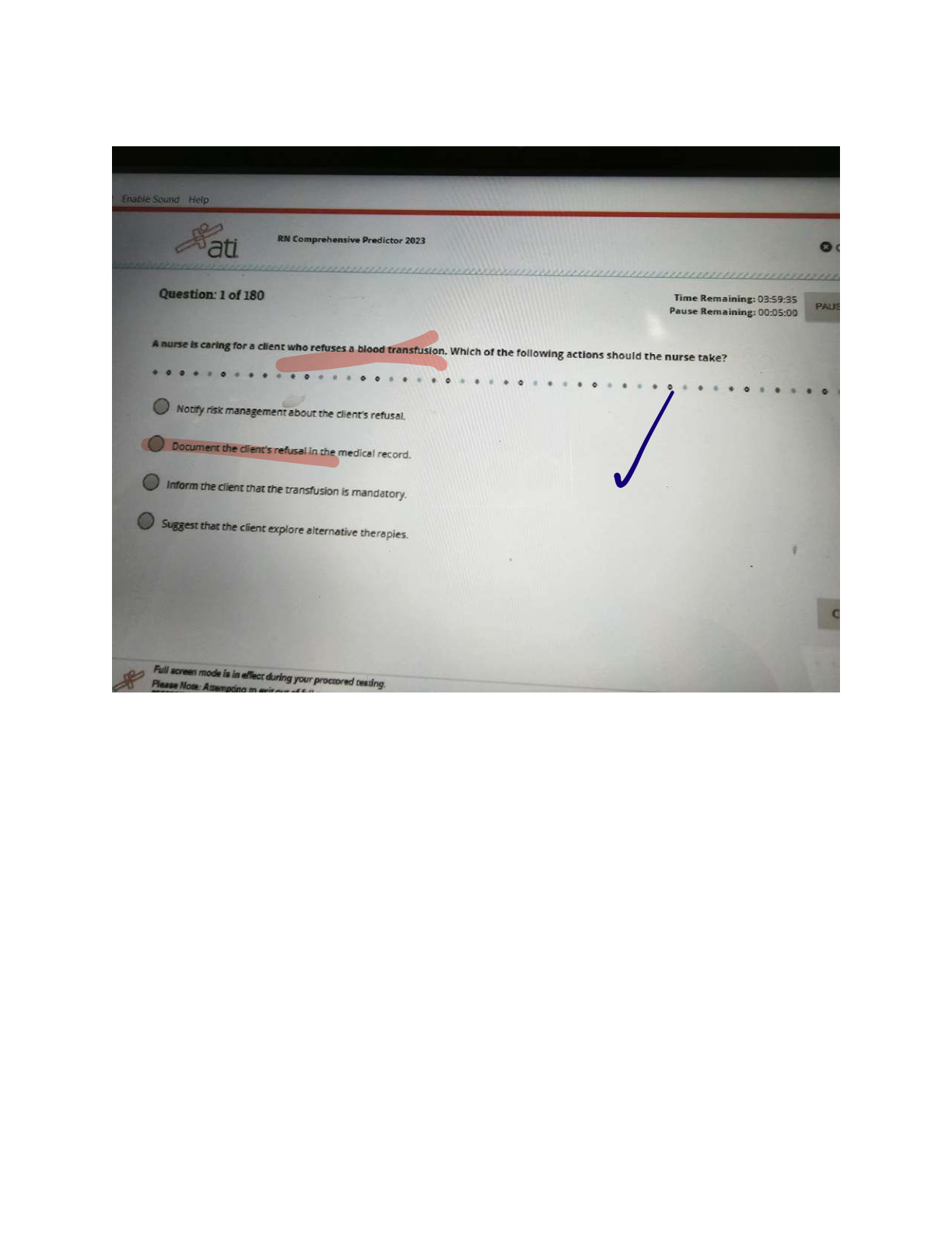
ATI COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM. This document contains 1000 of the highly tested Quetions in any ATI COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM. Best last minute exam prep. SAMPLE Q&A: Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT)
a. 30 to 4
...
ATI COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM. This document contains 1000 of the highly tested Quetions in any ATI COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM. Best last minute exam prep. SAMPLE Q&A: Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT)
a. 30 to 40 seconds
b. Critical value is greater than 70 seconds
21. Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT)
a. 60 to 70 seconds, greater than 100 seconds
b. Therapeutic range for anticoagulant therapy 1.5 to 2 times the normal or control value
22. INR
a. Normal 0.8 to 1.1
b. If the client requires anticoagulation, the desired value is increased to approximately 2 to
3
c. Critical value is greater than 5d. The INR is a corrected ratio of a client’s prothrombin time to normal
e. Universal test is not affected by variations in laboratory norms 23. Platelets
a. 150,000 to 400,000/mm3
b. Critical value is less than 20,000 or greater than 1 million / mm3
24. Alb umin
a. 3.5 to 5.0 g/dL
25. Am monia
a. 10 to 80 mcg/dL
26. Tot al bilirubin
a. 0.1 to 8 g/dL
27. Tot al Protein
a. 6 to 8 g/dL
28. Spe cific gravity
a. 1.005 to 1.030
29. Pro tein
a. 0 to 8 mg/dL
30. Glu cose
a. Less than 0.5 g/day
31. Ket ones
a. None
32. WB C
a. Males 0 to 3 per high-power field
b. Females 0 to 5 per high-power field
33. Ser um Creatinine
a. Males 0.5 to 1.2 mg/dL
b. Females 0.5 to 1.1 mg/dL
34. BUN
a. 10 to 20 mg /dL
35. Cre ati nine clearance test
a. Males 90 – 139 mL/min
b. Females 80 to 125 mL/min
c. This is a calculation of GFR and is the best indicator of overall renal function
36. Dig oxin level
a. 0.8 to 2.0 ng/mL
37. Lit hium Level
a. 0.4 to 1.4 mEq/L
38. Ph eno barbital
a. 10 to 40 mcg/mL
39. Th eop hylline
a. 10 to 20 mcg/mL
40. Dil antin
a. 10 to 20 mcg/mL41. Glu cose (testing
a. 70 to 105 mg/dL
42. Gly cos ylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)
a. 4% to 6% is within the expected reference range
b. Greater than 8% indicates poor diabetes mellitus control
43. pH less than 7.5 indicates acidosis
44. pH greater than 7.45 indicates alkalosis
45. Pa CO2 greater than 45 indicates respiratory
46. Pa CO2 less than 35 indicates metabolic
47. Flu id imbalances contributing to the plan of care for a client with dehydration
a. Monitor I&Os
b. Monitor vital signs
c. Monitor for LOC
d. Provide oral /I V therapy (rehydration)
e. Monitor serum levels (Increased in dehydration)
48. Inf ecti ons of the renal and urinary system (Manifestations of cystitis)
a. Dysuria
b. Nausea
c. Nocturia
d. Confusion
e. Urinary urgency59. Evaluating client understanding of dietary changes to prevent hypertension: Cardiovascular / hematologic
a. Decrease sodium intakeb. Limit alcohol
c. Stop smoking
d. Promote calcium intake
e. Include fruits and vegetables
f. Eliminate / decrease processed foods
60. Foods for clients recovering from Gastroenteritis
a. Easy to digest low fat carbohydrate foods
i. Crackers
ii. Oatmeal
iii. Bland fruit
iv. Toast
v. Pretzels
61. Osteoarthritis – interventions for feeding difficulty
a. Patient to assist with comfort measures (feeding difficulty)
b. Registered dietician (food / meal planning & modification)
c. Case management for home modifications
62. Evaluating client understanding of a TENS unit
a. Nonpharmacological pain strategies help improve coping by relieving stress associated with pain
63. A nurse is contributing to the plan of care for a client who has bipolar disorder and is experiencing acute
mania, which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the plan of care?
a. Provide the client with high calorie finger foods
64. A nurse is reinforcing with a new mother on facility security measures, which of the following statements
by the mother indicates an understanding of the teaching?
[Show More]