*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Mental_Health_Exam_NEWEST- 2022 (All)
Mental_Health_Exam_NEWEST- 2022
Document Content and Description Below
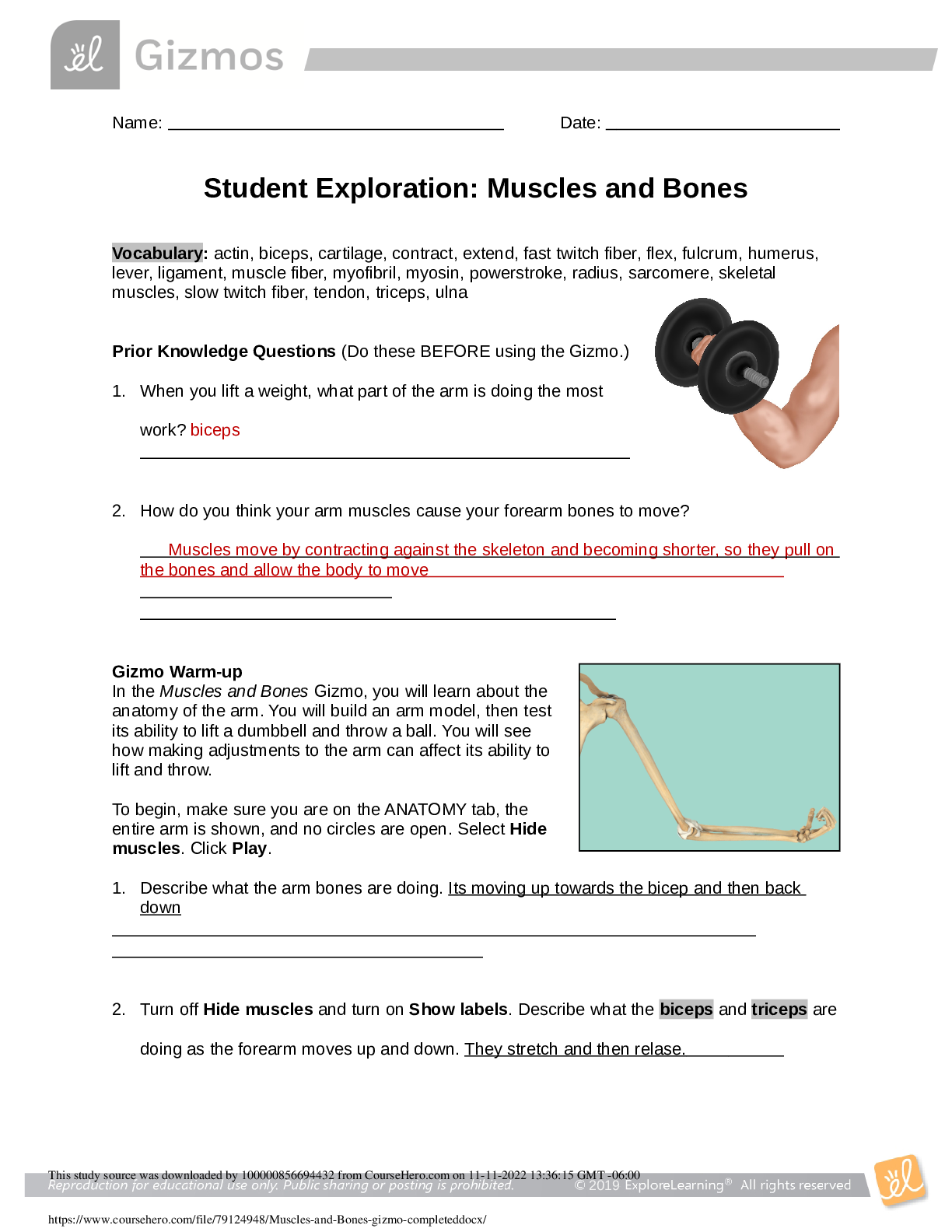
M e n t a l H e al t h E x a m 1 Theorists: Freud Id: The primitive, pleasure-seeking part of our personalities that lurks in the unconscious mind. Ego: Our sense of self. Acts as an ... intermediary between the Id and the world by using ego defense mechanisms, such as repression, denial, and rationalization. Engages in secondary process thinking, which is rational, realistic, and orientated towards problem solving. Superego: Assigned to those processes that Freud referred to as our conscience and is greatly influenced by our parents' or caregivers' morals and ethical stances. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 1. Physiological- food, water, oxygen, elimination, rest, sex 2. Safety- protection, security, stability, order, structure, limits 3. Love and Belonging Needs- affiliation, affection, lover 4. Esteem- competency, achievement, esteem from others 5. Self Actualization- becoming everything one is capable of Erikson’s Stages of Development Infant: Birth - 1.5 yrs old o Trust vs. Mistrust o Task: develop a basic sense of trust and comfort and minimal fear and uncertainty. Early childhood (toddler) - 1.5-3 yrs old o Autonomy vs. Shame/doubt o Task: gain self-control and independence Preschooler 3-6 yrs old o Initiative vs. Guilt o Task: achieve sense of purpose and task mastery School age 6-12 yrs old o Industry vs. Inferiority o Task: self-confidence thru learning and competition Adolescent 12-20 yrs old o Identity vs. Role confusion o Task: differentiation from parents leads to fidelity, integrate all the above for sense of self Young adult 20-30 yrs old o Intimacy vs. isolation o Task: form intense long term relationships Adult 30-65 yrs old o Generativity vs. Self-absorption o Task: achieve life goals and obtain concern for future generation Older adult 65+ o Integrity vs. Despair o Task: derive meaning from life and sense of self worth Page 2 Role of neurotransmitters as related disorders: Dopamine Increase: o Schizophrenia o Mania Decrease: o Parkinson's disease o Depression Functions: o Fine muscle movement o Integration of emotions and thoughts o Decision making o Stimulates hypothalamus to release hormones (sex, thyroid, adrenal) Serotonin Increase: o Anxiety states Decrease: o Depression Functions: o Mood o Sleep regulation o Hunger o Pain perception o Aggression and libido o Hormonal activity Norepinephrine Increase: o Mania o Anxiety o Schizophrenia Decrease: o Depression Functions: o Mood o Attention and arousal o Stimulates sympathetic branch of autonomic nervous system for "fight or flight" in response to stress GABA Increase: o Reduction of anxiety o Schizophrenia o Mania Decrease: o Mania o Anxiety o Schizophrenia [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 14 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 10, 2022
Number of pages
14
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 10, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
51





.png)

.png)

.png)
.png)













