Physics > Lab Experiment > 4.4.3 Lab: Optics Dry Lab Physics Sem 2_investigate the relationship between the focal lengths of a (All)
4.4.3 Lab: Optics Dry Lab Physics Sem 2_investigate the relationship between the focal lengths of a mirror and lens and the type of image that is generated.
Document Content and Description Below
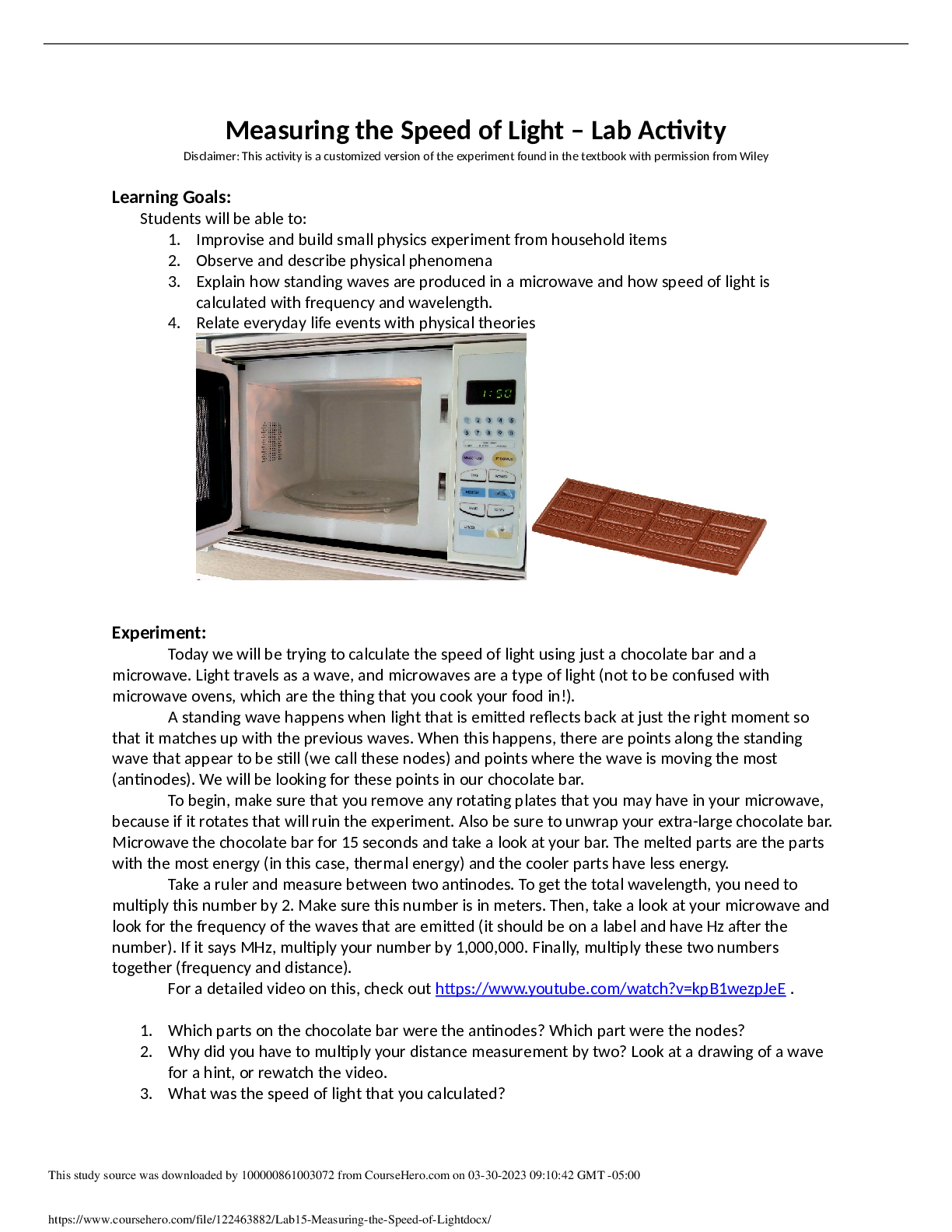
4.4.3 Lab: Optics Dry Lab Physics Sem 2 Points Possible:50 Name: Date: Optics Materials: Optics bench Optics kit, including a lens/mirror mount Convex lens of known focal length ... Concave mirror of known focal length Light source/candle Screen Meter stick/metric ruler Two polarized films Prism Laser pointer Protractor Graph paper Electromagnetic spectrum chart Materials for Exploring Further: Plane mirror Ripple tank, with sheet of plastic or glass that fits on part of the bottom of the tank, and objects that can be used as boundaries to obstruct the pathway of waves Wave-motion rope Tuning-fork kit Stroboscope Resonance-tube kit In this lab, you will investigate the relationship between the focal lengths of a mirror and lens and the type of image that is generated. Procedure Part 1: Image from a Lens 1. Place the light source, convex lens, and screen on the optics bench as shown in figure 1. Start with the light source at a distance greater than 2ƒ from the lens. Figure 1 2. Measure the height of the light source, or "object" (ho), and record it in data table 1. Also measure and record the distance between the lens and the light source (do) in the data table. Using the lens equation and the given focal length, calculate the distance from the lens to the image (di) and the height of the image (hi): and . Record your calculations in the "Calculated" section of data table 1. 3. Keeping the light source and lens in the same position, turn on the light source and adjust the screen until a clear, real image is formed on the screen. Measure the experimentally determined di and hi, and record your observations in the "Experimental" section of data table 1.4. Place the light source a distance of exactly 2ƒ from the lens. Record the distance between the lens and the light source (do) in data table 1. Using the lens equation and the given focal length, calculate the distance from the lens to the image (di) and the height of the image (hi). Record your calculations in the "Calculated" section of data table 1. 5. Turn on the light source, keeping it 2ƒ from the lens, and adjust the screen until a clear, real image is formed on the screen. Measure the experimentally determined di and hi, and write your observations in the "Experimental" section of data table 1. 6. Place the light source at a distance of somewhere between ƒ and 2ƒ from the lens. Record the distance between the lens and the light source (do) in the data table. Using the lens equation and the given focal length, calculate the distance from the lens to the image (di) and the height of the image (hi). Record your calculations in the "Calculated" section of data table 1. 7. Keeping the light source and lens in the same position, turn on the light source and adjust the screen until a clear, real image is formed on the screen. Measure the experimentally determined di and hi, and write your observations in the "Experimental" section of data table 1. Data Table 1 ho = 1.5 cm ƒ = 25 cm Calculated results Calculated results Experimental results Experimental results di hi di hi Greater than 2ƒ do = 54 cm 46cm -.56cm 46.4 cm 1.3 cm 2ƒ do = 50 cm 48cm -.64cm 49.5 cm 1.4 cm Between ƒ and 2ƒ do = 42 cm 61cm -.96cm 61.5 cm 2.1 cm Part 2: Image from a Mirror 8. Repeat steps 1 - 7, this time using the concave mirror. Be sure to anglethe mirror to project the image onto the screen, as shown in figure 2. Record your calculations and measurements in data table 2. Figure 2 Data Table 2 [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$5.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 11, 2023
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 11, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
116

.png)









-2.png)
-2.png)