Latest Bios 252 Final exam review
Document Content and Description Below
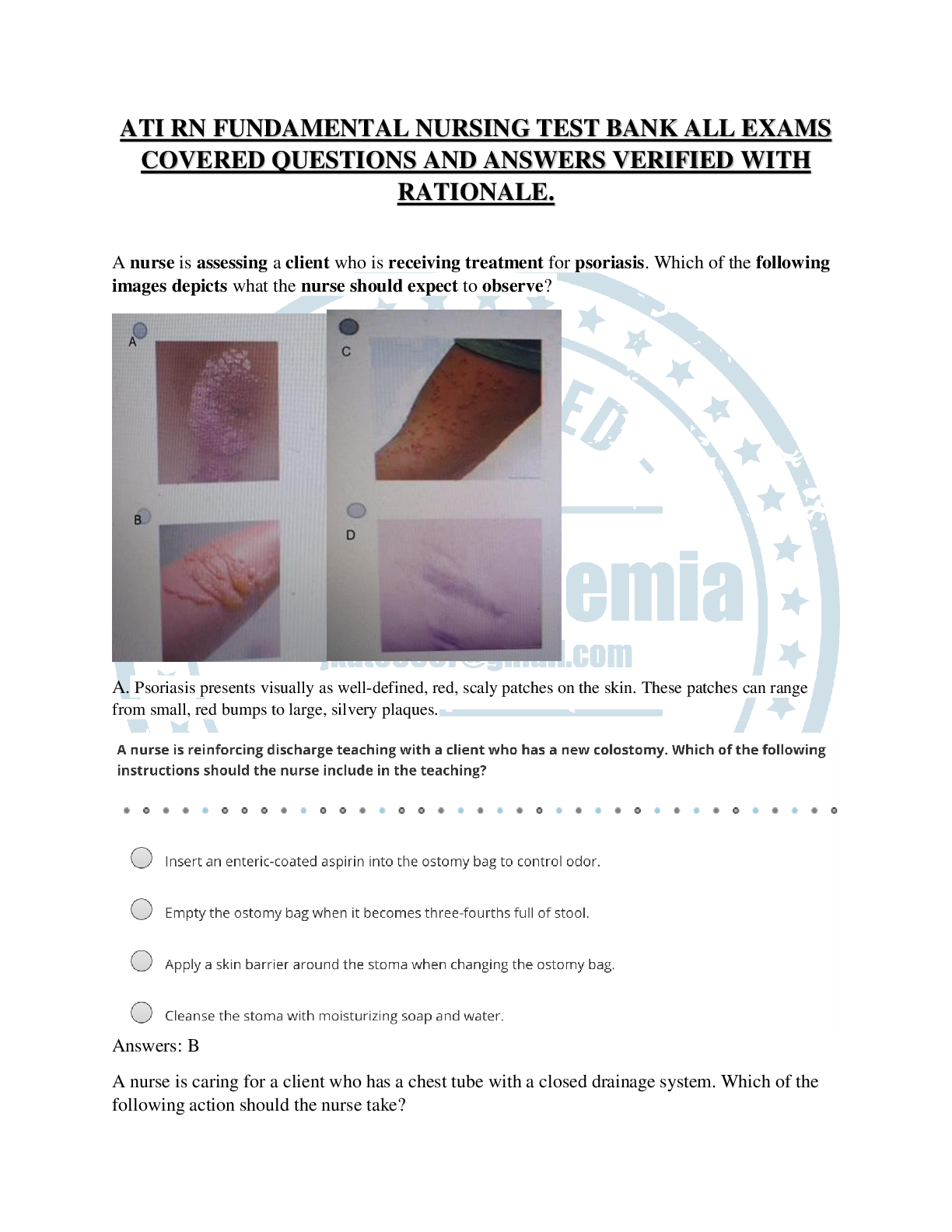
Latest Bios 252 Final exam review The sacral plexus is located in? A. CNS B. PNS C. In both the CNS and PNS D. In neither the CNS or PNS B. PNS Neuron cell bodies are located in? A. CNS ... B. PNS C. In both the CNS and PNS D. In neither the CNS or PNS C. In both the CNS and PNS The dorsal ramus is located in? A. CNS B. PNS C. In both the CNS and PNS D. In neither the CNS or PNS B. PNS A neuron with its cell body in the dorsal root ganglion is: A. in the nucleus B. a multipolar neuron C. a mixed neuron D. could be a somatic motor neuron E. controls effectors D. could be a somatic motor neuron These are sensory neurons of the eye and ear. A. efferent B. unipolar C. bipolar D. anaxonic C. bipolar Interneuron cell bodies are found in? A. dorsal root ganglion B. ventral gray horn C. dorsal gray horn D. lateral gray horn E. lateral white column C. dorsal gray horn Oligodendrocytes are glial cells of _____ matter of the CNS? a. dura b. gray c. white d. pia C. white Nissl bodies Rough endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes that act as the site of protein synthesis in neurons. Found in CNS neuron somas of gray matter. Ependymal cells In contact with CSF. Line ventricles of brain and central canal of spinal cord. Form single layer of cuboidal to columnar cells with cilia and microvilli. Modified epithelial cells. Astrocytes CNS cells responsible for physical support and maintaining blood brain barrier. Schwann cells Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin. Microglia Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brains immune system Satellite cells -Provide physical support to PNS neurons Diffusion of what neurons across a neuron membrane causes a depolarization? A. K+ B. Cl- C. Na+ C. Na+ Graded potentials The magnitude of the change in membrane potential varies with the strength of the stimulus. Includes: hyperpolarization, depolarization. Action potentials A. are initiated where dendrites meet the soma B. propagate due to voltage-gated ion channels C.vary in strength in response to stimulus D. may travel in either direction along the axolemma E. are sometimes initiated by hyperpolarizing the axon hillock B. propagate due to voltage-gated ion channels Absolute refractory period In an action potential is the limiting factor for the frequency of action potential conduction. Saltatory conduction Rapid transmission of a nerve impulse along an axon, resulting from the action potential jumping from one node of Ranvier to another, skipping the myelin-sheathed regions of membrane. Neurotransmitter receptors are found on the axolemma. True of False False Upon arrival at the axon terminal. synaptic vessels move toward the cell membrane in response to an elevated intracellular _________ ion concentration. A. K+ B. Cl- C. Na+ D. Ca ++ D. Ca ++ Presynaptic inhibition - Allows less neurotransmitter to be released at the synapse The limbs are innervated by: A. the intercostal nerves B. dorsal rami C. ventral rami D. gray rami C. ventral rami The skin of the back of the torso is innervated by: A. ventral ramus B. ventral root C. dorsal ramus C. dorsal ramus Which lack motor axons? A. dorsal ramus B. dorsal root C. ventral ramus D. ventral root B. dorsal root Impulses that control intestinal activity for digestion are initiated in the: A. dorsal gray horn B. ventral gray horn C. dorsal root ganglion D. lateral gray horn D. lateral gray horn Convergent neuronal circuit converging multiple impulses to one focal point Divergent neuronal circuit contain neurons that have branching axons that influence many different neurons. Send sensory input to many receiving neurons. Parallel processing neuronal circuit one neuron diverges into multiple lines of serial processing. this allows many things to happen at once. so if you get hurt you can move away from the pain and shout simultaneously Reverberation neuronal circuit The neuronal circuit involved with memory. Patellar reflex is what type of reflex? A. visceral B. learned C. cranial D. somatic D. somatic Muscle spindles Clusters of specialized muscle fibers scattered within each skeletal muscle Medulla oblongata Part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.h Pons A mound inferior to the brain, caudal to the midbrain, contains respiratory centers. Modifies respiratory rate and depth Thalamus Filters somatic sensory information. A forebrain structure that processes sensory information for all senses, except smell, and relays it to the cerebral cortex. Midbrain Contains nuclei for auditory reflexes and nuclei that control upper limb position. A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward. What part of the brain receives proprioceptive information? The cerebellum receives proprioceptive information. Reticular activation system excitatory fibers responsible for consciousness, arousal, degree of alertness, a filter process that allows for concentration. Limbic system Basis for link between emotion and memory. Hypothalamus A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward. Mammillary body receive and relay olfactory impulses as well as feeding reflexes of chewing, licking and swallowing. Basal nuclei Determine the specific sequence of movement needed. Damage to these causes loss of smooth muscle movement. Coordination of learned patterns. Arcuate fibers Connect neighboring gyri within a single cerebral lobe. Prefrontal cortex part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language. Precentral gyrus The strip of frontal cortex, just in front of the central sulcus, that is crucial for motor control. Contains primary motor cortex and somas of upper motor neurons. Olfactory cortex Smell - Receive information from receptors in the nasal lining of the nose, located deep in the temporal lobe. Primary sensory cortex Regions of the cerebral cortex that initially process information from the senses. Speech center Broca area; regulates the patterns of breathing and vocalization needed for normal speech. Part of somatic motor cortex. Premotor cortex Area of the frontal cortex, just anterior to the primary motor cortex, active during the PLANNING of a movement. Prefrontal cortex part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language. Helps ponder consequences of motor activity. Motor cortex Initiates motor activity An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movement. Vagus nerve - innervates many of the thoracic and abdominal viscera. Carries most of the parasympathetic output. Sensation an impulse initiated by activation of a receptor. Posterior column also known as the dorsal column it conducts sensory impuleses of light touch pressure and body movement Corticospinal tract starts in precentral gyrus, goes down decasates at medulla and comes down on the opposite side. Example stroke on right side, motor damage on left. Tectospinal tract Carries descending fibers from the superior and inferior colliculus. Facilitates head and neck movements related to visual reflexes. Anterior spinothalamic tract Ascending tract (sensory pathways) that convey crude touch. Located in the anterior white column; begins in the spinal cord and ends in the thalamus. Corticobulbar tract Controls all voluntary movement for speech production. Descends from motor cortex through internal capsule but terminates at cranial nerves. Proprioceptive information sensory information from the muscles, tendons, and joints that help one to locate the position of one's body (or body parts) in space. Somas of lower motor neurons of somatic motor pathways are located in? The cranial nerve nuclei and anterior horn of the spinal cord. Spinocerebellar tracts Ascending tract (sensory pathways) that convey proprioception information from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, and touch and pressure receptors to cerebellum for control of voluntary movements Referred pain Pain that is felt at the particular site but originated from another location, difficult for the brain to differentiate the point of origin, may originate from visceral or somatic structures. Visceral sensory pathway carry info collected by interoceptors monitoring visceral tissues and organs. Integrating center is solitary nucleus. Solitary nucleus integrates and relays visceral sensory information to autonomic processing centers; located in the medulla oblongata Somatic motor fibers in cranial nerves These fibers are part of the corticobulbar tract. Vestibulospinal tract Tract of brainstem, balance and equilibrium, head position. Is the subconcious motor component of a reflex elicited by a loud sound. Splanchnic nerve Preganglionic sympathetic fibers that pass through the diaphragm to the abdominal viscera. Also innervate urinary bladder. Sympathetic innervation of adipose tissue causes? This causes lipolysis What neurotransmitter is used in sympathetic ganglia? Ach is used in sympathetic ganglia. Alpha 1 receptors In plasma membrane stimulate smooth muscle contraction. Ex. Vasoconstrict blood vessels, contract uterine, contract arrector pili muscles. When NE binds to them, intracellular Ca levels increase. Beta 1 receptors Act on heart to increase rate and strength of contraction and on the kidneys to increase renin secretion. Intramural ganglia located adjacent to or within the walls of the viscera they supply - parasympathetic outflow system Muscarinic receptors Found at cholinergic neuromuscular or neuroglandular junctions in the parasympathetic division; the effects of stimulating these receptors are longer lasting than nicotinic and may be excitatory or inhibitory. Nicotinic receptors Parasympathetic receptors found on the surface of ganglionic cells of sympathetic & parasympathetic systems. Activated by acetylcholine. Always excitatory. Fovea centralis area consisting of a small depression in the retina containing cones and where vision is most acute Ciliary muscle Located in the eye; changes the lens shape. Cochlear branch of CN VIII a nerve in the head that carries signals from the cochlea of the inner ear to the brain. It is part of the vestibulocochlear nerve, the 8th cranial nerve. Does not conduct sound waves, mechanical vibrations or pressure waves. Tectorial membrane A membrane located above the basilar membrane; serves as a shelf against which the cilia of the auditory hair cells move Tympanic membrane The eardrum. A structure that separates the outer ear from the middle ear and vibrates in response to sound waves. Cortical blindness blindness caused by damage to the optic radiations or primary visual cortex. Endocrine communication Method of intercellular communication in which one cell communicates through the bloodstream with target cells throughout the body by using hormones. Direct communication Cellular communication across gap junctions. Paracrine communication uses chemical signals to transfer information from cell to cell within a single tissue, most common form of intercellular communication. Synaptic communication Method of intercellular communication in which neural cells communicate to adjacent neural cells by using neurotransmitters. T3 hormone Hormone that originates in thyroid, controls metabolic rate. Has receptor on thyroid and increase ATP synthesis rate. Adrenal cortex hormones exert their effects on their target tissues via what? They exert their effects on their target tissues via actions in the target cell nucleus. Elevated blood plasma concentration of amino acids elicits secretion of what hormone? Elevated AA blood plasma concentration elicits a secretion of GH. Insulin growth factor Plays an important role in childhood growth and continues to have anabolic effects in adults. What is an indirect effect of GH? An indirect effect of GH is to stimulate AA uptake by all cells through the actions of IGF. Secretions of what gland contain seminalplasmin and proteases? Secretions of the prostate gland contain seminalplasmin and proteases. Thecal cells -surround follicle and work with granulosa cells to produces estrogens. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 2 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 07, 2022
Number of pages
2
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
100