Operations and Supply Chain
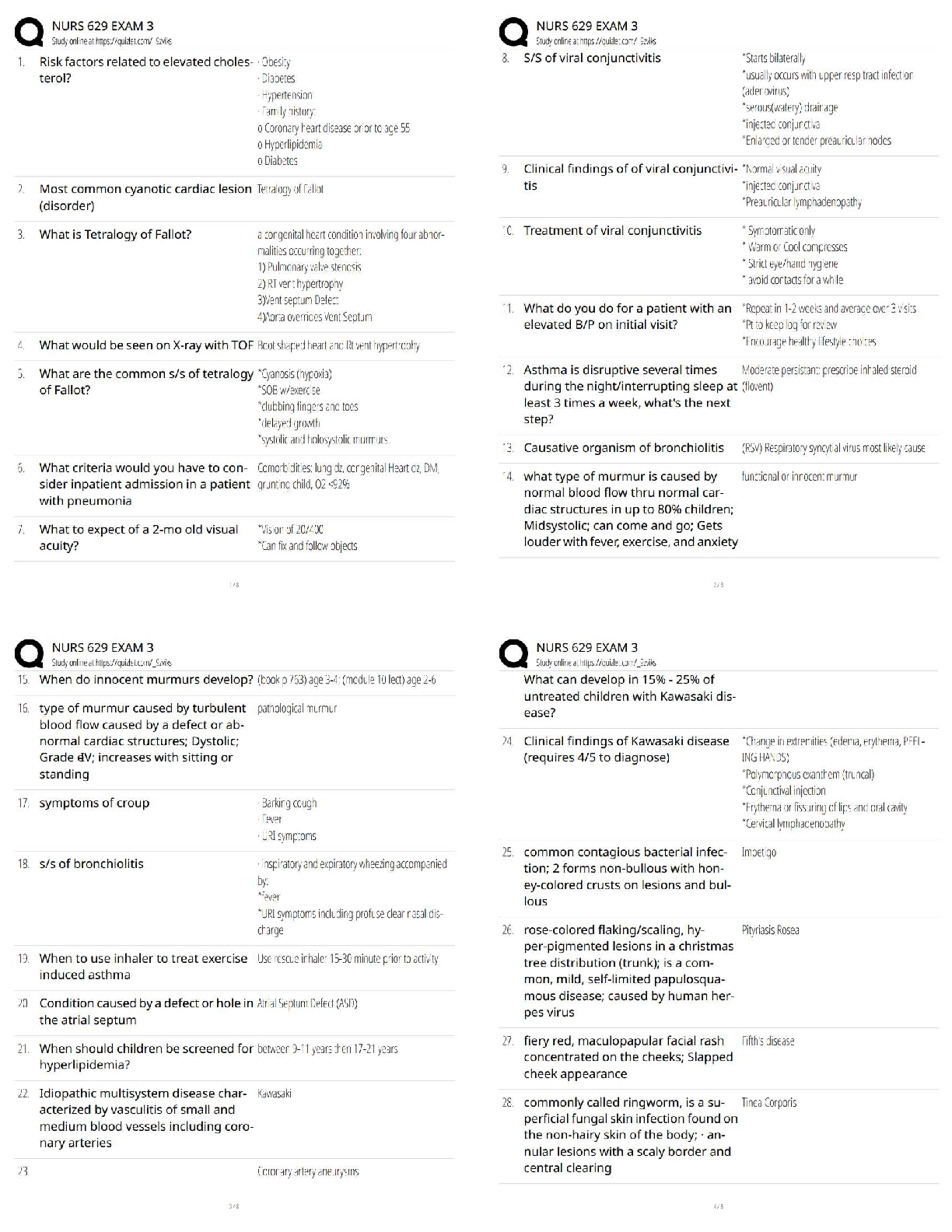
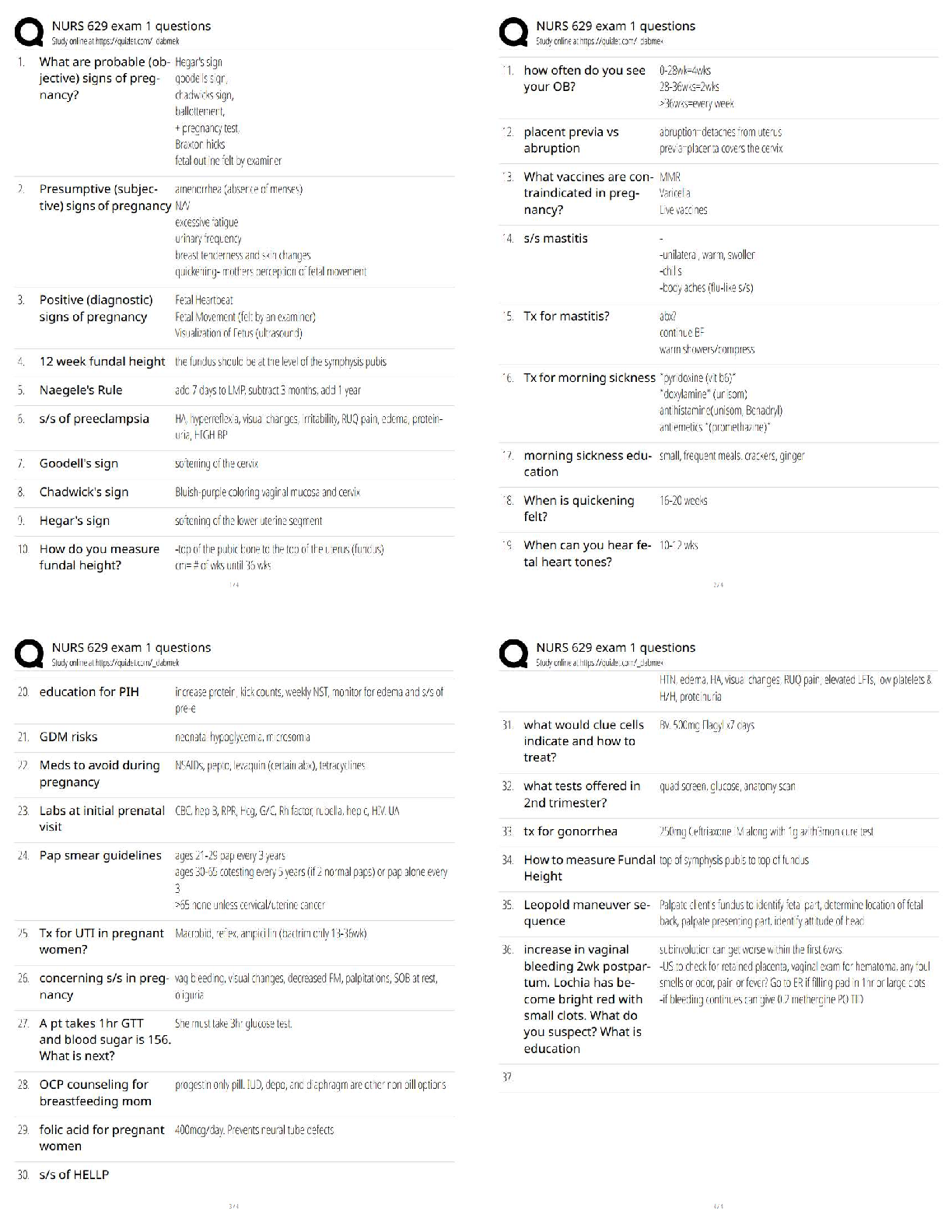
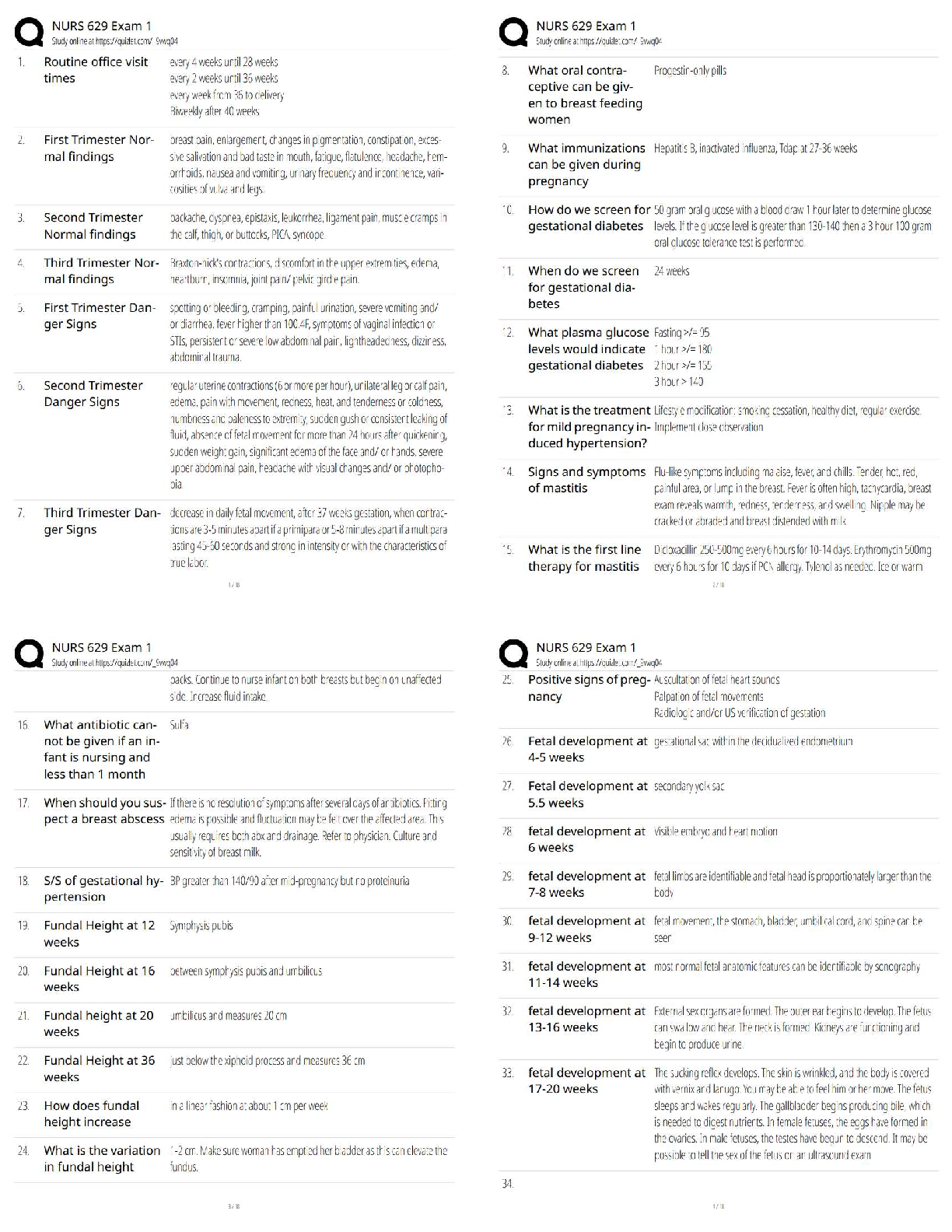
Management WGU - C720, Complete
study guide, graded A+
Service Quality - ✔✔-Reliability—ability to perform the promised service dependably and
accurately.
Responsiveness—willingness to
...
Operations and Supply Chain
Management WGU - C720, Complete
study guide, graded A+
Service Quality - ✔✔-Reliability—ability to perform the promised service dependably and
accurately.
Responsiveness—willingness to help customers and provide prompt service.
Assurance—knowledge and courtesy of employees and their ability to convey trust and
confidence.
Empathy—provision of caring, individualized attention to customers.
Tangibles—appearance of physical facilities, equipment, personnel, and communication
materials, including access and effectiveness of Internet-based information.
Quality of Goods - ✔✔-Performance—primary operating characteristics of a product.
Features—secondary characteristics that supplement the product's basic functioning.
Reliability—length of time a product will function before it fails, or the probability it will
function for a stated period of time.
Conformance—degree to which a product's design and operating characteristics match pre�established standards.
Durability—ability of a product to function when subjected to hard and frequent use.
Serviceability—speed, courtesy, and competence of repair.
Aesthetics—how a product looks, feels, sounds, tastes, or smells.
Perceived Quality—image, advertising, or brand name of a product.
Deming - ✔✔-Basic premise notes that the system, not employees, causes defects. Management
is responsible for changing the system, and must accept that responsibility instead of blaming
employees when defects occur
Used Statistical process control (SPC) - is the use of statistical methods to determine when a
process that produces a good or service is getting close to producing an unacceptable level of
defects
14 Points - No quota, inspections, pure price cost cutting (1 supplier for loyalty and trust).
Inclusive work environment
Juran - ✔✔-defining quality as "fitness for use."
He also emphasized the need for continuous improvement and stressed that quality must be built
on three elements: 1)quality planning,
2)quality control (Inspections),
3)quality improvement.
Focus on customer
Crosby - ✔✔-Reduce failure costs ("Quality is Free" book) or eliminate all errors. Zero defects
and do it right the first time
Taguchi - ✔✔-Quality cannot be achieved through inspections after the good is made or the
service is provided
Robust design - designs that guarantee high quality regardless of variations
perfecting of experiments to create higher quality products and processes
Ishikawa - ✔✔-Ishikawa/fishbone diagram
Quality circles and cycles (Include all employees, agree with Deming)
teamwork is essential for quality leadership
Total quality management - ✔✔-Whole business focused on quality vs. a quality control
department
Focus on the customer, quality function deployment, responsibility for quality, team problem
solving, employee training, fact-based management.
Group problem solving techniques - ✔✔-Pareto charts, fishbone diagrams, house of quality
Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle (Deming or Shewhart wheel) - ✔✔-1)Plan—Before making any
changes, be sure everything is documented and standardized. Use appropriate tools to identify
problems or opportunities for improvement. Develop a plan to make changes.
2)Do—Implement the plan and document any changes made.
3)Check—Analyze the revised process to determine if goals have been achieved.
4)Act—If the goals have been achieved, then standardize and document the changes.
Communicate the results to others that could benefit from similar changes. If the goals have not
been achieved, determine why not, and proceed accordingly.
Statistical Process Control - ✔✔-1-Cause-and-effect diagrams or fishbone diagrams or Ishikawa
diagrams (Help find root causes/bottlenecks in process)
2-Check sheets (Record data on site/'Raw data', NOT analyze)
3-Histograms - Useful for frequency and probability
4Pareto charts - Similar to histogram but always shows descending order.
5-Scatter diagrams - Relationship between two variables. Only one can be influenced
6-Control charts - Line charts with a Upper and lower limit (Anything out of limits means
process too varied) to control process stability
7-Flow charts or run charts - Common scale or features (Generally time)
Six Sigma - ✔✔-Six sigma = 6 standard deviations or....3.4 defects per 1 million units, or
99.99966% error free
5 step (DMAIC)
Define - The Six Sigma expert uses a project charter to define a problem or improvement
opportunity. Plan process to satisfy customer
Measure - Measuring current, or "as-is", process performance is accomplished with a process
map of the activities performed at each step of the process. Each step is assessed to determine the
ability to meet customer specification in a capability analysis.
Analyze - The main objective of the Analysis phase is to determine the root causes of variation
in the process that result in failures or defects. (Use charts and other tools)
Improve - The current process is changed by addressing the root causes identified in the Analysis
stage to improve process performance.
Control - Maintaining and standardizing the improved performance is the final step of the
DMAIC methodology. This can be accomplished through a control plan to document the
requirements to reduce process variation. The control plan may include SPC to maintain process
stability. Also mistake-proofing a product or a tool can make errors immediately detectable.
Another tool for Control is the 5S methodology (sort, straighten, shine, standardize, sustain). The
5S methodology creates visual control of the workplace.
A secondary methodology of Six Sigma is the DMADV process. This is used specifically for
new products or processes and is also known as Design for Six Sigma (DFSS). The five steps of
DMADV are summarized as: Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify.
Reverse logistics - ✔✔-When it is necessary to return defective products to the manufacturer for
repair or replacement, the process is known as reverse logistics. Also recycle.
Lean Supply Chain - ✔✔-These products have long product life cycles, stable and predictable
demand, and minimal innovation. They are also often characterized by low profit margins. For
these products, the supply chain must focus on operating efficiently to minimize costs.
Eliminate non-value operation
[Show More]