view that claims phenomenon of globalization was initially driven by the desire of Western economies to
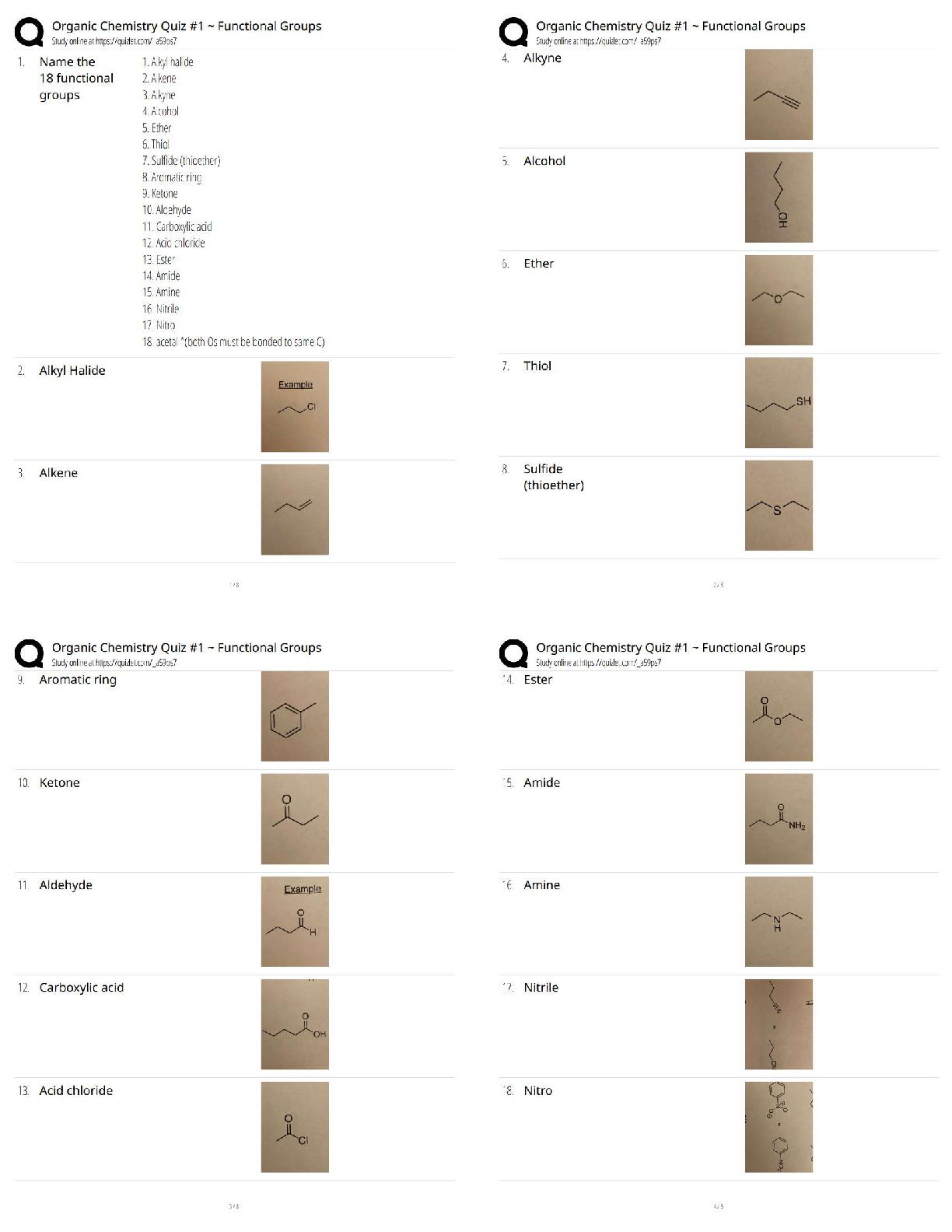
exploit their power through MNE's Ans- new
view that claims globalization is a long-run historical evolution sinc
...
view that claims phenomenon of globalization was initially driven by the desire of Western economies to
exploit their power through MNE's Ans- new
view that claims globalization is a long-run historical evolution since the dawn of humanity. Says it is
nothing new and that it will always exist Ans- evolutionary
view that claims globalization is swinging from one extreme to another from time to time Ans�pendulum
investment in, controlling, and managing value-added activities in other countries Ans- foreign direct
investment
political view hostile to FDI. believes it is an instrument of imperialism and vehicle for exploitation of
domestic resources by foreign capitalists and firms Ans- radical
suggests that FDI, unrestricted by government intervention, will enable countries to tap into their
absolute or comparative advantages by specializing in the production of certain goods and services Ans�free market
views FDI as having pros and cons and only approving FDI when its benefits outweigh costs Ans�pragmatic nationalis
what benefits exist to a country receiving FDI? Ans- capital inflow, technology spillovers, advanced
management know-how, creates jobs
what costs exist to a country receiving FDI? Ans- loss of sovereignty, adverse effects on competition, net
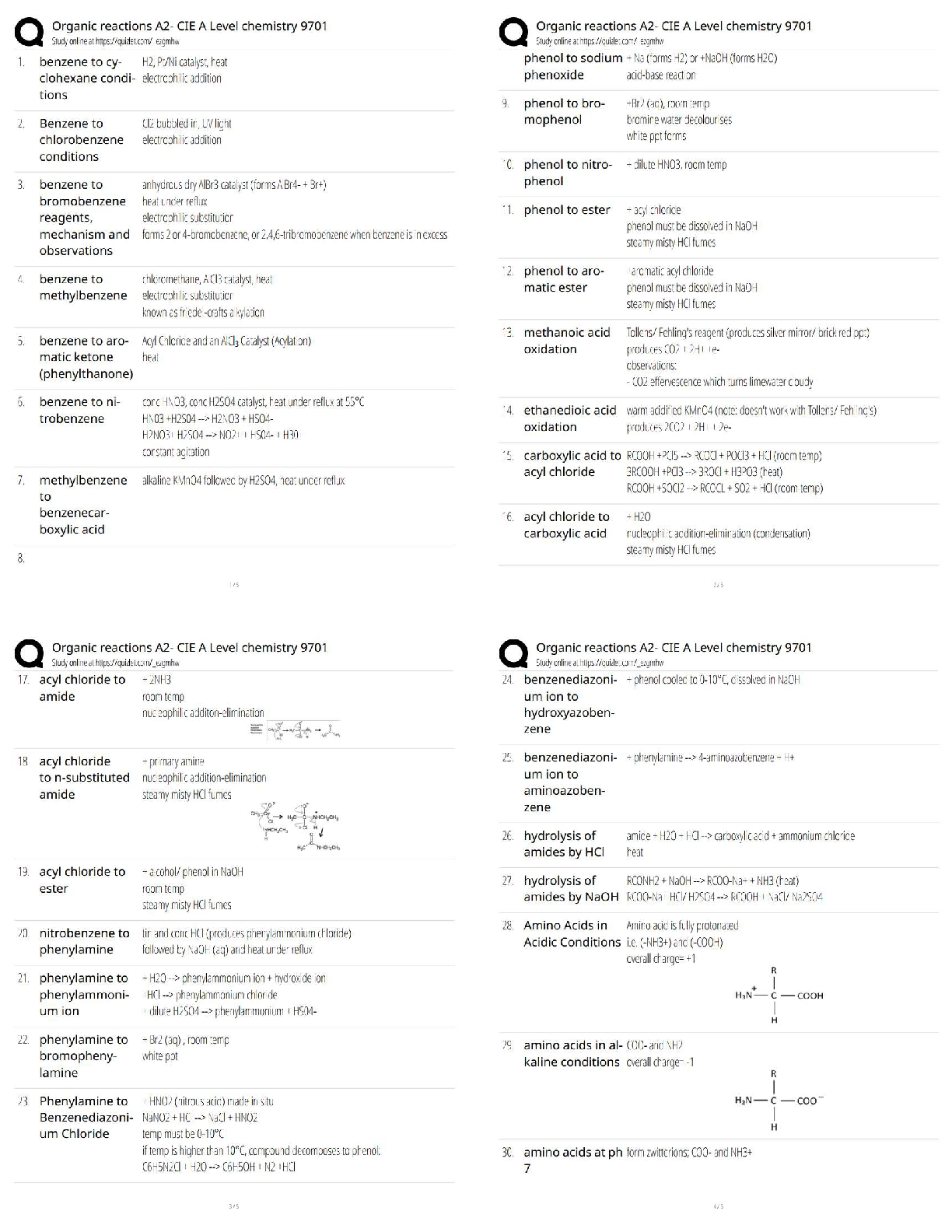
outflow in the capital account
The aggregation of importing and exporting that leads to the country-level trade surplus or deficit. Ans�balance of trade
firms with a _____ degree of resource similarity are likely to have similar competitive actions Ans- high
a high degree of resource similarity but low market commonality = _______ intensity of rivalry Ans�highest
little resource similarity but high market commonality = _____ intensity of rivalry Ans- lowest
mercantilism, absolute advantage and comparative advantage belong to what theory of international
trade Ans- classical
theory of international trade that relies on more realistic product life cycles and first mover advantages
Ans- modern
under free trade, a nation gains by specializing in economic activities in which it has _____advantage
Ans- absolute
focuses on the idea that if a country does not have absolute advantage, they can still choose to
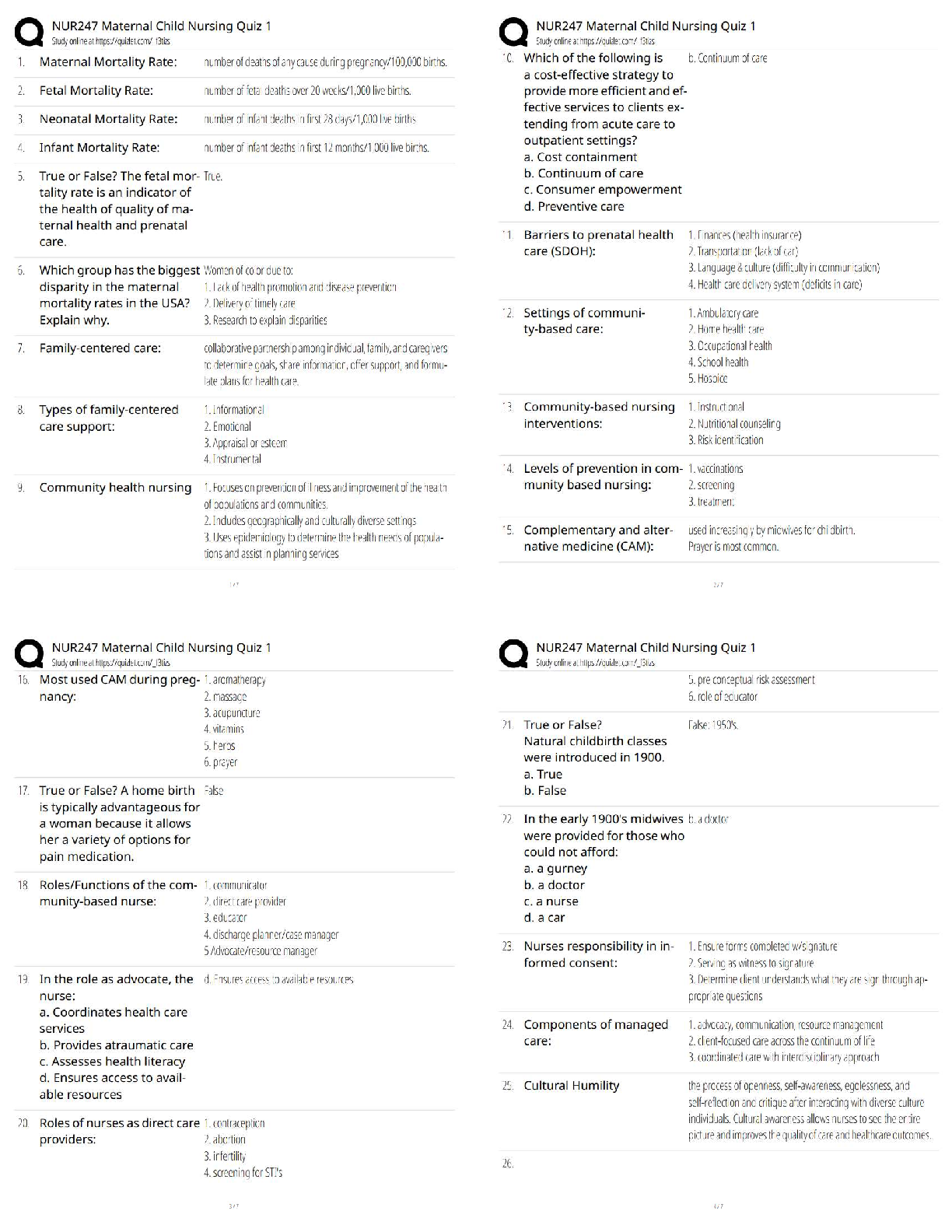
specialize in the production of one good where it has ______ advantage Ans- comparative
comparative advantage and absolute advantage stem from Ans- factor endowments
theory that the wealth of the world is fixed and that a nation that imports more and exports less will be
richer Ans- mercantilism
stage of the product life cycle where production of a new product that commands a price premium will
concentrate in the US Ans- new
stage of the product life cycle where demand and ability to produce grow in other developed nations
Ans- maturing
stage of the product life cycle where the previously new product is commoditized and production will
now move to low-cost developing nations Ans- standardized
comparative advantage may change over time because patterns of ______ change over time Ans- trade
theory that suggests that intervention by governments in certain industries can enhance their odds for
international success Ans- strategic trade
if a company seeks to limit foreign exchange rate exposure in the forward direction, what is the most
effective way to do this? Ans- currency hedging
exchange rate risk associating with the time delay between entering a contract and settling it Ans�transaction risk
forward transaction that protects traders and investors from exposure to fluctuations of the spot rate
Ans- hedging
a means of spreading out activities in different currency zones in order to offset the currency losses in
certain regions through gains in other regions Ans- strategic heding
amount of resources committed to entering a foreign market Ans- scale of entry
how do institutions reduce uncertainty? Ans- by signaling which conduct is legit and which is not
pillar of formal institution, coercive power of government Ans- regulatory
pillar of informal institution, the mechanism through which norms influence individual and firm behavior
Ans- normative
pillar of informal institution, taken for granted values and beliefs that guide behavior Ans- cognitive
institutions represented by laws, regulations and rules Ans- formal
institutions represented by norms, culture and ethics Ans- informal
[Show More]