AP Environmental Science Vocabulary.
Full coverage, latest update. Verified.
air pollution - ✔✔-presence of unwanted substances in air
noise pollution - ✔✔-presence of unwanted noise
Water pollution - ✔✔-presence of
...
AP Environmental Science Vocabulary.
Full coverage, latest update. Verified.
air pollution - ✔✔-presence of unwanted substances in air
noise pollution - ✔✔-presence of unwanted noise
Water pollution - ✔✔-presence of unwanted substance in water
Point Source - ✔✔-pollution that can be traced to specific source
Non-point Source - ✔✔-source of pollution is many or specific, but can't be traced
Sustainable Yield - ✔✔-amount of resources that can be removed/harvested w/o compromising
ecosystem/initial natural capital
sustainable society - ✔✔-society whose processes/function can continue forever
Sustainability - ✔✔-ability to maintain function, state of being, processes
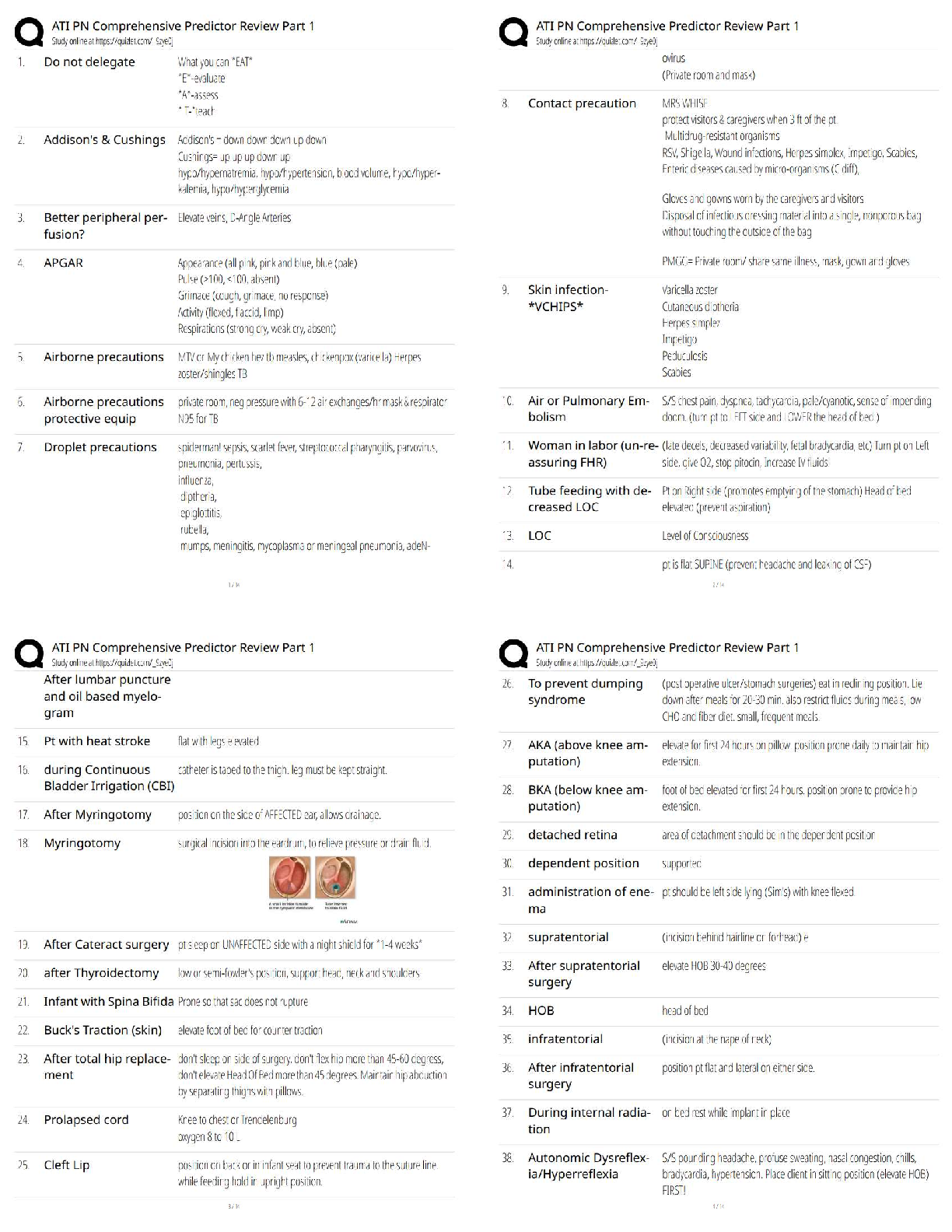
Greenwashing - ✔✔-marketing term for practices that suggest sustainability when its not
hunter-gather - ✔✔-small, mobile bands of humans that survive on whatever resources they have in
territory
pastoralism - ✔✔-herding of animals that have been domesticated/partly domesticated
Agriculture - ✔✔-process of raising crops & livestock in single, sml area
Renewable - ✔✔-Resources that can be replenished at rate =/> rate at which used
Non-Renewable - ✔✔-Resources that cannot be replenished at rate they are used
Potentially Renewable - ✔✔-Resources that are generally renewable, but can become nonrenewable if
not used wisely
Reduce - ✔✔-Limiting the consumption of products, decreases amount of trash & resources needed
overall
Includes producing and buying fewer goods and services, buying long-lasting products that do not need
to be replaced frequently, and buying smaller sizes of items
Reuse - ✔✔-Taking old products and using them again, keep waste out of landfills
•Reusing goods in the way they were intended to be used and repurposing them
Recycle - ✔✔-processing used materials into new materials
Breaking down the original product by some physical or chemical means, retrieving the materials, and
using them as raw materials to make new products
Degradable - ✔✔-Resources that break down over shorter amts of time & include biodegradable waste
that originates from plants/animals
Slowly Degradable - ✔✔-Resources that break down over long periods of time
Non-degradable - ✔✔-Resources that virtually never break down & have indefinite life spans
Biodiversity - ✔✔-# & variety of species living in area
Public Land - ✔✔-any areas controlled by gov (in city, county, state, federal), funded by taxpayers
Conservationalists - ✔✔-lobby to preserve/maintain land & natural resources so that they may be cont
to be used by humans
Preservationists - ✔✔-lobby to preserve lands & resources so they can't be used by humans
Theory - ✔✔-explanation that has been tested & supported by wide variety of observations & that new
info in unlikely to discredit
Data - ✔✔-points that are measurable = quantitative or observations w/o numbers = qualitative
Experiment - ✔✔-organic way of testing hypotheses
Environmental Science - ✔✔-interdisciplinary field of study of interactions in the environment
Peer Review - ✔✔-scientific research is evaluated by experts in same field
Technology - ✔✔-application of science to human problems/needs
Model - ✔✔-Representation of process or object
Scientific Law - ✔✔-statement/math relationship that describes single concept & is widely accepted by
science community, but is not modified over time
First Law of Thermodynamics - ✔✔-In physical & chemical changes, energy cannot be
created/destroyed, only transformed
Boyle's Law - ✔✔-PV = k where P = pressure, V = volume, K = constant
Globalization - ✔✔-process in which countries all over world are related in terms of global market in
goods
Natural Resources - ✔✔-resources existing in nature
Manufactured Capital - ✔✔-resources such as tools/factories
Human Capital - ✔✔-human beings w/ skills, talents, abilities
Marginal Cost - ✔✔-Cost of producing 1 additional unit of product
External costs / externalities - ✔✔-Costs that are incurred in the process but not reflected in cost of
product
External benefits - ✔✔-benefits that are received by those not immediately involved in economic
transaction
Cost-benefit analysis - ✔✔-analysis compares potential cost/benefits of product or process
Full-cost pricing - ✔✔-products that include external costs, especially negative externalities
Economy - ✔✔-system that produces, distributes, & consumes goods/services
Centrally Planned - ✔✔-Economy that relies on gov/another central authority to determine allocation of
goods & services & to set prices
Market - ✔✔-Economy that relies on marketplace where buyers & sellers interact to determine
allocation of goods/services & to set prices
Mixed - ✔✔-Economy that relies on blend of gov & markets to determine allocation of goods/services &
to set prices
Arable - ✔✔-Able to be used for agriculture
Gross Domestic Product - ✔✔-Value of final goods/services produced over time period in county
Gross National Product - ✔✔-value of everything produced by nation's residents, no matter where they
live
Sustainable Development - ✔✔-concept that sustainable methods for meeting humans needs & wants
are possible
Endangered - ✔✔-organism at risk for extinction in signif # of habitats
Threatened - ✔✔-organism at risk of being endangered in future
Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) - ✔✔-Required by NEPA (National Environment Policy Act)
Is complex prediction of environmental changes filed for proposed federal action
Second Law of Thermodynamics - ✔✔-when energy is transformed, some useful energy is degraded into
a less useful form, like heat
Photosynthesis - ✔✔-Converting the energy in sunlight into food;
Producers take in carbon dioxide, water and light energy to yield glucose and oxygen
Cellular Respiration - ✔✔-process in which cells release energy stored in food
Done by ALL organisms
6CO2 + 6H20 + light energy -> C6H12O6 + 6O2 - ✔✔-Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy - ✔✔-Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) - ✔✔-All energy absorbed by Producers
Net Primary Productivity (NPP) - ✔✔-Energy available to the next trophic level
Is difference b/t gross primary productivity & cellular respiration
Biotic - ✔✔-Living
Abiotic - ✔✔-Non-living
Producer / Autotroph - ✔✔-Organisms that preform photosynthesis
First level of food chain / web
Heterotroph / Consumer - ✔✔-Organisms that must eat other organisms for energy
Primary Consumer - ✔✔-Eats producers
Secondary Consumer - ✔✔-Eats Primary consumers
Tertiary Consumer - ✔✔-Eats Secondary consumers
Omnivore - ✔✔-Eats both plants and animals
Ten Percent Rule - ✔✔-relates to energy flow in food webs and food chains
only about 10% of useful energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next
Primary Succession - ✔✔-development of communities in a previously lifeless area without soil
Individual - ✔✔-Smallest level of organization of living things;
A single organism
Population - ✔✔-Collection of individuals of same species
Community - ✔✔-Group of populations
Ecosystem - ✔✔-Organization of living things that consists of all living and nonliving things in the area as
well as interactions b/t them
Biosphere - ✔✔-Combination of all biomes, highest level of organization of living things
Consumer - ✔✔-Organisms that eat other organisms
Photosynthesizers - ✔✔-Producers that convert sunlight into own food
Chemosynthesizers - ✔✔-Bacteria that have developed the ability to make their own food at deep ocean
vents by turning carbon into organic matter using energy from inorganic compounds
CO2 + O2 + 4H2S → CH2O + 4S + 3H2O
Detrivore - ✔✔-Organism that eat dead matter
Decomposer - ✔✔-Organism that breaks down remains of organisms into simpler, inorganic substances
Aerobic Respiration - ✔✔-cellular respiration that uses oxygen to release energy
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Anaerobic Respiration - ✔✔-process where kinds of organisms that can break down dead matter w/o
oxygen
C6H12O6 + 3NO3 + 3H2O -> 6HCO3 + 3NH4
Watershed - ✔✔-Drainage basin for water
Ecosystem Services - ✔✔-services we get from functioning ecosystems like clean water, soil, air, habitat,
timber
Bioaccumulation - ✔✔-buildup of chemical within bodies of organisms
Biomagnification - ✔✔-occurs when toxic substances that are present in small amounts in organisms low
in food chain are concentrated in larger amounts in organisms high in the chain
Algal Bloom - ✔✔-growing mass of algae within an aquatic ecosystem; sign of pollution in water; will
cont to grow until it covers the stream
Hydrosphere - ✔✔-Zone that includes all waters on Earth (including oceans, lakes, rivers, stream, water
vapor)
Atmosphere - ✔✔-zone includes all gases (mostly nitrogen & oxygen) that exists above Earth's surface
Lithosphere - ✔✔-zone includes Earth's crust & upper mantle
Trophic Level - ✔✔-Feeding position in food chain
Biomass - ✔✔-Dry weight of all living things on earth
Entropy - ✔✔-Uncertainty or randomness
Hydrologic Cycle - ✔✔-cont cycle that moves water through atmosphere, on surface of earth, below
surface
Evaporation & transpiration (evotranspiration) & sublimation -> Condensation -> Precipitation -> Runoff
& infiltration
Closed system - ✔✔-system that cannot exchange matter w/ environment
Open System - ✔✔-system that can exchange matter w/ environment
Evaporation - ✔✔-liquid changes to gas at temp below boiling
Transpiration - ✔✔-process through which plants give off water through leaves
Evapotranspiration - ✔✔-combo of transpiration & evaporation
Sublimation - ✔✔-solid changes directly to gas; water moves from solid form (ice) on surface to gaseous
form in atmosphere
Condensation - ✔✔-process where gas changes to liquid
Precipitation - ✔✔-water that falls from clouds in form of rain, snow, sleet, hail
Runoff - ✔✔-water that falls as precipitation on surface & flows over surface to water bodies; surface
movement of water
Infiltration - ✔✔-movement of water through soil
Law of Conservation of Matter - ✔✔-matter cannot be created or destroyed during chemical/physical
processes
Carbon Cycle - ✔✔-pathway through which carbon travels b/t living things & nonliving environment
Environmental Phase - ✔✔-parts of nutrient cycle in which nutrients exist in soil, water, air
Organismic Phase - ✔✔-parts of nutrient cycle in which nutrients are found in organisms
Weathering - ✔✔-physical, chemical, biological processes through which Earth materials are exposed to
atmosphere & change in color, texture, composition, form
Erosion - ✔✔-physical movement of materials that are weathered
Sink - ✔✔-process & location that acts to remove/absorb substance in system
Combustion - ✔✔-process in which organic substance (fuels) combines with oxygen to produce carbon
dioxide and water
DNA - ✔✔-Deoxyribonucleic acid; found in nucleus of cell, and essential for transmission of genetic info
RNA - ✔✔-Ribonucleic acid; found mostly in cytoplasm of cell & responsible for transmitting generic
information w/ DNA to cytoplasm
Amino Acids - ✔✔-essential component of proteins
Nitrogen Cycle - ✔✔-Cycling of nitrogen through the biosphere
Nitrogen fixation -> nitrificaiton -> assimilation -> ammonification or denitrification
Nitrogen Fixation - ✔✔-process that converts nitrogen gas to usable form through lightning fixation or
biological fixation;
Most converts N2 to ammonia (NH3) at plant nodules of legumes
2N2 + 6H2O → 4NH3 + 3O2
Legumes - ✔✔-Plants with seed pods
Nitrification - ✔✔-process of which bacteria convert ammonia to nitrites & nitrates
o 2NH3 + 3O2 → 2NO2- + 2H+ + 2 H2O
o 2NO2- + O2 → 2NO3-
Assimilation - ✔✔-process through which plants absorb nitrate/ammonium ions from soil
Ammonification - ✔✔-process through which bacteria/fungi convert nitrogen within dead organisms
into ammonium (NH4)
Denitrification - ✔✔-process by which anaerobic bacteria turn nitrate ions into nitrogen gas
4NO3 + 2H20 -> 2N2 + 5O2 + 4OH
Eutrophication - ✔✔-Rapid algal growth (algal bloom) caused by an excess of nitrogen & phosphorus,
blocks sunlight, causing the death/decomposition of aquatic plants, decreasing dissolved oxygen (DO),
suffocating fish
Condition in which bodies of water contain excess nutrients, usually as result of sewage/fertilizers
ATP - ✔✔-Primary source of energy in cellular reactions
Acid Precipitation - ✔✔-rain, snow, fog that has low pH (acidic) due to presence of transformed sulfur &
nitrogen compounds
Humidity - ✔✔-Amount of Water vapor in air
Biological Community - ✔✔-group of populations living in certain area, which consists of plants, animals,
fungi, microorganisms, other living things
Wetlands - ✔✔-areas that are completely saturated w/ water during at least part of the year; may have
standing water or saturated soil
Includes: marshes, swamps, bogs, fens
Ecosystem Services: Habitat, Filters water, recharge aquifers, provide flood & erosion control
Niche - ✔✔-roll organism play in environment
Fundamental Niche - ✔✔-Theoretical role that organism can occupy w/o limiting factors
Realized Niche - ✔✔-actual niche that organism occupies
Competitive Exclusion Principle - ✔✔-biological principle that states that specific niche in environment
can be occupied by only 1 species at time
Trophic Cascade - ✔✔-relationship b/t populations of predators & resources consumed by predators'
prey
Predation - ✔✔-relationship b/t 2 species in which one hunts other for food
Symbiotic Relationship - ✔✔-close, long term interaction b/t species
Parasitism - ✔✔-one species benefits, other is harmed
Commensalism - ✔✔-one species benefits & other is unaffected
Mutualism - ✔✔-Both species benefit
Competition - ✔✔-Neither species benefits
Neutralism - ✔✔-Neither species benefits or is harmed
Succession - ✔✔-changes in community over time in terms of numbers & distribution of species
Pioneer - ✔✔-1st community in succession
Climax - ✔✔-natural & stable community that is the endpoint of succession
Carrying capacity - ✔✔-community that given ecosystem can sustain over long term; can be calculated
by averaging high & low of population
Primary Succession - ✔✔-changes in community beginning with new/barren habitat; must begin with
bare rock
Secondary Succession - ✔✔-changes in community begging w/ disturbance; soil is already present in the
beginning
Invasive species - ✔✔-Species not native to ecosystem, but can thrive & displace native species
Evolution - ✔✔-change in allele frequencies (genetic material) over time
Natural selection - ✔✔-The process in which organisms with adaptive characteristics are more likely to
survive and pass on their traits to their offspring; a primary mechanism of evolution
Coevolution - ✔✔-The process in which changes in the traits of one population lead to changes in
another species
Biological Species Concept - ✔✔-organisms are members of same species if they can mate & produce
fertile offspring
Speciation - ✔✔-process in which new species arise from other species
Gene flow - ✔✔-addition/subtraction of genetic info from group b/c of movements of breeding
individuals b/t groups
Reproductively isolated - ✔✔-unable to interbreed under normal circumstances to produce fertile
offspring
Alleles - ✔✔-Different versions of genes
Genetic drift - ✔✔-Change in allele frequency in pop due to chance event
Genetic bottleneck - ✔✔-Extreme reduction in genetic variation in pop due to breeding of closely
related individuals
Extinction - ✔✔-Death of all members of species and speciation
Background extinction - ✔✔-normal, low-level rate of extinction of species b/c of naturally changing
environment conditions
Hotspot - ✔✔-area of high levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human activities
Endemic species - ✔✔-native species found in 1 particular place
Ecotones - ✔✔-transitional areas b/t ecosystems
Species richness - ✔✔-total number of species in area
Species evenness - ✔✔-relative abundance of each species
Weather - ✔✔-Current, daily conditions of atmosphere
Climate - ✔✔-Weather averaged over long term (usually 30 years)
Topography - ✔✔-Surface features
Orographic Effect - ✔✔-result of air ascending 1 side of mountain, cooling, condensing, & bringing
precipitation to other side of mountain as it descends
Rainshadow - ✔✔-dry region on side of mountain that is sheltered from wind
Karst Topography - ✔✔-landscape influenced by dissolution of underlying carbonate rocks w/ water,
results in caves & sinkholes
Latitude - ✔✔-Distance from equator
Altitude - ✔✔-How high something is
Cells - ✔✔-Made of hot air that rises and cold air that cools and descends;
Control the flow of air, which contributes to overall climate
Hadley Cell - ✔✔-Cell that drives air around tropical regions
Ferrel Cell - ✔✔-Cell that moves air form 30 degrees to 60 degrees latitude
Coriolis Effect - ✔✔-Deflection on moving objects due to Earth's rotation
In Northern Hemisphere, objects are deflected to the right
In Southern Hemisphere, objects are deflected to the left
Biome - ✔✔-Large area with specific climate and characteristic plants/animals that have adaptations for
conditions
[Show More]