*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NR602 WEEK 8 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS,GRADE A.LATEST FOR 2022-2023 (All)
NR602 WEEK 8 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS,GRADE A.LATEST FOR 2022-2023
Document Content and Description Below
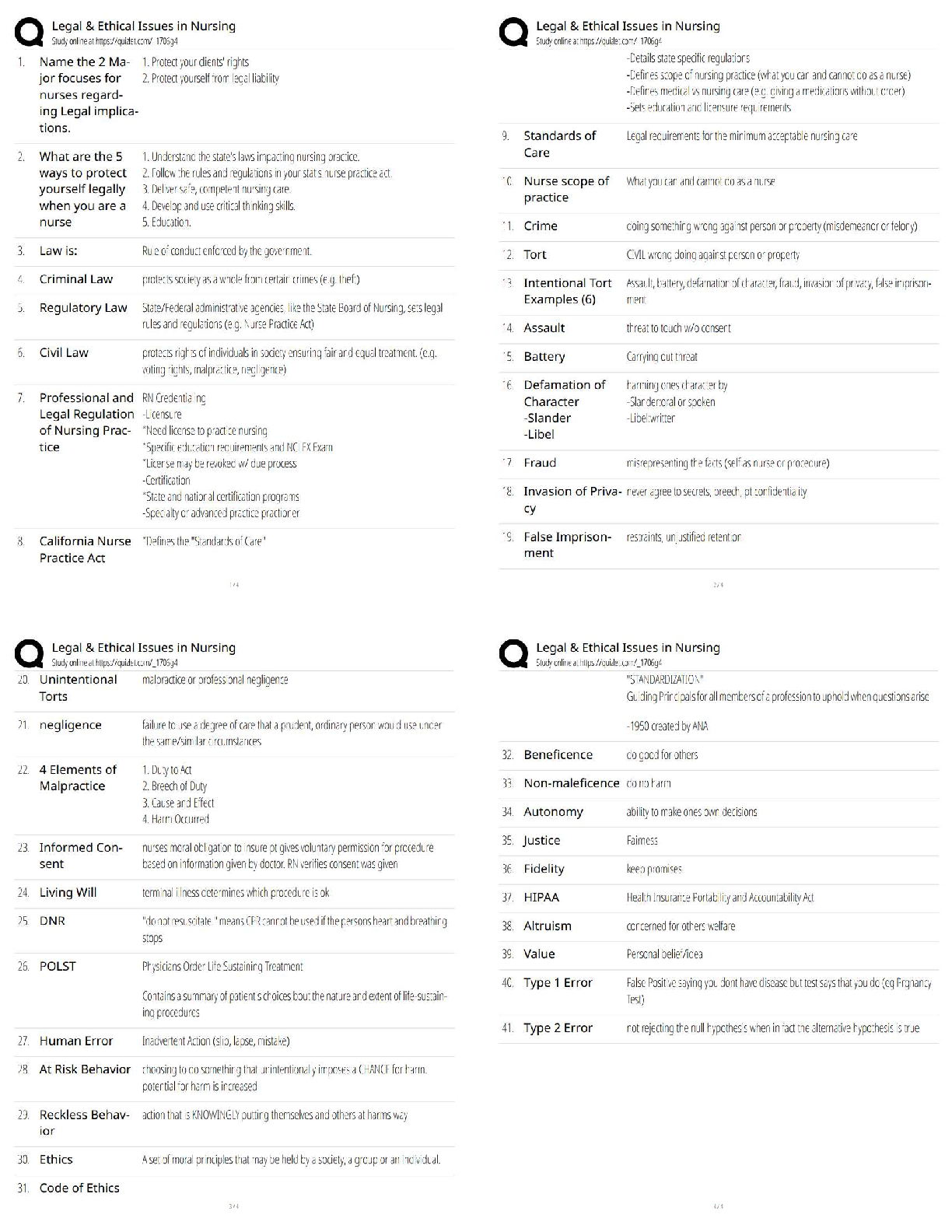
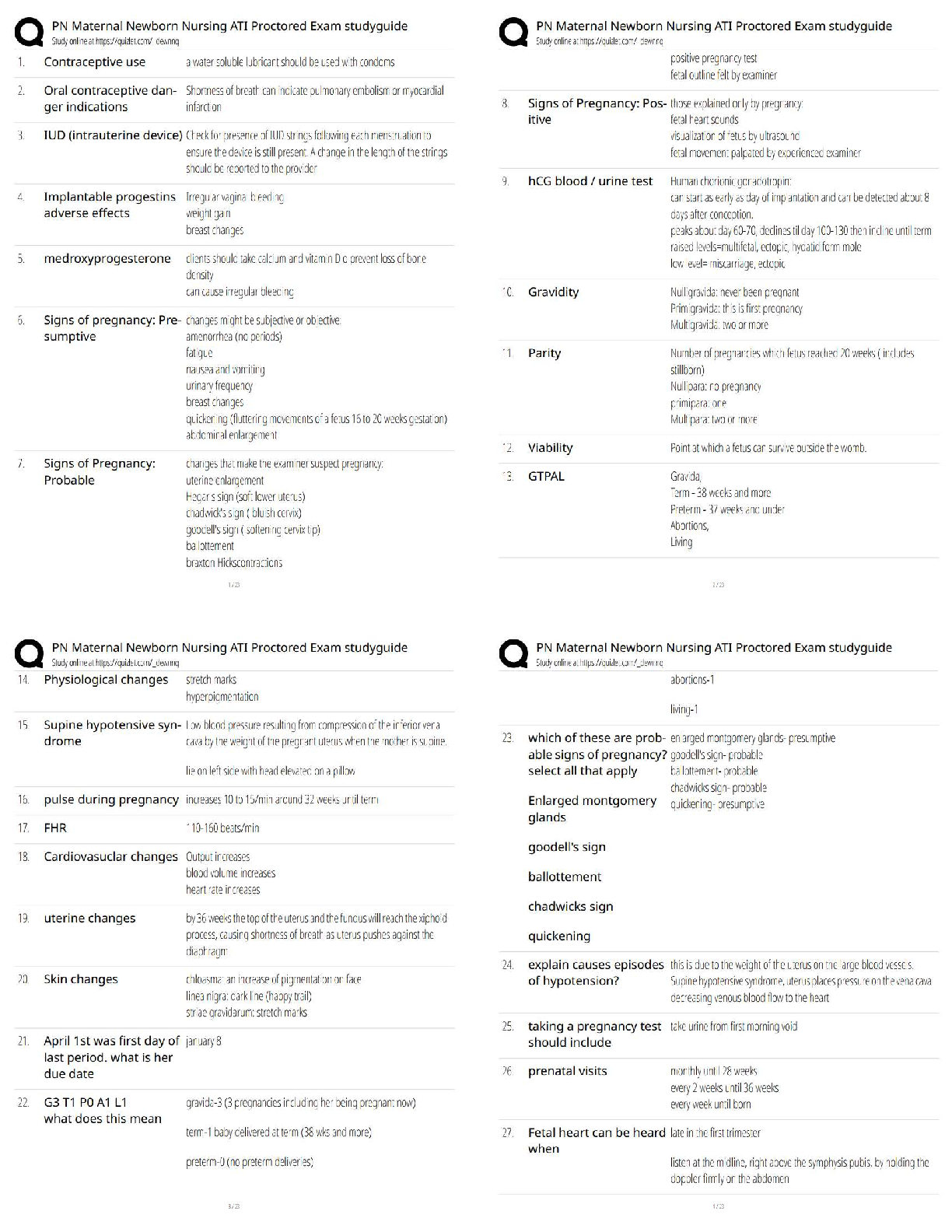
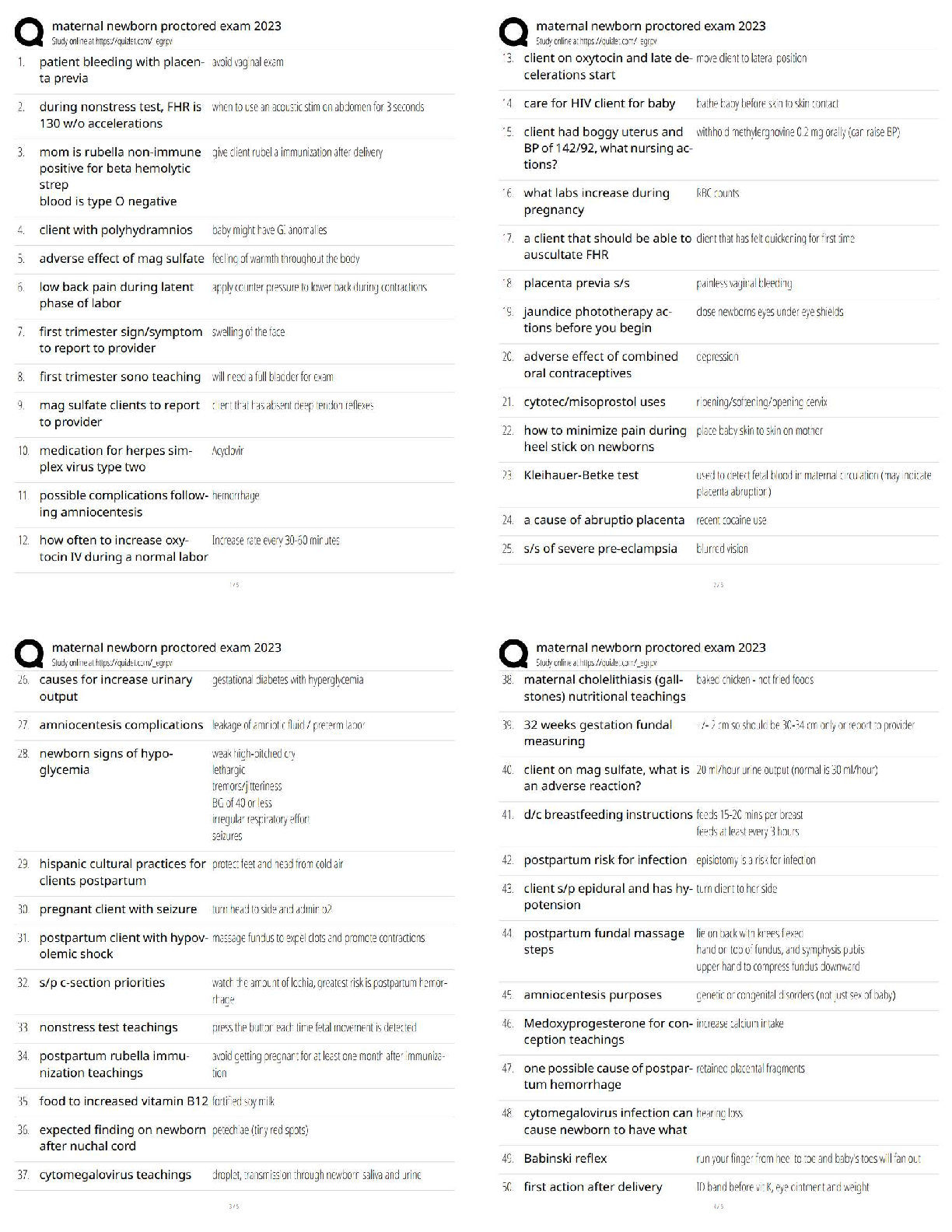
Nr 602 wk 8 poss questions ACOG guidelines regarding well women exams- age specific screening, laboratory tests, evaluation and counseling and immunizations Ages 13-18: Ages 19-39: Ages 40-65: A ... ges 65 and older: What is the ASCCP recommended management for an ASCUS (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance) pap result with a positive high-risk HPV 16 cotest in a 26-year-old woman without a history of abnormal pap smears? Colposcopy A well-woman visit for an adolescent should include which of the following? A general health history focusing on reproductive and sexual health concerns (menses, gynecologic, and pregnancy related) and psychosocial (family related, peer related, emotional, and physical as well as related to abuse, drug use, and alcohol use) concerns Physical exam, screening tests, and immunizations as indicated by the health history and gynecologic considerations for an external-only inspection of the genitalia ACOG Pap smear guidelines- starts at age 21 and is done every three years. Age 30 and older doe a pap and HPV every five years if co test is done, if just pap then do every 3 years. Can stop at age 65 if a negative history for 1o years or if the patient has had a hysterectomy with no history of cervical cancer. A Bethesda system Pap smear report that reads LSIL is most consistent with which classification? CIN 1 A single Pap smear reading of ASCUS in a patient negative for HPV infection should have what as follow-up? Routine screening A female patient is 35 years old. She has never had an abnormal PAP smear and has had regular screening since age 18. If she has a normal PAP smear with HPV testing today, when should she have the next cervical cancer screening? 5 years A young sexually active client at the family planning clinic is advised to have a Papanicolaou (Pap) smear. She has never had a Pap smear before. What should the nurse include in the explanation of this procedure? The Pap smear can detect cancer of the cervix Lab results on your 26-year-old patient show a negative Pap smear with a positive human papillomavirus (HPV) screen. Which procedure will be required next? Repeat Pap and HPV screen Which of the following is not part of the criteria for an older woman to cease having any future Pap tests performed? Over 55 years of age Amenorrhea (Primary and Secondary) Primary and Secondary Amenorrhea Primary amenorrhea : No menarche by the age of 15 years (with or without development of secondary sexual characteristics). Half of cases are caused by chromosomal disorders (50%) such as Turner syndrome. Puberty is delayed if there is no breast development by age 13 years, absence of pubic hair at age 14 years, and no menarche by age 15 years. Secondary amenorrhea : No menses for three cycles, or 6 months if previously had menses. Most common cause is ). Secondary Amenorrhea Associated With Exercise and Underweight Excessive exercise and/or sports participation have a higher incidence of amenorrhea (and infertility) due to relative caloric deficiency "Female athlete triad"; anorexia nervosa/restrictive eating, amenorrhea, and osteoporosis Labs Pregnancy test (serum human chorionic gonadotropin [hCG]) Serum prolactin level (rule out prolactinoma-induced amenorrhea) Serum TSH; also follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH; rule out premature ovarian failure) If amenorrhea for more than 6 months, measure bone density Treatment Plan Educate about increasing caloric intake and decreasing exercise Prescribe calcium with vitamin D 1,200 to 1,500 mg daily and vitamin E 400 IU daily 2 Nr 602 wk 8 poss questions Complications Osteopenia/osteoporosis (stress fractures) Myocardial atrophy, arrhythmia (sudden death), bradycardia, hypotension Hypoglycemia, dehydration, electrolytes Lanugo (fine downy hair), telogen effluvium (hair loss), xerosis (dry skin), infertility Low body mass index (BMI), cachexia, anemia, respiratory failure You are evaluating a 17-year-old Emily who presented with amenorrhea and normal secondary sex characteristics. The purpose of the progesterone challenge is to ascertain the presence of? Endogenous estrogen A 17-year-old female patient presents with amenorrhea for 4 months she did experience menarche at age 15 but had not had a menstrual cycle since. On physical examination, it is noticed that she has normal secondary sexual characteristics. The nurse practitioner will consider a progesterone challenge to determine the presence of adequate Endogenous estrogen A teenage patient presents with amenorrhea and moral secondary sex characteristics. A progesterone challenge is ordered. The purpose is to determine the presence of ____________? Endogenous estrogen A 16year old girl who comes to your office with a history of secondary amenorrhea. She experienced menarche at age 10, regular cycles for 2 years. She has not menstruated now for 4 years. In your initial consideration of differential diagnoses, what is the most frequent etiology of this problem: Eating disorder 18yo female c/o secondary amenorrhea. On exam, there is normal secondary sex characteristics and normal genitalia. Pregnancy is ruled out. What would necessitate further eval? Galactorrhea Primary amenorrhea is best described as: Failure to menstruation to occur by 13 yr A nurse practitioner is caring for a woman with primary and secondary amenorrhea. The pelvic exam was normal. Which of the following may be the cause if etiology originates in the hypothalamus? Sheehan’s syndrome American Cancer Society recommendations Mammography remains the single best screening procedure for the early detection of breast cancer. The majority of breast cancers in the United States are detected as a result of an abnormal screening study A positive family history of breast cancer is recognized as a risk factor for the subsequent development of breast cancer. With the discovery of 2 major breast cancer predisposition genes, BRCA1 (17q21) and BRCA2 (13q12-13), there has been increasing interest in genetic testing. Mutations in these 2 genes are associated with an elevated risk for breast cancer, as well as ovarian, colon, prostate, and pancreatic cancers. Brest Cancer Breast cancer is the main cause of death for women between the ages of 40 and 59 breast cancer is the most common cancer among women of all ethnic groups, although the incidence of the disease is highest among white patients. Inherited genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations, Fibrocystic changes of the breast and other nonproliferative breast lesions are not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer. Clinical staging is based on the TNM (tumor, node, metastasis) system of the International Union Against Cancer. Most patients with palpable breast cancers present with painless masses in the breast, most of which are discovered by the patient herself physical examination should be carried out with the patient sitting, arms at sides and then overhead. Symptoms- Early findings are a Single, nontender, firm to hard mass with ill-defined margins; mammographic abnormalities and no palpable mass. Late findings are Skin or nipple retraction; axillary lymphadenopathy; breast enlargement, redness, edema, brawny induration, peau d'orange, pain, fixation of mass to skin or chest wall. Late late findings Ulceration; supraclavicular lymphadenopathy; edema of arm; bone, lung, liver, brain, or other distant metastases. Reccomendations: After completion of treatment a patient should undergo a physical examination every 4 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months until year 5, and annually thereafter. A mammogram should be obtained annually for all patients and no less than 6 months after the completion of radiation therapy Breast Disorders Fibrocystic breast: Benign breast disease [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 04, 2022
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 04, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
57