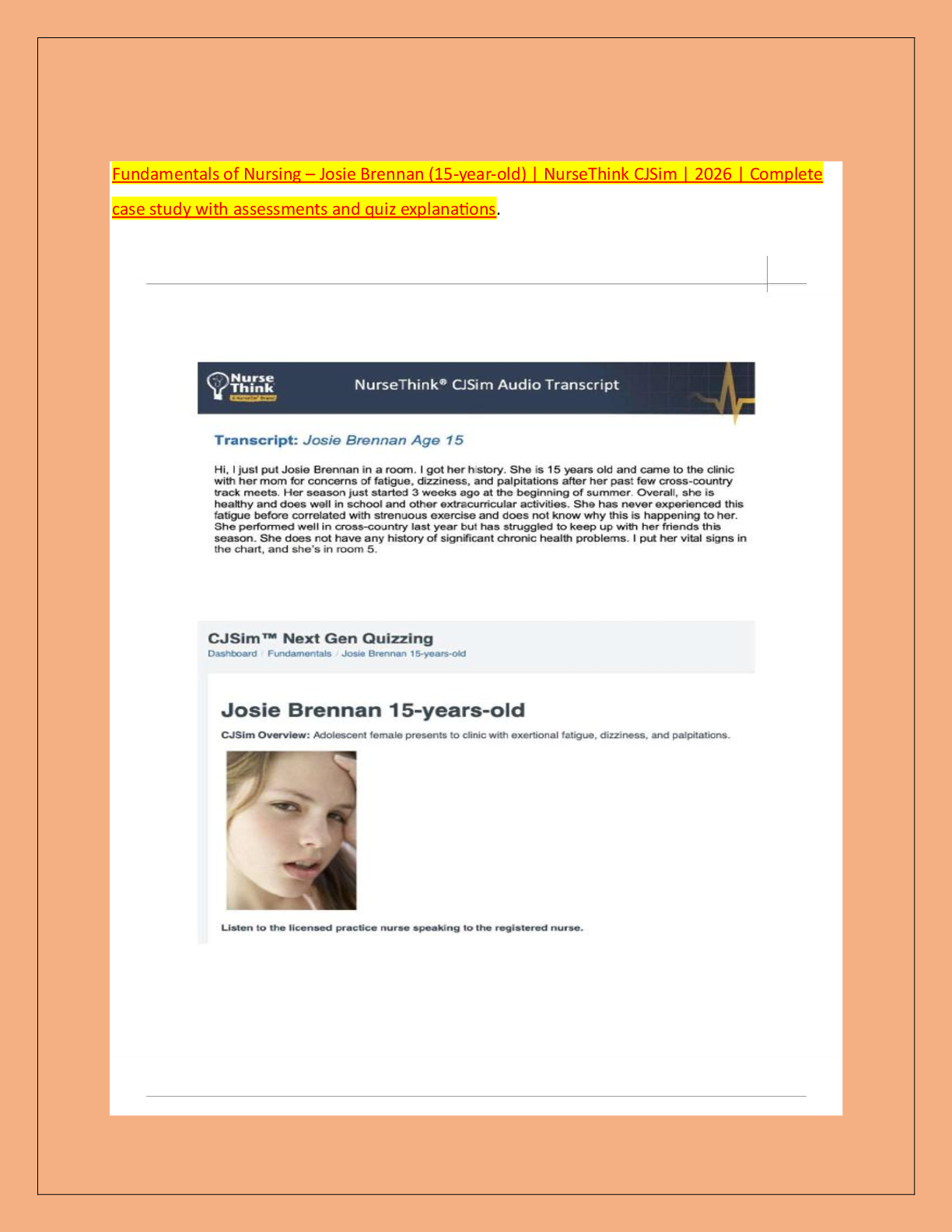
Teas science section 2021-2022 with complete solutions
Document Content and Description Below
Macromolecules carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes Carbohydrates Sugars and starches, which the body breaks down into glucose *Structural function: cellulose and chitin ... *Energy storage: amylose, amylopectin, glycogen *Recognition molecules: glycoproteins and glycolipids 00:20 01:35 Lipids Fatty acids and their derivatives that are insoluble in water * H and C and main components * Fats * Hydrophobic, nonpolar * Store energy ( fats, oils, adipose ) Proteins molecules composed of amino acids joined by peptide bonds * Monomer: amino acids (amino group + carboxylic acid)(20 types) * Keratin and collagen (hydrophobic) not soluble in water, found in structural protein * Globular proteins are hydrophilic (hemoglobin, antibodies, enzymes *Function as transport carries or signal transfer Nucleic acids Long molecules made of nucleotides; DNA and RNA * DNA stores genetic material * Chromosomes * RNA is a messenger (mRNA) also rRNA and tRNA Enzymes a class of proteins that catalyses chemical reactions. * Not consumed in reaction * Speed up reaction by lowering activation energy * Exergonic: release energy * Endergonic: require energy * Energy is supplied and releases as ATP * Lock and Key (substrate must fit into enzyme active site) purines and pyrimidines Purines: Adenine and Guanine Pyrimidines: Thymine and Cytosine DNA and RNA Macromolecule that contains coded instructions for the body to produce proteins * Nucleotide: the building block of DNA and RNA * Nitrogenous base: Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine * Purines: Adenine and Guanine Pyrimidines: Thymine and Cytosine * Codon: a group of three nitrogenous bases used to synthesize amino acids (synthesized from RNA during Translation * Hydrogen Bonds: Connect a Purine to a Pyrimidine ( A-T ) and ( C-G ). Non-Covalent, weak. - RNA: Uracil replaces Thymine *Double Helix structure * Coded or read 5' -> 3' * Sugar(Pentose)- Phosphate backbone (deoxyribose and phosphate group bound to 4 oxygen atoms) DNA helicase unzips and unwinds DNA DNA primase Generates RNA primer. Act as a template for starting point of DNA replication DNA polymerase Synthesize new DNA molecules by assign nucleosides to leading and lagging DNA strands in a 5'—> 3' direction Topoisomerase A protein that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork. ( prevents super-coiling) DNA ligase A linking enzyme essential for DNA replication; catalyzes the covalent bonding of the 3' end of a new DNA fragment to the 5' end of a growing chain. ( joins DNA fragments together and forms bonds between nucleotides ) Okazaki fragments short, newly synthesized DNA fragments that are formed on the lagging template strand during DNA replication single strand binding proteins bind to and stabilize single-stranded DNA during replication leading strand The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction. lagging strand replicated discontinuously in short sections Nucleus Houses DNA, 'brain' of the cell Mitochondria Powerhouse of the cell, organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production Golgi apparatus A system of membranes that sorts, packages and transports proteins for export by the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum Synthesize and processing of proteins, lipid expression Chloroplast An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs Flagellum A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move. (Locomotion and sensory functions) Vacuole A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area and maintaining homeostasis Lysosome A small, round cell structure containing chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones. Peroxisomes Contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals Ribosome site of protein synthesis Proteasomes breakdown and recycling of damaged or abnormal intracellular proteins Mitosis cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes Meiosis (genetics) cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms Meiosis II Sister chromatids separate, Results in 4 haploid daughter cells with unreplicated chromosomes Mitosis: Interphase (First Phase) 90% of cell life spent in interphase; during this time each chromosome is replicated, after replication, chromosomes consist of 2 identical sister chromatins (held together at center by centromere) Mitosis: Prophase (Second) Chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. The pairs of centrioles move to opposite sides of the nucleus. Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell. The nuclear envelope breaks down. Mitosis: Metaphase (Third) The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere. Mitosis: Anaphase (Fourth) The centromeres split. The two chromatids separate, and each chromatid becomes a new chromosome. The new chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell. The cell stretches out as the opposite ends are pushed apart. Mitosis: Telophase (Fifth) The chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rodlike appearance. A new nuclear envelope forms around each region of chromosomes. Mitosis: Cytokinesis (Final) Division into two daughter cells is completed Meiosis I Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I and Cytokinesis Synapsis and crossing over occur, tetrads line up on the metaphase plate, homologous pairs separate, on to Prophase II Meiosis Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II and Cytokinesis Chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate, sister chromatids separate, 4 haploid daughter cells are formed having only one chromosome of each homologous pair. States of Matter solid, liquid, gas Solid Rock, wood, paper Molecules are packed together tight, orderly pattern. Vibrational motion, not translational motion. A form of matter that has a definite shape and volume/density Liquid Water, juice, soda [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 08, 2022
Number of pages
8
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 08, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
49