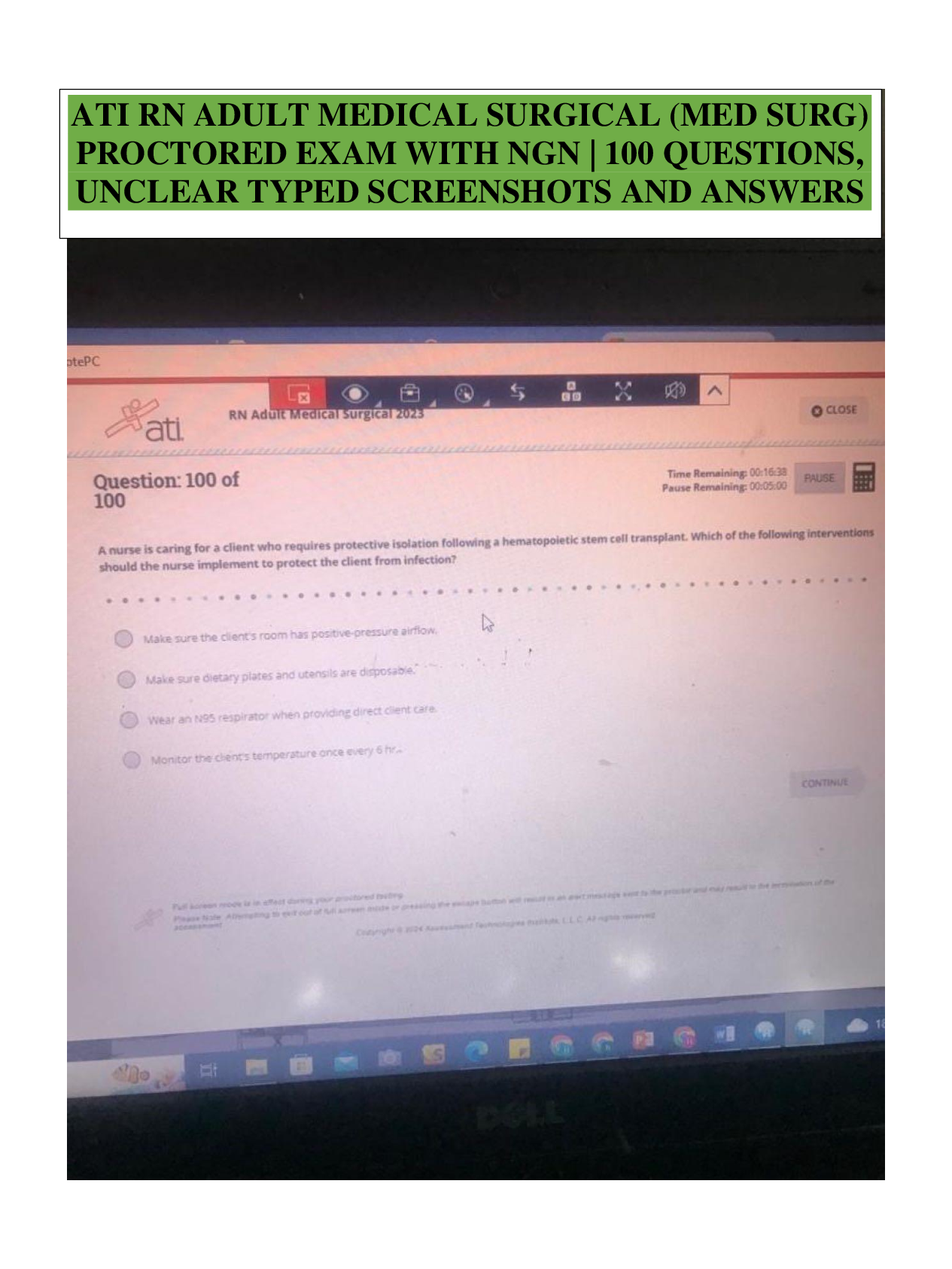
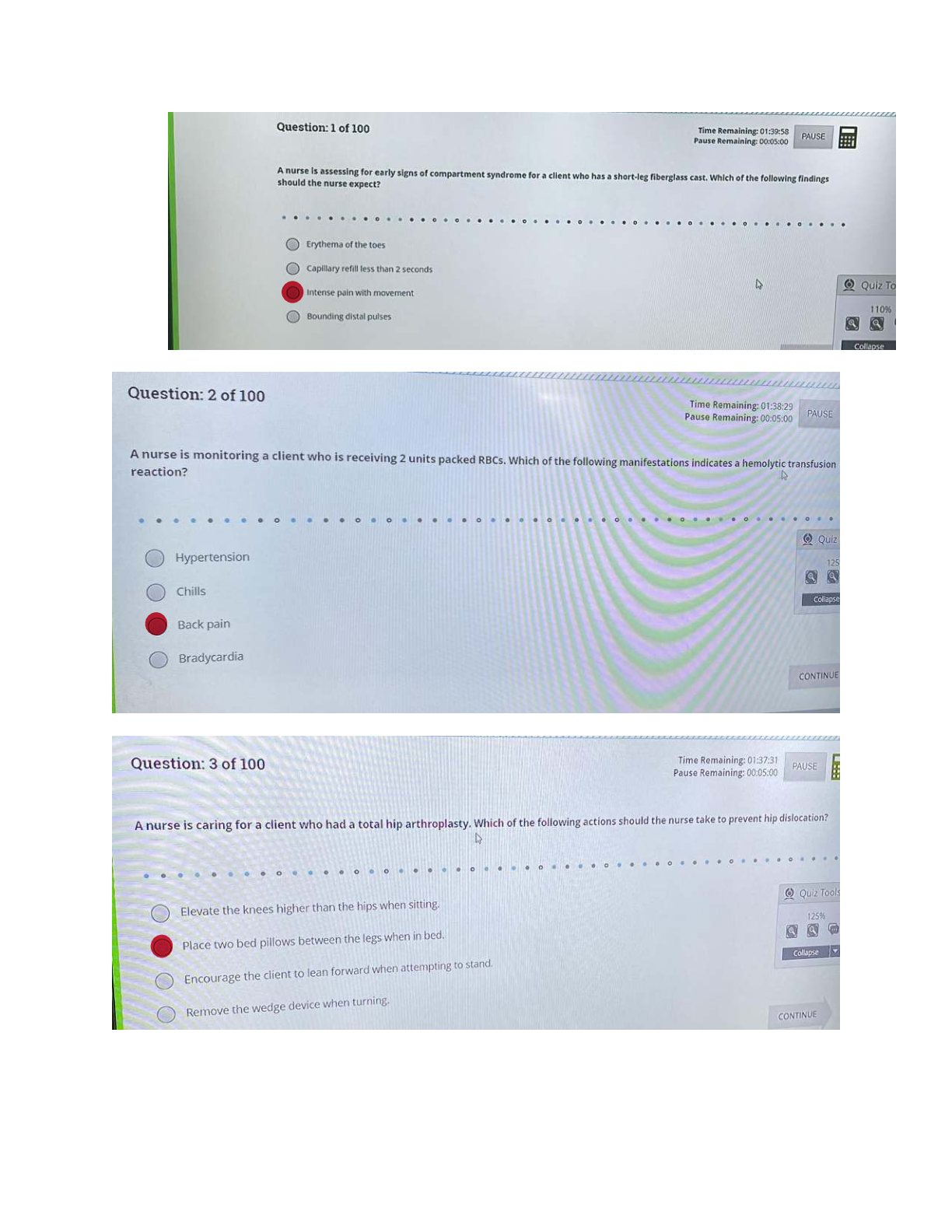
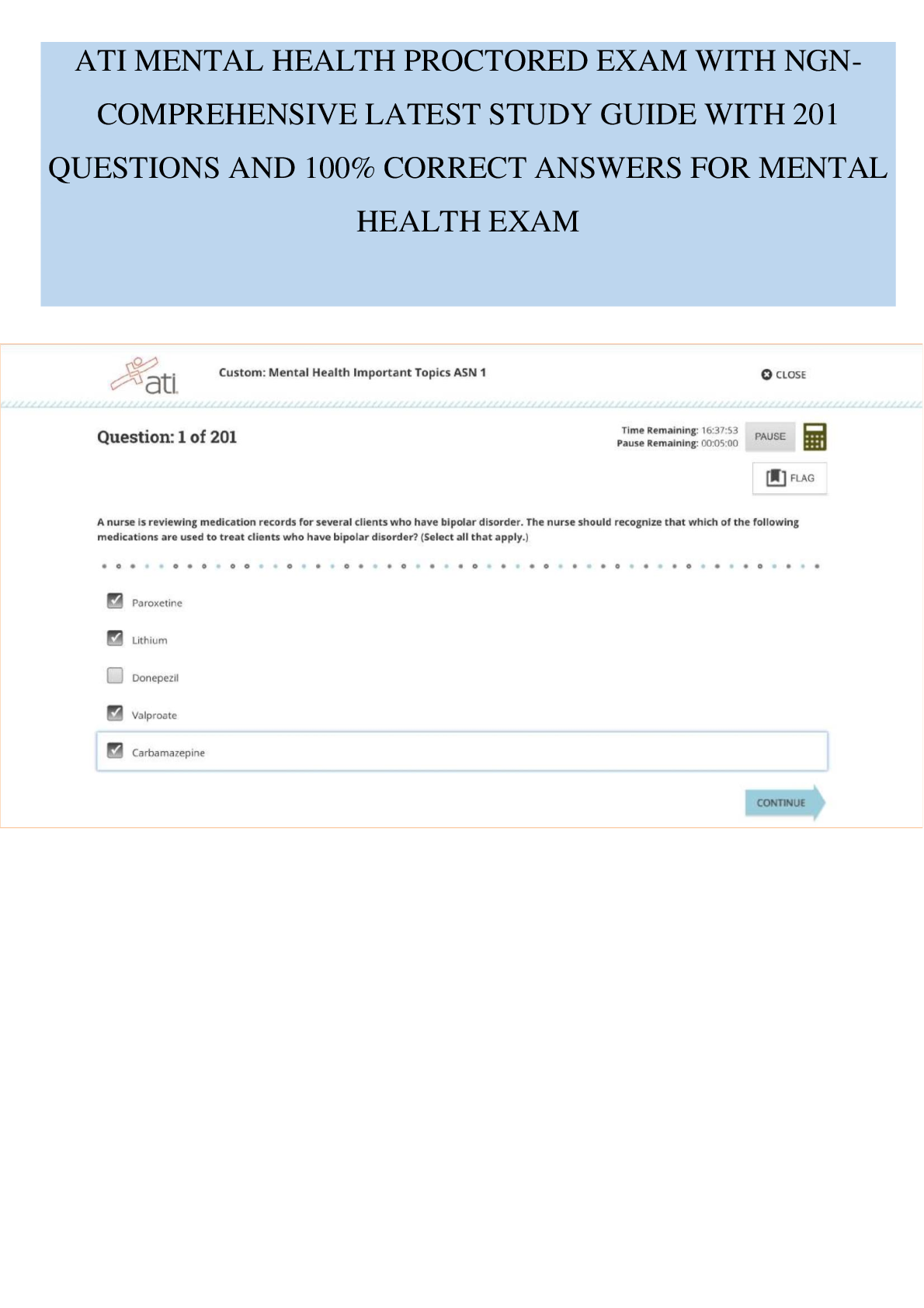
1. Question :
(TCO 1) Which of the following is NOT an essential nutrient?
Student Answer: Water Alcohol Vitamins Minerals
...
1. Question :
(TCO 1) Which of the following is NOT an essential nutrient?
Student Answer: Water Alcohol Vitamins Minerals
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 1
Question 2. Question :
(TCO 1) Which of the following nutrients contains the element nitrogen?
Student Answer: Carbohydrates
Lipids Water Proteins
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 1
Question 3. Question :
(TCO 1) Which statement is FALSE concerning the field of nutrition?
Student Answer: Nutrition is the study of how food nourishes the body.
Nutrition encompasses how we consume, digest, metabolize, and store food.
Nutrition is an ancient science that dates back to the 14th century.
Nutrition involves studying the factors that influence eating
Instructor Explanation:
patterns.
Chapter 1
Question 4. Question :
(TCO 1) Which of the following nutrients is the most energy dense?
Student Answer: Carbohydrate Lipid
Protein Vitamin
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 1
Question 5. Question :
(TCO 1) For dinner, Bill consumes 255 grams of carbohydrate, 70
grams of protein, and 50 grams of fat. In addition, Bill decides that he
wants a glass of wine with his meal. If he drinks one glass of wine
containing 8 grams of alcohol, how many total kilocalories does he
consume in this meal?
Student Answer: 56 kilocalories 540 kilocalories
1,675 kilocalories
1,806 kilocalories
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 1
Question 6. Question :
(TCO 1) Which of the following is a micronutrient?
Student Answer: Carbohydrates Vitamins Lipids
Alcohol
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 1
Question 7. Question :
(TCO 2) Reduced rates of hypertension is the central objective of the:
Student Answer: Food Guide Pyramid.
5-A-Day for Better Health Program.
DASH diet.
the Exchange System.
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 2
Question 8. Question :
(TCO 2) Which of the following is required on all food labels?
Student Answer: the net contents of the package ingredient list
the name and address of the vendor all of these
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 2
Question 9. Question :
(TCO 2) In which group are cheeses listed in the Exchange System?
Student Answer: milk
meat fruit starch
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 2
Question 10. Question :
(TCO 2) The type of study that observes a large population to determine factors that may influence nutritional habits and disease trends is called a(n):
Student Answer: case controlled study. clinical trial. epidemiological study. animal study.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 1
Question 11. Question :
(TCO 2) The second step of the scientific method is:
Student Answer: observation and description of a phenomenon.
testing a research question or hypothesis. generating a hypothesis.
collecting data.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 1
Question 12. Question :
(TCO 2) The 5-A-Day for Better Health Program was developed by the:
Student Answer: American Dietetic Association.
National Centers for Disease Control. National Dairy Council.
National Cancer Institute.
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 2
Question 13. Question :
(TCO 3) Digestion and absorption occur at the level.
Student Answer: tissue organ system organism
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 3
Question 14. Question :
(TCO 3) What is chyme?
Student Answer: ulcerations of the esophageal lining healthy bacteria of the small intestine
mixture of partially digested food, water, and gastric juices substance that allows for the emulsification of dietary lipid
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 3
Question 15. Question :
(TCO 3) Responding to the presence of protein and fat in our meal,
cholecystokinin (CCK) signals the gallbladder to release a substance
called:
Student Answer: lipase.
pepsin. chyme. bile.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 3
Question 16. Question :
(TCO 3) Which best explains why carbohydrate digestion ceases when
food reaches the stomach?
Student Answer: Carbohydrate is completely digested in the mouth.
Salivary enzymes cannot function in the acid environment of the stomach.
Carbohydrate is completely absorbed in the esophagus. Intestinal bacteria are needed for carbohydrate digestion.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 3
Question 17. Question :
(TCO 3) All of the following are found in saliva EXCEPT:
Student Answer: water and mucus.
enzymes. antibodies. bicarbonate.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 3
1. Question :
(TCO 4) Peggy Sue's doctor wants to screen her for reactive hypoglycemia. If her doctor's suspicions are correct and Peggy Sue does have reactive hypoglycemia, what would you expect her blood glucose concentration to be at approximately TWO HOURS after she had begun her glucose tolerance test?
Student Answer: elevated as compared to a normal individual depressed as compared to a normal individual
normal; two hours after consuming the glucose load, her blood
Instructor Explanation:
concentrations will be no different from those of a normal individual.
Chapter 4
Question 2. Question :
(TCO 4) Gluconeogenesis is:
Student Answer: the synthesis of new glucose from amino acids.
the release of stored glycogen from the liver.
the process by which plants use sunlight to synthesize glucose. the uptake of glucose by the body's cells.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 4
Question 3. Question :
(TCO 4) Which of the following does NOT describe the cell membrane
of an animal cell?
Student Answer: rigid barrier resistant to all noncellular molecules
structurally organized into a lipid bilayer dynamic and continuously changing
perimeter structure of the cell that is composed of phospholipids,
Instructor Explanation:
cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrate chains Chapter 3
Question 4. Question :
(TCO 4) Which of the following is associated with the development of ketosis?
Student Answer: a diet that contains too much fat a diet that contains insufficient fat
a diet that contains too much carbohydrate a diet that contains insufficient carbohydrate
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 4
Question 5. Question :
(TCO 4) The term complex carbohydrates refers to:
Student Answer: monosaccharides. disaccharides. polysaccharides. glucose.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 4
Question 6. Question :
(TCO 4) Over 16 million Americans have diabetes. Which of the
following is the most prevalent form of diabetes?
Student Answer: type 1
type 2 gestational pediatric
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 4
Question 7. Question :
(TCO 4) Which of the following enzymes is found in the mouth?
Student Answer: lactase
maltase
pancreatic amylase salivary amylase
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 4
Question 8. Question :
(TCO 4) Which of the following is a disaccharide?
Student Answer: sucrose
fructose galactose glucose
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 4
Question 9. Question :
(TCO 1-6) Which government agency regulates organic farming
standards in the United States?
Student Answer: Food and Drug Administration
United States Department of Agriculture Environmental Protection Agency Centers for Disease Control
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 18
Question 10. Question :
(TCO 1-6) Pesticides are:
Student Answer: chemicals added to food to enhance them in some way.
chemicals added to food that help prevent microbial spoilage and enzymatic deterioration.
chemicals used in the field and in storage areas to decrease
destruction caused by insects and fungus.
chemicals produced by microorganisms that harm tissue and elicit
Instructor Explanation:
an immune response.
Chapter 18
Question 11. Question :
(TCO 1-6) Which government agency regulates the labeling, sale, distribution, use, and disposal of all pesticides in the United States?
Student Answer: Food and Drug Administration
United States Department of Agriculture Environmental Protection Agency Centers for Disease Control
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 18
Question 12. Question :
(TCO 1-6) Which human organ system is most affected by toxic levels of mercury?
Student Answer: nervous renal
cardiovascular digestive
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 18
Question 13. Question :
(TCO 1-6) Which of the following are the most common form of
pesticides?
Student Answer: insecticides
herbicides fungicides biopesticides
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 18
Question 14. Question :
(TCO 1-6) The food-borne illness caused by Campylobacter jejuniis associated with consuming:
Student Answer: grains that have been stored in a moist environment.
water that has been contaminated with fecal material. tapeworms.
contaminated beef or pork.
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 18
Question 15. Question :
(TCO 1-6) The easiest and most effective way to prevent food-borne illnesses is to:
Student Answer: wash hands before handling food.
separate foods to avoid cross-contamination. chill foods to prevent microbes from growing. cook foods to their proper temperature.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 18
Question 16. Question :
(TCO 1-6) An estimated of all chicken eggs in the U.S. are
contaminated with Salmonella.
Student Answer: one-fifth one-fourth one-third one-half
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 18
Question 17. Question :
(TCO 1-6) In which of the following environments doesClostridium
botulinum flourish?
Student Answer: acidic
alkaline F
> 140F
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 18
1. Question :
(TCO 5) All of the following are major classes of dietary lipids EXCEPT:
Student Answer: glycogens.
triglycerides. sterols. phospholipids.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 2. Question :
(TCO 5) Transport vehicles for most lipids are called:
Student Answer: lipoproteins.
peptides. monoglycerides. glycerols.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 3. Question :
(TCO 5) The two essential fatty acids are:
Student Answer: cholesterol and bile.
linoleic and alpha-linolenic acid. butyric and stearic acid.
cis and trans.
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 4. Question :
(TCO 5) Which type of dietary fat is known to elevate blood cholesterol levels?
Student Answer: Saturated Trans
Monounsaturated
Both saturated and trans
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 5. Question :
(TCO 5) Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the process of hydrogenation?
Student Answer: Hydrogenation creates trans fatty acids.
Hydrogenation is the process in which hydrogen atoms are added to double bonds.
Hydrogenation creates a heart-healthy product.
Hydrogenation makes a product more solid at room temperature.
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 6. Question :
(TCO 5) A fatty acid that contains a chain of 10 carbons and one double bond is termed a:
Student Answer: saturated, medium-chain fatty acid. saturated, long-chain fatty acid. monounsaturated, medium-chain fatty acid. monounsaturated, long-chain fatty acid.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 7. Question :
(TCO 5) Which of the following is a rich source of polyunsaturated fatty
acids?
Student Answer: Corn oil
Coconut oil Beef fat Butter
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 8. Question :
(TCO 5) The process of adding hydrogen to an unsaturated fatty acid and creating a more solid fat is called:
Student Answer: emulsification. pressurization. hydrogenation. deamination.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 5
Question 9. Question :
(TCO 6) Oligopeptides are a string of amino acids.
Student Answer: one to two
four to nine 10-15
more than 25
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 6
Question 10. Question :
(TCO 6) Well-planned vegetarian diets can reduce the risk of all of the following chronic diseases EXCEPT:
Student Answer: obesity.
heart disease. anemia. cancer.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 6
Question 11. Question :
(TCO 6) Which of the following proteins are fundamental to the immune
system?
Student Answer: Enzymes
Antibodies Buffers
Transport proteins
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 6
Question 12. Question :
(TCO 6) Which of the following is a genetic disorder resulting in
debilitating protein abnormalities?
Student Answer: Cystic fibrosis Mad cow disease Acidosis Kwashiorkor
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 6
Question 13. Question :
(TCO 6) Which of the following is associated with marasmus?
Student Answer: Distended abdomen
"Skin and bones" appearance Enlarged, fatty liver
All of these
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 6
Question 14. Question :
(TCO 6) All of the following are parts of an amino acid molecule
EXCEPT:
Student Answer: a central carbon.
an amine group.
an acid group.
a fatty acid group.
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 6
Question 15. Question :
(TCO 6) The process of combining two incomplete proteins to make a complete protein is called:
Student Answer: the protein combining method. amino acid sequencing method. mutual supplementation. protein.
Instructor
Explanation:
Chapter 6
Question 16. Question :
(TCO 6) Which of the following health problems has been associated
with high protein intakes?
Student Answer: Elevated blood cholesterol
Marasmus Edema
Sickle cell anemia
Instructor Explanation:
Chapter 6
[Show More]
.png)








 Questions and Answers 100% VERIFIED.png)
 Questions and Answers 100% correct Solutions.png)