SCCJA PRE ACADEMY FINAL EXAM 2025 (100 EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT ANSWERS) || ALREADY GRADED A+ || BRAND NEW!!!
$ 16.5

Tina Jones Nursing Progress Note Skin, Hair, and Nails Completed Shadow Health
$ 8

(ASU) GPH 111 Physical Geography Final Exam Guide 2024
$ 11

Ancient Greek Chapter 7 Textbook Questions and Study notes,GRADED A
$ 10

WGU D115 OA Study Guide Unit 7 Exam Questions and Answers Solved
$ 19.5

ASL Trueway Unit 2 Worksheet Complete Solution | All Answers Correct
$ 9

ACQ 202 Module 5 Exam: Producing System Questions. 100% pass rate,
$ 8
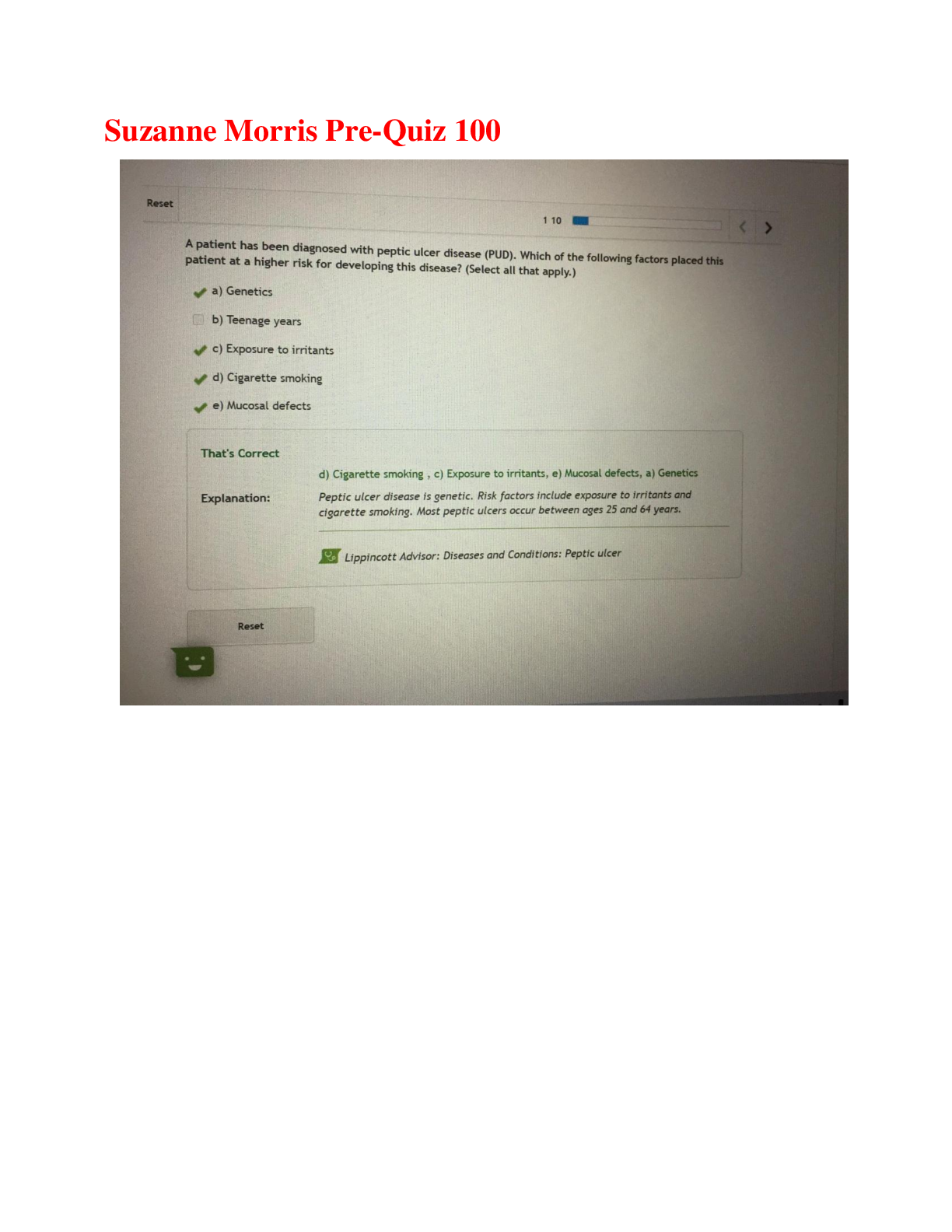
Suzanne Morris Pre-Quiz 100 | Complete Solutions
$ 13.5

AS Biology 2020 Paper 1.pdf
$ 7

WALDEN UNIVERSITY NRNP 6645 MIDTERM EXAM (THE MAN FROM EASTLANDO) PHYCHOTHERAPY WITH MULTIPLE QUESTIONS.
$ 13.5
.png)
WGU C777 Unit 2: Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) Complete Solution for 2022/2023
$ 13
.png)
MARK SCHEME – GCSE FRENCH – 8658/WH – JUNE 2020 | Download for quality grades |
$ 13

[eBook][PDF] Understanding Islam A Guide For Teachers, 1st Edition By Imran Mogra
$ 14.5
.png)
Intro to Cryptography WGU C839 Module 4 Already Passed
$ 6
 Questions and Answers with Explanations.png)
2022/2023 NCLEX-PN Test Prep (Exam 1) Questions and Answers with Explanations
$ 15

HESI A2 Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide [100% VERIFIED and information NEEDED]A+GRADE
$ 42

A-level ACCOUNTING 7127/1 Paper 1 Financial Accounting Mark scheme June 2020. GRADED A+ LATEST PREDICTOR
$ 12
 (1).png)
NURS 6550 Final Exam 2,100% Correct
$ 10

Diagnostic Testing HESI prep- Adult Care Latest Exam Questions & Answers (With Rationales)
$ 12

Gizmos -Mineral Identification Updated answer key 2022
$ 6

eBook [PDF] Concrete Structures Design and Residual Capacity Assessment 1st Edition By Enrique Hernández-Montes, Luisa María Gil-Martín
$ 30

TEST BANK for Essentials of Genetics, 10th Edition BY William S. Klug, Cummings, Spencer, Palladino & Killian
$ 19

Python for IT Automation OA WGU D522 Practice Exam (Questions and correct Answers (Verified Answers) with Rationales 2025)
$ 16

[eTextBook] [PDF] Machine Learning and Metaheuristic Computation By Erik Cuevas, Jorge Galvez, Omar Avalos, Fernando Wario
$ 25

eBook [PDF] Statistical Methods For The Social Sciences 5th Global Edition By Alan Agresti
$ 28

PICAT PRE-ASVAB GO NAVY | 100% Correct Answers | Verified | Latest 2024 Version
$ 7

Mosby's Comprehensive Preparation for the Canadian Practical Nurse Registration Exam (REx-PN/CPNRE)