*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ACSM Certified Exercise Physiologist, Questions with accurate answers, 100% ACCURATE. (All)
ACSM Certified Exercise Physiologist, Questions with accurate answers, 100% ACCURATE.
Document Content and Description Below
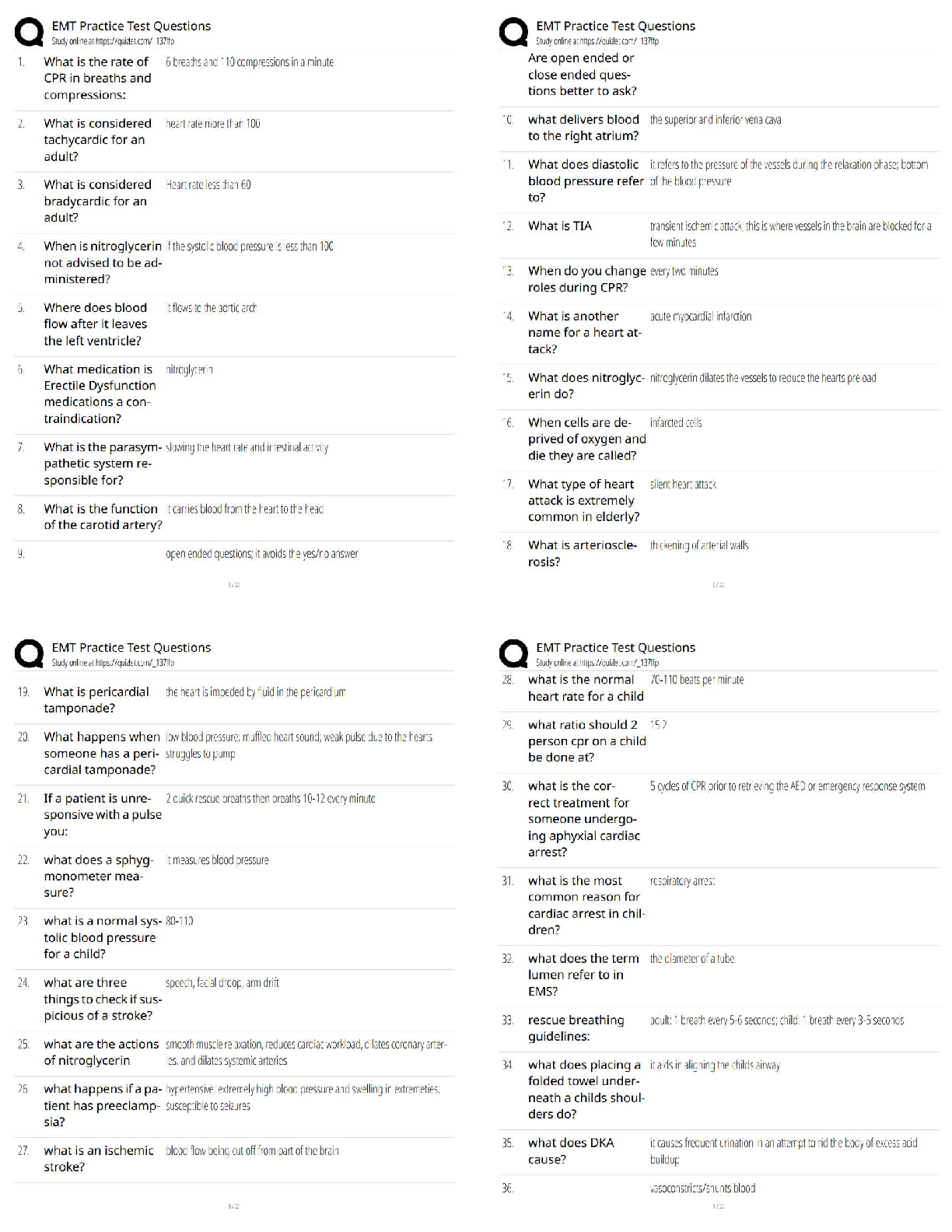
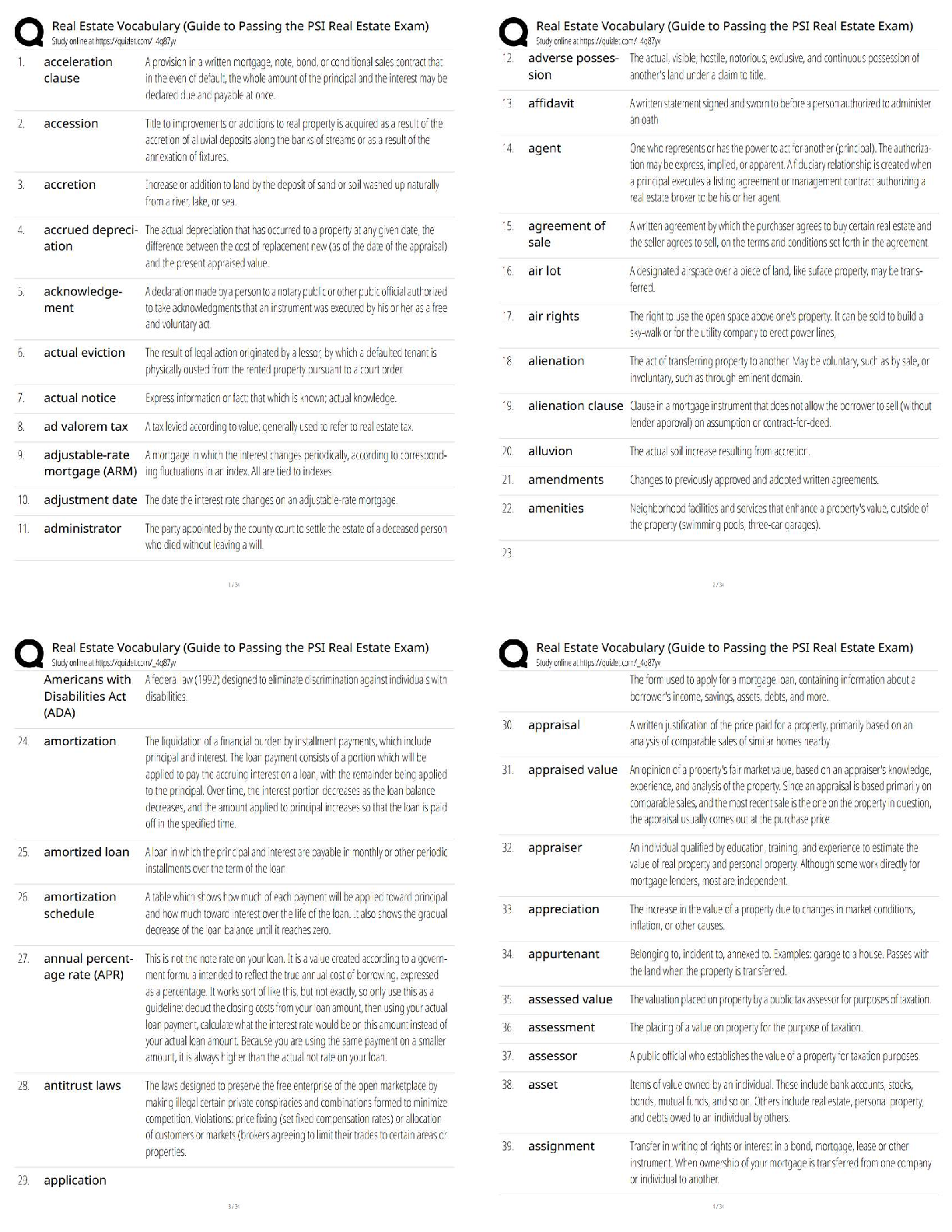
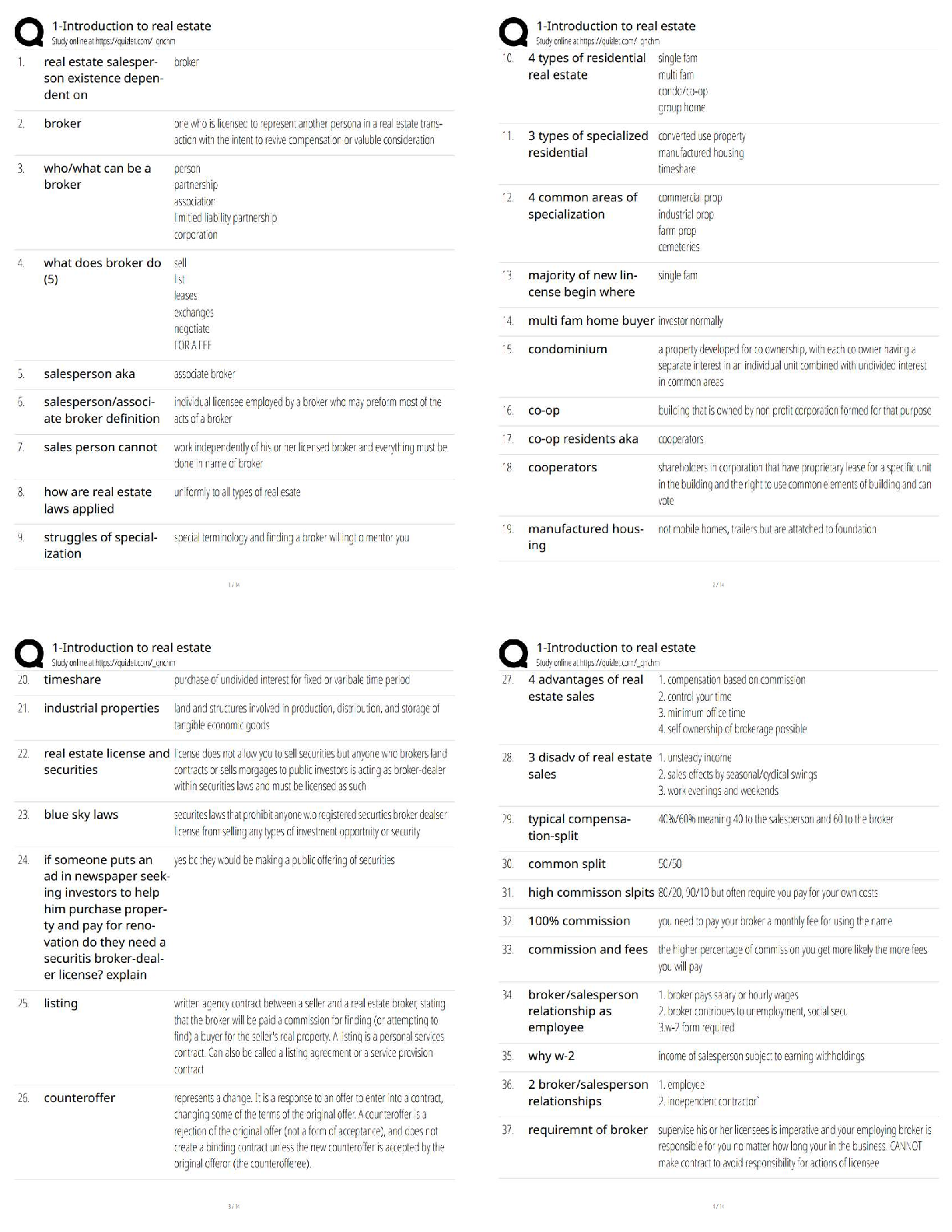
ACSM Certified Exercise Physiologist, Questions with accurate answers, 100% ACCURATE. Pre-activity screening procedures and tools that provide accurate information about the individual's health ... /medical history, current medical conditions, risk factors, signs/symptoms of disease, current physical activity habits, and medications - ✔✔-1. Self-guided methods such as the Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire (PAR-Q) or the modified AHA/ACSM Health/Fitness Facility Preparticipation Screening Questionnaire. 2. CVD risk factor assessment and classification by qualified health/fitness, clinical exercise, or health care professionals 3. Medical evaluation including a physical examination and stress test by a qualified health care provider. The key components included in informed consent and health/medical history - ✔✔-Informed Consent: 1. Purpose and explanation of the test 2. Attendant risks and discomforts 3. Responsibilities of the participant 4. Benefits to be expected 5. Inquiries 6. Use of medical records 7. Freedom of consent Health/Medical History: 1. Medical diagnosis 2. Previous physical examination findings 3. History of symptoms 4. Recent illness, hospitalization, new medical diagnosis, or surgical procedures. 5. Orthopedic problems 6. Medication use and drug allergies 7. Other habits including caffeine, alcohol, tobacco use, or recreational drug use 8. Exercise history 9. Work history 10. Family history of cardiac, pulmonary, or metabolic disease, stroke, or sudden death The limitations of informed consent and health/medical history - ✔✔-1. Breach of contract claims 2. Failure to obtain adequate informed consent 3. Negligence in procedural explanation 4. Doesn't provide legal immunity 5. Improper test administration 6. Personnel qualifications 7. Poor safety procedures 8. Informed consent process can be used as defense Risk factor thresholds for ACSM risk stratification including genetic and lifestyle factors related to the development of CVD. - ✔✔-Age: Men >_ 45 years old. Women >_ 55 years old Family History: Myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, or sudden death before 55 years old in father or other first degree male relative or before 65 years old in mother or other first degree female relative. Cigarette smoking: Current cigarette smoker or those who quit within the previous 6 months or exposure to environmental tobacco smoke Sedentary lifestyle: Not participating in at least 30 min of moderate intensity physical activity (40%-60% VO2R) on at least 3 days of the week for at least 3 months. Obesity: Body mass index >_ 30 kg/m2 or waist girth >102 cm (40 in) for men and >88 cm (35 in) for women Hypertension: Systolic blood pressure >_ 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure >_ 90 mmHg, confirmed by measurements of at least 2 separate occasions, or on anti-hypertensive medication. Dyslipidemia: low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol >_ 130 mg/dL or high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol < 40 mg/dL or on lipid-lowering medication. If total serum cholesterol is all that is available, use >_ 200 mgd/L Prediabetes: Impaired fasting glucose = fasting plasma glucose >_ 100 mg/dL and <_ 125 mg/dL or impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) = 2 hours values in oral glucose tolerance test >_ 140 mg/dL and <_ 199 mg/dL confirmed by measurements on at least 2 separate occasions. Negative risk factors: High density lipoprotein (HDL): >_ 60 mg/dL The major signs or symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular, pulmonary and metabolic disease. - ✔✔-1. Pain, discomfort in the chest, neck, jaw, arms, or other areas that may result from ischemia. 2. Shortness of breath at rest or with mild exertion. Dyspnea. 3. Dizziness or syncope 4. Orthopnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea 5. Ankle edema 6. Palpitations or tachycardia 7. Intermittent claudication 8. Known heart murmur 9. Unusual fatigue or shortness of breath with usual activities Cardiovascular risk factors or conditions that may require consultation with medical personnel prior to exercise testing or training - ✔✔-Individuals at moderate risk with 2 or more CVD risk factors Inappropriate changes in resting heart rate and/or blood pressure New onset discomfort in chest, neck, shoulder, or arm Changes in the pattern of discomfort during rest or exercise Fainting Dizzy spells Claudication The pulmonary risk factors or conditions that may require consultation with medical personnel prior to exercise testing or training - ✔✔-Asthma Exercise induced asthma/bronchospasm Extreme breathlessness at rest or during exercise Chronic Bronchitis Emphysema The metabolic risk factors or conditions that may require consultation with medical personnel prior to exercise testing or training - ✔✔-Obesity Metabolic syndrome Diabetes or glucose intolerance Hypoglycemia The musculoskeletal risk factors or conditions that may require consultation with medical personnel prior to exercise testing or training - ✔✔-Acute or chronic pain Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Osteoporosis Inflammation/pain Low back pain ACSM risk stratification categories and their implications for medical clearance before administration of an exercise test or participation in an exercise program - ✔✔-Low Risk: Asymptomatic, <2 risk factors No medical exam required before exercise No exercise test required before exercise No supervision of exercise test if done Moderate Risk: Asymptomatic, >_ 2 risk factors Medical exam before vigorous exercise but not moderate exercise No exercise test required before exercise No medical supervision of exercise test if done High Risk: Symptomatic, or known cardiovascular, pulmonary, renal, or metabolic disease. Medical exam required before exercise Exercise test required before exercise Medical supervision of exercise test if done. Risk factors that may be favorably modified by physical activity habits - ✔✔-- Improvement in cardiovascular and respiratory function - Reduction in cardiovascular disease risk factors - Decreased morbidity and mortality - Decreased anxiety/depression - Improved cognitive function - Enhanced physical function and independent living in older individuals - Enhanced feeling of well being - Enhanced performance of work, recreational, and sport activities. - Reduced risk of falls and injuries from falls in older individuals - Prevention or mitigation of functional limitations in older adults - Effective therapy for many chronic diseases in older adults Total Cholesterol - ✔✔-Sum of all forms of cholesterol in the blood. Healthy TC typically below 200 mg/dL. Borderline high 200-239. High >_ 240 mg/dL High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-C) - ✔✔-"Good" cholesterol. Low <40. High >_60. Low HDL is strongly and inversely associated with CVD risk. Raising HDL cholesterol reduces CVD risk. Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (LDL-C) - ✔✔-"Bad" cholesterol. Optimal <100, near optimal/above optimal 100-129, borderline high 130-159, high 160-189, very high >_ 190. Elevated LDL cholesterol is a powerful risk factor for CVD. Triglycerides - ✔✔-Normal <150, borderline high 150-199, high 200-499, very high >_ 500. Elevated triglycerides increase CVD risk. Impaired fasting glucose - ✔✔-Prediabetes, elevated blood glucose in response to dietary carbohydrates in a fasted state. 100-125 mg/dL fasting at least 8 hours. Impaired glucose tolerance - ✔✔-2 hour values in oral glucose tolerance test. 140-199 mg/dL during an oral glucose tolerance test. Hypertension - ✔✔-Resting systolic blood pressure (SBP) >_ 140 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) >_ 90 mmHg, taking anti-hypertension medication, or being told by a physician or other health care professional on at least 2 occasions that an individual has high Bp. Increased risk of CVD, stroke, heart failure, peripheral artery disease, and chronic kidney disease. Risk of CVD doubles for each incremental increase in SBP or 20 mmHg of DBP of 10 mmHg. Atherosclerosis - ✔✔-Process where fatty streaks develop causing the artery wall to thicken while reducing luminal diameter. Progressive and dangerous arterial build up of fat and fibrous plaques. Myocardial Infarction - ✔✔-Complete obstruction of blood flow to the cardiac myocardial tissue. Heart attack and results in tissue death or narcosis. Dyspnea - ✔✔-Shortness of breath Tachycardia - ✔✔-Rapid beating or fluttering of the heart Claudication - ✔✔-Pain and/or cramping in the lower leg due to inadequate blood flow to the muscles Syncope - ✔✔-Fainting and dizziness during exercise may indicate poor blood flow to the brain because of inadequate cardiac output from a number of cardiac disorders Ischemia - ✔✔-Shortage of oxygenated blood flow to the heart myocardium Recommended plasma cholesterol levels for adults based on National Cholesterol Education Program/ATP guidelines - ✔✔-LDL Cholesterol: Optimal <100 Near optimal/above optimal 100-129 Borderline High 130-159 High 160-189 Very high >_ 190 HDL Cholesterol: Low <40 High >_ 60 Total Cholesterol: Desirable <200 Borderline high 200-23 [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 27 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

ACSM Certification EXAM BUNDLE. EXAM PAPERS
ACSM Certification Review, Exam Questions and answers, 100% Accurate. Graded A+. EXAM PREDITOR QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS, VERIFIED.
By Topmark 2 years ago
$40
26
Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 11, 2023
Number of pages
27
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 11, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
156