Engineering > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > AFOQT Aviation Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, graded A+. Approved Exam Quizzes. (All)
AFOQT Aviation Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, graded A+. Approved Exam Quizzes.
Document Content and Description Below
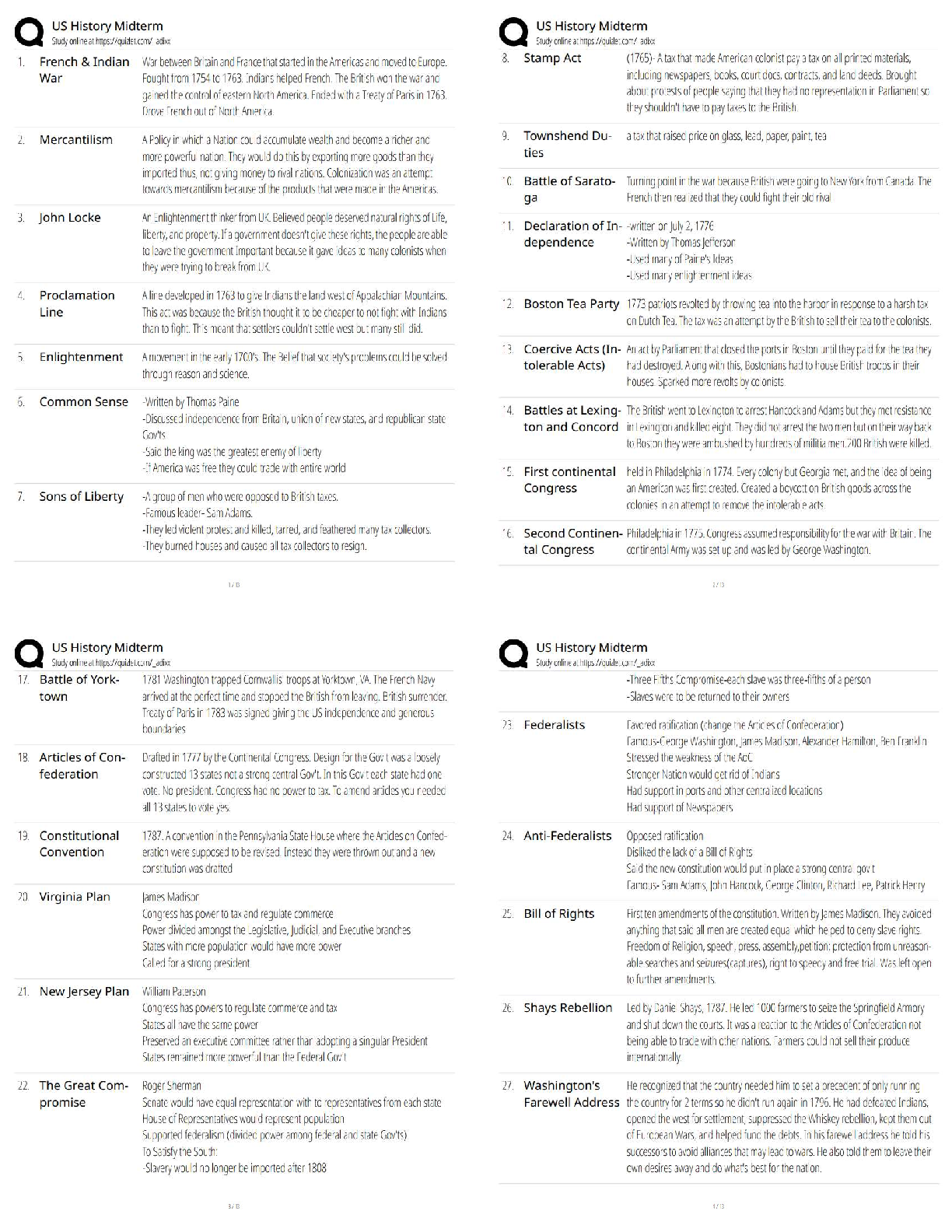
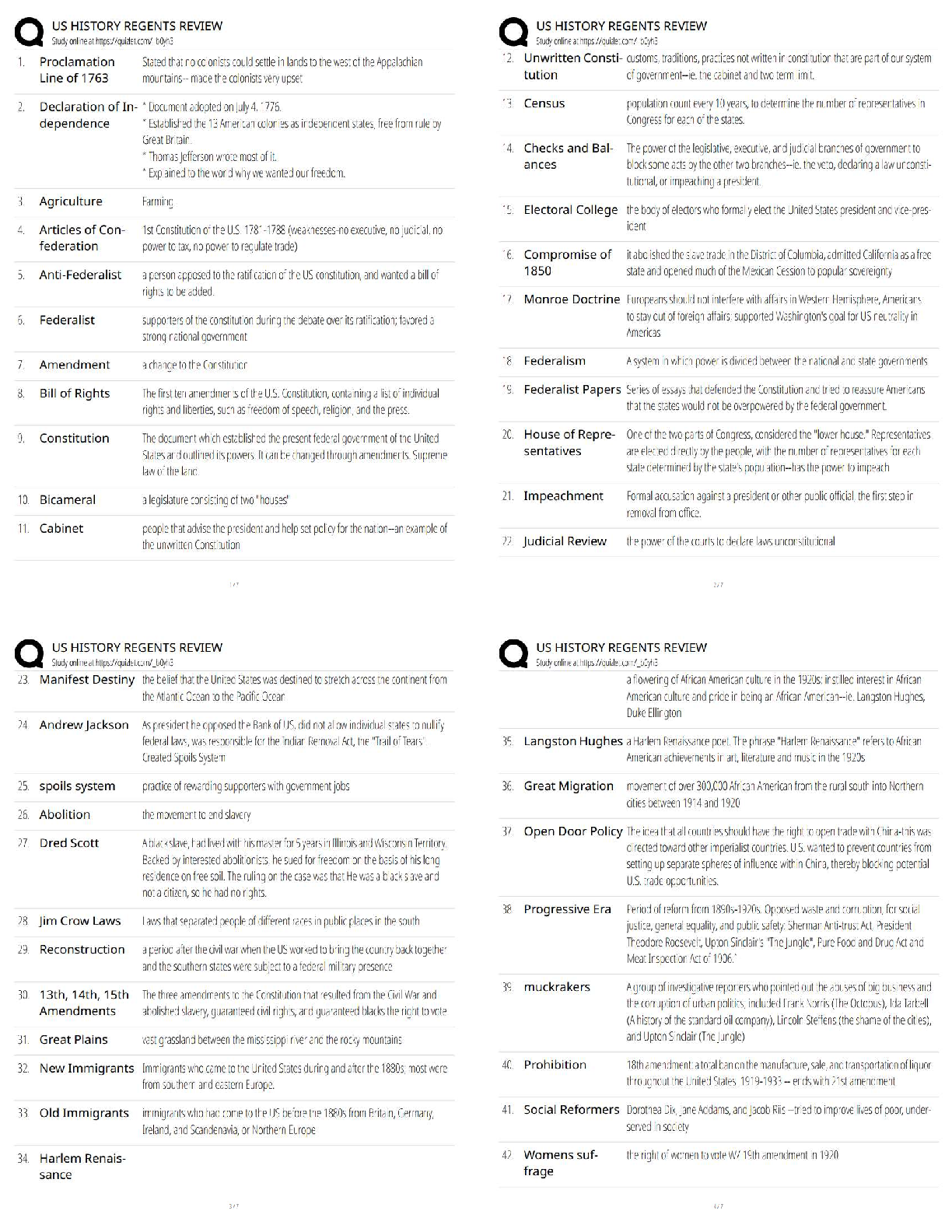
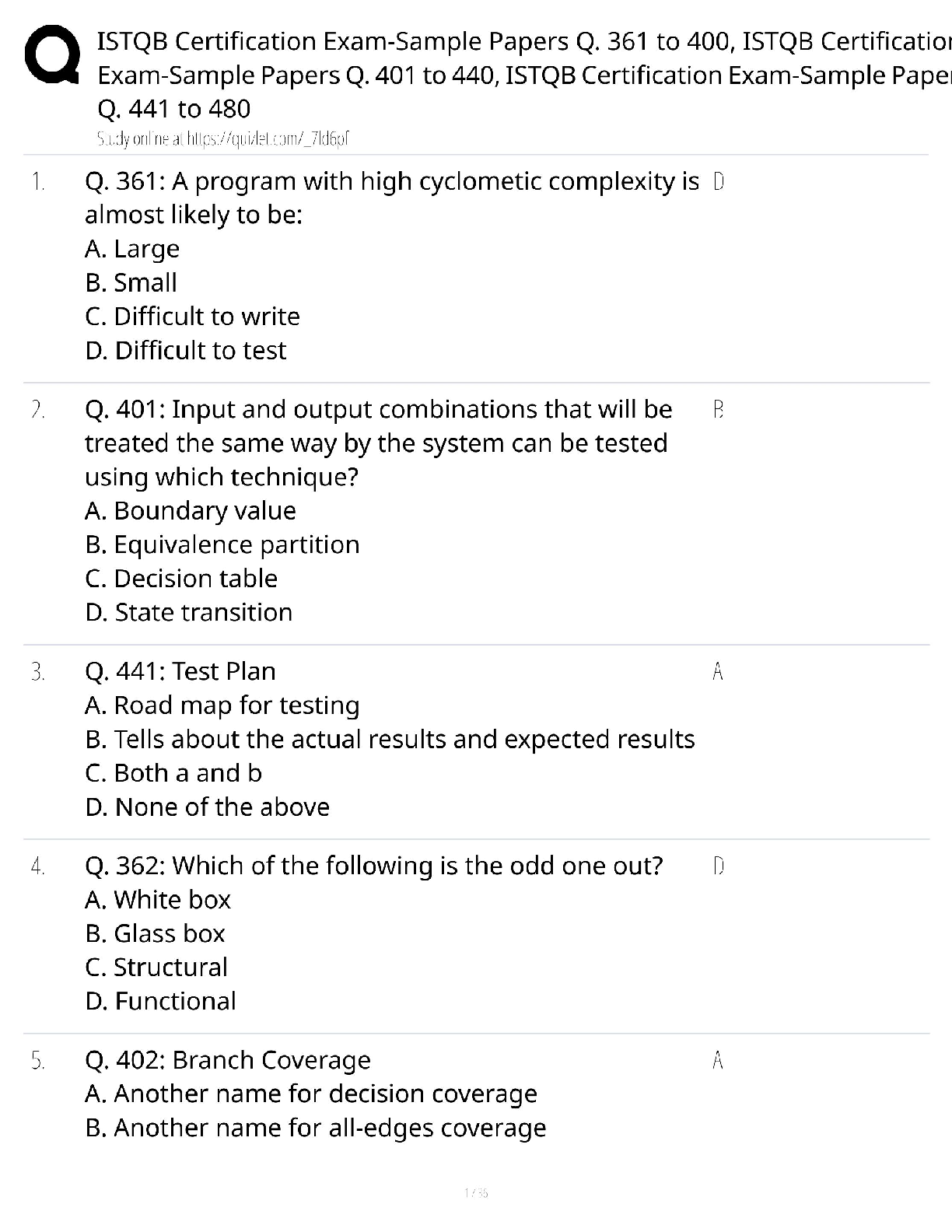
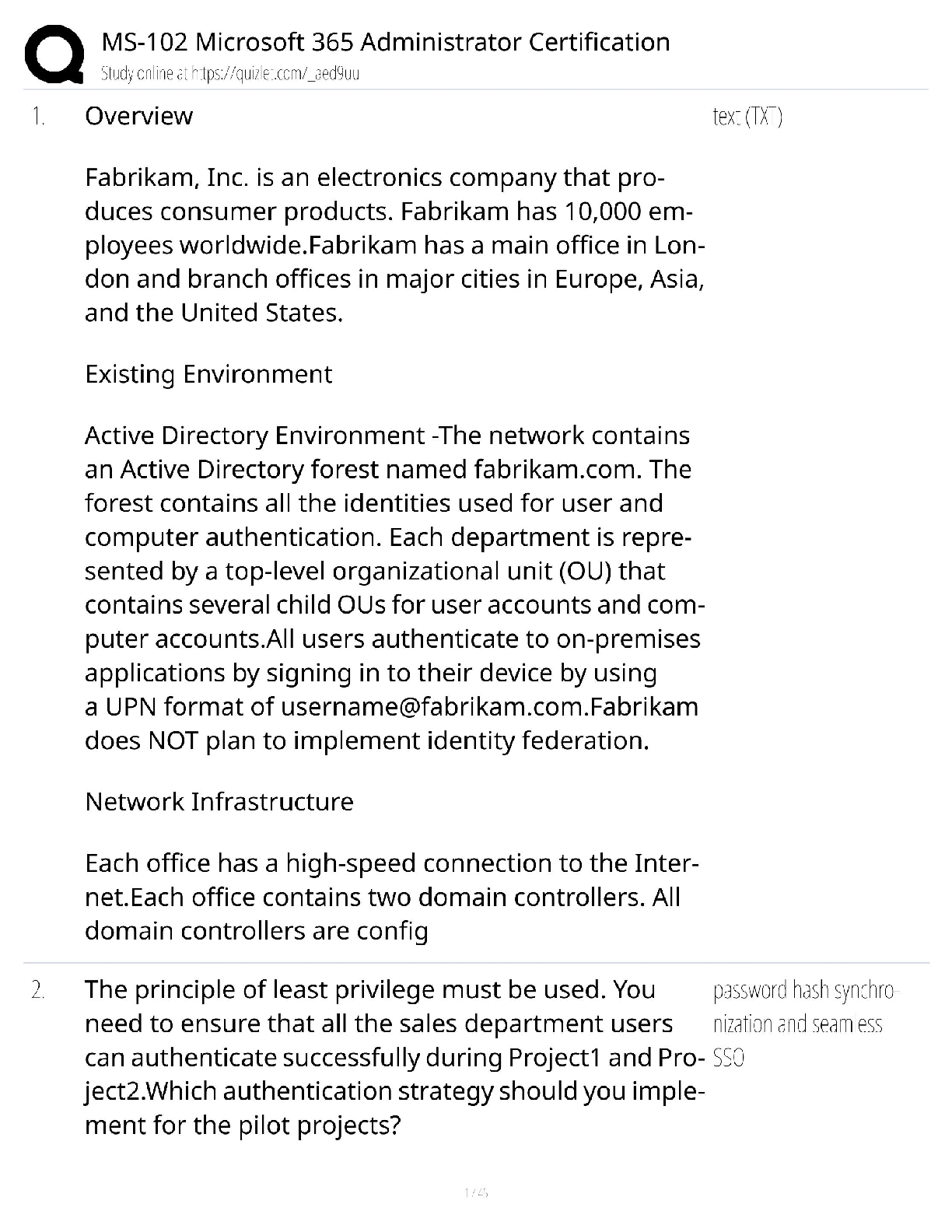
AFOQT Aviation Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, graded A+. Approved Exam Quizzes. The angle between the chord line of a wing or airfoil and the direction of the relative wind or airflow is ... called the (a) angle of pitch (b) degree of roll (c) angle of deflection (d) angle of attack - ✔✔(d) angle of attack A conventional fixed-wing aircraft is controlled around its longitudinal axis by means of the (a) ailerons (b) elevators (c) rudder (d) trim tab - ✔✔(a) ailerons Two statute miles are equal to (a) 2.0 nautical miles (b) 1.74 nautical miles (c) 2.3 nautical miles (d) 2.3 knots - ✔✔(b) 1.74 nautical miles The altimeter typically shows the height of the aircraft above a particular pressure level in (a) feet (b) hundreds of feet (c) thousands of feet (d) hundreds of meters - ✔✔(c) thousands of feet When a pilot pulls back on the control stick, the elevators will (a) extend (b) retract (c) move upward (d) move downward - ✔✔(c) move upward If one end of a runway was numbered 09, what number would designate the other end of the same runway? (a) 90 (b) 27 (c) 18 (d) 10 - ✔✔(b) 27 The coordinates of latitude and longitude are used to express _________ in __________. (a) direction, degrees (b) position, degrees (c) distance, time (d) location, meridians - ✔✔(b) position, degrees Which of the following engines could operate outside the earth's atmosphere? (a) jet engine (b) turbofan engine (c) rocket engine (d) four-stroke diesel engine - ✔✔(c) rocket engine Which of the following is a flight instrument? (a) tachometer (b) fuel flow indicator (c) control column (d) altimeter - ✔✔(d) altimeter The empennage of an airplane is usually referred to as the (a) vertical stabilizer (b) horizontal stabilier (c) main body (d) tail section - ✔✔(d) tail section VFR stands for (a) Velocity Flight Resistance (b) Venturi Flight Resonance (c) Vertical Flight Rules (d) Visual Flight Rules - ✔✔(d) Visual Flight Rules The four aerodynamic forces acting on an aircraft in flight are (a) gravity, lift, thrust, and friction (b) lift, gravity, thrust, and drag (c) velocity, drag, lift, and thrust (d) lift, gravity, velocity, and drag - ✔✔(b) lift, gravity, thrust, and drag A flashing green air traffic control directed to an aircraft on the ground is a signal that the pilot (a) should radio the tower (b) should stop taxiing (c) has clearance to take off (d) has clearance to taxi - ✔✔(d) has clearance to taxi ___________ are designed to help minimize a pilot's workload by aerodynamically assisting movement and position of the flight control surfaces to which they are attached. (a) labor-saving devices (b) secondary flight controls (c) trim systems (d) spoilers - ✔✔(c) trim systems Ailerons (a) extend from the midpoint of the wing outward toward the tip (b) create aerodynamic forces that cause the airplane to roll (c) move in opposite directions (d) all of the above - ✔✔(d) all of the above The two types of turn indicators used in an aircraft are (a) turn and slip indicator and attitude indicator (b) attitude indicator and automatic gyroscope (c) turn and slip indicator and turn coordinator (d) left and right indicators - ✔✔(c) turn and slip indicator and turn coordinator When an airplane banks into a turn, (a) the horizontal lift component acts parallel to the earth's surface and opposes inertia (b) the horizontal lift component acts parallel to the earth's surface and opposes gravity (c) the horizontal lift component acts perpendicular to the earth's surface and opposes inertia (d) the horizontal lift component acts perpendicular to the earth's surface and opposes gravity - ✔✔(a) the horizontal lift component acts parallel to the earth's surface and opposes inertia If a fixed-wing aircraft has tricycle landing gear, it (a) has landing gear supporting the nose of the aircraft (b) has three sets of landing gear evenly spaced under the aircraft (c) has three sets of landing gear mounted closely together (d) has three sets of landing gear spaced longitudinally along the fuselage - ✔✔(a) has landing gear supporting the nose of the aircraft What is the nickname for the EA-6B? (a) Growler (b) Prowler (c) Tomcat (d) Hornet - ✔✔(b) prowler Who was Yuri Gagarin? (a) inventor of the helicopter (b) Father of the Navy (c) first man into space (d) first woman into space - ✔✔(c) first man into space The wings of an airplane design are angled upwards. This is called (a) armature (b) angulation (c) attitude of attack (d) dihedral - ✔✔(d) dihedral When a pilot pushes forward on the control stick, the elevators will (a) extend (b) retract (c) move upward (d) move downward - ✔✔(d) move downward From where is longitude measured? (a) the prime meridian (b) the equator (c) the international date line (d) Greenwich village - ✔✔(a) the prime meridian If one end of a runway was numbered 10, what number would designate the other end of the same runway? (a) 11 (b) 28 (c) 12 (d) 20 - ✔✔(b) 28 From where is latitude measured? (a) the prime meridian (b) the equator (c) the international date line (d) Greenwich, England - ✔✔(b) the equator Who was the first American to complete an orbital space mission? (a) Alan Shepard (b) John Glenn, Jr (c) Neil Armstrong (d) Deke Slayton - ✔✔(b) John Glenn Jr For the F/A-18 aircraft, what does "F/A" stand for? (a) fighter, advanced (b) fighter/attack (c) fueler, airborne (d) fighter/assault - ✔✔(b) fighter/attack What is hypoxia? (a) too much oxygen in the bloodstream, resulting in euphoria (b) too little oxygen in the bloodstream, resulting in blackout (c) too much smallpox vaccine, resulting in mild smallpox symptoms (d) an early stage of rust below the waterline of a ship - ✔✔(b) too little oxygen in the bloodstream, resulting in blackout Above what altitude would you normally need oxygen? (a) 5,500 ft (b) 10,000 ft (c) 12,000 ft (d) 14,200 ft - ✔✔(b) 10,000 ft Who first broke the sound barrier, and in what year? (a) Billy Mitchell, 1942 (b) Charles Lindbergh, 1952 (c) Robert Goddard, 1949 (d) Chuck Yeager, 1947 - ✔✔(d) Chuck Yeager 1947 Who was the first man to walk on the moon? (a) Neil Young (b) Tip O'Neal (c) Neil Armstrong (d) Lance Armstrong - ✔✔(c) Neil Armstrong Who was the first American woman in space and in what year? (a) Sally Wright, 1981 (b) Sally Forth, 1985 (c) Sally Ride, 1983 (d) June Cleaver, 1982 - ✔✔(c) Sally Ride, 1983 The first conflict to see widespread use of the helicopter was the (a) Korean War (b) Vietnam War (c) Cuban Missile Crisis (d) Persian Gulf War - ✔✔(a) Korean War Aircraft position lights (a) should be on from dusk till dawn (b) show red on the left wing (c) show green on the left wing (d) all of the above - ✔✔(d) all of the above The first American spacecraft to explore the outer solar system was the (a) Pioneer 1 (b) Pioneer 10 (c) Freedom 7 (d) Voyager 2 - ✔✔(b) Pioneer 10 The four types of airspeed are (a) instrument, calibrated, equilibrium, and true (b) indicated, calculated, equivalent, and temperature-dependent (c) indicated, calibrated, equivalent and true (d) instrument, calibrated, equivalent, and true - ✔✔(c) indicated, calibrated, equivalent and true The airspeed indicator measures and shows the difference between (a) equivalent and indicated airspeed (b) true airspeed and equivalent groundspeed (c) above-ground altitude and altitude above mean sea level (MSL) (d) impact and static pressure - ✔✔(d) impact and static pressure A nuclear-powered aircraft carrier has what designation? (a) CV (b) CVN (c) CGN (d) CVA - ✔✔(b) CVN When in the down (extended) position, wing flaps provide (a) increased lift and decreased drag (b) decreased lift and increased drag (c) increased lift and increased drag (d) increased lift only (e) decreased wing camber (curvature) - ✔✔(c) increased lift and increased drag Municipal airports often provide at least one extended or unusually long runway to facilitate the takeoff of (a) heavily loaded aircraft in calm conditions (b) lightly loaded aircraft taking off in a crosswind (c) small aircraft in rainy weather (d) aircraft with higher than average climbing speeds (e) rotary-wing aircraft in trail formation - ✔✔(a) heavily loaded aircraft in calm conditions The small hinged section on the elevator of most airplanes is known as the (a) aileron (b) flap (c) stabilator (d) elevon (e) trim tab - ✔✔(e) trim tab The rearward retarding force on the airplane known as drag is opposed by (a) lift (b) thrust (c) weight (d) laminar air flow (e) compression - ✔✔(b) thrust At night, airport taxiways are identified by omnidirectional edge lights that are ______ in color. (a) red (b) white (c) alternating red and white (d) blue (e) green - ✔✔(d) blue A runway with the Approach Lighting System (ALS) would show an incoming pilot (a) a pair of synchronized flashing lights at the runway threshold (b) a series of lightbars and/or strobe lights extending outward from the runway approach end (c) white elevated lights running the length of the runway on both sides (d) white lights embedded in the runway centerline at 50-foot intervals (e) unidirectional blue lights - ✔✔(b) a series of lightbars and/or strobe lights extending outward from the runway approach end The thrust of a turbojet is developed by compressing air in the inlet and compressor, mixing the air with the fuel and burning it in the combustor, and (a) venting the combusted air through side nozzles (b) rerouting the airflow through the compressor for extra power (c) expanding the gas stream through the turbine and nozzle (d) using the resulting accelerated airflow to turn the propeller shaft (e) diffusing the gas stream through the designated relief valves - ✔✔(c) expanding the gas stream through the turbine and nozzle A ramjet engine consists of (a) an intake, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and an outlet (b) an inlet, a turbine, a compressor, and a nozzle (c) an intake, a compression chamber, and a nozzle (d) an inlet, a combustion zone, and a nozzle (e) an inlet, a compression chamber, a turbine, and a nozzle - ✔✔(d) an inlet, a combustion zone, and a nozzle The four forces that act on an aircraft in flight are (a) lift, gravity, thrust, and drag (b) lift, mass, propulsion, and resistance (c) aerodynamics, mass, propulsion, and drag (d) lift magnitude, mass, thrust, and drag (e) roll, pitch, yaw, and magnitude - ✔✔(a) lift, gravity, thrust, and drag For a fixed-wing aircraft, lift is generated ____________ to the direction of flight. (a) parallel (b) reciprocal (c) proportionate (d) vectored (e) perpendicular - ✔✔(e) perpendicular The angle formed by the chord of an airfoil or wing and the direction of the relative wind is known as the (a) critical angle (b) stall angle (c) angle of pitch (d) delta angle (e) angle of attack - ✔✔(e) angle of attack Pitot tubes furnish data to an instrument that is used by aircraft pilots in about the same way that a(n) ________ is used by an automobile driver. (a) pressure transducer (b) odometer (c) speedometer (d) tachometer (e) ohmmeter - ✔✔(c) speedometer The part of an airplane that holds the cargo and/or passengers - as well as providing a base for the other aircraft parts - is known as the (a) fuselage (b) empennage (c) cargo compartment (d) cockpit array (e) static line - ✔✔(a) fuselage On a conventional fixed-wing aircraft, the ________ maintain(s) pitch and the _______ maintain(s) yaw. (a) elevators, rudder (b) horizontal stabilizers, vertical stabilizer (c) elevons, stabilator (d) rudder, elevators (e) trim tabs, wing flaps - ✔✔(b) horizontal stabilizers, vertical stabilizer ____________ are additional hinged rear sections mounted to the wing near the body that are deployed downward on takeoff and landing to increase the amount of force produced by the wing. (a) Ailerons (b) Elevators (c) Flaps (d) Trim tabs (e) Elevons - ✔✔(c) flaps Which one of the following does not affect density altitude? (a) temperature (b) atmospheric pressure (c) humidity (d) wind velocity (e) altitude - ✔✔(d) wind velocity The degree of movement of an aircraft around its longitudinal axis is known as (a) pitch (b) sideslip (c) yaw (d) angle of attack (e) bank - ✔✔(e) bank The Venturi theory of lift says that faster airflow over the curved upper portion of a wing surface causes (a) decreased pressure according to Bernoulli's equation (b) increased pressure according to Avogadro's constant (c) increased drag proportionate to crosswinds (d) decreased drag proportionate to the thrust vector (e) decreased drag perpendicular to the thrust vector - ✔✔(a) decreased pressure according to Bernoulli's equation The maneuver in which a rotary-wing aircraft (helicopter) is maintained in nearly motionless flight over a ground reference point at a constant altitude and heading (direction) is known as (a) feathering (b) autorotation (c) hovering (d) torque balance (e) freewheeling - ✔✔(c) hovering The ratio of the speed of an aircraft to the speed of sound in the air around it is the aircraft's (a) compressibility factor (b) Mach angle (c) Mach number (d) aerodynamic heating ratio (e) isentropic threshold - ✔✔(c) Mach number In a level turn, the acceleration experienced by the aircraft and its pilot in the direction perpendicular to the wing is solely determined by the (a) relative airspeed (b) angle of attack (c) bank angle (d) altitude (e) local air density and temperature - ✔✔(c) bank angle The flight envelope of an aircraft is (a) the airspeed at which it achieves takeoff (b) the region of altitude and airspeed in which it can be operated (c) the volume of air it displaces in flight (d) the envelope containing the aircraft registration documents (e) the geographical area covered by the officially filed flight plan - ✔✔(b) the region of altitude and airspeed in which it can be operated The locus of points equidistant from the upper and lower surfaces of an airfoil is called the (a) angle of attack (b) leading airfoil edge (c) upper camber measurement (d) mean camber line (e) wing chord - ✔✔(d) mean camber line The straight line joining the ends of the mean camber line is called the (a) lower camber curve (b) mean airfoil throughpoint (c) wing chord (d) angle of attack (e) relative lift threshold line - ✔✔(c) wing chord A(n) ________ is the point at which the airflow over the wings ceases to be a smooth (laminar) flow and the wing starts to lose lift (a) Mach threshold (b) tactile feedback (c) relative wind camber (d) maximum bank limit (e) aerodynamic stall - ✔✔(e) aerodynamic stall The two basic types of drag are (a) parasitic and induced (b) simple and complex (c) high pressure and low pressure (d) induced and incidental (e) parasitic and peripheral - ✔✔(a) para [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 87 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

AFOQT BUNDLE, MOST EXAMINABLE QUESTIONS COVERAGE, 100% ACCURATE.
AFOQT Aviation Questions and answers, 100% Accurate, graded A+. Approved Exam Quizzes.
By Topmark 2 years ago
$38
10
Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 11, 2023
Number of pages
87
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 11, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
173