BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > WGU Biochemistry, Exam Questions and answers, graded A+ Verified. (All)
WGU Biochemistry, Exam Questions and answers, graded A+ Verified.
Document Content and Description Below
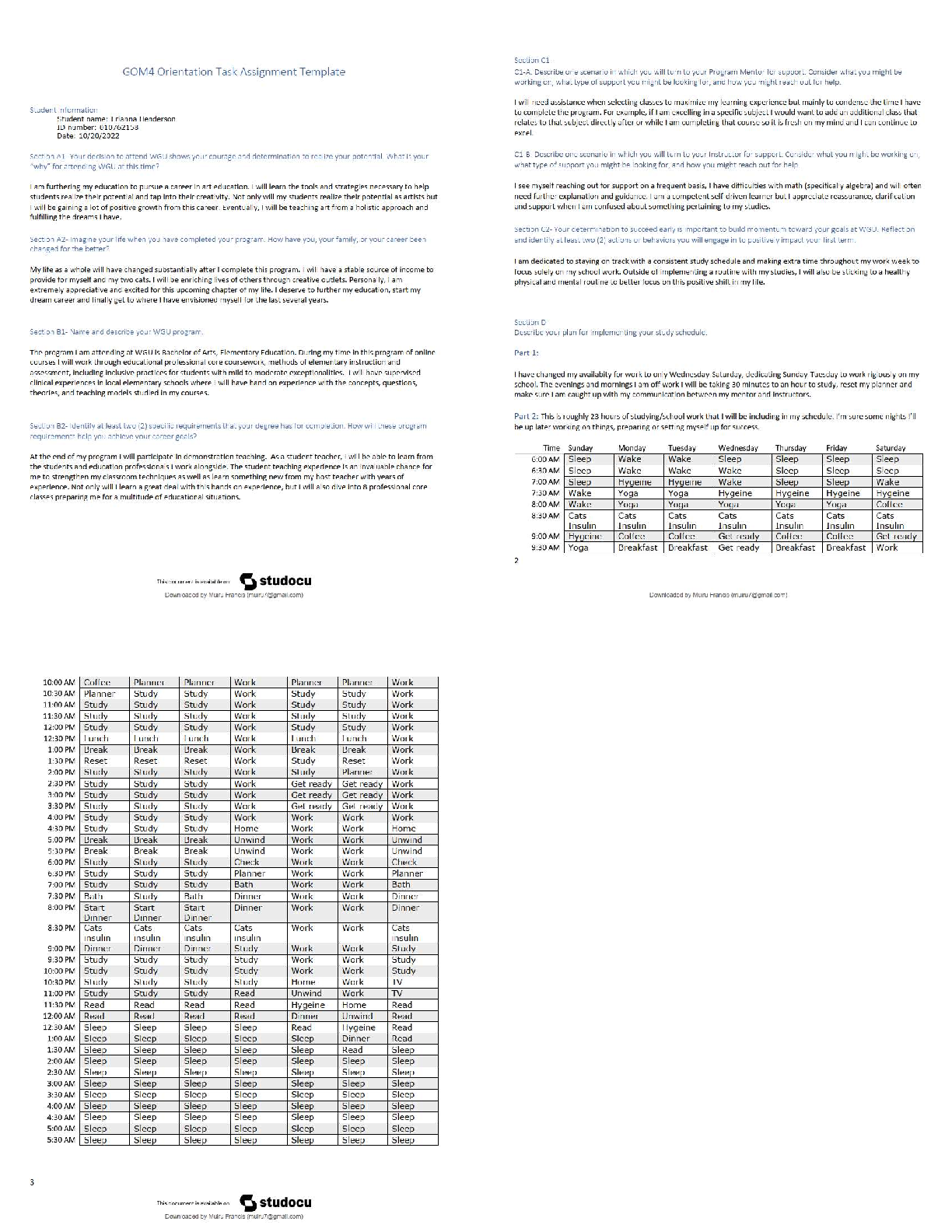
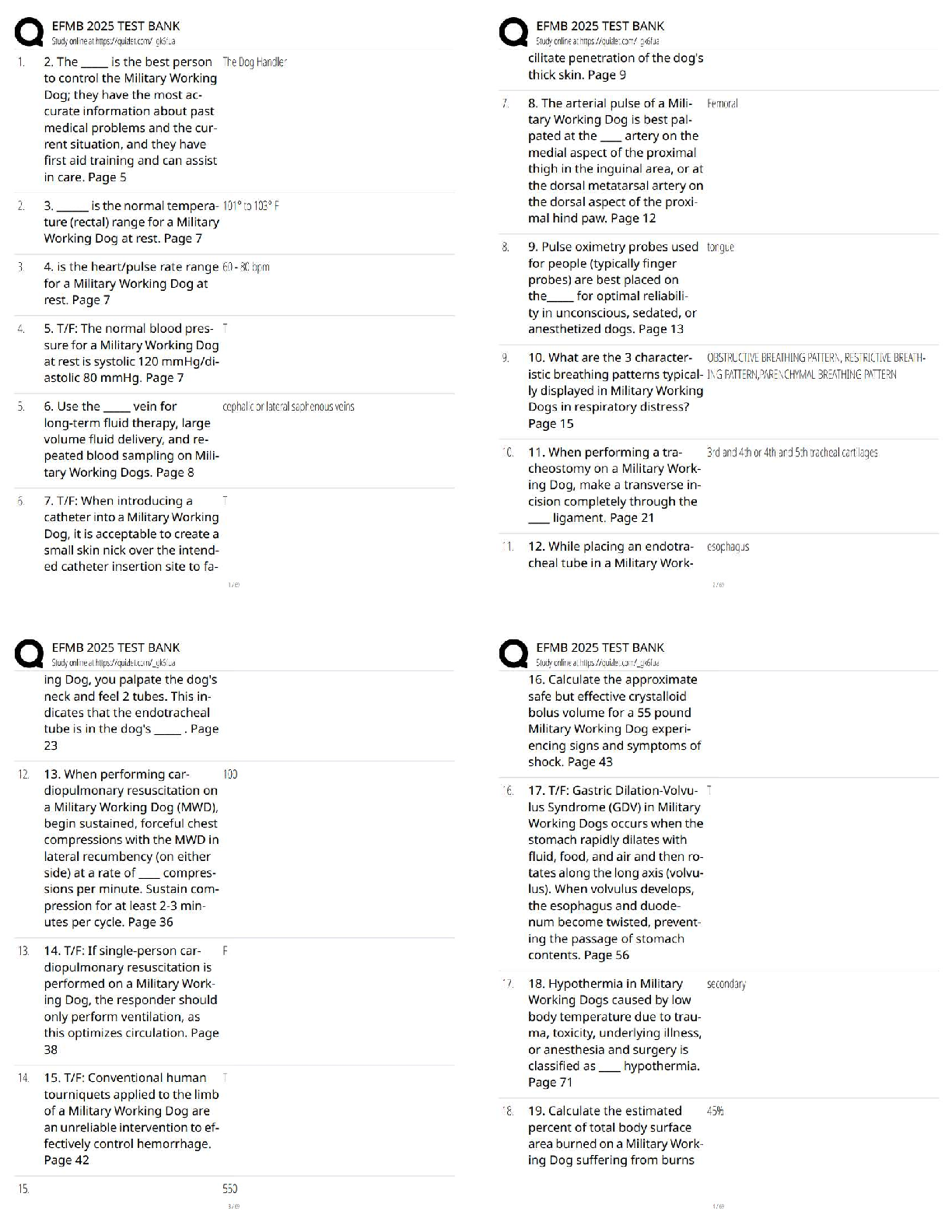
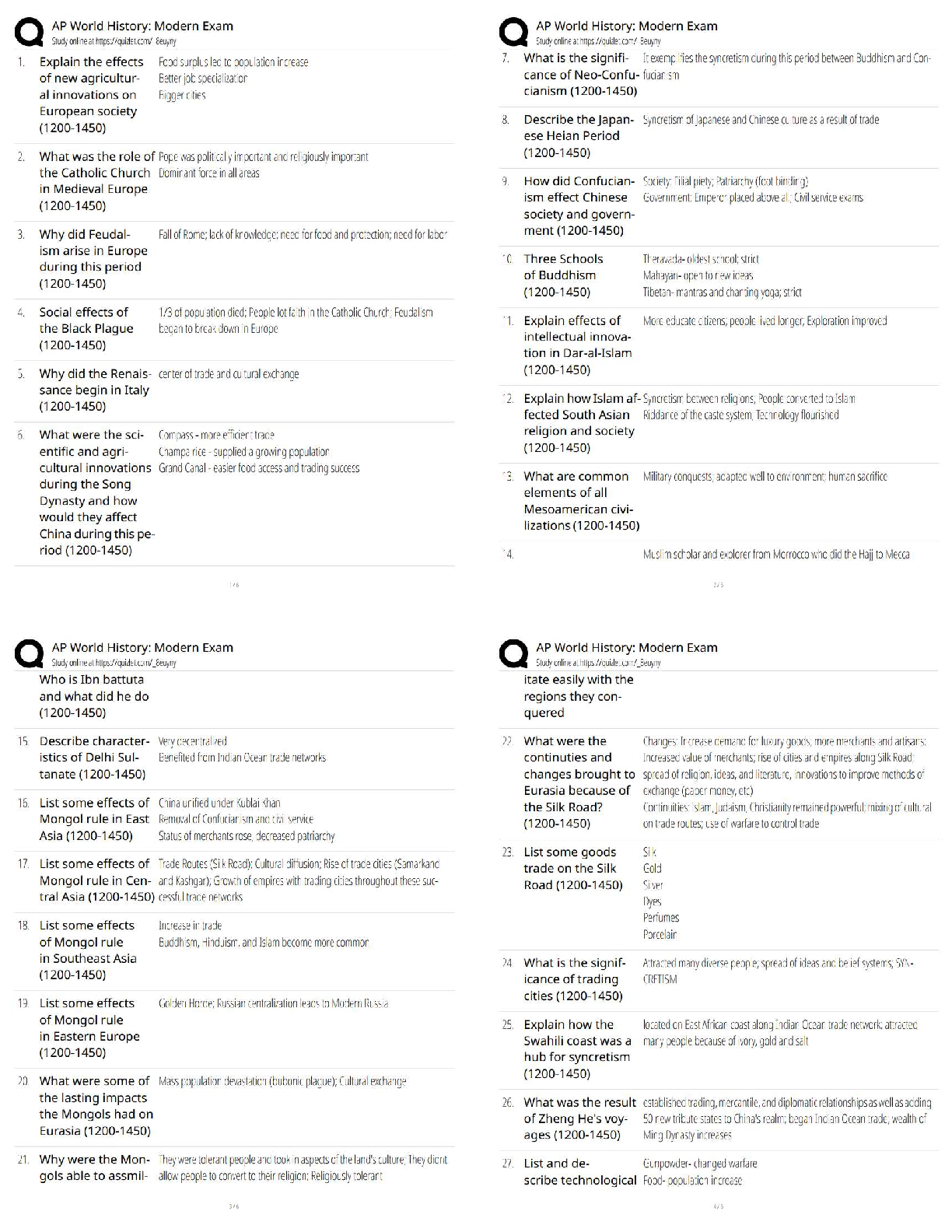
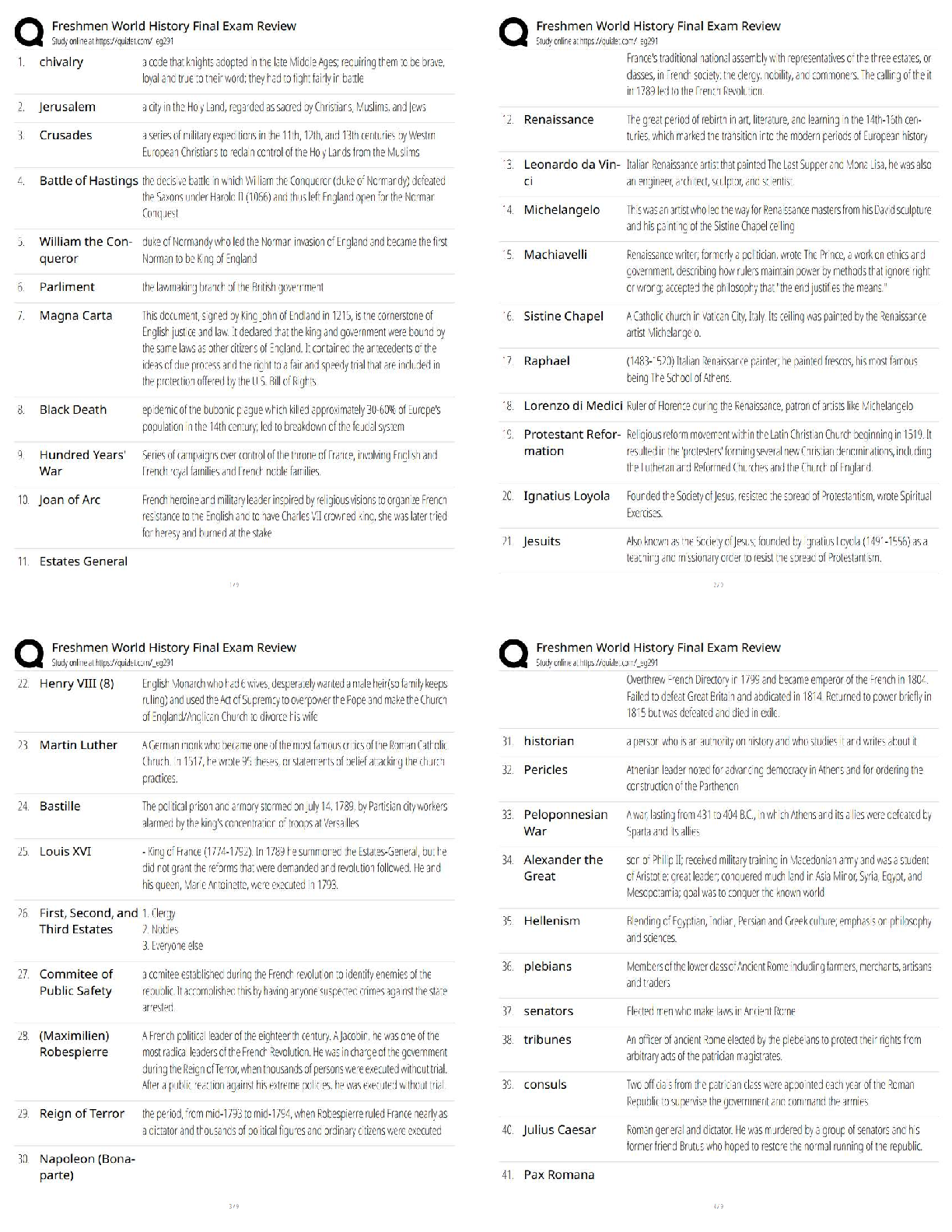
WGU Biochemistry, Exam Questions and answers, graded A+ Verified. DNA replication is ___________, which allows each of the two strands to serve as a _______ for the new strands. b. semiconservat ... ive, template - ✔✔-DNA replication is semiconservative, meaning that each new duplex has one original (parent) strand and one new strand. Because the two parent strands are separated during replication and the base pairing is predictable, each parent strand can serve as a template for the new strand synthesis. Which of the following enzymes does NOT assist the DNA polymerase on the lagging strand to overcome its two problems? (Recall that the DNA polymerase can only make DNA in the 5'->3' direction, and it must bind a double-stranded nucleotide polymer before it can start making its own DNA polymer.) c. Helicase - ✔✔-Helicase unwinds the double stranded DNA to allow for replication, but this is not a problem for the DNA polymerase. Several components of cigarette smoke, including benzopyrene, insert themselves (intercalate) into the DNA and lead to several types of mutations such as frameshift mutations, including both insertions and deletion. Which of the following repair pathways would be used to repair this type of damage? c. Nucleotide Excision Repair - ✔✔-Nucleotide excision repair is used to repair deletions, insertions, and helix-distorting lesions, such as thymine dimers. Maternal smoking during pregnancy is hazardous yet common in many places. Many studies have associated prenatal smoking to unhealthy physical and psychological outcomes for the baby. Researchers know that maternal smoking affects are epigenetic in nature. Which of the following events can be considered epigenetic in nature? a. Changes in chromatin structure - ✔✔-Frame shift mutations are a kind of mutations which result from addition of deletion of a nucleotide base resulting in an altered reading frame and ultimately a different protein, than the one the gene originally encoded. Frameshift mutations are genetic changes because they alter the DNA sequence, whereas epigenetic changes do not alter the DNA sequence. Epigenetic changes are modifications to genomic structure (not sequence) that are caused by the external environment. These environmental factors affect the overall chromatin structure to allow more or less "access" to the DNA by gene expression machinery to turn the genes "on" or "off". In other words, epigenetics can alter gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequences. The changes may or may not be heritable, depending on the location and circumstances. Blood type is an example of what type of inheritance? a. Codominance - ✔✔-The genes that produce the A and B antigen proteins can both be expressed independently, and a heterozygote (someone with both genes) will be produce both A and B proteins - neither will dominate the other. The is an example of codominance. What is the expected probability that a child will have an autosomal dominant disease if their father is heterozygous for the allele and their mother is homozygous for the normal allele? a. 50% - ✔✔-If D is the disease-conferring dominant allele and d is the normal allele, the father has the genotype Dd and the mother's genotype is dd. Each child can only inherit a d allele from their mother, and they have a 50% chance of inheriting the D allele from their father. As a result, the expected probability that their child will inherit the disease is 50%. The physical trait of lip protrusion exhibits a characteristic type of inheritance, as shown by the pedigree above. What type of inheritance best describes this inheritance pattern? a. Incomplete dominance - ✔✔-The correct answer is incomplete dominance. The blending of the large and small lip protrusion into an intermediate, medium lip protrusion, as well as the presence of all three variations in the offspring, demonstrate a clear example of incomplete dominance. The normal sequence of a section of the HLA-B27 gene, a genetic marker of the inflammatory disease Ankylosing spondylitis, is given below. Match each mutation of the sequence to the type of mutation it exhibits. A genetic code table is provided for your use in answering the question. 5'- CGG CAG AAU UUA -3' 5'- CAG CAG AAU UUA -3' - Missense mutation 5'- CGG CAG AAA UUU A-3' - Insertion 5'- CGG CAG AAC UUA -3' - Silent mutation 5'- CGG CAG AAU UA -3' - Deletion 5'- CGG UAG AAU UUA-3' - Nonsense mutation - ✔✔-Silent mutations are those in which the amino acid encoded doesn't change as a result of the mutation. Missense mutations are those in which the amino acid encoded changes to a different amino acid as a result of the mutation. Nonsense mutations are those in which the amino acid encoded changes to a stop codon as a result of the mutation, yielding a smaller protein. Insertions are the inclusion of extra nucleotides compared to the original sequence. They can result in other mutations, such as nonsense mutations. Deletions are the removal of nucleotides compared to the original sequence. They can result in other mutations, such as nonsense mutations. PCR is a powerful tool that can do all of the following.... b. detect mutations that lead to disease c. copy small segments of DNA, less than 6kb d. amplify DNA from samples that have just a few cells - ✔✔-PCR's ability to amplify is powerful, and products can even be generated from samples with just a few cells. PCR is less reliable for amplifying large segments of DNA greater than 6 kb, though some careful changes to the techniques can allow it. Which of the following is a required "ingredient" in a PCR reaction? a. DNA nucleotides b. DNA primers c. DNA polymerase - ✔✔-The primers used in PCR are made from DNA, rather than RNA. RNA primers are used in DNA replication inside the cell, but the quick degradation of RNA makes it less useful for PCR reactions. Instead, PCR reactions contain primers made of DNA to anneal to the region of DNA that will be amplified and serve as a starting point for DNA polymerase. Which of the following changes can be detected using PCR? a. Differences in DNA sequence b. Insertions c. Deletions - ✔✔-Differences in DNA sequence can be detected since these changes can alter the ability of primers to anneal to the DNA. They can also be detected by DNA sequencing of the PCR product. Epigenetic changes are not detectable via PCR because they don't affect the DNA sequence. A small segment of Kevin's green opsin gene is shown below. What would be the resulting mRNA sequence? Kevin's opsin gene at nucleotide positions 936 to 941. 5'-G.C.C.T.A.G-3' (coding strand) 3'-C.G.G.A.T.C-5' (template strand) c. 5'-GCCUAG-3' - ✔✔-This sequence is the same as the coding sequence, and the "T" bases have been replaced with "U", as is found in RNA. The gene for blue opsin protein is located on chromosome 7, a non-sex chromosome. What kind of inheritance pattern would you expect to see with color blindness due to a mutated blue opsin? a. An equal distribution of blue color blindness between males and females. - ✔✔-The blue opsin gene is located on a somatic (non-sex) chromosome, and therefore will be inherited with the same frequency for both sexes. In Kevin's case, a specific kind of mutation in the opsin gene resulted in the premature termination of the translation process. This resulted in a shorter opsin protein than usual. What specific mutation could have caused this? c. Nonsense mutations - ✔✔-Missense mutations are point mutations that change a single base pair in a codon such that the codon now encodes a different amino acid. In Kevin's case, a nonsense mutation, which is a point mutation that changes a single base pair in a codon to a stop codon resulted in termination of the translation signal. This further led to the synthesis of truncated protein. After consultation with a genetic counselor and an examination of extended family history, the following pedigree was generated. Who did Kevin most likely inherit this mutation from? a. Maternal grandfather - ✔✔-Red-green color blindness occurs more frequently in males than females because these genes are located on the X chromosome, and males inherit only one X chromosome and will express whatever alleles are on that chromosome. Females, on the other hand, inherit two X chromosomes, and thus have two alleles for each gene. If one of the alleles is mutated on one X chromosome, there is usually a correct allele on the other that can provide the needed gene. A woman must have two mutated opsin alleles to be color blind, while men need only one. This is known as sex-linked inheritance. Kevin inherited his Y chromosome from his father and his X chromosome from his mother, so his X chromosome with the defective opsin gene most likely came from his maternal grandfather and was passed to him by his mother. Thus, both grandfathers is not correct because his paternal grandfather would have contributed a Y chromosome. The nonsense mutation that causes Kevin's color blindness could have resulted from a malfunction of __________. b. DNA polymerase - ✔✔-Helicase unwinds the DNA during replication, but doesn't add or remove nucleotides. The correct choice is the DNA polymerase. DNA polymerase could have added an erroneous nucleotide, and it's proofreading activity could have missed it. While this type of event is rare, DNA polymerase is known to make a mistake that it doesn't correct about one in one hundred million! Primary structure consists of the order of ______ in a protein. These are held together with ______ bonds that are formed by a ______ reaction. a. Amino acids, peptide, dehydration - ✔✔-Correct Correct! Several types of side chain interactions stabilize the tertiary structure of proteins, including which of the following? c. Ion pairs, hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, disulfide bonds - ✔✔-The stability of a tertiary structure of a protein depends on the various interactions and bonds that occur between the side chains of different amino acids. Which of the following statements is true about the secondary structure of proteins? a. It includes alpha helices as a common form. c. It includes beta pleated sheets as a common form. d. It involves hydrogen bonding between the backbone atoms. - ✔✔-A secondary structure of protein consists of hydrogen bonds between backbone atoms, includes alpha helices and beta sheets as common forms. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 40 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 11, 2023
Number of pages
40
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 11, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
113