Edhesive : 2.1 - 2.7 Questions &
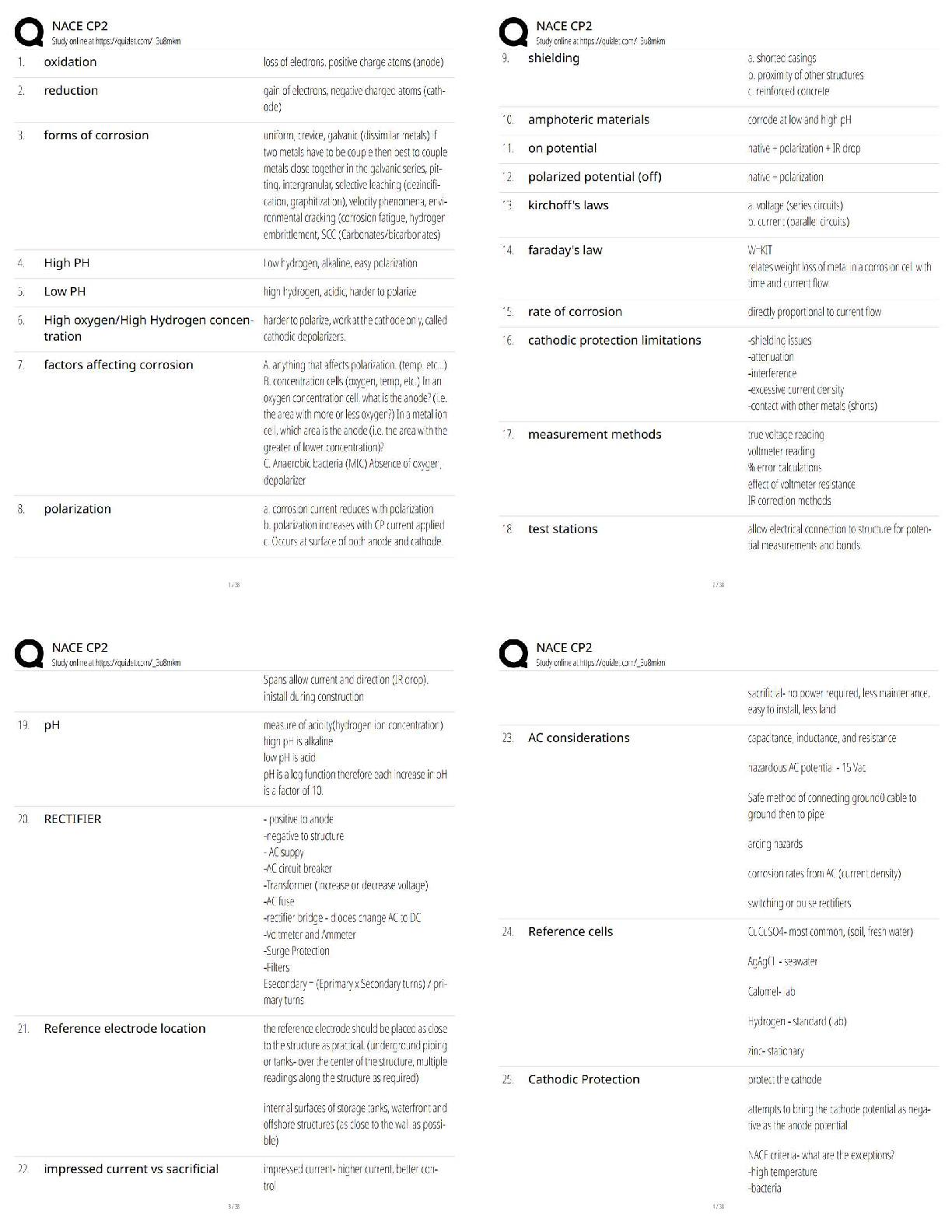
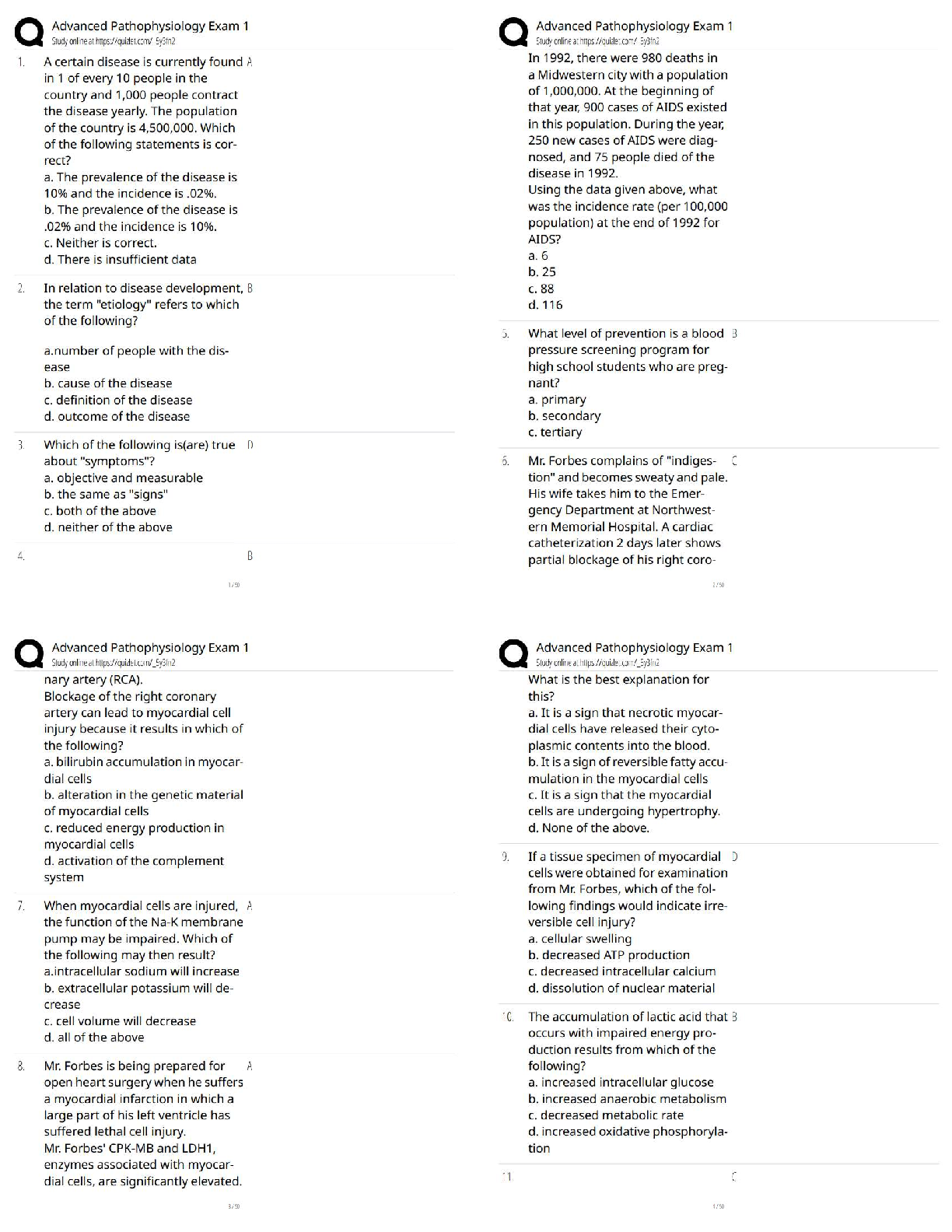
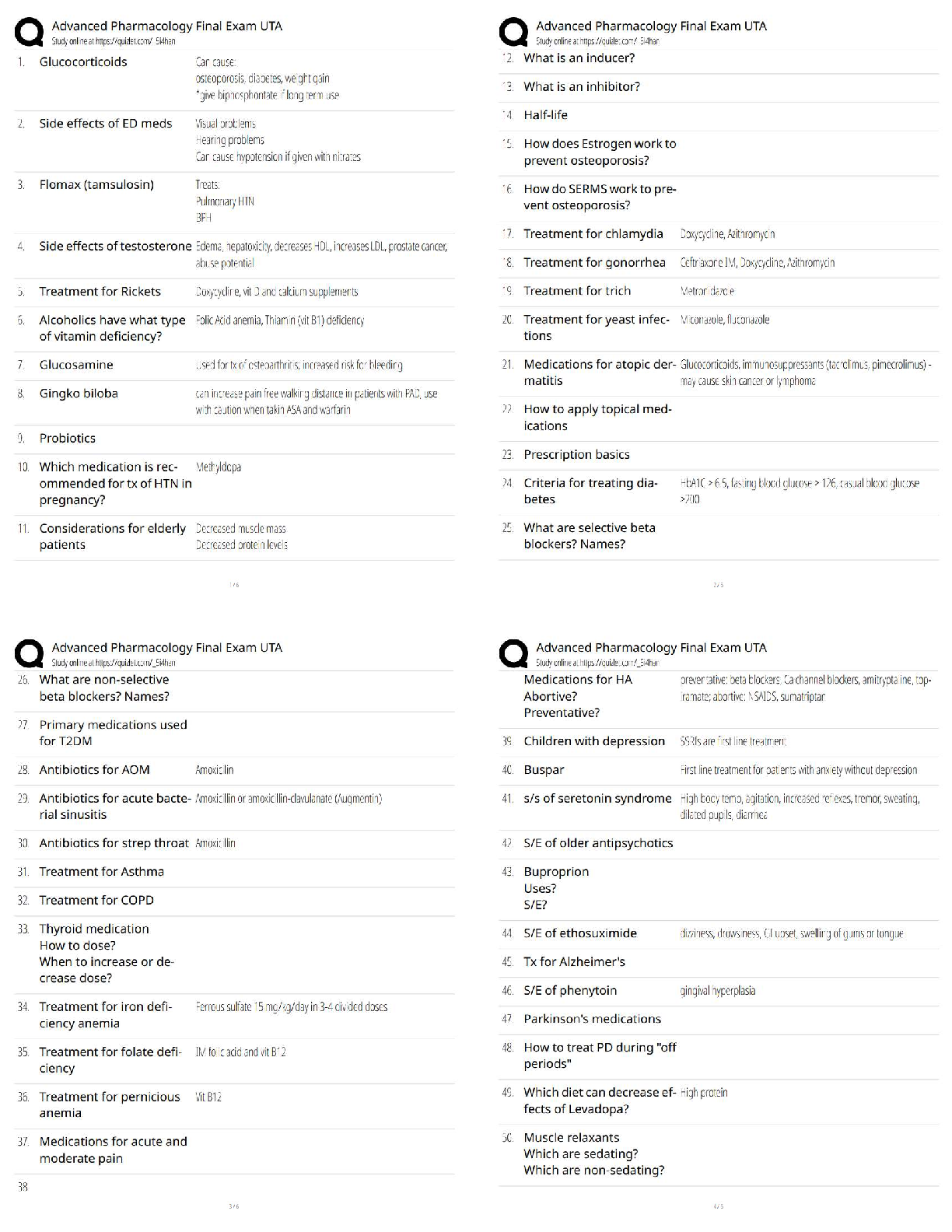
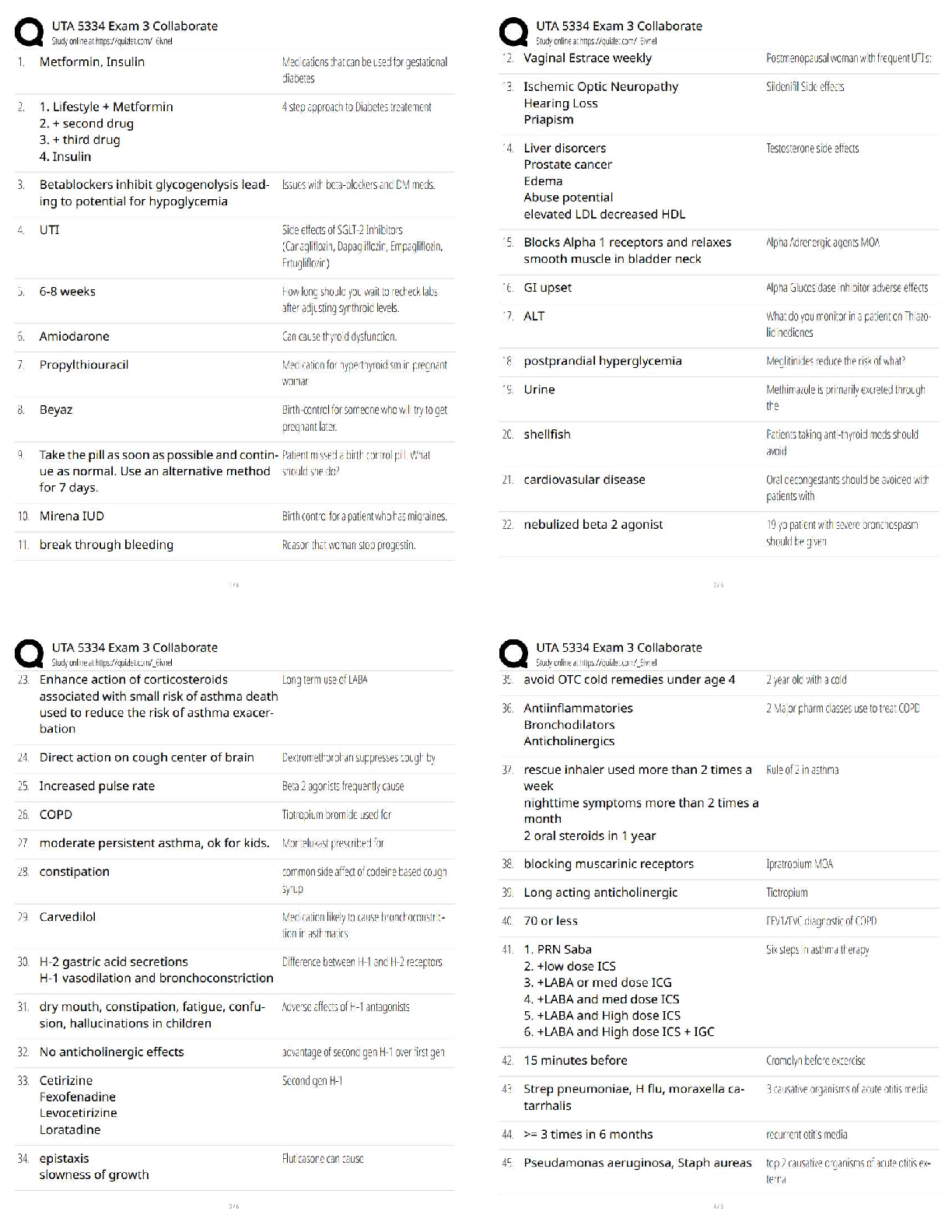
Answers
2.1 Lesson Practice
__________ invented the Analytical Engine, a machine that did calculations. - ✔✔Charles
Babbage
2.1 Lesson Practice
___________ created the idea of a gen
...
Edhesive : 2.1 - 2.7 Questions &
Answers
2.1 Lesson Practice
__________ invented the Analytical Engine, a machine that did calculations. - ✔✔Charles
Babbage
2.1 Lesson Practice
___________ created the idea of a general Purpose Computing Machine. - ✔✔Alan Turing
2.1 Lesson Practice
__________ created the earliest programmed machine. - ✔✔Konrad Zuse
2.1 Lesson Practice
The __________ was the first all electronic computer. - ✔✔ENIAC
2.1 Lesson Practice
In __________ the first computer ran a program from memory. - ✔✔1948
2.2 Lesson Practice
Which of the following correctly prints the following calculation if x is 17 and y is 5?
Sum is: 22 - ✔✔print ("Sum is: " + str(x + y))
2.2 Lesson Practice
What is the symbol for exponent? - ✔✔**
2.2 Lesson Practice
What is output?
a = 10
b = 23
print (a + b * a) - ✔✔240
2.2 Lesson Practice
Which of the following is NOT a correct variable assignment? - ✔✔5 + y = x
2.2 Lesson Practice
Which of the following correctly does the calculation 7^6? - ✔✔a = 7 ** 6
2.2 Lesson Practice
A symbol that defines a math calculation is: - ✔✔Operator
2.2 Lesson Practice
Which of the following calculates to 19? - ✔✔(3 * 6) + 2 /2
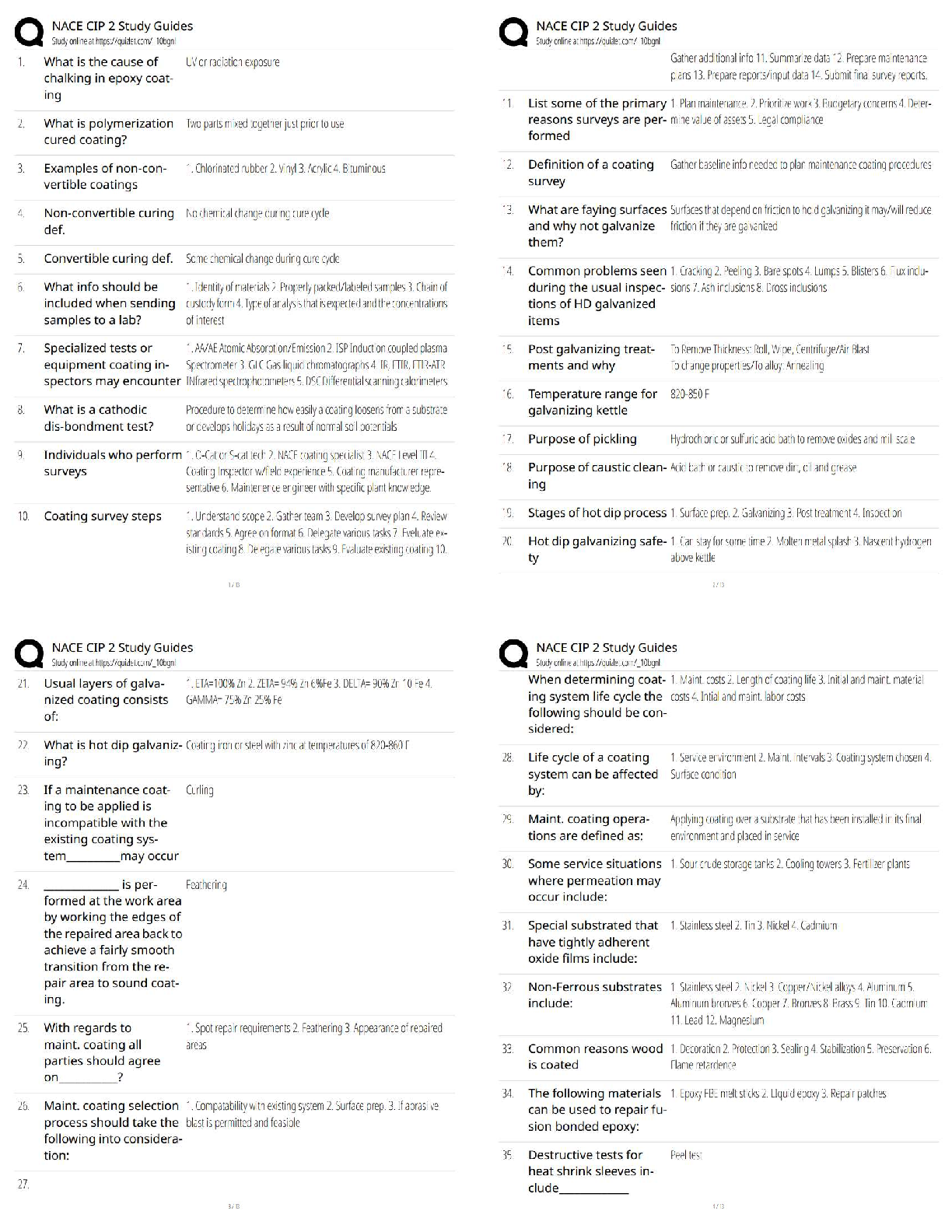
2.2 Lesson Practice
This program takes two numbers as input, and prints their quotient.
a = float(input("Enter a number: "))
b = float(input("Enter a number: "))
print ("Quotient: " + str(a/b))
What is output when when you enter 1 as the second number (regardless of what you enter as a
value for the first number)? - ✔✔The value of a
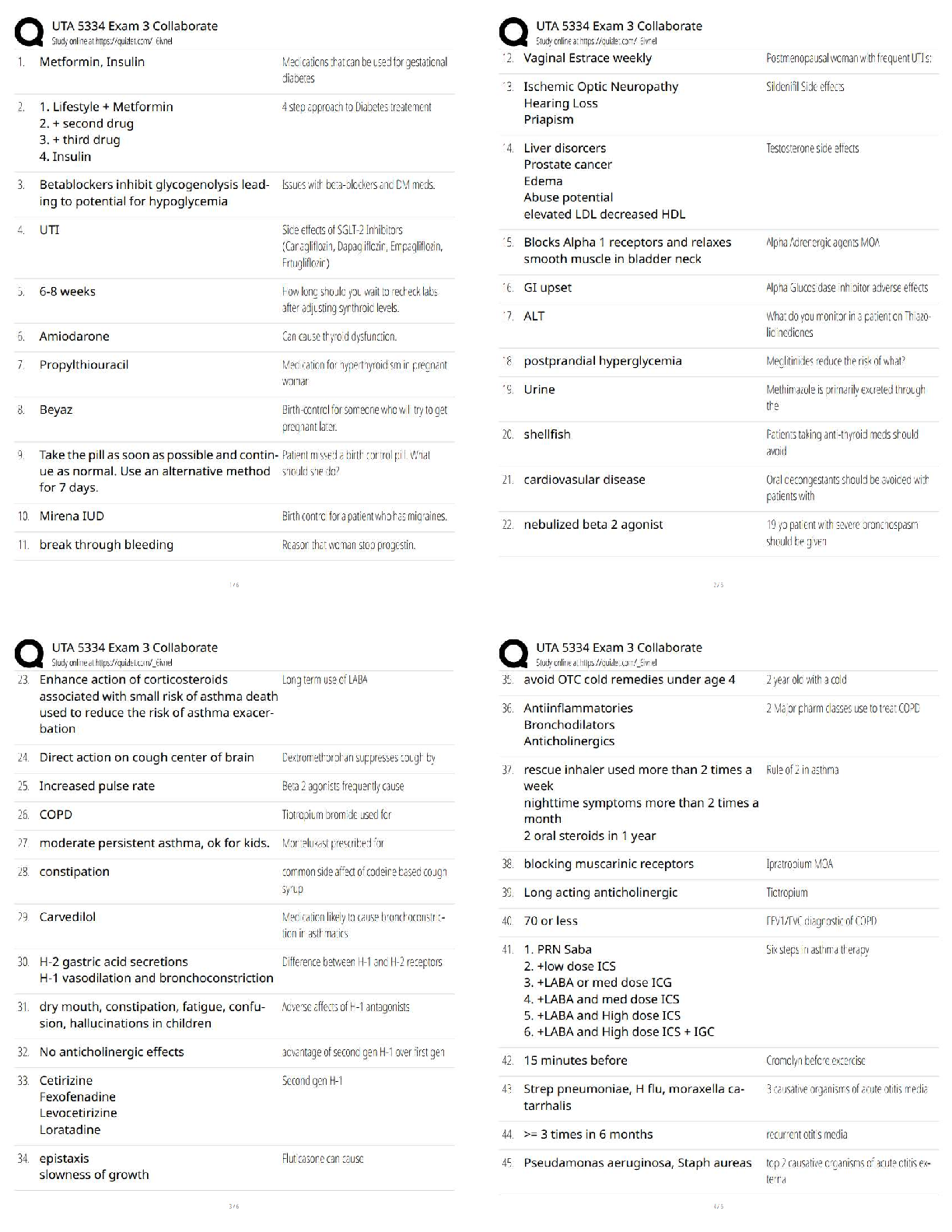
2.2 Lesson Practice
This program accepts a number as input and raise it to the .5 power (i.e., x ** .5).
a = float(input("Enter a number: "))
print (a ** .5)
The program is run, using the following numbers as input: 16, 25, 36, 49. The outputs are 4, 5, 6
and 7 respectively. Based on this output, what can you conclude this code does? - ✔✔It finds the
square root of the input number.
2.2 Lesson Practice
Watch the videos, read the text and complete the questions at the following link from "How to
Think Like a Computer Scientist": Order of Operations (Links to an external site.)
In this video, you will see "Integer Division" with the symbol //.
Integer division is a different process from modular division. It it does the division problem
between two numbers and only displays the whole number portion, not the remainder. This is
essentially the opposite of modular division.
Examples:
5 // 3 = 1 (3 goes into 5 once)
10 // 2 = 5 (5 goes into 10 two times)
19 // 4 = 4 (4 goes into 19 four times) - ✔✔Do the assigmnet
2.2 Code Practice: Question 1 - ✔✔num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print(num + 1)
print(num + 2)
print(num + 3)
2.2 Code Practice: Question 2 - ✔✔num1 = float(input("Enter a number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter a number: "))
num3 = float(input("Enter a number: "))
print('Sum: '+str(num1+num2+num3))
2.3 Lesson Practice
What does the % find? - ✔✔The remainder
2.3 Lesson Practice
Which of the following is NOT a problem modular division is used for? - ✔✔Finding the mode
2.3 Lesson Practice
If you are doing modular division with a divisor of 3, what are the only possible answers? - ✔✔0
1 2
2.3 Lesson Practice
What is 7 % 24 - ✔✔7
2.3 Lesson Practice
Read the text and complete the questions in the following link from "How to Think Like a
Computer Scientist": Operators and Operands. - ✔✔Complete the assigmnet
2.3 Code Practice: Question 1 - ✔✔dividend =float(input('Enter the dividend:'))
divisor =float(input('Enter the divisor:')
[Show More]














.png)