BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > WGU Biochem C785: Unit 4 DNA and RNA, Question and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+ (All)
WGU Biochem C785: Unit 4 DNA and RNA, Question and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+
Document Content and Description Below
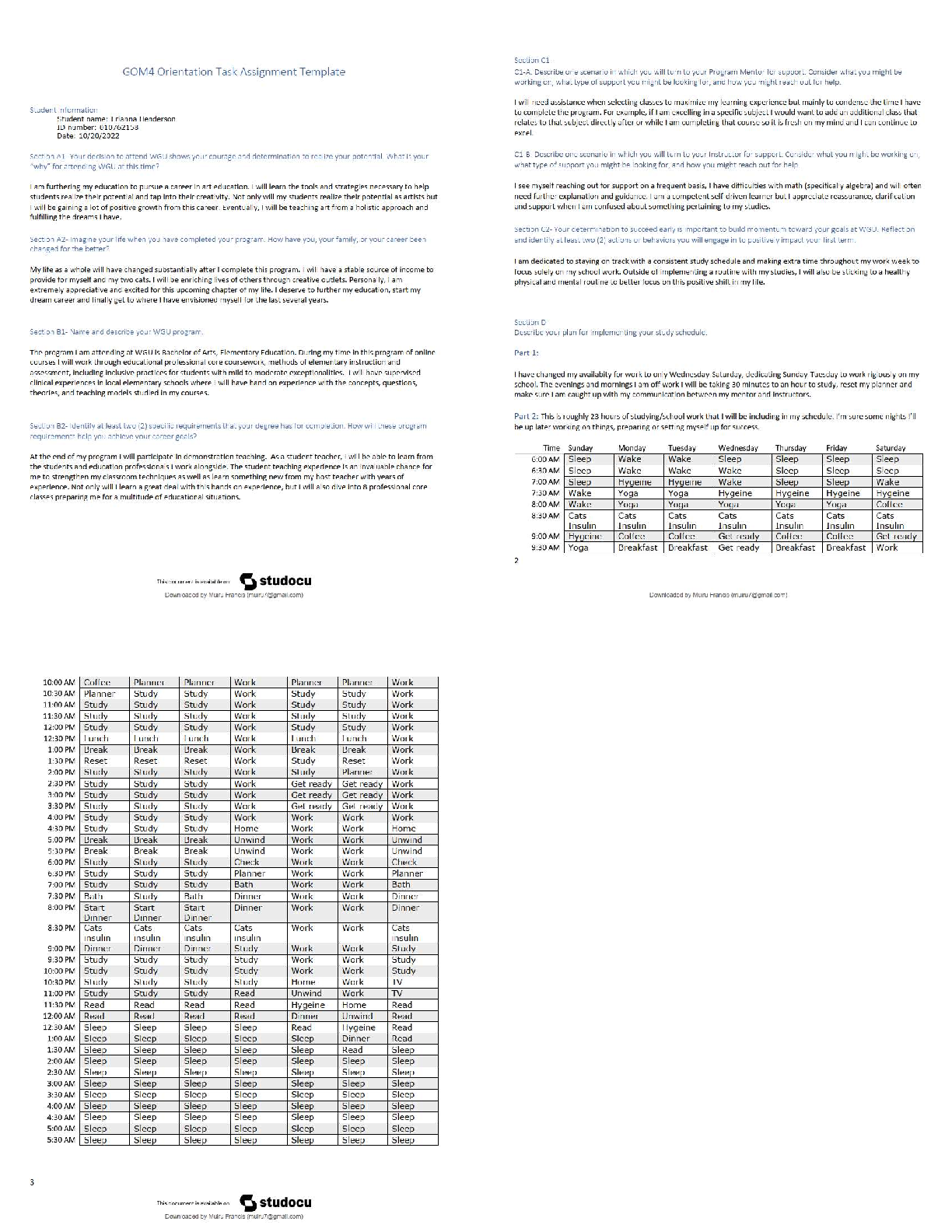
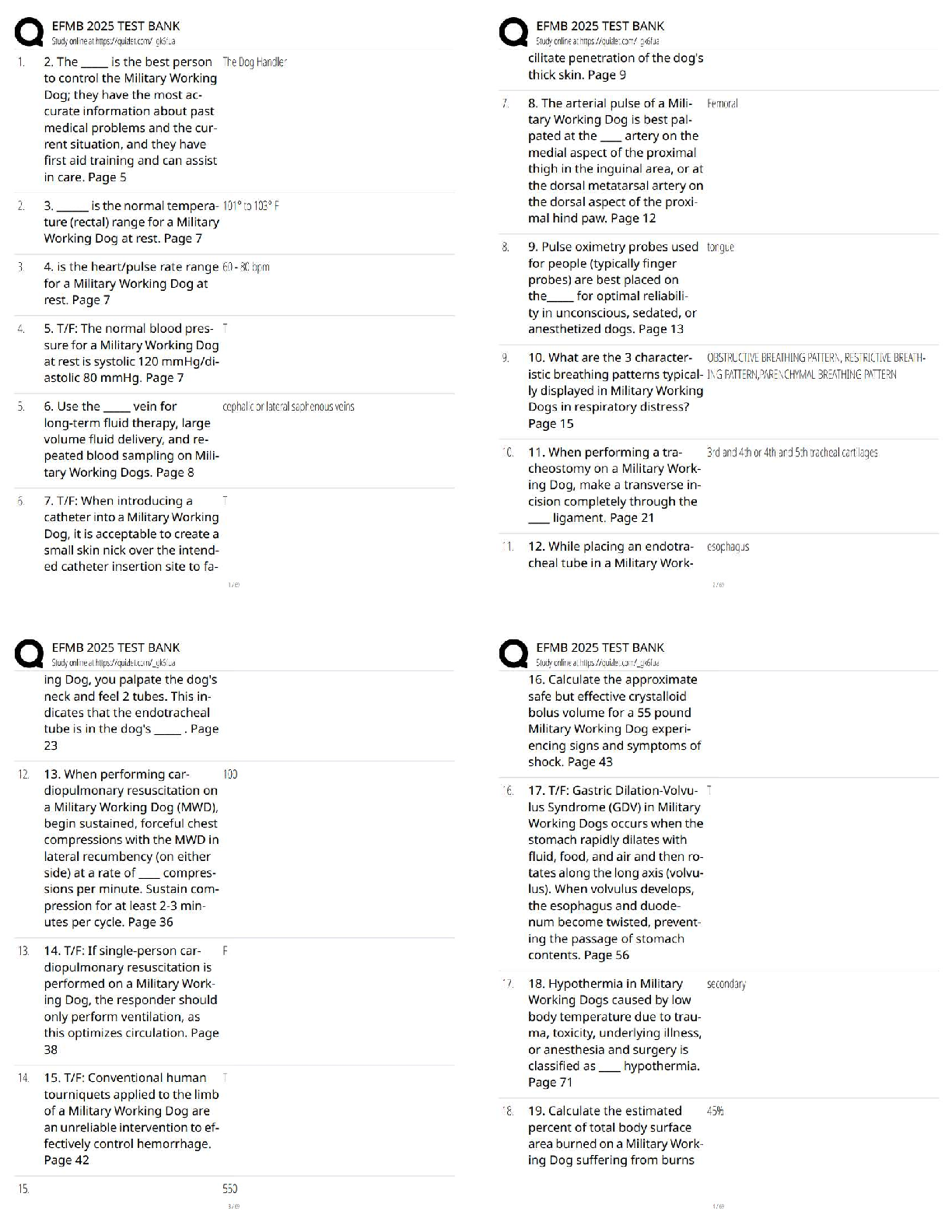
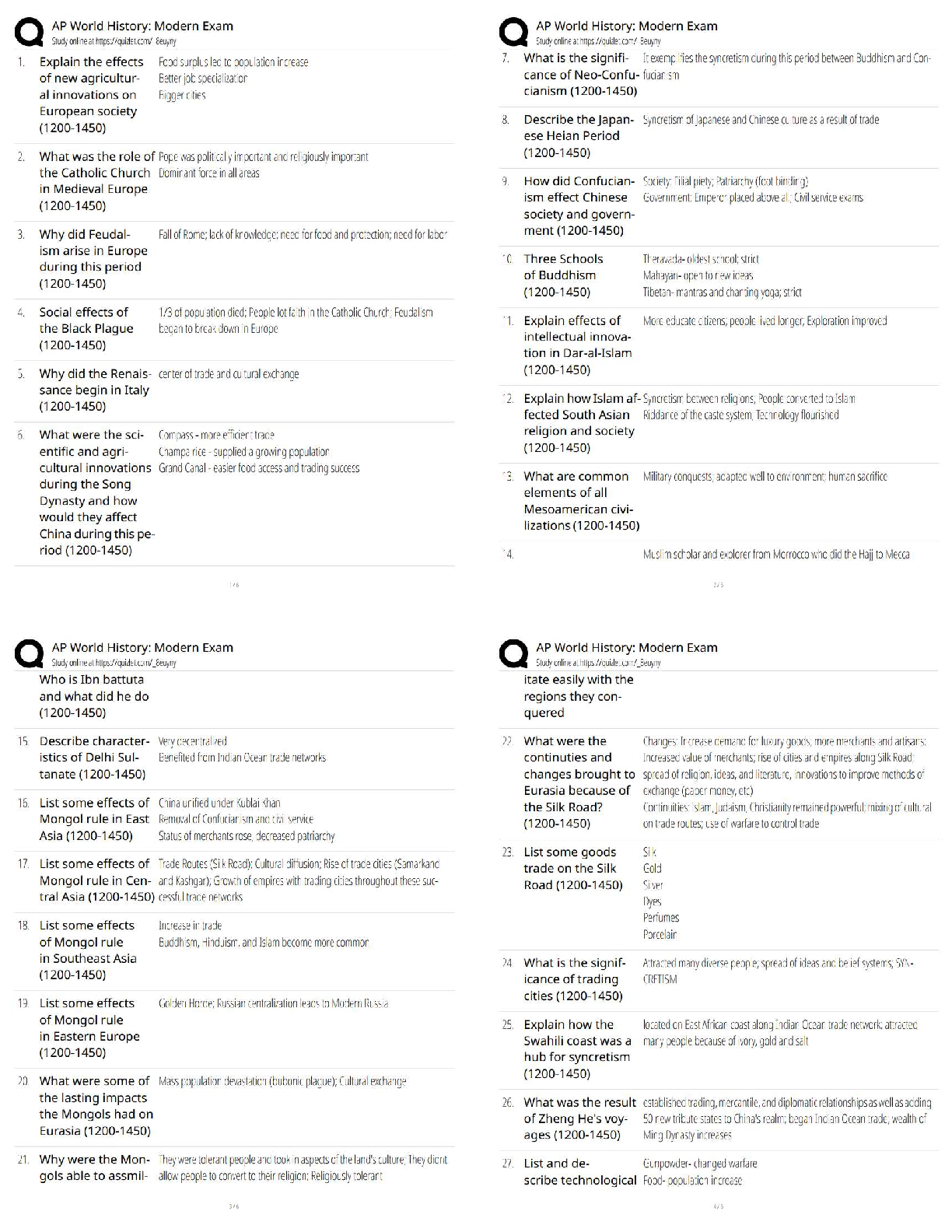
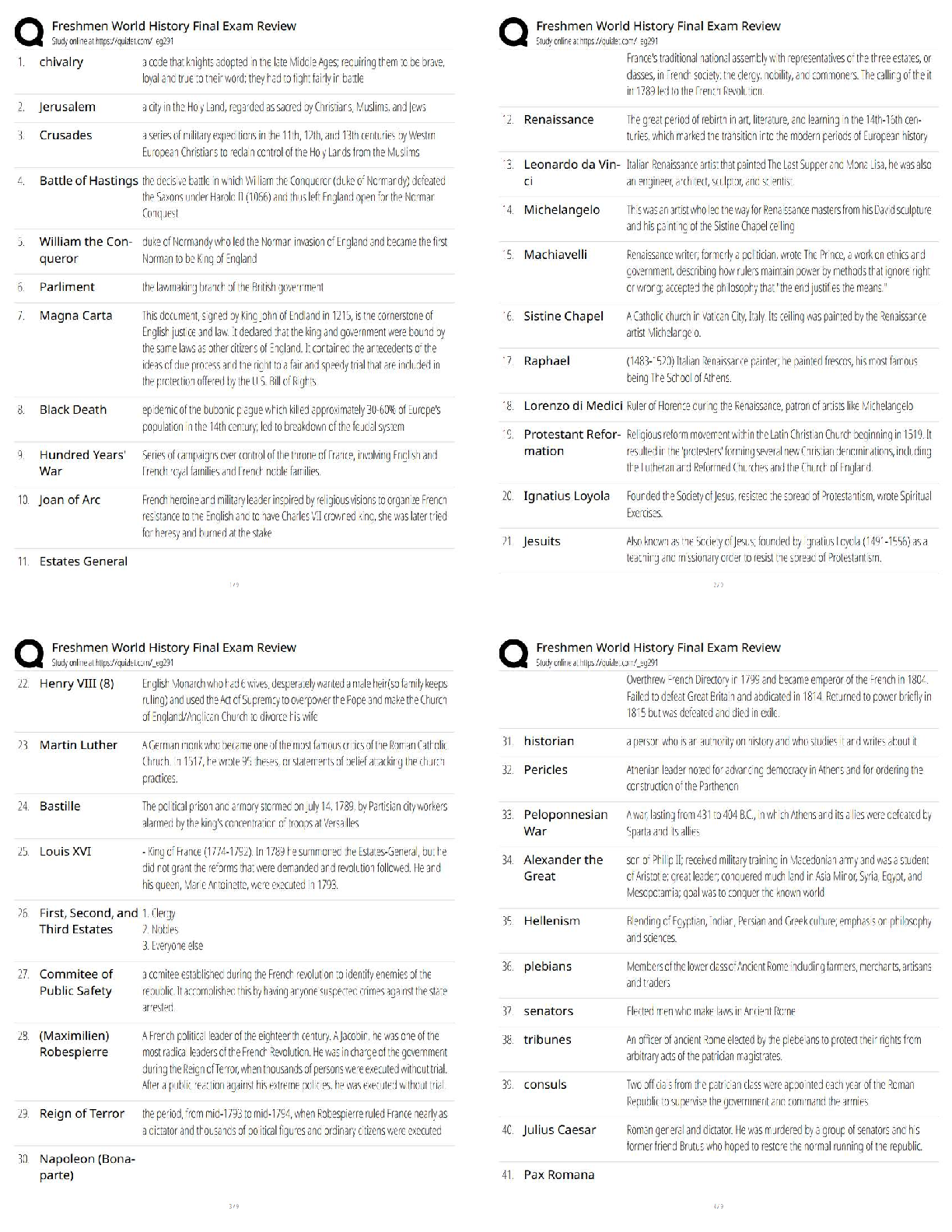
WGU Biochem C785: Unit 4 DNA and RNA, Question and answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+ DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) - ✔✔-An organisms genetic material found in the nucleus of a cell Double stran ... ded helical nucleic acid molecule consisting of nucleotide monomers with deoxyribose sugar and nitrogenous bases (A, C, G, T) capable of replicating Which nucleotides/bases are used in DNA? - ✔✔-A - Adenine C - Cystine G - Guanine T - Thymine RNA (ribonucleic acid) - ✔✔-A nucleic acid consisting of nucleotide monomers with a ribose sugar and nitrogenous bases (A, C, G, U) Usually single stranded Functions in protein synthesis, gene regulation, and as the genome of some viruses Central Dogma - ✔✔-DNA -> RNA -> Protein DNA -> Transcription ->mRNA -> Translation -> Protein The process by which the instructions in DNA are converted into a functional product The flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA protein Which nucleotides/bases are used in RNA? - ✔✔-A - Adenine C - Cystine G - Guanine U - Uracil Which nucleotides/bases pair together to form DNA? - ✔✔-A - T C - G Which nucleotides/bases pair together to form RNA? - ✔✔-A - U C - G Genes - ✔✔-A segment of a DNA molecule that information or directions on how to build a protein Gene Expression - ✔✔-When a gene in DNA is "turned on" or used to make the protein is specifies Includes 2 Stages: Transcription and Translation Nucleotides - ✔✔-Basic units of DNA molecule, composed of a sugar, a phosphate, and one of 4 DNA bases Antiparallel - ✔✔-The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix (5'-3', 3'-5') Complementary (coding) Strand - ✔✔-A strand of DNA or RNA that has complementary bases to the template strand, another strand of DNA or RNA Ex/ During DNA replication, the new strand that is formed is a complementary strand Complementary Bases: A-U, C-G Runs in 5' to 3' direction Template DNA - ✔✔-The piece of DNA that the RNA polymerase enzyme assembles the messenger (mRNA) along. Called a template because it fits the formal definition fo a template Coding DNA - ✔✔-The opposite strand of DNA in the double helix The complementary, antiparallel partner DNA strand Also called the Non-Template Strand Replication - ✔✔-The process of copying a molecule of DNA Transcription - ✔✔-The process where a gene's DNA is copied and (transcribed) into an RNA molecule to make a protein 3 Phases - Initiation -Elongation - Termination Initiation - ✔✔-The DNA molecule unwinds and separates Elongation - ✔✔-RNA polymerase moves along the template strand, synthesizing mRNA molecules Termination - ✔✔-When a stop codon is reached and translation is stopped The point at which the ribosome releases the polypeptide RNA Polymerase - ✔✔-Enzyme that attaches to the DNA strand and moves to the promoter It breaks hydrogen bonds in the DNA double helix so that free nucleotides can attach to the exposed strand which develops the RNA strand Promoter - ✔✔-A specific nucleotide sequence or "spot" in DNA located near the start of a gene that is the binding site for RNA Polymerase and the place where transcription begins Transcription Factors - ✔✔-Important proteins that help determine which genes are active in each cell Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription mRNA - ✔✔-Messenger RNA: A pre messenger molecule of RNA that encodes a chemical "blueprint" for a protein product Type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes Can be read by multiple ribosome at a time Must be read from 5' to 3' to interpret codons correctly Translation - ✔✔-The synthesis of a of a polypeptide using genetic information encoded in an mRNA molecule There is a change of "language" from nucleotides to amino acids Ribosomes - ✔✔-The sites of Translation that facilitate the orderly linking of amino acids into polypeptide chains tRNA - ✔✔-Transfer RNA An RNA molecule that functions as an carrier by picking up specific amino acids in the cytoplasm and transferring them to the ribosome putting them where the codon and anticodon attach creating a chain of amino acid [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 19 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 11, 2023
Number of pages
19
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 11, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
148