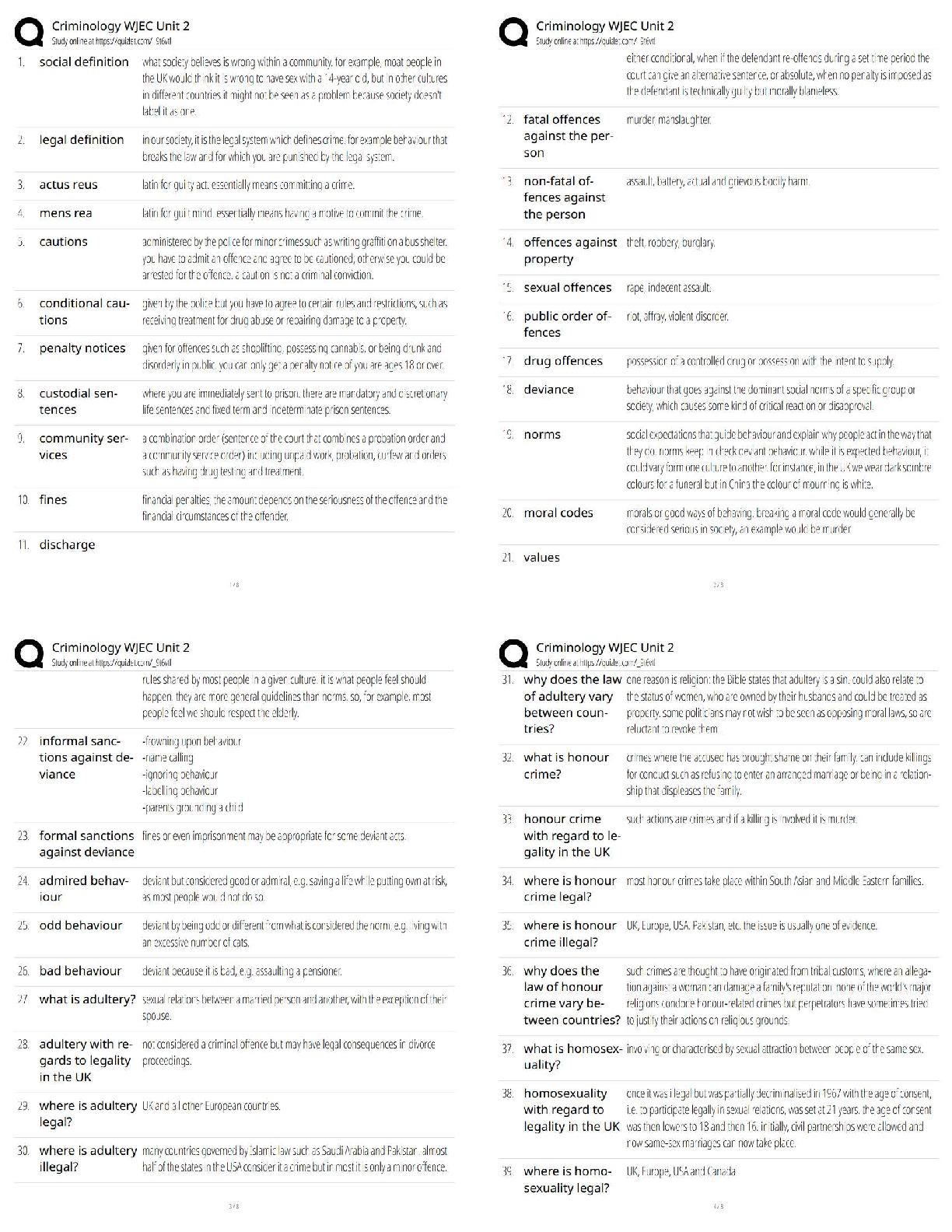
NYSTCE CST Multi-subject 241. Exam
Predictor. Complete Coverage. Rated A.
Alphabet recognition - ✔✔-*Can identify the letters of the alphabet* both capital and lowercase when
asked to do so
Alphabetic principle - ✔✔
...
NYSTCE CST Multi-subject 241. Exam
Predictor. Complete Coverage. Rated A.
Alphabet recognition - ✔✔-*Can identify the letters of the alphabet* both capital and lowercase when
asked to do so
Alphabetic principle - ✔✔-Written language is comprised of *letters (graphemes)* that represent
*sounds (phonemes)* in spoken words
Analogical representations - ✔✔-*Declarative memories that preserve many of the aspects of the
original stimulus* (object or event).Example: mental imagery i.e., when you recall a mental picture of
what the something looked like.
Analogy-based phonics - ✔✔-A strategy taught to help students *use parts of words they have learned*
to attack words that are unfamiliar
Anecdotal notes (records) - ✔✔-*Short written observations*made by the teacher while student's work
making notes on their progress to look back at later.
Anticipation guides - ✔✔-Comprehension strategy that is *used before reading to activate students'
prior knowledge* and build curiosity about a new topic. They help students make connections between
new information and prior knowledge. Used to motivate reluctant readers by stimulating their
information
Attention - ✔✔-*Focus on a stimulus.* Involved in all three memory processes: Sensory Memory, Long�Term Memory, and Working Memory.
Automaticity - ✔✔-The ability to perform thoroughly *learned tasks without much mental effort.*
Examples include riding a bike and driving a car.
Availability vs accessibility - ✔✔-Availability: is info *stored in long term* memory? Accessibility: *how
easily* is info *retrieved*?
Balanced literacy models - ✔✔-Strategies teachers use to allow for *different learning styles*
Bias uncovering - ✔✔-*Question sources* writer uses, use of *fact or opinions* to support claim, what
was *left out*, how they *address contrary evidence* or opinions.
Blend - ✔✔-A sequence of *consonants before or after a vowel* in each syllable
Bloom's 1st level - ✔✔-*Remember* (Recognizing, Recalling)
Bloom's 2nd level - ✔✔-*Understand* (Interpreting, Exemplifying, Classifying, Summarizing, Inferring,
Comparing, Explaining)
Bloom's 3rd level - ✔✔-*Apply* (Executing, Implementing)
Bloom's 4th level - ✔✔-*Analyze* (Differentiating, Organizing, Attributing)
Bloom's 5th level - ✔✔-*Evaluate* (Checking, Critiquing)
Bloom's 6th level - ✔✔-*Create* (Generating, Planning, Producing)
Bloom's Q for (1) remember - ✔✔-Can the student *recall* the information?
Bloom's Q for (2) understand - ✔✔-Can the student *explain* ideas or concepts?
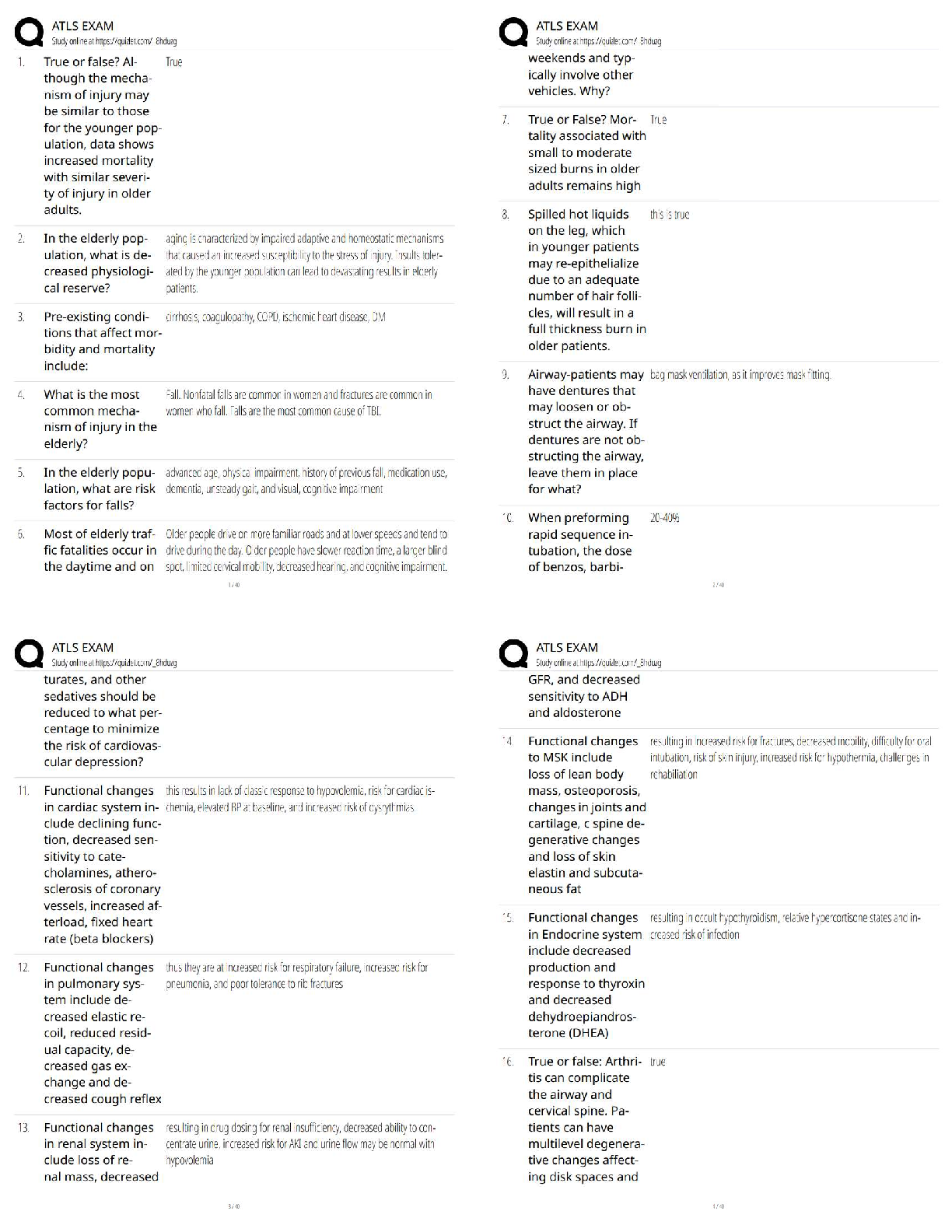
Bloom's Q for (3) apply - ✔✔-Can the student use the information in a *new way*?
Bloom's Q for (4) analyze - ✔✔-Can the student *distinguish* between the *different parts*?
Bloom's Q for (5) evaluate - ✔✔-Can the student *justify* a stand or decision?
Bloom's Q for (6) create - ✔✔-Can the student *create a new product* or point of view?
Bloom's tasks for (1) remember - ✔✔-Define, duplicate, list memorize, *recall*, repeat, reproduce, state
Bloom's tasks for (2) understand - ✔✔-Classify, describe, discuss, *explain*, locate, recognize
Bloom's tasks for (3) apply - ✔✔-Choose, *demonstrate*, dramatize, employ, illustrate, interpret, solve
Bloom's tasks for (4) analyze - ✔✔-*Compare*, distinguish, examine, experiment, test, question,
contrast
Bloom's tasks for (5) evaluate - ✔✔-Judge, select, choose, *decide*, justify, select, support, argue,
verify, discus, criticize
Bloom's tasks for (6) create - ✔✔-Construct, design, develop, predict, compose, *invent*
Bottom-up processing - ✔✔-Perceiving based on noticing separate *defining features* and
*assembling*them into a recognizable pattern. Also called data-driven.
Cause-and-effect - ✔✔-Determine *why something happens* as well as the *results*.
Characteristics of prose - ✔✔-*No formal arrangement* but there *may be* some sort of *rhythm*
Chunking - ✔✔-*Grouping items of information*, which expands the amount of information that can be
stored in short-term memory.
Closed word sort - ✔✔-The *teacher defines the process* for categorizing the words. This requires
students to engage in critical thinking as they examine sight vocabulary, corresponding concepts, or
word structure.
Cloze exercise - ✔✔-Involves getting students to *fill in words deliberately omitted* from a passage of
text; assists students in the predictions and the use of context clues.
Code - ✔✔-*Notes made on the reading* that highlight *passages that "speak"* to them personally
Cognitive approaches - ✔✔-A focus on *changes and thought that are part of learning.* They differ from
behavioral approaches in that they emphasize the mental mechanisms that underlie the processing and
representation of information during learning.
Cognitive science - ✔✔-The *interdisciplinary study of thinking*, language, intelligence, knowledge
creation, and the brain.
Cognitive view of learning - ✔✔-A general approach that views *learning as an active mental process* of
acquiring, remembering, and using knowledge.
Comprehension - ✔✔-*Construct understanding* and/or meaning from the words
Concluding - ✔✔-*Drawing together the main ideas* of something and *restating* them in a succinct
way.
Conditional knowledge - ✔✔-*Knowing when and how to apply* the declarative and procedural
knowledge you have learned. Might be stored as cognitive strategies, or information about the
conditions under which declarative and procedural knowledge is useful.
Connectionist model of memory - ✔✔-Focuses on the ways *declarative and procedural knowledge* are
combined via *connections* among elements.
Consonant Clusters - ✔✔-Consonants that occur *side by side within the same syllable*. No intervening
vowel sound. Also called blends.
Constructing meaning strategies - ✔✔-1. Prior *Knowledge*
2. *Inferencing*
3. Monitoring
4. Summarizing
5. *Asking Questions*
Constructivist approaches - ✔✔-*Memory is largely built on prior experience* in context. It is not
merely reproductive. People often use existing cognitive frameworks, or schemas, to construct
organizations for new information. Mental scripts, or stereotypical sequences of events, also can affect
students' expectations and memories.
Context clues - ✔✔-Content in *surrounding text* that help the reader determine the meaning of an
unknown word.
Cornel Notes Method - ✔✔-Left side is for recording *main idea*, right side is for *details* about the
main ideas. Bottom = *summary*
Criterion-referenced tests - ✔✔-*Determine the point* at which the student has achieved *mastery.*
They enable educators to assess whether a student has met a *predetermined goal.*
Cueing systems - ✔✔-*Semantic*: did that sentence make sense? *Syntactic*: does that sound right?
*Graphophonemic*: does that look right?
CVC - ✔✔-*Consonant-vowel-consonant *pattern which produces a short vowel sound or a closed
syllable.
Declarative knowledge - ✔✔-Knowledge described as "*knowing that*," e.g., knowing that the sun rises
in east. Categorical knowledge is declarative. Stored in semantic to episodic memory.
Decoding - ✔✔-An ability use sound-symbol correspondence to *sound out new words* or to interpret
a word from print to speech.
Details - ✔✔-Pieces of information that *support or tell more about the main idea*. Uses words like
who, what, where, when, how and why to identify main ideas. News articles are good for practicing.
Diagnostic assessment - ✔✔-*Standardized tests* that aim to determine a student's strengths and
weaknesses.
Digraph - ✔✔-A union of *two characters representing a single sound*.
Diphthong - ✔✔-The sound produced by combining *two vowels in to a single syllable* or running
together the sounds.
Discuss - ✔✔-Group connection-making after reading. Includes *literature circles, Socratic seminars and
fishbowls*.
Distributed learning - ✔✔-Learning/study spaced out over *several sessions*.
Domain-specific knowledge - ✔✔-Information that applies *mainly to one specific topic*.
Domain-Specific vocabulary words - ✔✔-Used when reading nonfiction to *develop content clues*.
Double-entry journal - ✔✔-Two column format; left column is used to *record specific statements from
a text* that are important to the reader in understanding the text. The right column is used to record
*responses and reactions*to those statements
Early emergent reader - ✔✔-*Beginning to learn sound/symbol relationship*; can read cvc words.
Embedded phonics - ✔✔-Explicit instruction for using letter-sound relationships during the reading of
connected text to sight read new words
Emergent reader - ✔✔-Can distinguish between fiction and nonfiction; can recognize that reading has a
variety of purposes. Has command of many high frequency words.
Encoding - ✔✔-How you *transform a sensory input* into representation that can be placed into
memory.
Encoding specificity principle - ✔✔-What is encoded determines in large part what is later retrieved.
Episodic memory - ✔✔-Long term memories that hold knowledge of *personally experienced events or
episodes.* Used when people learn lists of words or need to recall something they learn in a particular
personal context.
Explicit memory - ✔✔-*Consciously* recallable information, e.g., words from a list.
Explicit vs. Implicit memory - ✔✔-*Explicit memory*: Consciously acting to recall/recognize particular
info, e.g., trying to remember a list of words you just saw.
*Implicit memory*: Recalling/recognizing info without consciously being aware of doing so, e.g.,
remembering (without effort) meanings of words as you read .
Fluency - ✔✔-Coordinate the words and meaning so reading becomes automatic
Fluency checks - ✔✔-Fast tests, usually one-minute timed readings, focusing on accuracy, rate and
prosody; what a student's words per minute or words correct per minute are calculated.
Four elements of working memory - ✔✔-1. Central executive.
2. Phonological loop.
3. Visuospatial sketchpad.
4. Episodic buffer.
GRTA - ✔✔-Guided reading-thinking activities that offer support by engaging students in the reading
and improving comprehension of narrative text.
They teach how to make predictions, focus their reading on confirming or disproving, adjustments in
thinking. A cycle. A form of scaffolding that will be removed once the process is internalized
Implicit memory - ✔✔-Recall and recognize information without consciously being aware of doing so.
Inference-building approaches - ✔✔-Think-alouds, referents, asking questions that are often "Think and
Search." Write down a sequence of events from the story line and ask students to script the missing
pieces using what they know about characters, setting and other related clues.
Students can read their own sentences and look for referents, context clues and details of events
Inferencing - ✔✔-Making predictions before, during, and after reading
Inferential Comprehension Skills - ✔✔-"Reading between the lines. "
Skills that assist students to make connections to new info in texts by drawing conclusions, determining
relationships, conceptualizing implied ideas.
Making inferences requires several reading behaviors: recognizing a pronoun's antecedent, learning
unknown words from context clues, identifying bias, etc...
Inflectional suffixes - ✔✔-Indicate in:
Nouns: possession, gender, number
Verbs: tense, voice, person & number & mood Adjectives: comparison
Inflectional suffixes do not change the part of speech of the base. (-ed, -ing)
Information processing - ✔✔-The human mind's activity of taking in, storing, and using information.
Interference theory - ✔✔-Forgetting is caused by competing information that renders the sought-after
information inaccessible.
K-W-L - ✔✔-"Know", "Want to Know", "Learned" charts encourage students to use prior knowledge and
personal curiosity while researching a subject or a topic.
This strategy is especially useful in reading classes, but is also useful in other subjects such as science
and social studies.
Letter-sound correspondence - ✔✔-Refers to the identification of sounds associated with individual
letters and letter combination.
Levels-of-processing model - ✔✔-Memory is not made up of any specific number of separate stores.
Instead, storage varies along a continuous dimension in terms of depth of encoding.
Literal comprehension - ✔✔-Refers to the understanding of information that is explicitly stated in a
written passage.
Includes main idea, sequence of events, knowledge of vocabulary, details, and cause-effect patterns,
etc.
Literature Circles - ✔✔-Small groups who read and discuss same materials together (facilitator,
connector, summarizer, vocabulary master, illustrator).
Teachers provide role sheets but do not direct discussion
Loaded word - ✔✔-Word used to evoke very strong positive or negative attitudes toward a person,
group, or idea by using connotation
Long term memory - ✔✔-Stores info for very long periods of time, possibly indefinitely. Examples: the
name of your favorite candy bar; how to open your bicycle lock; the square root of 144 is 12.
Main idea identification - ✔✔-Find the topic or subject of a text. Look at the details that the author uses
to clarify his / her topic.
Maintenance rehearsal (rote learning) - ✔✔-Learning strategy that involves learning and memorizing
new information by simply repeating it.
Massed learning - ✔✔-Cramming all the information into one sessi
[Show More]