Geography > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > EOSC 114 waves and tsunami multiple choice - University of British Columbia EOSC 114 (All)
EOSC 114 waves and tsunami multiple choice - University of British Columbia EOSC 114
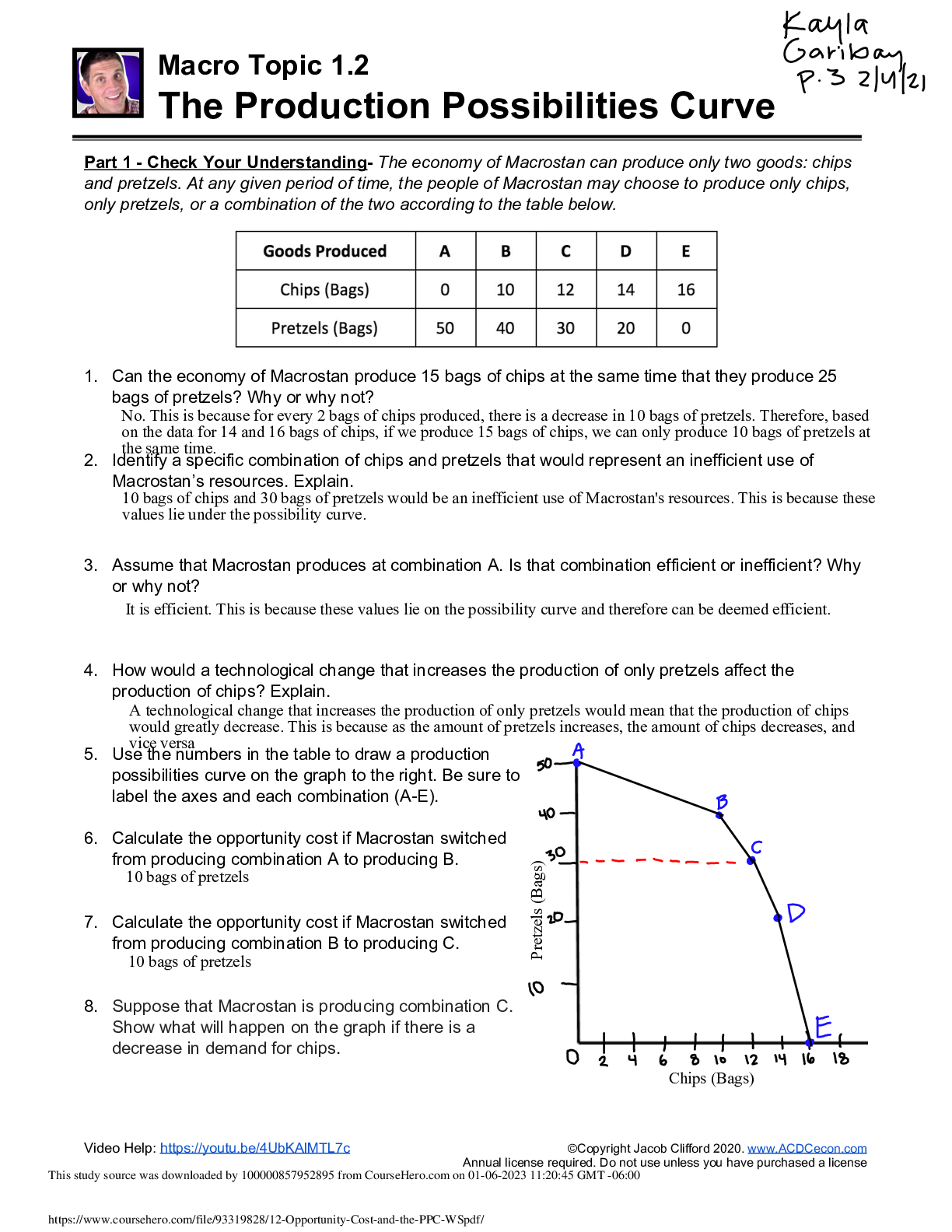
Document Content and Description Below
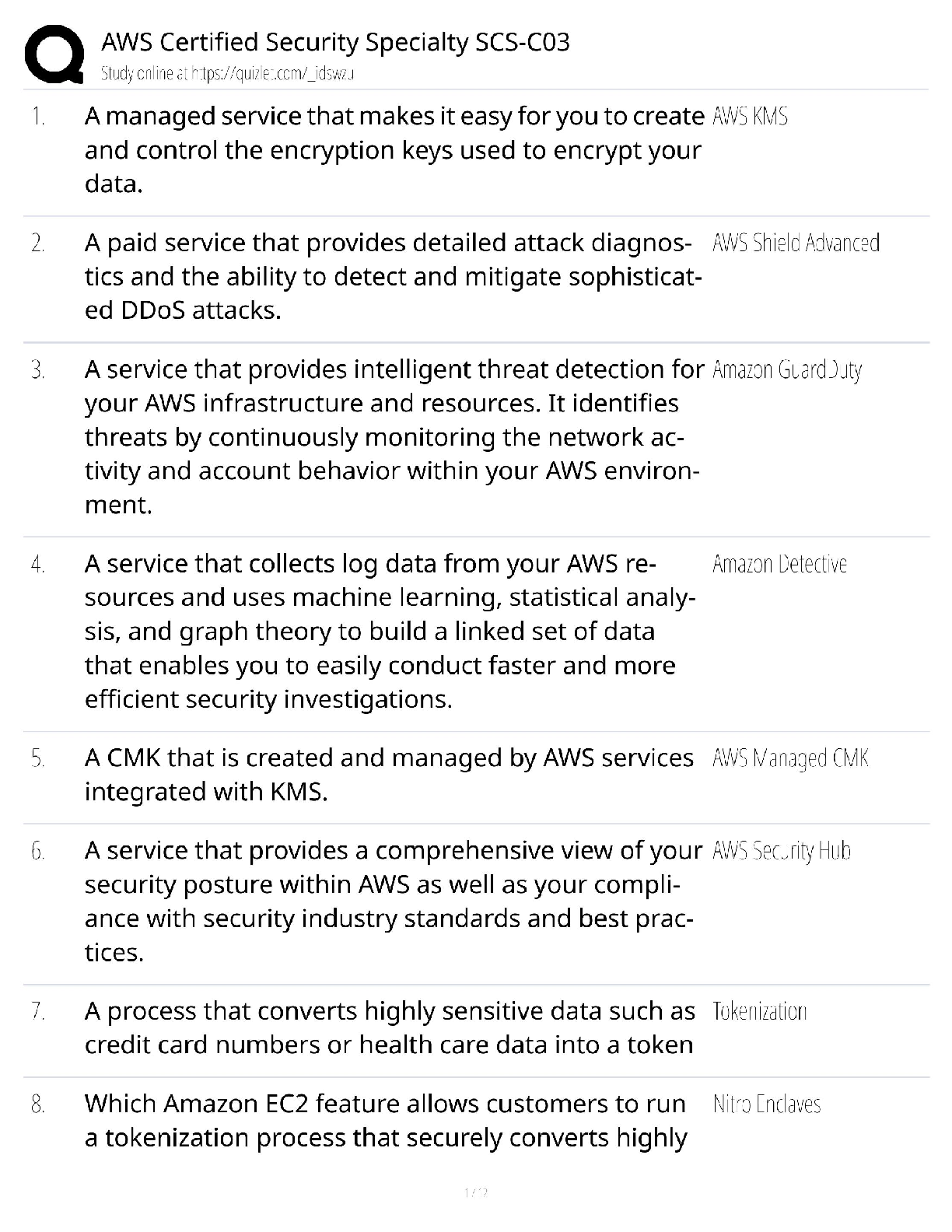
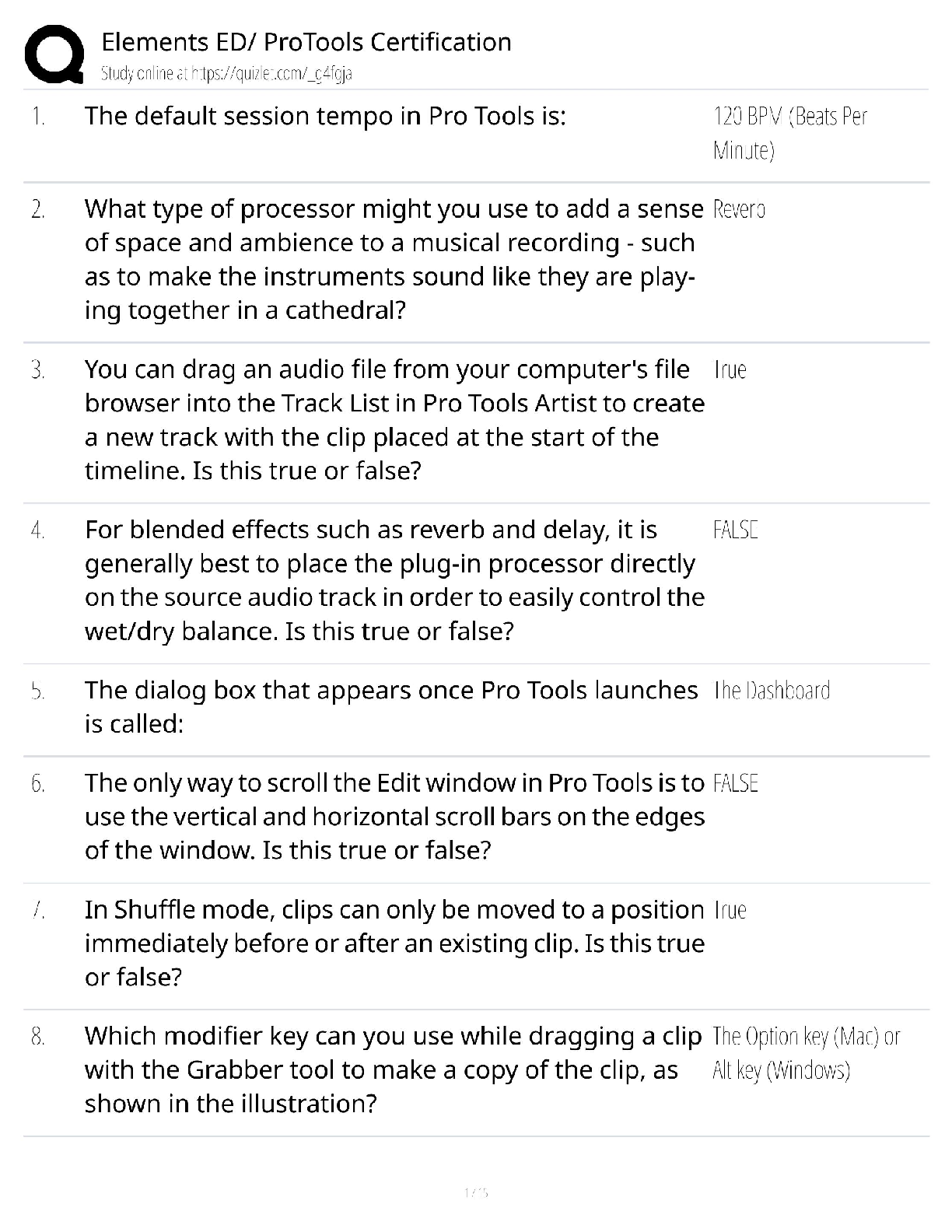
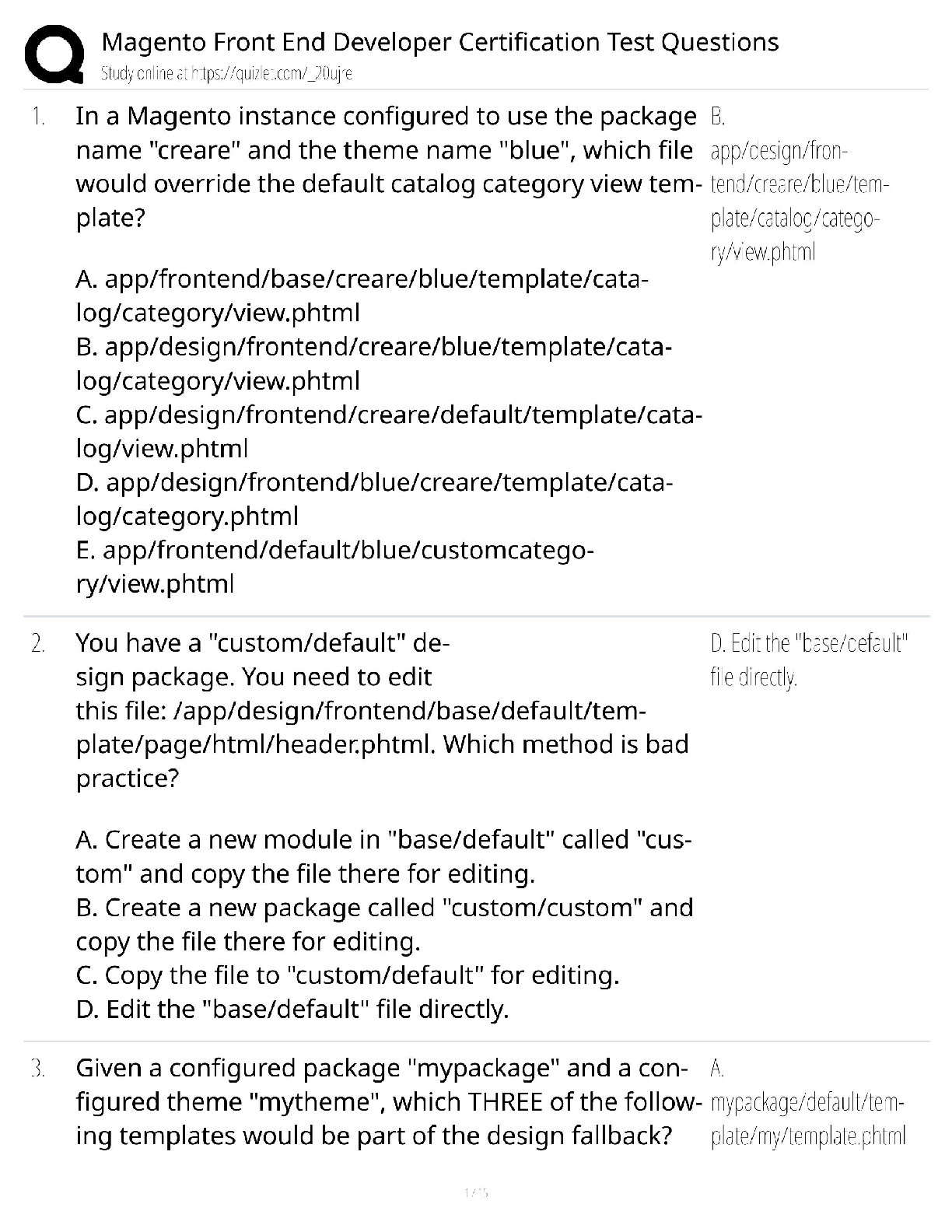
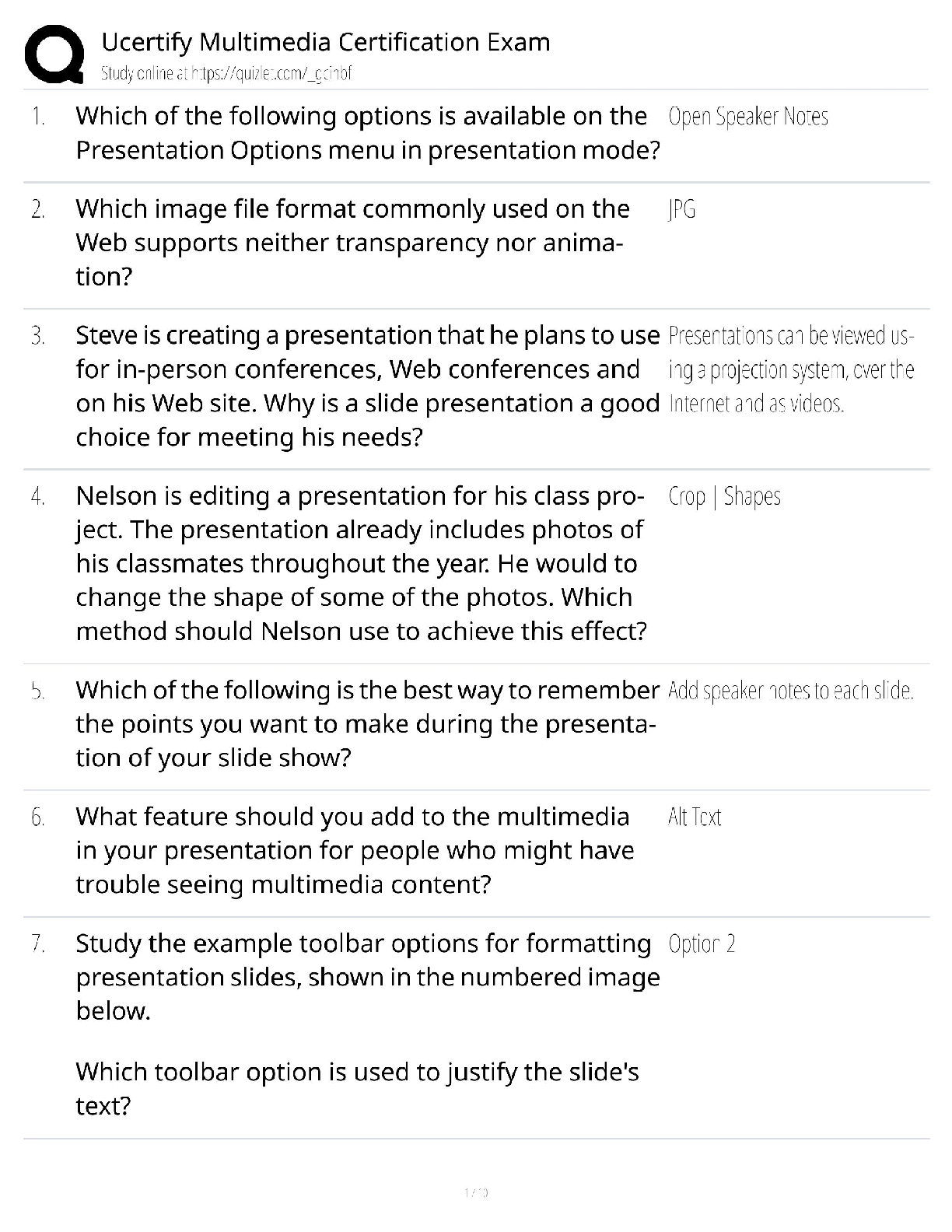
EOSC 114 waves and tsunami multiple choice 1. The restoring force for capillary waves is _______. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. gravity B. relaxation C. Coriolis force D. density E . s ... urface tension 100% Score: 1/1 2. Why are tsunami difficult to detect in the open ocean? Choose the BEST reason. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. Tsunami usually have only 3-7 wave crests in a row, so are only evident in a small area at any one time. B. Tsunami have very long wavelengths and small heights in the open ocean, so changes in the sea surface are very small. 100% C. We don’t yet have any technology that can detect tsunami in the open ocean. D. Tsunami move at speeds similar to jet planes, so they go by too fast. E. The technology available can only detect tsunami heights greater than 1 meter in the open ocean. Score: 1/1 3. If a wave with a wavelength of 100 m travels in a body of water 2 km deep, water particles at a depth of 70 m will ____. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. move rapidly toward the shore B. not be affected by the passing wave C. move in orbits that are 1/23rd of the orbits of water particles in the surface Student Response Value Correct AnsD . trace circular orbits 0% E. move in flattened ellipses Score: 0/1 4. Which of the following is TRUE about wave speed? Student Response Value Correct AnsA. The speed of a shallow water wave depends on wavelength and period. B. The speed of a tsunami depends on wavelength only. C. At the same depth, shallow water waves with longer L are faster than those with shorter L. D . In deep water, longer wavelength waves travel faster than those with shorter wavelengths. 100% E. Shoaling waves speed up as they approach shore. Score: 1/1 5. Which statement is TRUE? Student Response Value Correct AnsA. In shallow water, long-period waves travel faster than short-period waves. B. Deep water waves travel faster at water depth d=1000 meters than at d=1,500 meters. C. In shallow water, steeper waves are more stable than lower (less steep) waves. 0% D. In the Atlantic Ocean, most of the waves are generated by gravity. E. Deep water waves with longer wavelengths travel faster than those with shorter lengths. Score: 0/1 6. Imagine you’re a sailor at sea. You observe the sea state and determine that it is Beaufort Force 5. You record this in the ship’s logbook. The captain has been asleep for the past 8 hours and doesn’t know what’s going on. So you wake her up to report on the conditions. Of the following choices, what’s your most likely message to the captain? Student Response Value Correct AnsA. Conditions are very calm and you recommend stopping the ship for a swim. B. You recommend that everyone be kept inside because the danger of getting swept overboard is high. C. It’s likely that the ship is headed into a hurricane and it would be wise to change course. D . Conditions are fine and you recommend that the ship proceed on course. 100% E. It’s time to consider making an emergency rescue call to the Canadian Coast Guard. Score: 1/1 7. In the middle of the Southern Ocean, waves with the greatest speed ___________. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. have the shortest wavelengths B. maintain their speed as they approach shore C. have the longest wavelengths 100% D. are generated by winds blowing over the shortest fetch E. are shallow water waves Score: 1/1 8. In the Northern Hemisphere, in which part of the hurricane is storm surge the MOST disastrous for the coastline? Choose the BEST answer. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. to the west of the eye of the hurricane B. to the north of the eye of the hurricane C. directly under the eye of the hurricane D. on the left side of the hurricane (if you’re facing in the direction the hurricane is traveling) E . on the right side of the hurricane (if you’re facing in the direction the hurricane is traveling) 100% Score: 1/1 9. The following are ways British Columbia residents can protect themselves after a tsunami warning is issued EXCEPT ______. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. stay away from rivers and streams that lead to the ocean B. move boats out of harbours into deeper water C. be aware that the greatest danger is only due to the first wave D. if you are close to shore, move immediately away from shore to higher ground E . if unable to move away from shore, evacuate to at least the 5th floor or higher of multi-storey buildings 0% Score: 0/1 10 . The distance measured from trough to trough of a wave is the __________. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. orbital B. wave height C. wavelength 100% D. wave period E. Amplitude Score: 1/1 11 . Which of the following is FALSE about the Pacific Tsunami Warning Center (PTWC)? The PTWC ______. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. needs about one hour to gather information before they know enough to issue a tsunami warning B. uses data from DART™ to detect tsunami as small as 1 cm C. is directly in charge of alerting populations in the Pacific Northwest for regional tsunami events 100% D. issued a tsunami warning to Indonesia on 26 December 2004 E. depends on the assistance of government agencies to alert and evacuate coastal Student Response Value Correct Anscommunities in the event of a tsunami Score: 1/1 12 . The San Andreas Fault extends offshore under water in some sections to the north of San Francisco. Imagine that a magnitude 8.5 earthquake occurs along an underwater section of the fault. Is it likely or unlikely to generate a large tsunami? Student Response Value Correct AnsA . It is unlikely because the movement along the fault is horizontal. 100% B. It is likely because most underwater earthquakes generate tsunami. C. It is likely because earthquakes along the San Andreas fault are typically shallow. D. It is unlikely because the fault is still too close to shore. E. It is likely because the magnitude of the earthquake is large. Score: 1/1 13 . When waves shoal, all of the following occur EXCEPT __________. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. wave height increases B. wave period decreases 100% C. wavelength shortens D. the wave steepens E. wave speed decreases Score: 1/1 14 . Larger wind-driven waves can develop in the North Atlantic Ocean than in the Strait of Georgia. Why? Choose the BEST reason. Student Response Value Correct AnsA. Wind speed is faster over the North Atlantic Ocean than over the Strait of Georgia. Student Response Value Correct AnsB. Low atmospheric pressure over the North Atlantic Ocean tends to amplify large wind-driven waves. C. The wind blows constantly over the North Atlantic Ocean but only rarely blows hard over the Strait of Georgia. D. The Strait of Georgia is affected by daily wind reversals due to the proximity of land on all sides. E . The fetch is smaller in the Strait of Georgia than in the North Atlantic Ocean. 100% Score: 1/1 15 . Tsunami can be generated by all of the following EXCEPT _ [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 41 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 09, 2022
Number of pages
41
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 09, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
162





.png)




.png)