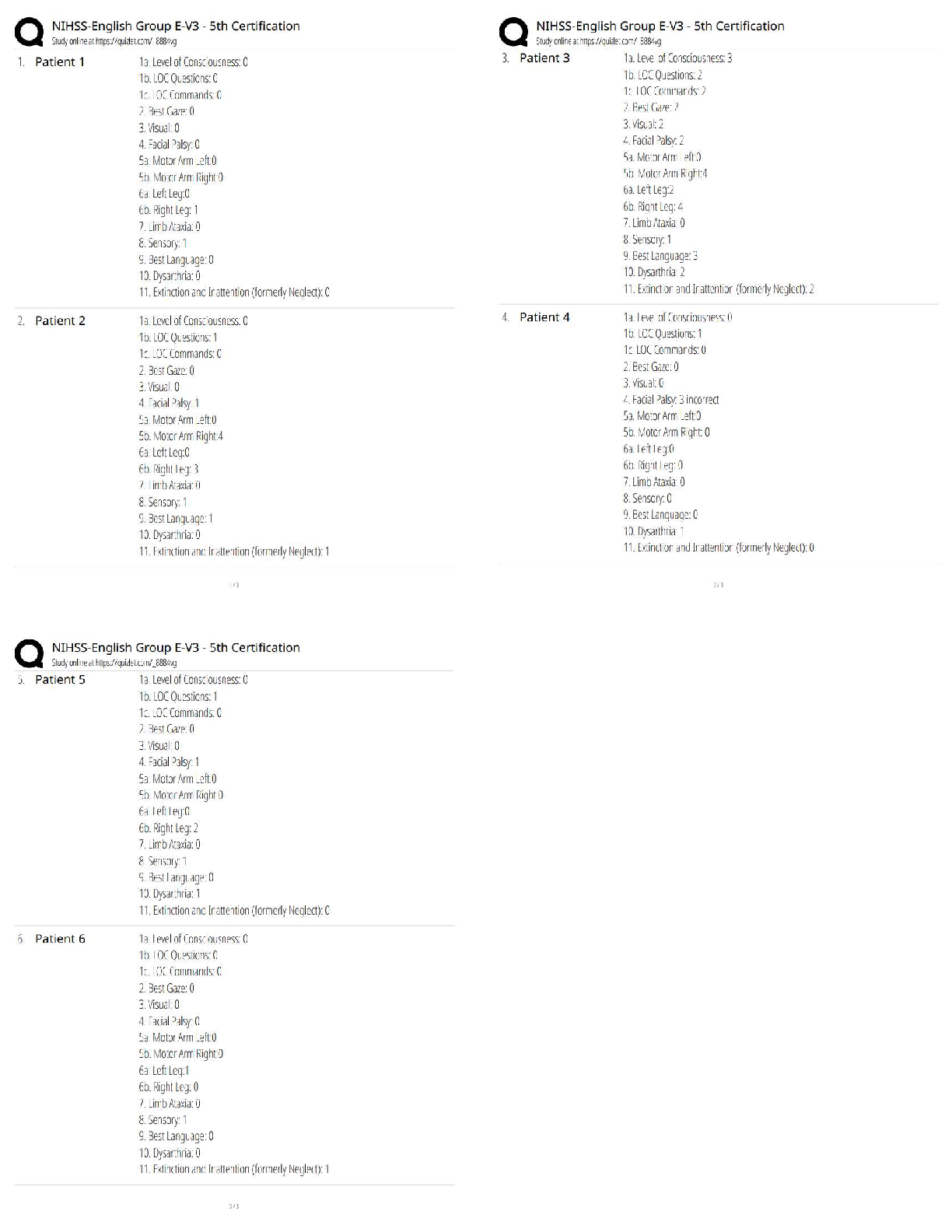
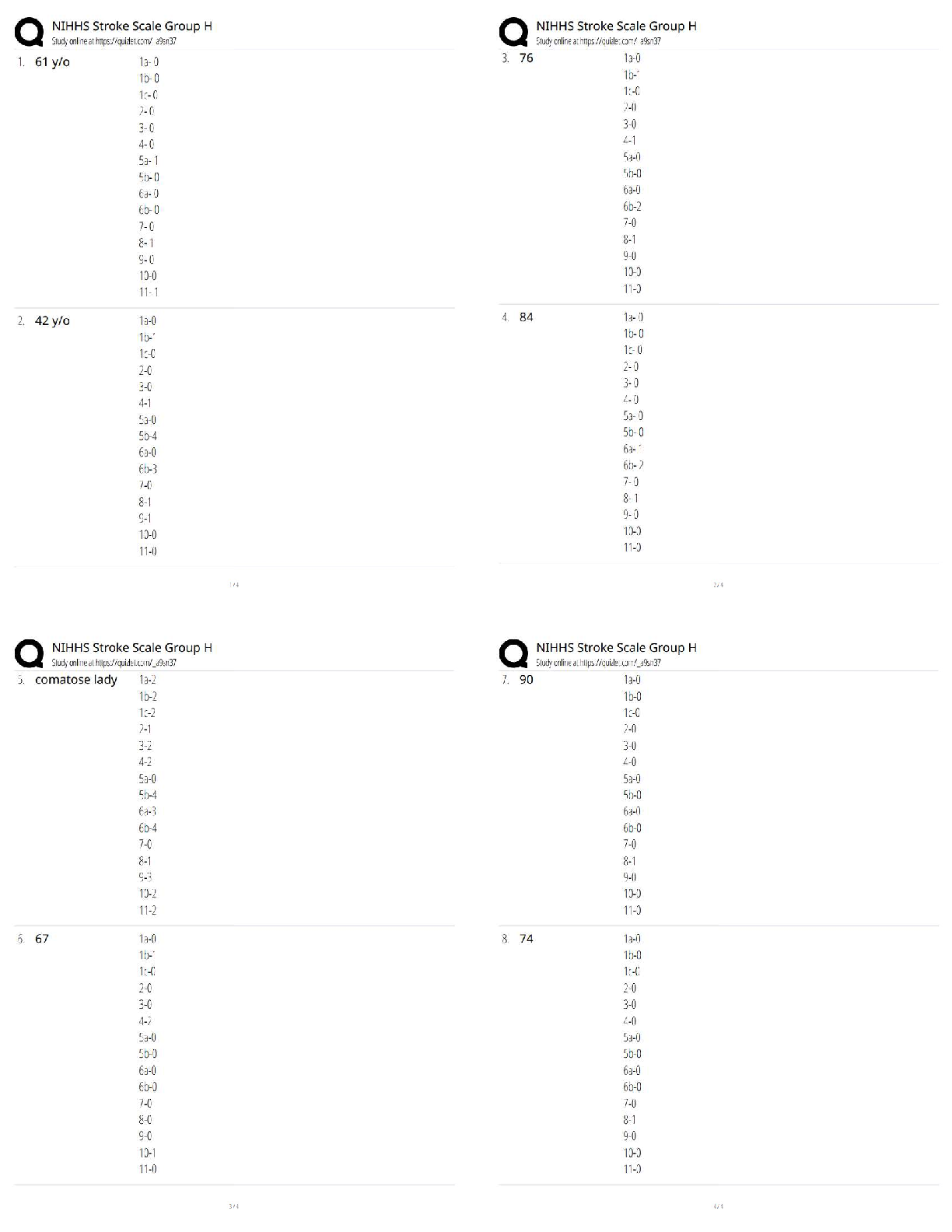
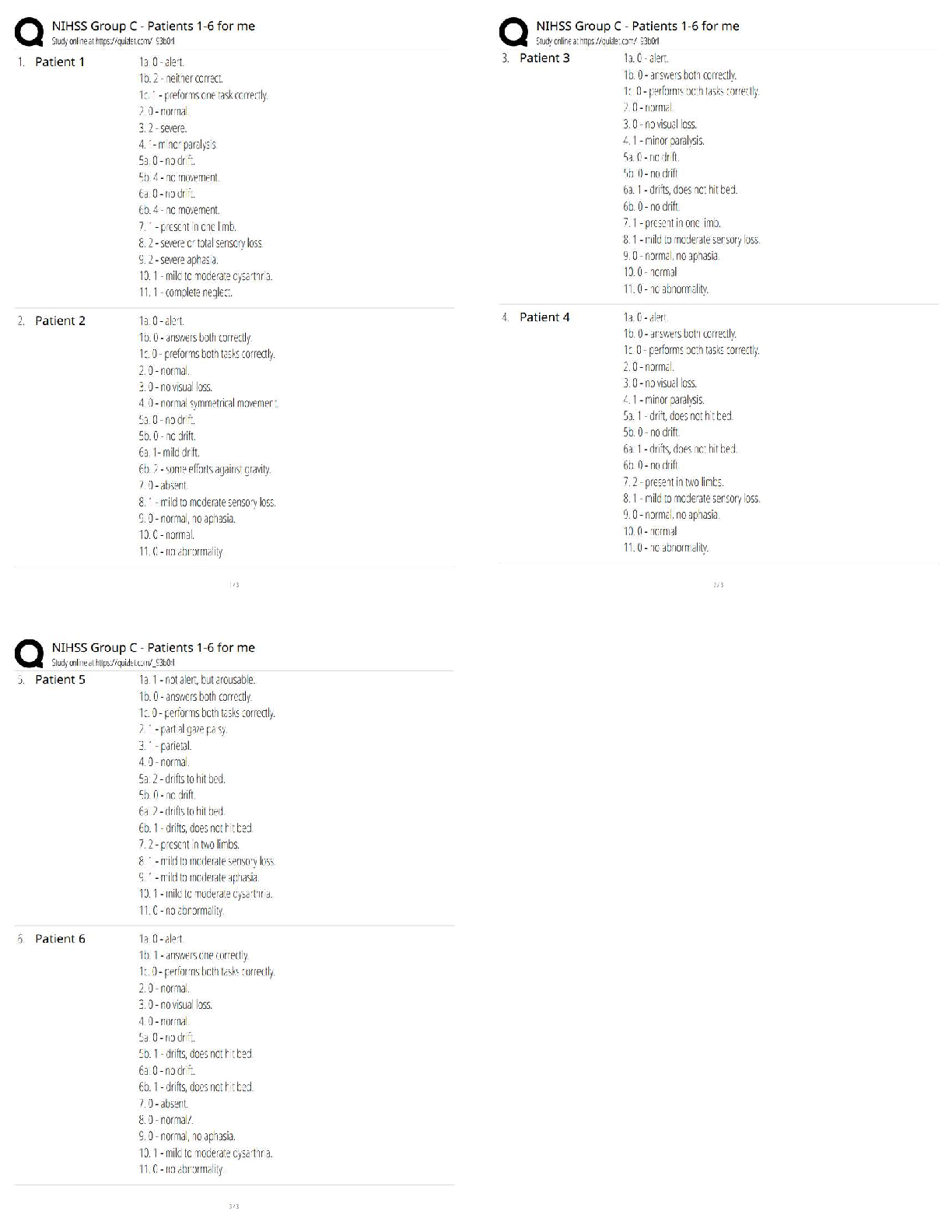
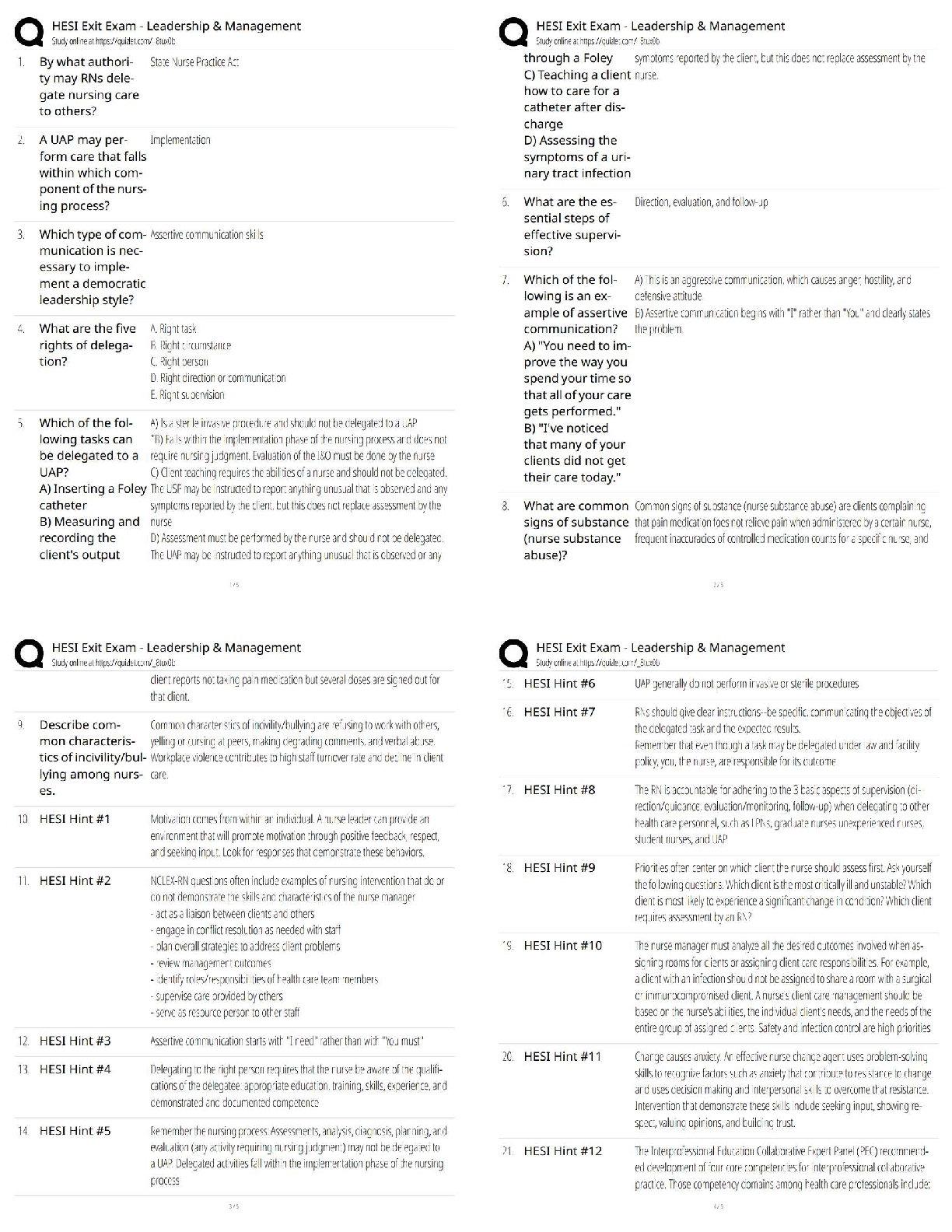
Pathophysiology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NURSING NR 507 advanced patholphysiology midterm week 4 questions and answers 2021 (All)
NURSING NR 507 advanced patholphysiology midterm week 4 questions and answers 2021
Document Content and Description Below
. Question : What is the ratio of coronary capillaries to cardiac muscle cells? Student Answer: 1:1 (one capillary per one muscle cell) 1:2 (one capillary per two muscle cells) ... 1:4 (one capillary per four muscle cells) 1:10 (one capillary per ten muscle cells) Instructor Explanation: The heart has an extensive capillary network, with approximately 3300 capillaries per square millimeter (ca/mm2) or approximately one capillary per one muscle cell (muscle fiber). Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 2. Question : What part of the kidney controls renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin secretion? Student Answer: Macula densa Visceral epithelium Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) Filtration slits Instructor Explanation: Control of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin secretion occur at the JGA. Together, the juxtaglomerular cells and macula densa cells form the JGA. The control of renal blood flow, glomerular filtration, and renin secretion is not directed by any of the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 3. Question : What effect do natriuretic peptides have during heart failure when the heart dilates? Student Answer: Stimulates antidiuretic hormones. Inhibits antidiuretic hormones. Stimulates renin and aldosterone. Inhibits renin and aldosterone. Instructor Explanation: Natriuretic peptides inhibit renin and aldosterone during heart failure when the heart dilates. These make up a group of peptide hormones, including atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), secreted from myocardial cells in the atria and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) secreted from myocardial cells in the cardiac ventricles. When the heart dilates during volume expansion or heart failure, ANP and BNP inhibit sodium and water absorption by kidney tubules, inhibit the secretion of renin and aldosterone, vasodilate the afferent arterioles, and constrict the efferent arterioles. The result is increased urine formation, leading to decreased blood volume and blood pressure. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 4. Question : What is the primary site for uncomplicated local gonococci infections in men? Student Answer: Epididymis Lymph nodes Urethra Prostate Instructor Explanation: Uncomplicated local infections are observed primarily as urethral infections in men. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 5. Question : Which term is used to identify the movement of gas and air into and out of the lungs? Student Answer: Perfusion Ventilation Respiration Diffusion Instructor Explanation: Of the options available, ventilation is the only term used to identify the mechanical movement of gas or air into and out of the lungs. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 6. Question : Which manifestations of vasoocclusive crisis are associated with sickle cell disease (SCD) in infants? Student Answer: Atelectasis and pneumonia Edema of the hands and feet Stasis ulcers of the hands, ankles, and feet Splenomegaly and hepatomegaly Instructor Explanation: Symmetric, painful swelling of the hands and feet (hand-foot syndrome) caused by infarction in the small vessels of the extremities is often the initial manifestation of SCD in infants. This selection is the only option that accurately identifies the manifestations of a vasoocclusive crisis associated with SCD in infancy. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 7. Question : When a patient has small, vesicular lesions that last between 10 and 20 days, which sexually transmitted infection is suspected? Student Answer: Genital herpes Chancroid Syphilis Chlamydia Instructor Explanation: If symptoms occur, the individual may have small (1 to 2 mm), multiple, vesicular lesions that are generally located on the labia minora, fourchette, or penis. They may also appear on the cervix, buttocks, and thighs and are often painful and pruritic. These lesions usually last approximately 10 to 20 days. The other options do not demonstrate these symptoms. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 8. Question : What is the role of collagen in the clotting process? Student Answer: Initiates the clotting cascade. Activates platelets. Stimulates fibrin. Deactivates fibrinogen. Instructor Explanation: In the clotting process, collagen provides a particularly strong stimulus to activate platelets. Collagen does not bring about any of the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 9. Question : Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is associated with which type of hypersensitivity reaction? Student Answer: I II III IV Instructor Explanation: Hypersensitivity reactions have been divided into four distinct types: type I (IgE-mediated) hypersensitivity reactions, type II (tissue-specific) hypersensitivity reactions, type III (immune complex–mediated) hypersensitivity reactions, and type IV (cell-mediated) hypersensitivity reactions. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 10. Question : When an individual aspirates food particles, where would the nurse expect to hear decreased or absent breath sounds? Student Answer: Left lung Right lung Trachea Carina Instructor Explanation: The right mainstem bronchus extends from the trachea more vertically than the left main bronchus; therefore aspirated fluids or foreign particles tend to enter the right lung rather than the left or any of the other locations listed. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 11. Question : Research supports the premise that exercise has a probable impact on reducing the risk of which cancer? Student Answer: Liver Endometrial Stomach Colon Instructor Explanation: The World Cancer Research Fund summarizes the effects as convincing for cancers of the colon and probable for postmenopausal breast cancer and endometrial cancer. The relationship is not supported for the remaining options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 12. Question : In a normal, nonmutant state, an oncogene is referred to as a: Student Answer: Basal cell Target cell Caretaker gene Proto-oncogene Instructor Explanation: In its normal nonmutant state, an oncogene is referred to as a proto-oncogene. The other options are not terms used to identify a nonmutant oncogene. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 13. Question : What is the trigone? Student Answer: A smooth muscle that comprises the orifice of the ureter The inner mucosal lining of the kidneys A smooth triangular area between the openings of the two ureters and the urethra One of the three divisions of the loop of Henle Instructor Explanation: The trigone is a smooth triangular area lying between the openings of the two ureters and the urethra. The other options do not accurately identify the trigone. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 14. Question : Erythrocyte life span of less than 120 days, ineffective bone marrow response to erythropoietin, and altered iron metabolism describe the pathophysiologic characteristics of which type of anemia? Student Answer: Aplastic Sideroblastic Anemia of chronic disease Iron deficiency Instructor Explanation: Anemia of chronic disease results from a combination of (1) decreased erythrocyte life span, (2) suppressed production of erythropoietin, (3) ineffective bone marrow erythroid progenitor response to erythropoietin, and (4) altered iron metabolism and iron sequestration in macrophages. This result is not true of the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 15. Question : Which laboratory test is considered adequate for an accurate and reliable diagnosis of gonococcal urethritis in a symptomatic man? Student Answer: Ligase chain reaction (LCR) Gram-stain technique Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) DNA testing Instructor Explanation: Microscopic evaluation of Gram-stained slides of clinical specimens is deemed positive for Neisseria gonorrhoeae if gram-negative diplococci with the typical “kidney bean” morphologic appearance are found inside polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Such a finding is considered adequate for the diagnosis of gonococcal urethritis in a symptomatic man. The other options are not relevant to the diagnosis of this condition. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 16. Question : What is the life span of an erythrocyte (in days)? Student Answer: 20 to 30 60 to 90 100 to 120 200 to 240 Instructor Explanation: Because it cannot undergo mitotic division, the erythrocyte has a limited life span of approximately 120 days. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 17. Question : Which hepatitis virus is known to be sexually transmitted? Student Answer: A B C D Instructor Explanation: Only hepatitis B virus (HBV) is known to be sexually transmitted. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 18. Question : An infant has a loud, harsh, holosystolic murmur and systolic thrill that can be detected at the left lower sternal border that radiates to the neck. These clinical findings are consistent with which congenital heart defect? Student Answer: Atrial septal defect (ASD) Ventricular septal defect (VSD) Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) Atrioventricular canal (AVC) defect Instructor Explanation: On physical examination, a loud, harsh, holosystolic murmur and systolic thrill can be detected at the left lower sternal border. The intensity of the murmur reflects the pressure gradient across the VSD. An apical diastolic rumble may be present with a moderate-to-large defect, reflecting increased flow across the mitral valve. The presentations of the other congenital heart defects are not consistent with the described symptoms. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 19. Question : The risk for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) decreases for premature infants when they are born between how many weeks of gestation? Student Answer: 16 and 20 20 and 24 24 and 30 30 and 36 Instructor Explanation: Surfactant is secreted into fetal airways between 30 and 36 weeks. The other options are not true regarding the timeframe when the risk for RDS decreases. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 20. Question : An infant’s hemoglobin must fall below ___ g/dl before signs of pallor, tachycardia, and systolic murmurs occur. Student Answer: 11 9 7 5 Instructor Explanation: When the hemoglobin falls below 5 g/dl, pallor, tachycardia, and systolic murmurs may occur. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 21. Question : What is the primary problem resulting from respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of the newborn? Student Answer: Consolidation Pulmonary edema Atelectasis Bronchiolar plugging Instructor Explanation: The primary problem is atelectasis, which causes significant hypoxemia and is difficult for the neonate to overcome because a significant negative inspiratory pressure is required to open the alveoli with each breath. None of the other options are considered a primary problem associated with RDS. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 22. Question : What is the most common cause of iron deficiency anemia (IDA)? Student Answer: Decreased dietary intake Chronic blood loss Vitamin deficiency Autoimmune disease Instructor Explanation: The most common cause of IDA in well-developed countries is pregnancy and chronic blood loss. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 23. Question : A person with type O blood is considered to be the universal blood donor because type O blood contains which of the following? Student Answer: No antigens No antibodies Both A and B antigens Both A and B antibodies Instructor Explanation: Because individuals with type O blood lack both types of antigens, they are considered universal donors, meaning that anyone can accept their red blood cells. Type O individuals, who have neither A or B antigen but have both anti-A and anti-B antibodies, cannot accept blood from any of the other three types. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 24. Question : An individual is more susceptible to infections of mucous membranes when he or she has a seriously low level of which immunoglobulin antibody? Student Answer: IgG IgM IgA IgE Instructor Explanation: The IgA molecules found in bodily secretions are dimers anchored together through a J-chain and secretory piece. This secretory piece is attached to the IgA antibodies inside the mucosal epithelial cells and may function to protect these immunoglobulin antibodies against degradation by enzymes also found in the secretions, thus decreasing the risk of infections in the mucous membrane. The other options do not accurately identify the immunoglobulin antibody involved in mucous membrane infections. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 25. Question : It has been determined that a tumor is in stage 2. What is the meaning of this finding? Student Answer: Cancer is confined to the organ of origin. Cancer has spread to regional structures. Cancer is locally invasive. Cancer has spread to distant sites Instructor Explanation: Cancer confined to the organ of origin is stage 1; cancer that is locally invasive is stage 2; cancer that has spread to regional structures, such as the lymph nodes, is stage 3; and cancer that has spread to distant sites, such as a liver cancer spreading to the lung or a prostate cancer spreading to bone, is stage 4. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 26. Question : How is most of the oxygen in the blood transported? Student Answer: Dissolved in plasma Bound to hemoglobin In the form of carbon dioxide (CO2) Bound to protein Instructor Explanation: Oxygen is transported in the blood in two forms. A small amount dissolves in plasma, and the remainder binds to hemoglobin molecules. The other options are not involved in this process. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 27. Question : Which substance has been shown to increase the risk of cancer when used in combination with tobacco smoking? Student Answer: Alcohol Steroids Antihistamines Antidepressants Instructor Explanation: Alcohol interacts with smoke, increasing the risk of malignant tumors, possibly by acting as a solvent for the carcinogenic chemicals in smoke products. No current research supports the remaining options as having an increased effect on the incidence of cancer when used in combination with tobacco smoking. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 28. Question : Which organism is a common sexually transmitted bacterial infection? Student Answer: Staphylococcus aureus Clostridium perfringens Helicobacter pylori Treponema pallidum Instructor Explanation: Treponema pallidum (spirochete, syphilis) is a sexually transmitted disease. Staphylococcus aureus is commonly ingested, causing food poisoning; Clostridium perfringens (gas gangrene) is a skin or wound infection; andHelicobacter pylori (gastritis, peptic ulcers) is found in the gastrointestinal tract. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 29. Question : The coronary ostia are located in the: Student Answer: Left ventricle Aortic valve Coronary sinus Aorta Instructor Explanation: Coronary arteries receive blood through openings in the aorta, called the coronary ostia. Points Received: 0 of 2 Comments: Question 30. Question : Which type of immunity is produced by an individual after either natural exposure to the antigen or after immunization against the antigen? Student Answer: Passive-acquired immunity Active-acquired immunity Passive-innate immunity Active-innate immunity Instructor Explanation: An individual produces active-acquired immunity (active immunity) after natural exposure to an antigen or after immunization, whereas passive-acquired immunity (passive immunity) does not involve the host’s immune response at all. The innate immune system, also known as nonspecific immune system and the first line of defense, is composed of the cells and mechanisms that defend the host from infection by other organisms in a nonspecific manner, which means that the cells of the innate system recognize and respond to pathogens in a generic way. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 31. Question : What is the most common cause of insufficient erythropoiesis in children? Student Answer: Folic acid deficiency Iron deficiency Hemoglobin abnormality Erythrocyte abnormality Instructor Explanation: Similar to the anemias of adulthood, ineffective erythropoiesis or premature destruction of erythrocytes causes the anemias of childhood. The most common cause of insufficient erythropoiesis is iron deficiency. The other options may be causes but are not common ones. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 32. Question : Blood vessels of the kidneys are innervated by the: Student Answer: Vagus nerve Sympathetic nervous system Somatic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system Instructor Explanation: The blood vessels of the kidney are innervated by the sympathetic noradrenergic fibers that cause arteriolar vasoconstriction and reduce renal blood flow. The other options are not involved in this process. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 33. Question : Between which months of age does sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) most often occur? Student Answer: 0 and 1 2 and 4 5 and 6 6 and 7 Instructor Explanation: The incidence of SIDS is low during the first month of life but sharply increases in the second month of life, peaking at 2 to 4 months and is unusual after 6 months of age. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 34. Question : Which complex (wave) represents the sum of all ventricular muscle cell depolarizations? Student Answer: PRS QRS QT interval P Instructor Explanation: Only the QRS complex represents the sum of all ventricular muscle cell depolarizations. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 35. Question : Carcinoma in situ is characterized by which changes? Student Answer: Cells have broken through the local basement membrane. Cells have invaded immediate surrounding tissue. Cells remain localized in the glandular or squamous cells. Cellular and tissue alterations indicate dysplasia. Instructor Explanation: Carcinoma in situ (CIS) refers to preinvasive epithelial malignant tumors of glandular or squamous cell origin. These early stage cancers are localized to the epithelium and have not broken through the local basement membrane or invaded the surrounding tissue. Dysplasia refers to changes in mature cell structure. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 36. Question : If the sinoatrial (SA) node fails, then at what rate (depolarizations per minute) can the atrioventricular (AV) node depolarize? Student Answer: 60 to 70 40 to 60 30 to 40 10 to 20 Instructor Explanation: If the SA node is damaged, then the AV node will become the heart’s pacemaker at a rate of approximately 40 to 60 spontaneous depolarizations per minute. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 37. Question : What is the direct action of atrial natriuretic hormone? Student Answer: Sodium retention Sodium excretion Water retention Water excretion Instructor Explanation: Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) inhibit the secretion of renin, inhibit angiotensin-induced secretion of aldosterone, vasodilate the afferent and constrict the efferent glomerular arterioles, and inhibit sodium and water absorption by kidney tubules. The other actions are not a result of the atrial natriuretic hormone. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 38. Question : Causes of hyperkalemia include: Student Answer: Hyperparathyroidism and malnutrition Vomiting and diarrhea Renal failure and Addison disease Hyperaldosteronism and Cushing disease Instructor Explanation: Hyperkalemia should be investigated when a history of renal disease, massive trauma, insulin deficiency, Addison disease, use of potassium salt substitutes, or metabolic acidosis exists. The other options are not known to be causes of hyperkalemia. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 39. Question : Which cardiac chamber has the thinnest wall and why? Student Answer: The right and left atria; they are low-pressure chambers that serve as storage units and conduits for blood. The right and left atria; they are not directly involved in the preload, contractility, or afterload of the heart. The left ventricle; the mean pressure of blood coming into this ventricle is from the lung, which has a low pressure. The right ventricle; it pumps blood into the pulmonary capillaries, which have a lower pressure compared with the systemic circulation. Instructor Explanation: The two atria have the thinnest walls because they are low-pressure chambers that serve as storage units and conduits for blood that is emptied into the ventricles. This selection is the only option that correctly identifies which heart chambers have the thinnest walls and why that helps cardiac function. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 40. Question : Innervation of the bladder and internal urethral sphincter is supplied by which nerves? Student Answer: Peripheral nerves Parasympathetic fibers Sympathetic nervous system Tenth thoracic nerve roots Instructor Explanation: The innervation of the bladder and internal urethral sphincter is supplied by parasympathetic fibers of the autonomic nervous system. The process is not dependent on any of the other options. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 41. Question : The most common site of metastasis for a patient diagnosed with prostate cancer is which location? Student Answer: Bones Brain Bladder Kidney Instructor Explanation: The bone, especially the lumbar spine area, is the most common metastasis site for prostate cancer. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 42. Question : Why is nasal congestion a serious threat to young infants? Student Answer: Infants are obligatory nose breathers. Their noses are small in diameter. Infants become dehydrated when mouth breathing. Their epiglottis is proportionally greater than the epiglottis of an adult’s. Instructor Explanation: Infants up to 2 to 3 months of age are obligatory nose breathers and are unable to breathe in through their mouths. Nasal congestion is therefore a serious threat to a young infant. This selection is the only option that accurately describes why nasal congestion is a serious threat to young infants. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 43. Question : What is the final stage of the infectious process? Student Answer: Colonization Invasion Multiplication Spread Instructor Explanation: From the perspective of the microorganisms that cause disease, the infectious process undergoes four separate stages of progression: (1) colonization, (2) invasion, (3) multiplication, and (4) spread. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 44. Question : Which statement is true concerning the IgM? Student Answer: IgM is the first antibody produced during the initial response to an antigen. IgM mediates many common allergic responses. IgM is the most abundant class of immunoglobulins. IgM is capable of crossing the human placenta. Instructor Explanation: Typically, IgM is produced first (primary immune response), followed by IgG against the same antigen. The other options are not true statements regarding IgM. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 45. Question : What is the first stage in the infectious process? Student Answer: Invasion Colonization Spread Multiplication Instructor Explanation: From the perspective of the microorganisms that cause disease, the infectious process undergoes four separate stages of progression: (1) colonization, (2) invasion, (3) multiplication, and (4) spread. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 46. Question : Phagocytosis involves neutrophils actively attacking, engulfing, and destroying which microorganisms? Student Answer: Bacteria Fungi Viruses Yeasts Instructor Explanation: Invasion is the direct confrontation with an individual’s primary defense mechanisms against only bacteria, which include the complement system, antibodies, and phagocytes, such as neutrophils and macrophages. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 47. Question : How much urine accumulates in the bladder before the mechanoreceptors sense bladder fullness? Student Answer: 75 to 100 ml 100 to 150 ml 250 to 300 ml 350 to 400 ml Instructor Explanation: When the bladder accumulates 250 to 300 ml of urine, it contracts and the internal urethral sphincter relaxes through activation of the spinal reflex arc (known as the micturition reflex). Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 48. Question : What is the primary cause of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) of the newborn? Student Answer: Immature immune system Small alveoli Surfactant deficiency Anemia Instructor Explanation: RDS is primarily caused by surfactant deficiency and secondarily by a deficiency in alveolar surface area for gas exchange. None of the other options are related to the cause of RDS. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 49. Question : Hypersensitivity is best defined as a(an): Student Answer: Disturbance in the immunologic tolerance of self-antigens Immunologic reaction of one person to the tissue of another person Altered immunologic response to an antigen that results in disease Undetectable immune response in the presence of antigens Instructor Explanation: Hypersensitivity is an altered immunologic response to an antigen that results in disease or damage to the host. The other options are not accurate definitions of hypersensitivity. Points Received: 2 of 2 Comments: Question 50. Question : In which primary immune deficiency is there a partial-to-complete absence of T-cell immunity? Student Answer: Bruton disease DiGeorge syndrome Reticular dysgenesis Adenosine deaminase deficiency Instructor Explanation: The principal immunologic defect in DiGeorge syndrome is the partial or complete absence of T-cell immunity. The other options are not the result of either a partial or complete absence of T-cell immunity. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 28, 2021
Number of pages
21
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 28, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
73