I. TRUE or FALSE. Write A if the statement is true and B if it is false, on the answer sheet provided along with this
questionnaire. Erasures and alterations of any kind will not be given credit.
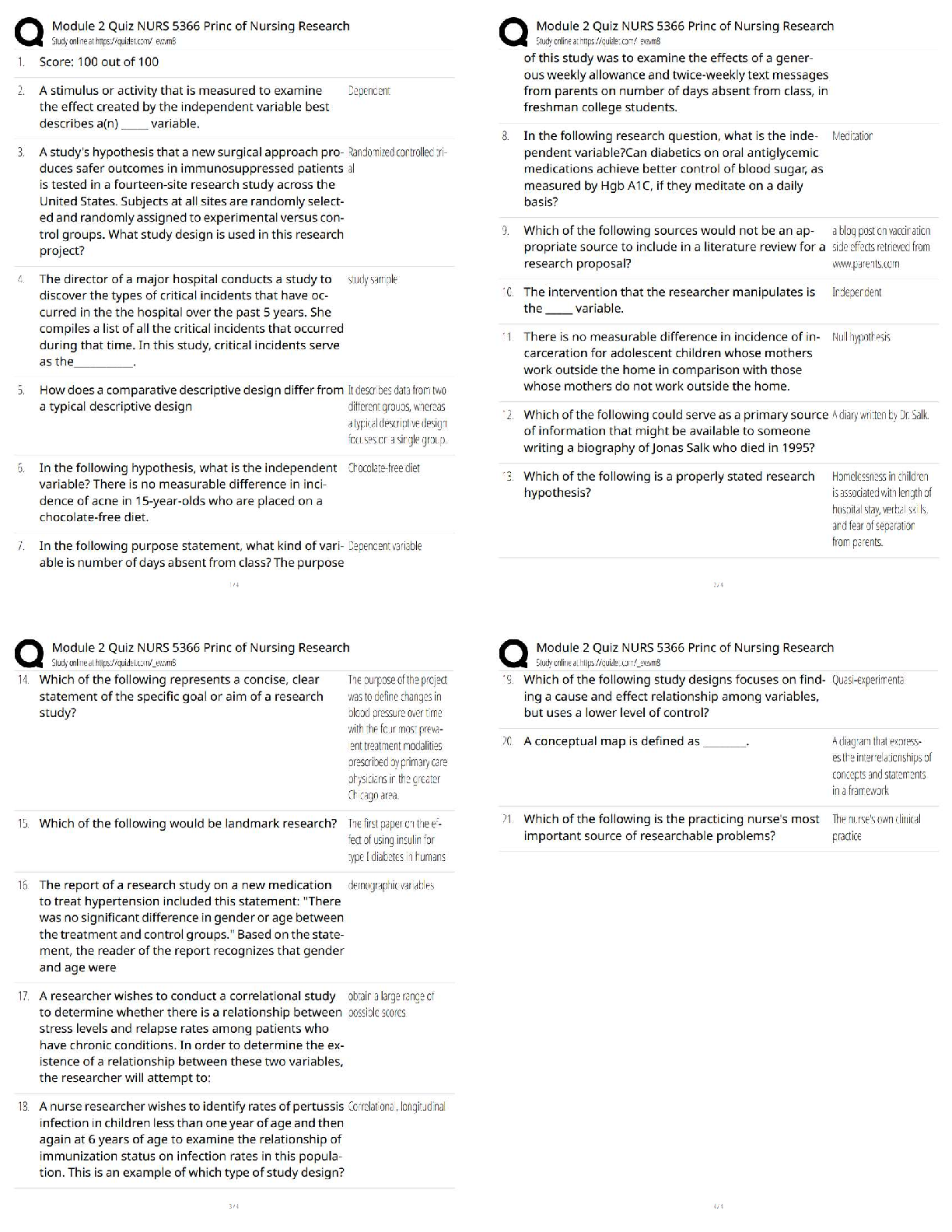
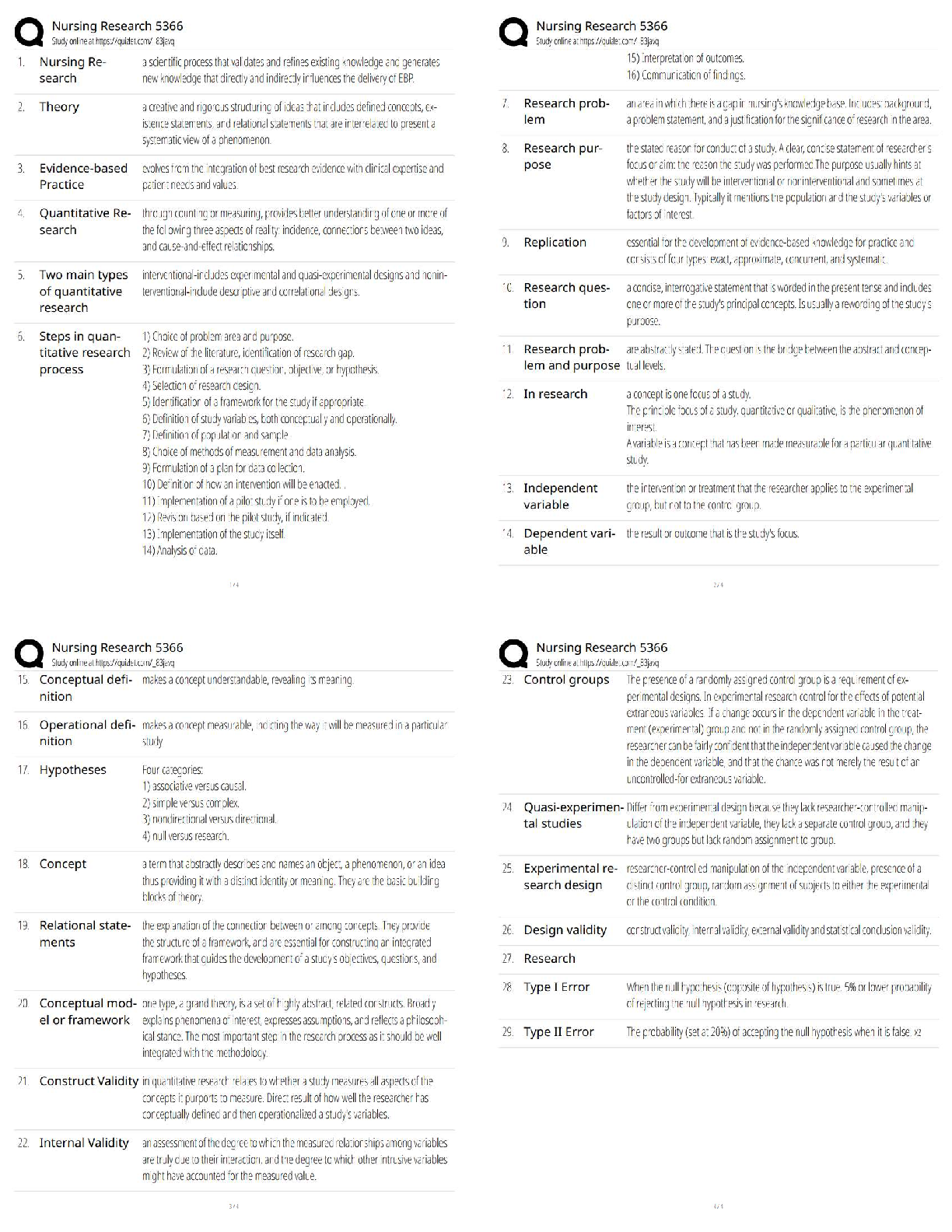
1. Audit sampling impl
...
I. TRUE or FALSE. Write A if the statement is true and B if it is false, on the answer sheet provided along with this
questionnaire. Erasures and alterations of any kind will not be given credit.
1. Audit sampling implies the gathering of evidence to use as a basis for making valid inferences about the
characteristics of the population as a whole without examining every transaction. T
2. Audit sampling is the application of an audit procedure to less than 100 percent of the items within an account
balance or class of transactions for the purpose of evaluating some characteristic. T
3. When performing substantive tests using sampling methods, the auditor's main concern is the risk of incorrect
rejection. FALSE
4. The risk of incorrect acceptance of an account balance as correct, when in fact it is not correct, bears directly
on the effectiveness of an audit. T
5. The tolerable misstatement is the confidence level needed to infer population values. FALSE
6. When an auditor chooses to examine all purchases of equipment exceeding P1,000.00 and to test the
remaining items by analytical procedures, the auditor is using statistical sampling. FALSE
7. The most efficient method of testing a large population is the use of non-statistical sampling. FALSE
8. Statistical sampling assists auditors in determining the sufficiency of evidence gathered. T
9. The use of haphazard selection of a sample allows for random, statistical evaluation. FALSE
10. The tolerable deviation rate is the minimum rate of control procedure failure that can occur sufficient to cause
the auditor to re-assess the preliminary assessment of control risk to a higher level. FALSE
11. The expected deviation rate is the auditor's best estimate of the percentage of transactions processed for
which the control procedure is not effectively applied. T
12. An attribute is defined as a characteristic of the population of interest to the auditor. T
13. The sample size decreases as the allowance for sampling error decreases. FALSE
14. For tests of control procedures the most commonly used statistical method is Attribute Sampling. T
15. Increasing the expected deviation rate will cause the sample size to increase. T
16. Sample size varies directly with the expected deviation rate.
[Show More]