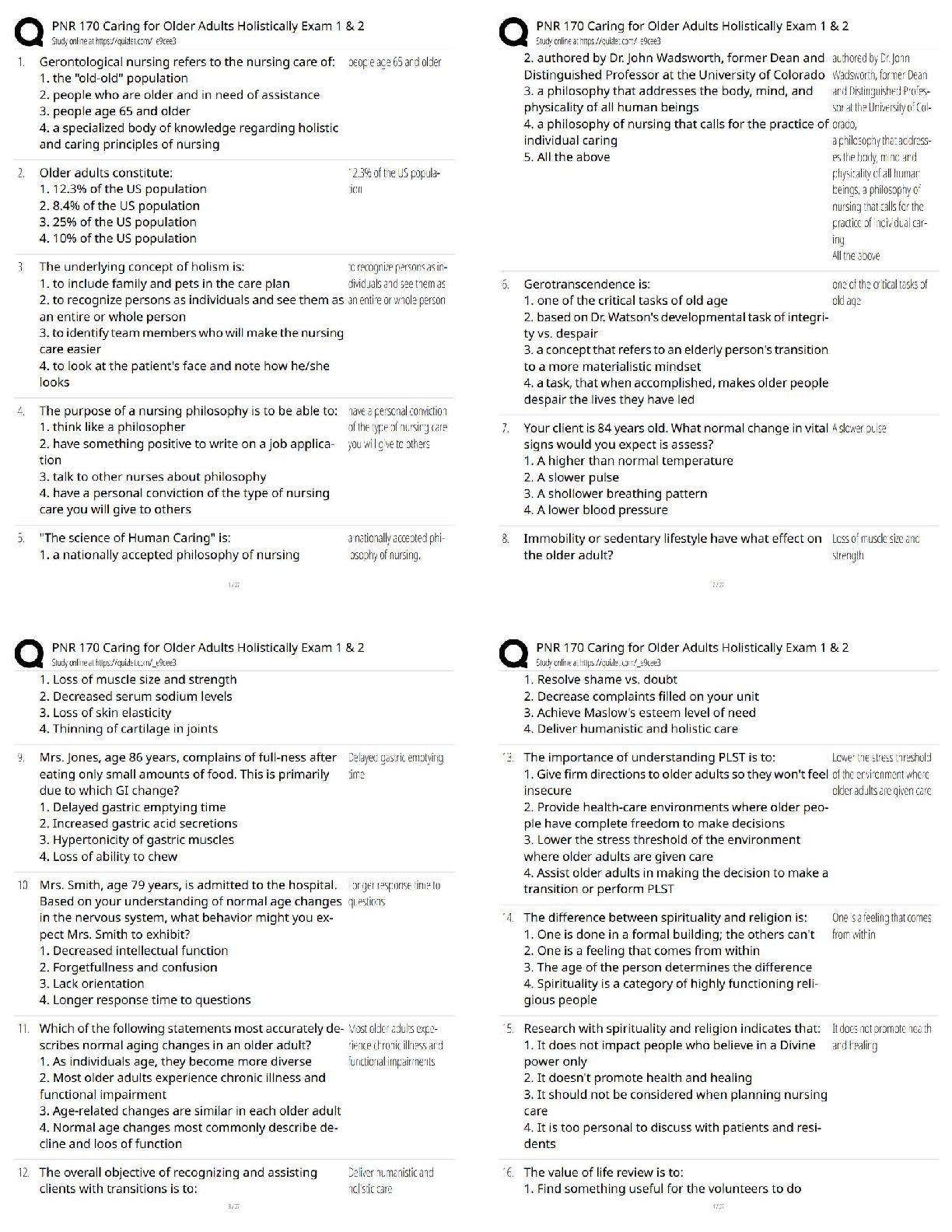
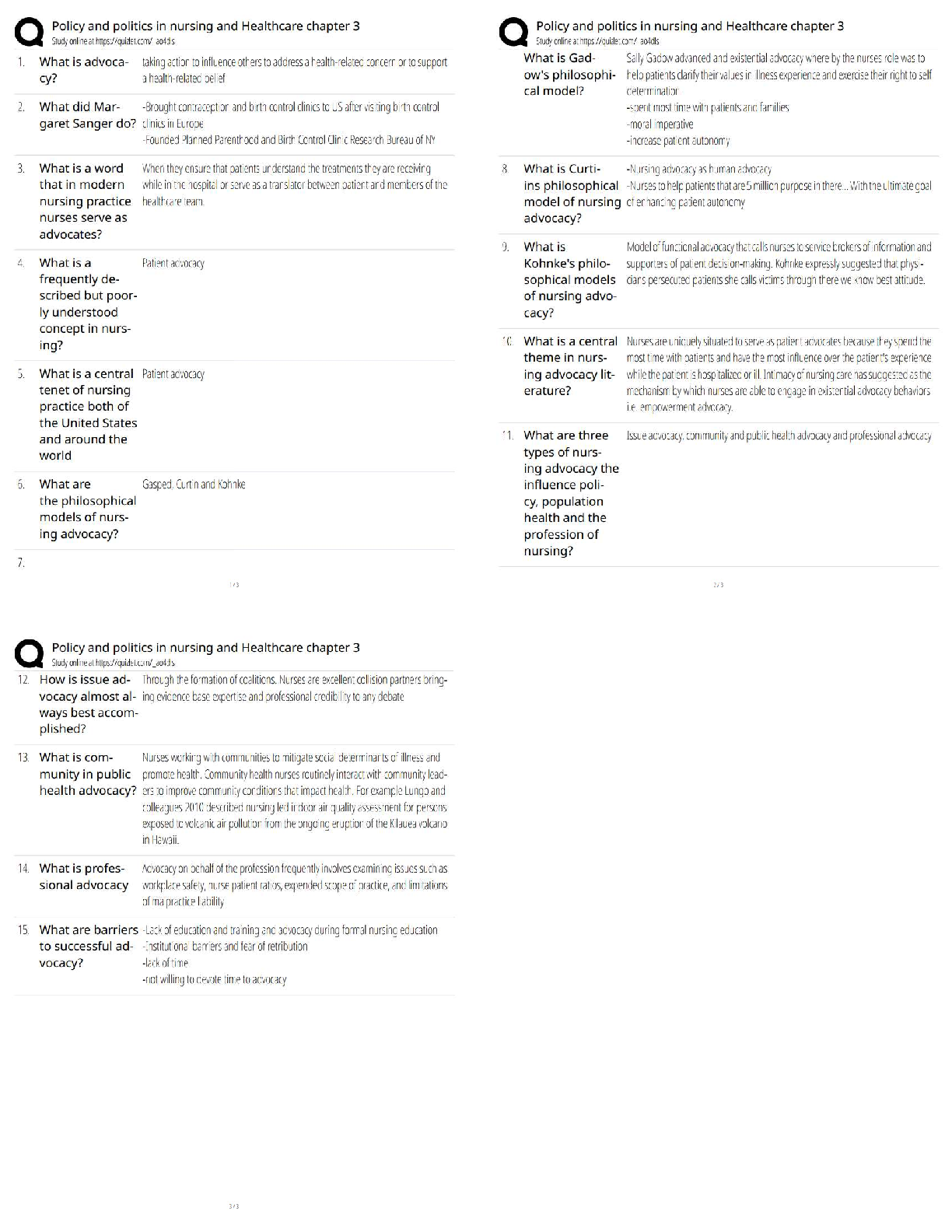
1. A 44 week old gestational age infant is delivered via C-section and is gasping, grunting and has tachycardia and tachypnea. At one minute his APgar score is 4 and at 5 minutes the score is at 5. The infant is most lik
...
1. A 44 week old gestational age infant is delivered via C-section and is gasping, grunting and has tachycardia and tachypnea. At one minute his APgar score is 4 and at 5 minutes the score is at 5. The infant is most likely suffering from
transient tachypnea of the newborn meconium aspiration bronchopulmonary dysplasia
apnea of prematurity: meconium aspiration
2. All of the following could cause a patient's right-hemidiaphragm to be elevated, Except...
right lower lobe atelectasis
right side hyperlucency, absent vascular markings hepatomegaly
right lower lobe consolidation with air bronchograms: right side hyperlucency, absent vascular markings
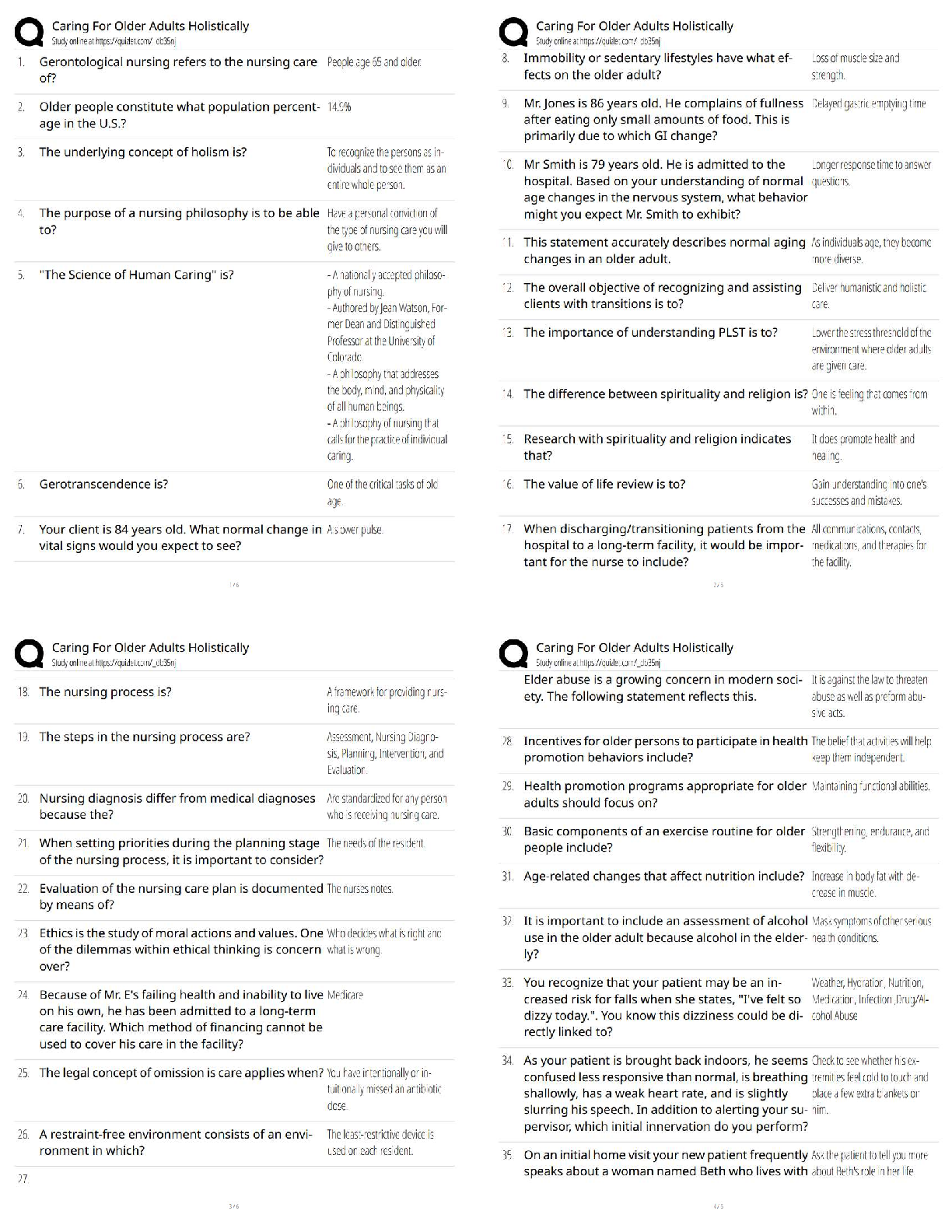
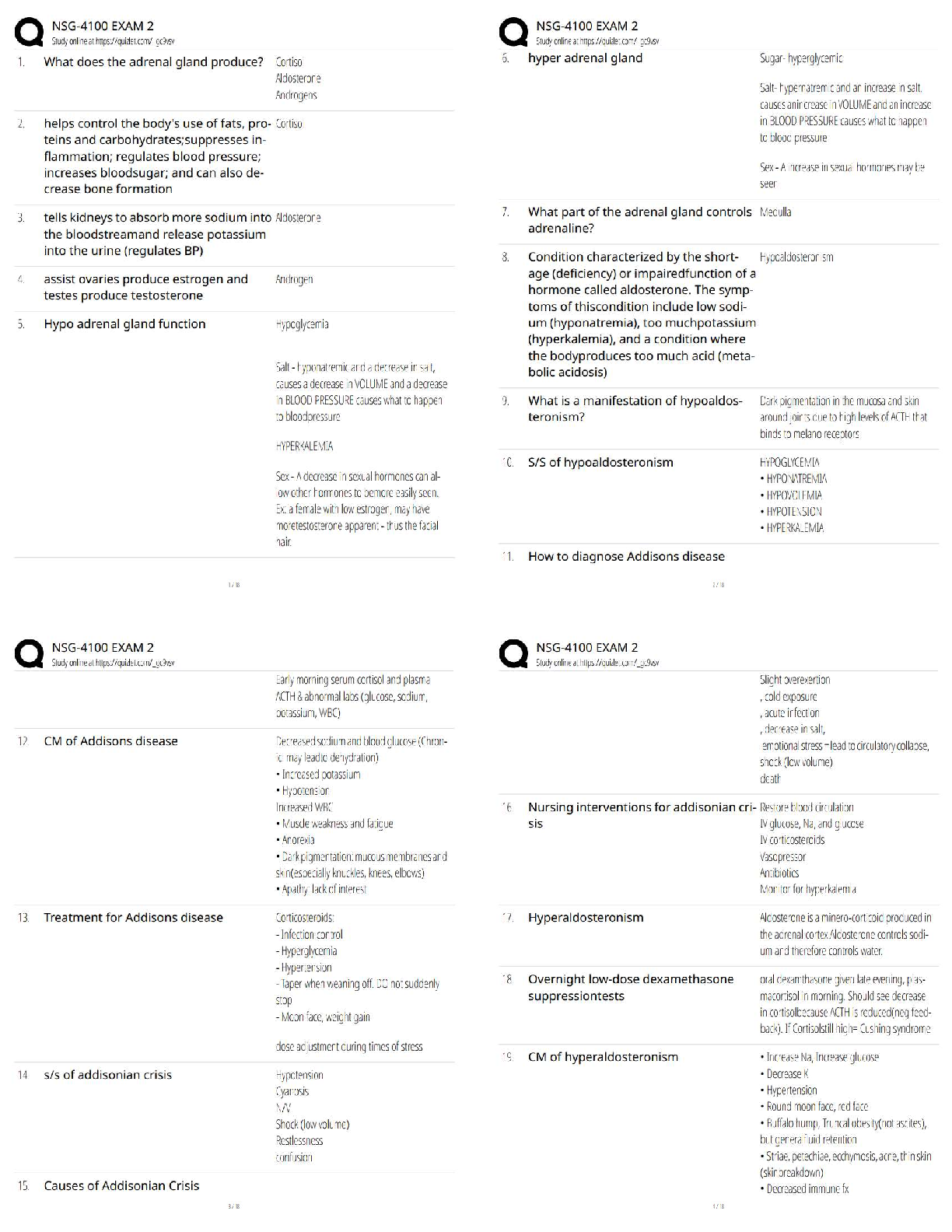
3. A 64 year old, 70 kg (154 lb) man with severe COPD receives independent (differential) lung ventilation following thoracotomy and right lower lobecto- my. Which of the following setting combinations would be most appropriate for this patient?
Right Lung 50 mL, left lung 459 mL Right lung 159 ml, left lung 359 ml Right lung 250, left lung 250 ml
Right lung 350 ml, left lung 150 ml: Right lung 150, left lung 350 ml
4. A 2 year old child with croup has been intubated for 4 days with a 4 mm ID uncuffed endotracheal tube. Heated aerosol at an FiO2 of 0.30 has been delivered to the patient. The physician asks the respiratory therapist
to evaluate the patient for possible extubation. Which of the following would most likely indicate that the patient is ready for extubation?
The patient is making normal quiet ventilatory efforts
A negative sputum culture and sensitivity has been reported The patients ABG are within normal range
Breath sounds are heard around the tube on auscultation: Breath sounds are heard around the tube on auscultation
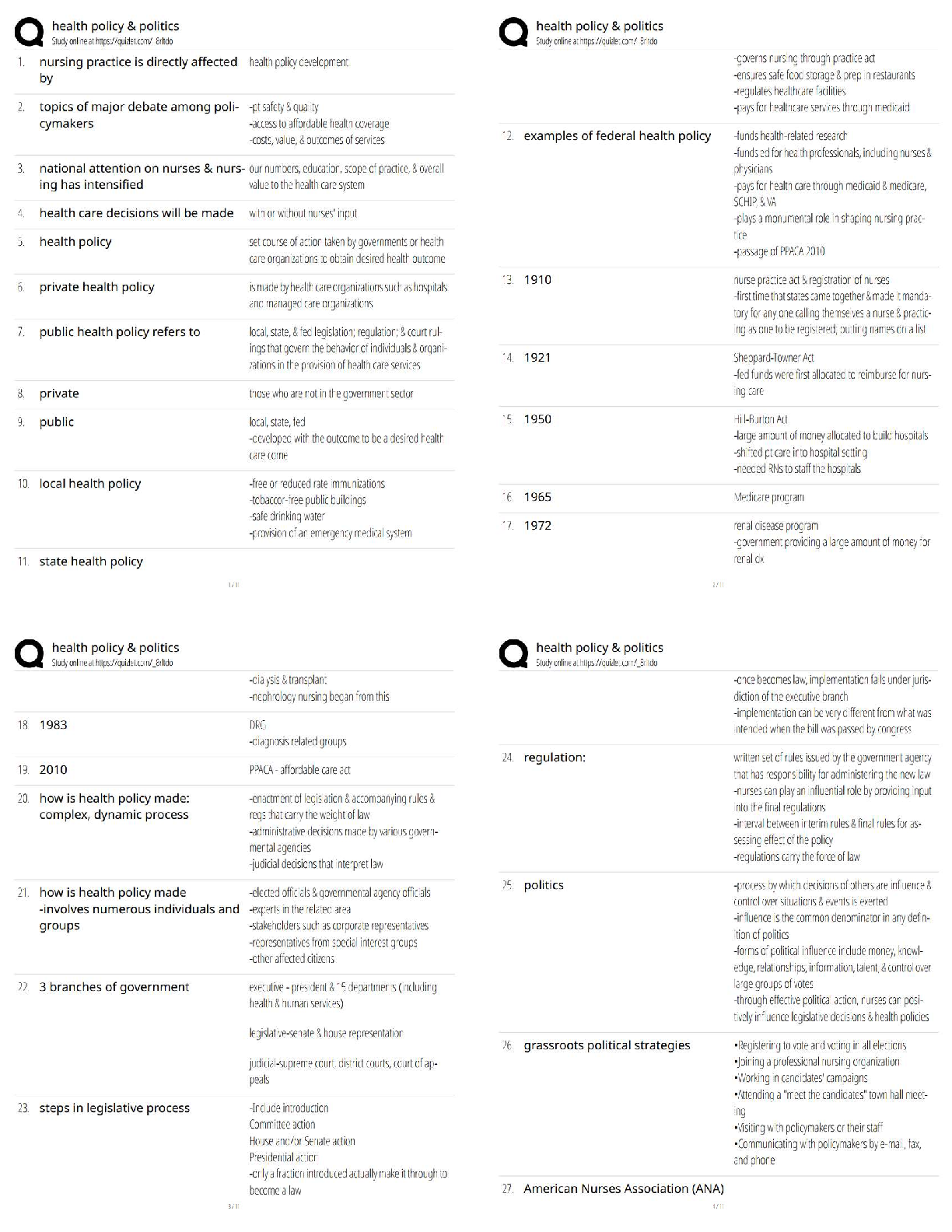
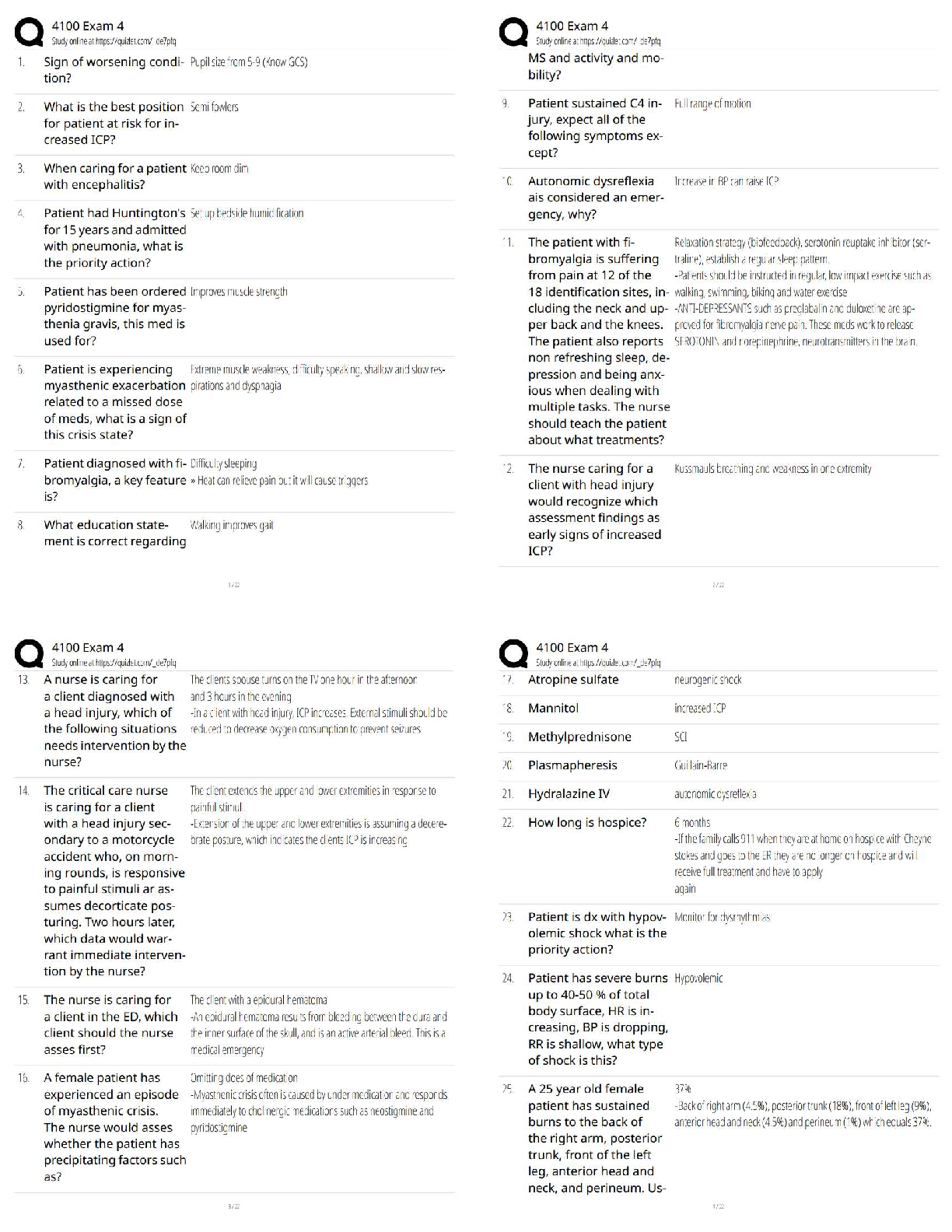
5. When instructing a patient prior to a vital capacity maneuver, the respira- tory therapist should direct the patient to....
exhale to residual volume and inhale to inspiratory capacity inhale to total lung capacity then exhale to residual volume exhale normally then inhale to TLC
inhale normally then exhale to FRC: inhale to TLC then exhale to RV
6. A patient with end-stage pulmonary fibrosis receieves oxygen at 2 L/min via transtracheal oxygen catheter. The patient complains of increased work of breathing and shortness of breath. The RT should...
Manually ventilate the patient with a resusitation bag increase the flow to the transtracheal catheter to 6 lpm evaluate the SpO2 with a pulse oximeter
flush the transtracheal device with saline: flush the transtracheal device with saline
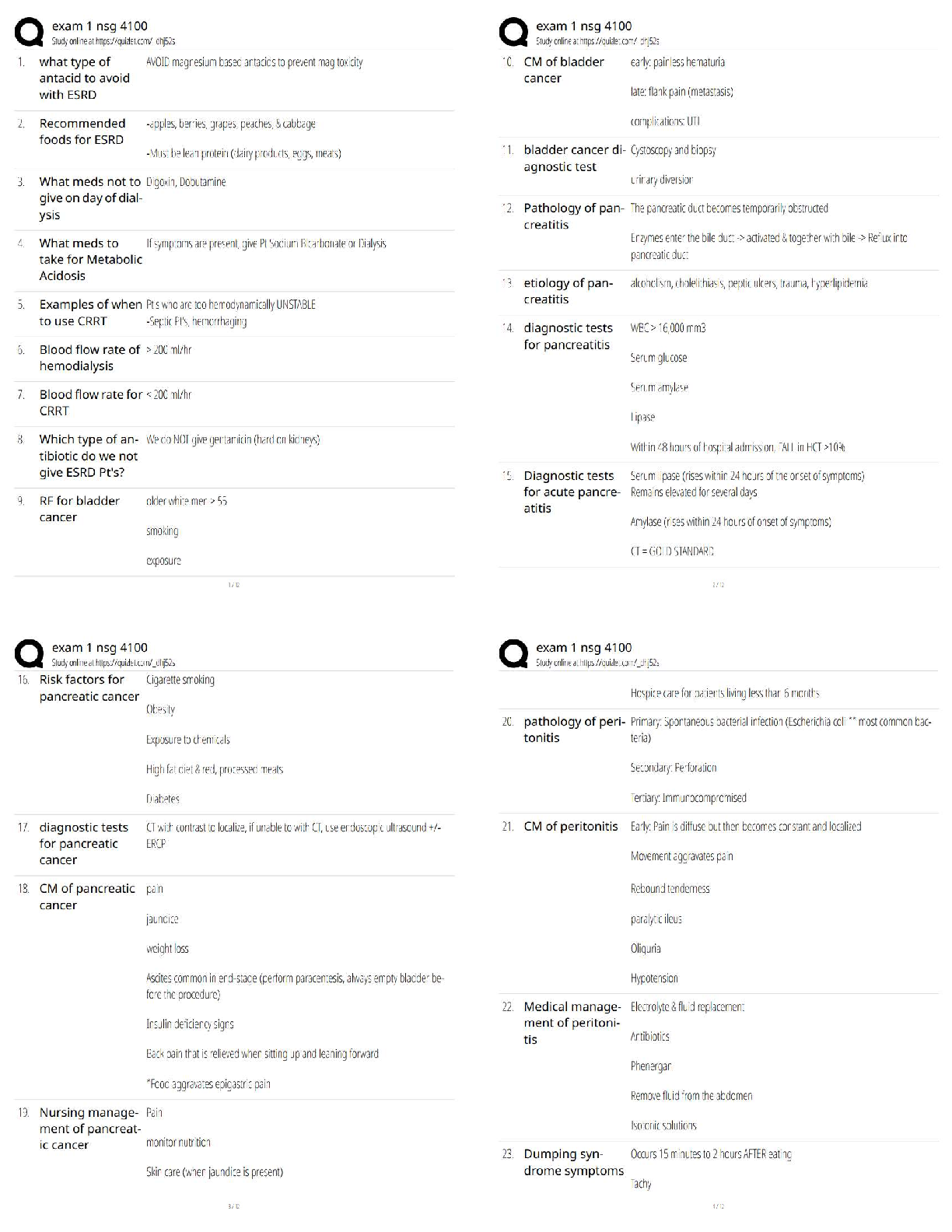
[Show More]





 with Complete Solution.png)
 Career Information with Complete Solution.png)


 for E-6 Career Information_watermark.png)