Language Development > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > CST 221, Questions with accurate answers, Examinable/ Graded A+ (All)
CST 221, Questions with accurate answers, Examinable/ Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
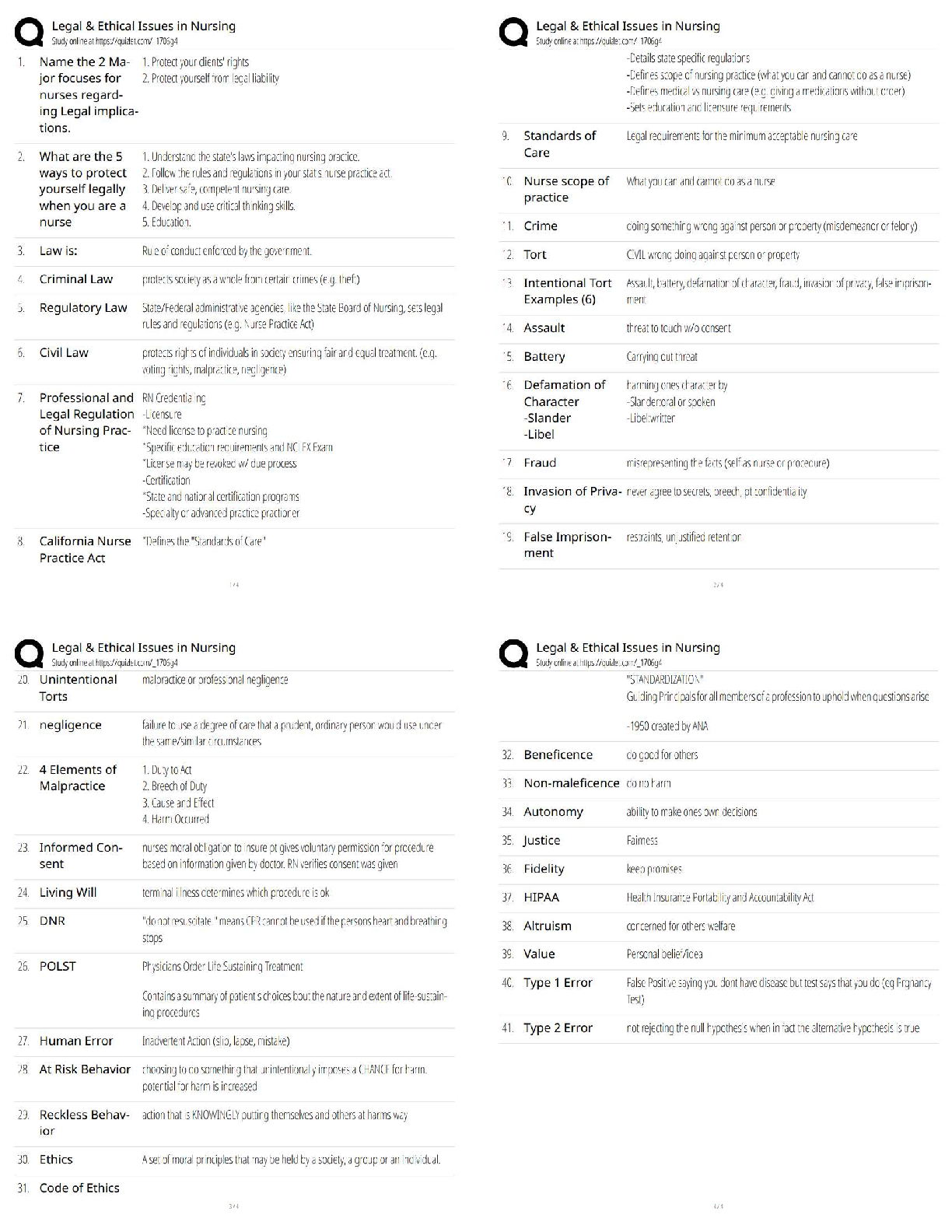
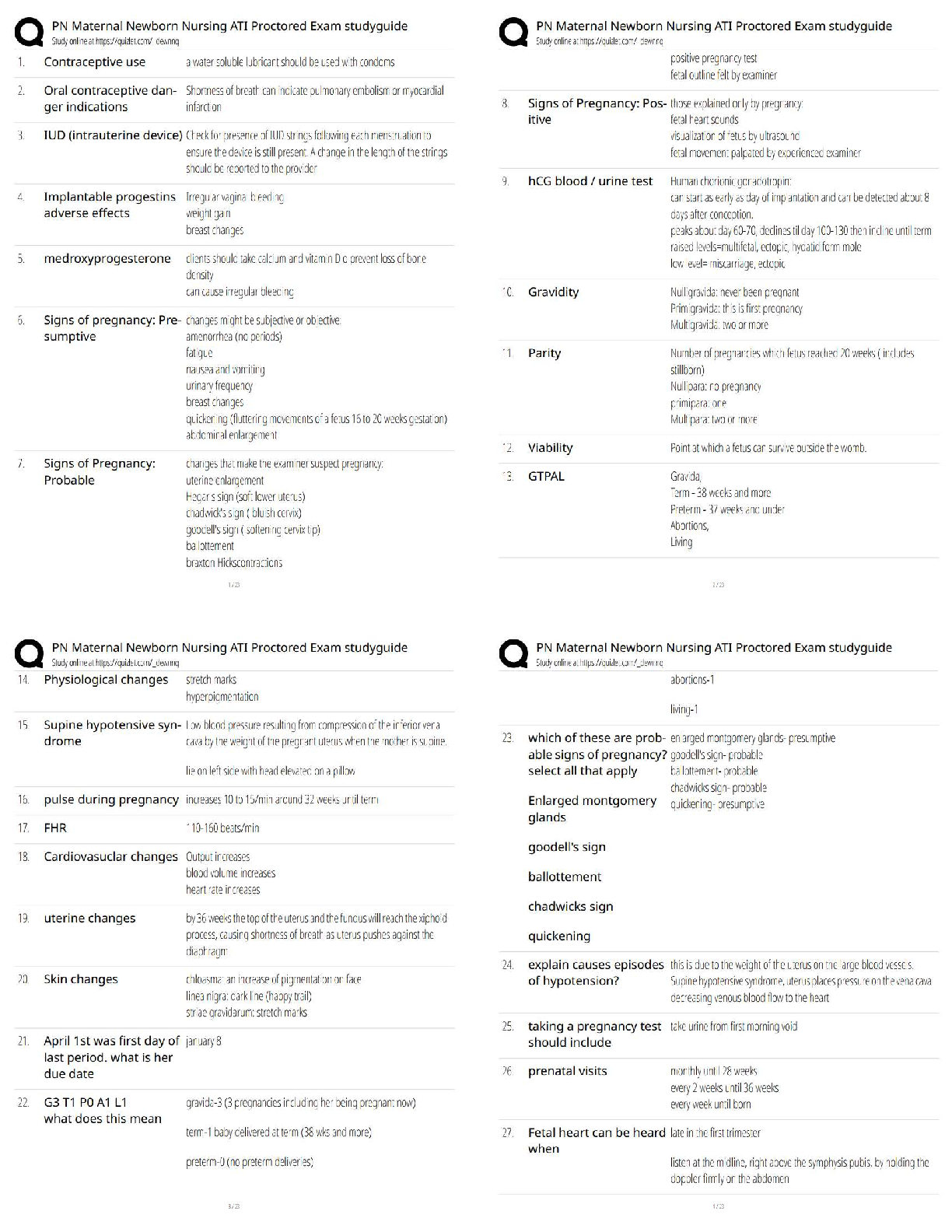
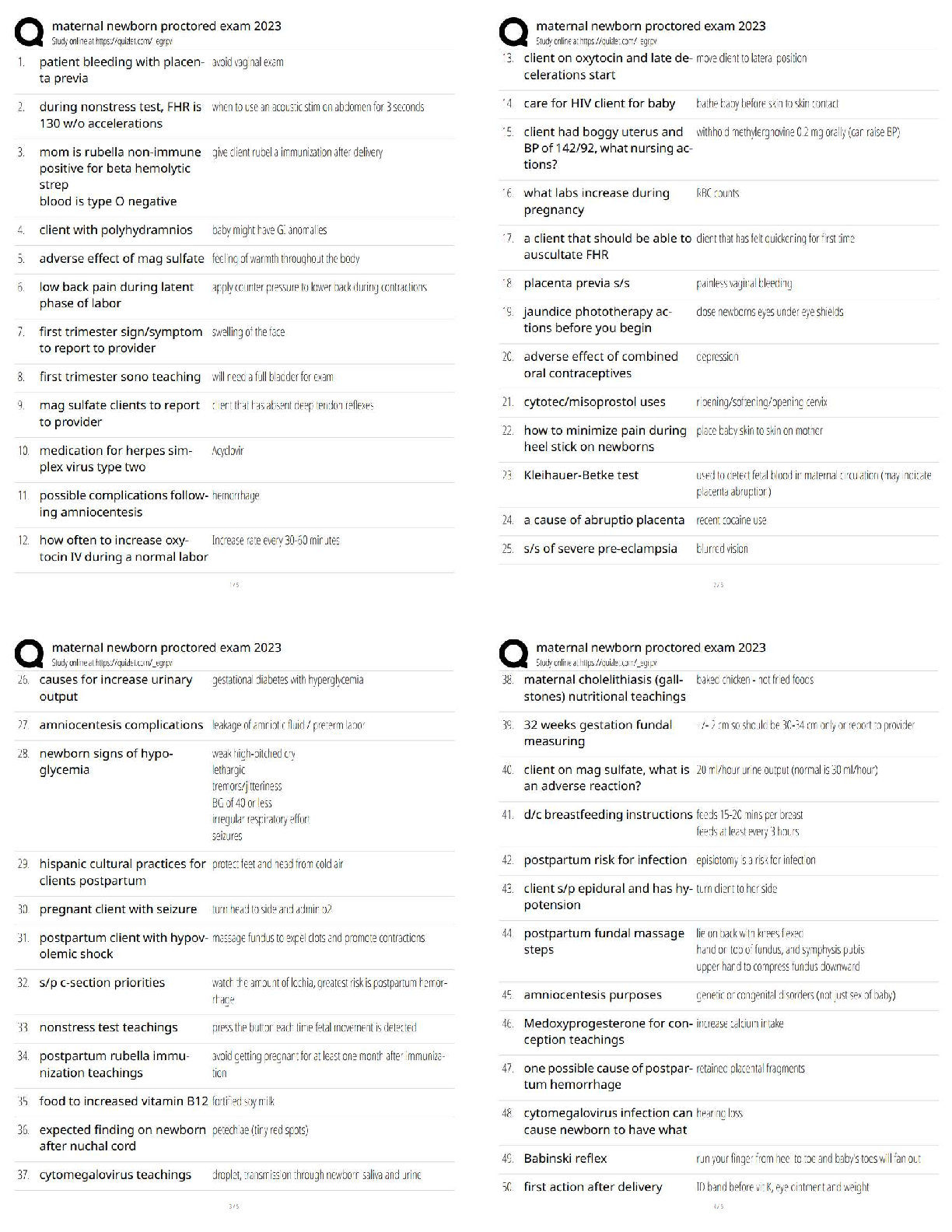
CST 221, Questions with accurate answers, Examinable/ Graded A+ When students practice fluency: - ✔✔They practice by reading connected pieces of text. they don't read word by word - they will ... read a sentence straight through. Reading fluently is important because: - ✔✔It enables students to comprehend what they are reading. Students who are not fluent in reading would: - ✔✔Sound out each letter or word slowly and pay more attention t the phonics of each word. Fluent readers: - ✔✔Will read a sentence aloud using appropriate intonations. The best way to test for fluently: - ✔✔Have a student read something ALOUD - preferably a few sentences in a row. Fluency is a good predictor of: - ✔✔Comprehension Reading aloud to young children is: - ✔✔One of the most important things that an adult can do because they are teaching children how to: 1. Monitor 2. Question 3. Predict 4. And confirm what they hear in in the stories Word Consciousness - ✔✔Children who have access to books can first tell the story through the pictures. They then begin to realize the connection between the spoken words and the printed words. They realize that the written words tell a story. Language and conventions of print - ✔✔During this stage, children learn how to: - hold a book - where to begin to read - the left-to-right motion - continue from one line to another Functions of print - ✔✔Children discover that print can be used for a variety of purposes and functions, including entertainment and information. Experiences with print will help preschool children: - ✔✔Develop an understanding of the: - conventions - purposes - and functions of print. Children learn about print and come to an understanding that: - ✔✔Print carries the story. Knowledge about the conventions of print enables children to understand: - ✔✔The physical structure of language The conceptual knowledge that printed words convey a message helps children: - ✔✔Bridge the gap between oral and written language. Phonological awareness and knowledge of print-speech relations: - ✔✔Play an important role in facilitating reading acquisition Phonological awareness instruction should be: - ✔✔An integral component of early reading programs. Story book reading affects: - ✔✔- children's knowledge about - strategies for - and attitudes towards reading Storybook reading - ✔✔This is the most strongly supported across the emergent literacy literature as a strategy to promote growth in literacy acquisition. Early language development follows a: - ✔✔Continuum. Early language development is important to later reading development. Learning Approach - ✔✔Language development evolved from learning the rules of language structure and applying them through imitation and reinforcement. According to this approach: language, cognitive and social development were independent of each other. Children were expected to learn language from patterning and imitating adults who spoke and wrote Standard English. Linguistic Approach - ✔✔Language ability is innate and develops through natural human maturation as environmental stimuli trigger acquisition of syntactical structures appropriate to each exposure level. In other words, language is innate and stimulated by triggers. According to this approach, linguists attributed language development to biological rather than cognitive or social influences. Cognitive Approach - ✔✔Language knowledge derives from both syntactic and semantic structures. Supporters of the cognitive approach maintained that: Children acquire knowledge of linguistic structures after they have acquired the cognitive structures necessary to process language. One must understand and process an idea or object cognitively before being able to produce it verbally. - One must recognize objects before having the ability to verbally name them. Sociocognitive Approach - ✔✔Language development results from sociolinguistic competence. - language, cognitive, and social competence are interactive elements of total human development The sociocognitive approach allowed that determining the appropriateness of of language in given situations for specific listeners is as important as understanding semantic and syntactic structures. - by engaging in conversation, children at all stages of development have the opportunities to test their language skills, receive feedback and make modifications. According to this theory: Language is a result of social reasons. You need language to communicate when in social settings - therefore you must learn language. Children are constantly applying cognitive skills to using language in social interactions. If the capacity to acquire language is inborn without an environment to practice it in then a child would not be able to communicate beyond grunts and gestures. Phonological Awareness - ✔✔This is the ability of the reader to recognize the sounds of spoken language. this includes how sounds can be: - blended together - segmented - and manipulated Phonological awareness leads to: - ✔✔Phonics: a method for teaching children to read. It helps children 'sound out words'. Phonemic Awareness - ✔✔An understanding that words are composed of sounds. to be phonemically aware means that the reader and the listener can recognize and manipulate specific sounds in spoken words. Phonemic Awareness Tasks - ✔✔1. Ability to hear rhymes and alliterations 2. Ability to do oddity tasks (recognize the member of a set that is different, or odd, among the group) 3. Ability to orally blend words and split syllables 4. Ability to orally segment words 5. Ability to do phonics manipulation tasks Why do children need a strong background in phonemic awareness? - ✔✔So that phonics instruction (sound-spelling relationship - printed materials) will be effective. The Alphabetic Principle/Graphophonemic Awareness - ✔✔The theory that written words are composed of patterns of letters that represent the sounds of spoken letters - this is sound-letter correspondence Four Basic Features of the Alphabetic Principle - ✔✔1. Students need to be able to take spoken words apart and blend different sounds together to make new words 2. Students need to apply letter sounds to all their reading 3. Teachers need to use a systematic effective program in order to teach children to read 4. The teaching of the alphabetic principle usually begins in kindergarten Morphology - ✔✔The study of word structure. - Morphemic skills: an ability to understand the patterns within words. For instance, cat, cats, and caterpillar all have similarities in structure. - Readers are able to recognize words at a faster and easier rate because they don't have to decode each individual word. Syntax - ✔✔The rules or patterned relationships that correctly create phrases and sentences from words. When you have an understanding of syntax then you will begin to understand the structure of how sentences are built and ultimately the beginning of grammar. Semantics - ✔✔The meaning expressed when words are arranged in a specific way. this is where connotation and denotation of words eventually will have a role with readers. Phonics - ✔✔The study of phonics must be done with the eyes opened. It is the connection between the sounds and letters on a page. This is sound to written letter correspondence - in other words, the connection of oral and written language. - When students learn phonics, they will see the word 'bad' and sound each letter out slowly until they recognize that they just said the word. Word Analysis/Phonics/Decoding - ✔✔The process readers use to figure out unfamiliar words based on written pattern Word Recognition - ✔✔The process of automatically determining the pronunciation and some degree of the meaning of an unknown word. - fluent readers will recognize most written words easily and correctly. they unconsciously decode or break down words. Decode - ✔✔This means to change communication signals into messages. Reading comprehension requires that: the reader will learn the code within which a message is written and be able to decode it to get the message. Endode - ✔✔This involves changing a message into symbols. Encoding an oral language into writing = spelling. Encoding a mathematical idea = you must use appropriate mathematical symbols. The Developmental Stages of Spelling - ✔✔1. Prephonemic Spelling: children know that letters stand for a message. They don't know the relationship between spelling and pronunciation. They can't decode or encode yet. 2. Early Phonemic Spelling: children are beginning to understand spelling. They usually write the beginning letter correctly, followed by consonants or long vowels. 3. Letter-Name Spelling: some words are consistently spelled correctly. The student is developing a sight vocabulary and a stable understanding of letters as representing sound. - Long vowels are used accurately - Silent vowels are omitted - Unknown words are spelled by the child attempting to match the name of the letter to the sound. 4. Transitional Spelling: this phase is typically entered in late elementary school. Short vowel sounds are mastered and some spelling rules are known. They are developing a sense of which spellings are correct and which are not. 5. Derivational Spelling: This is usually reached from high school to adulthood. this is the stage where spelling rules are being mastered. Constructing Meaning - ✔✔This phrase is synonymous with reading comprehension with regard to to the balanced literacy approach. The purpose of reading is to - ✔✔Convert visual images (the letters and words) into a message. Pronouncing the words IS NOT ENOUGH. The reader MUST be able to extract the meaning of the texts. When people read, they utilize four sources of background information to comprehend the meaning behind the literal text. Four sources of background information to comprehend the meaning behind the literal text: - ✔✔1. Word Knowledge 2. Syntax and Contextual Information 3. Semantic Knowledge 4. Text Organization Word Knowledge - ✔✔Information about words and letters. One's knowledge about word meanings is lexical knowledge (the words you know are part of your lexicon). Knowledge about spelling patterns and pronunciation is orthographic knowledge. Syntax and Contextual Information - ✔✔When children encounter unknown words in a sentence they rely on their background knowledge to choose a word that makes sense. Semantic Knowledge - ✔✔This includes the reader's background [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 46 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

CST BUNDLE. EXAMINABLE VERSIONS, RATED A+
CST EXAM QUESTIONS & answers. 100% Accurate. ALL Latest Version.
By Topmark 2 years ago
$35
27
Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 10, 2023
Number of pages
46
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 10, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
139