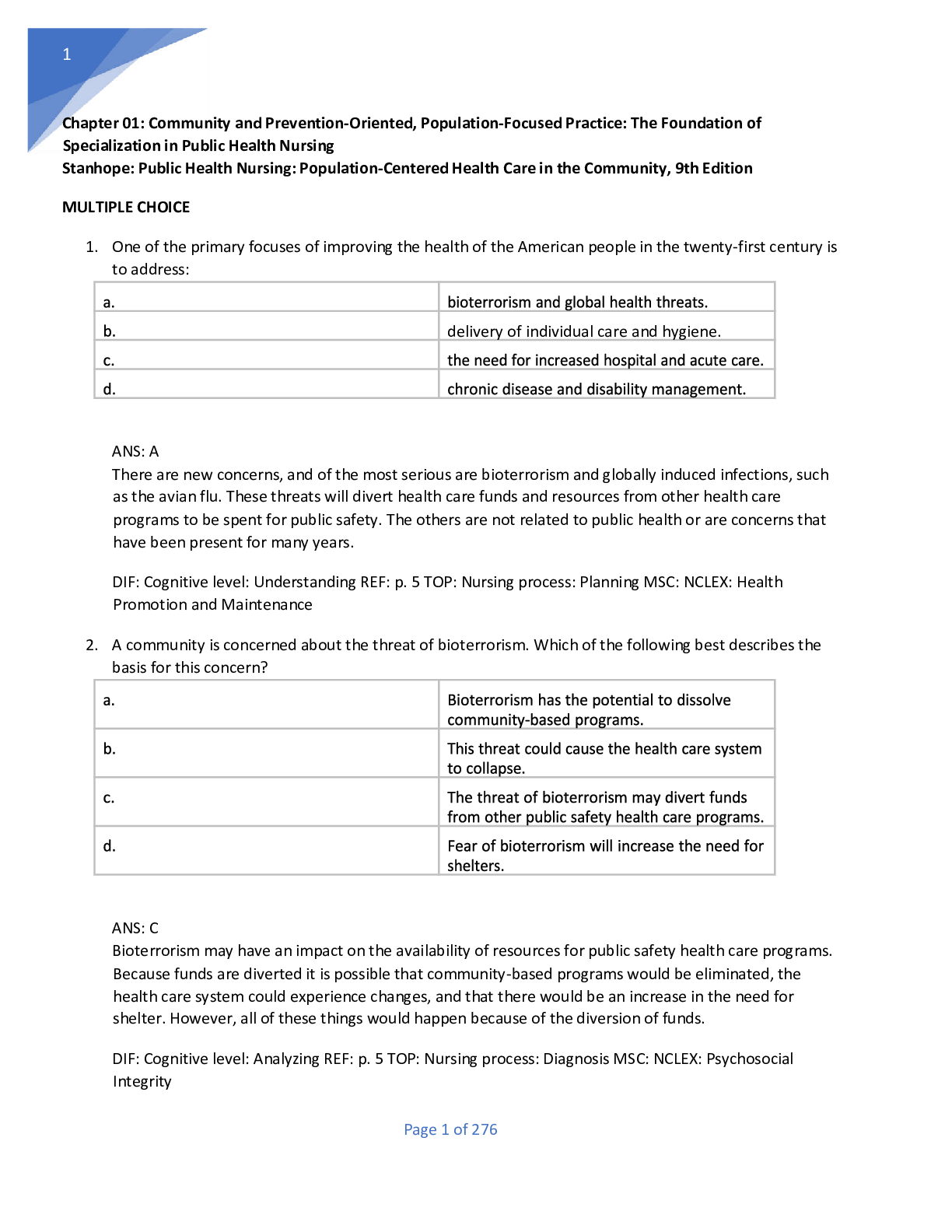
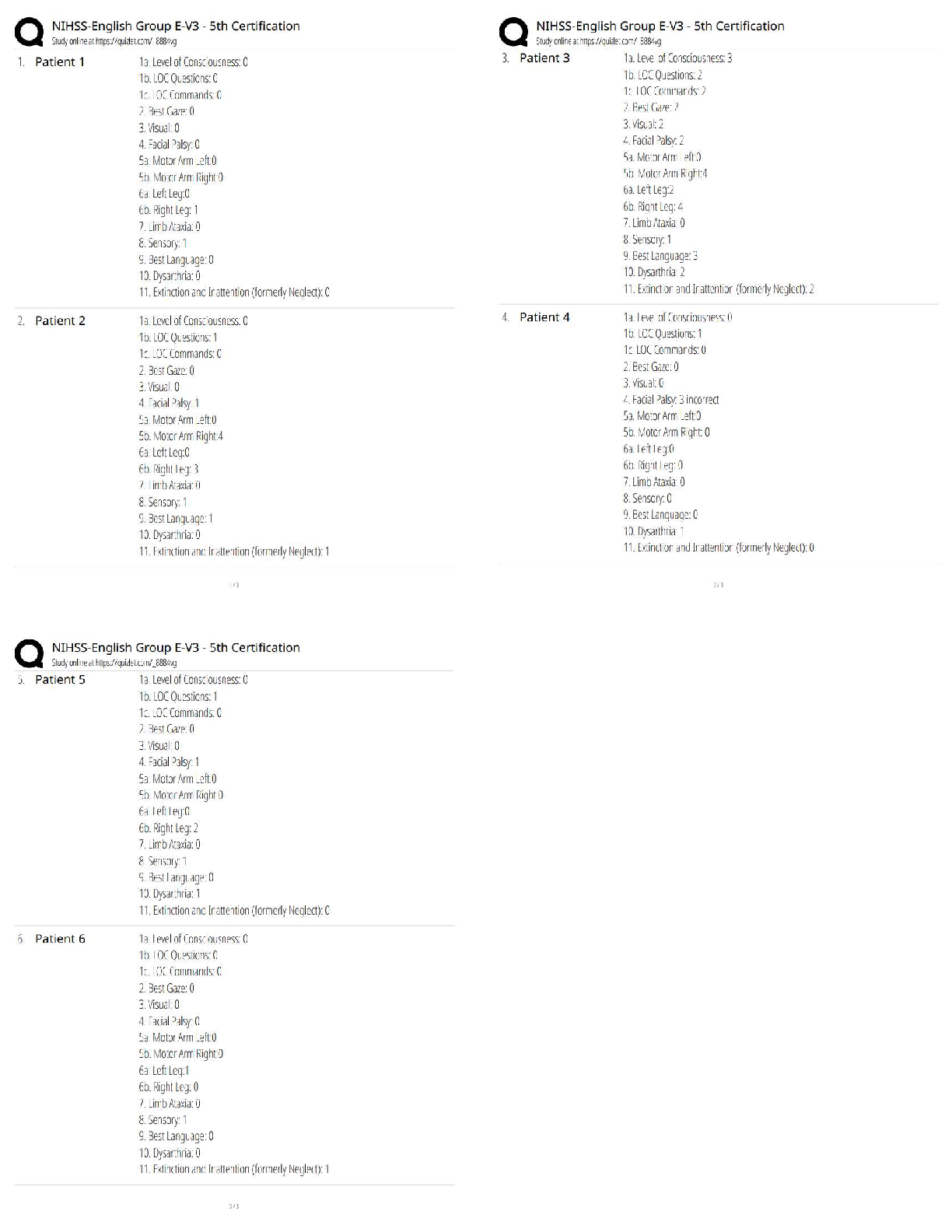
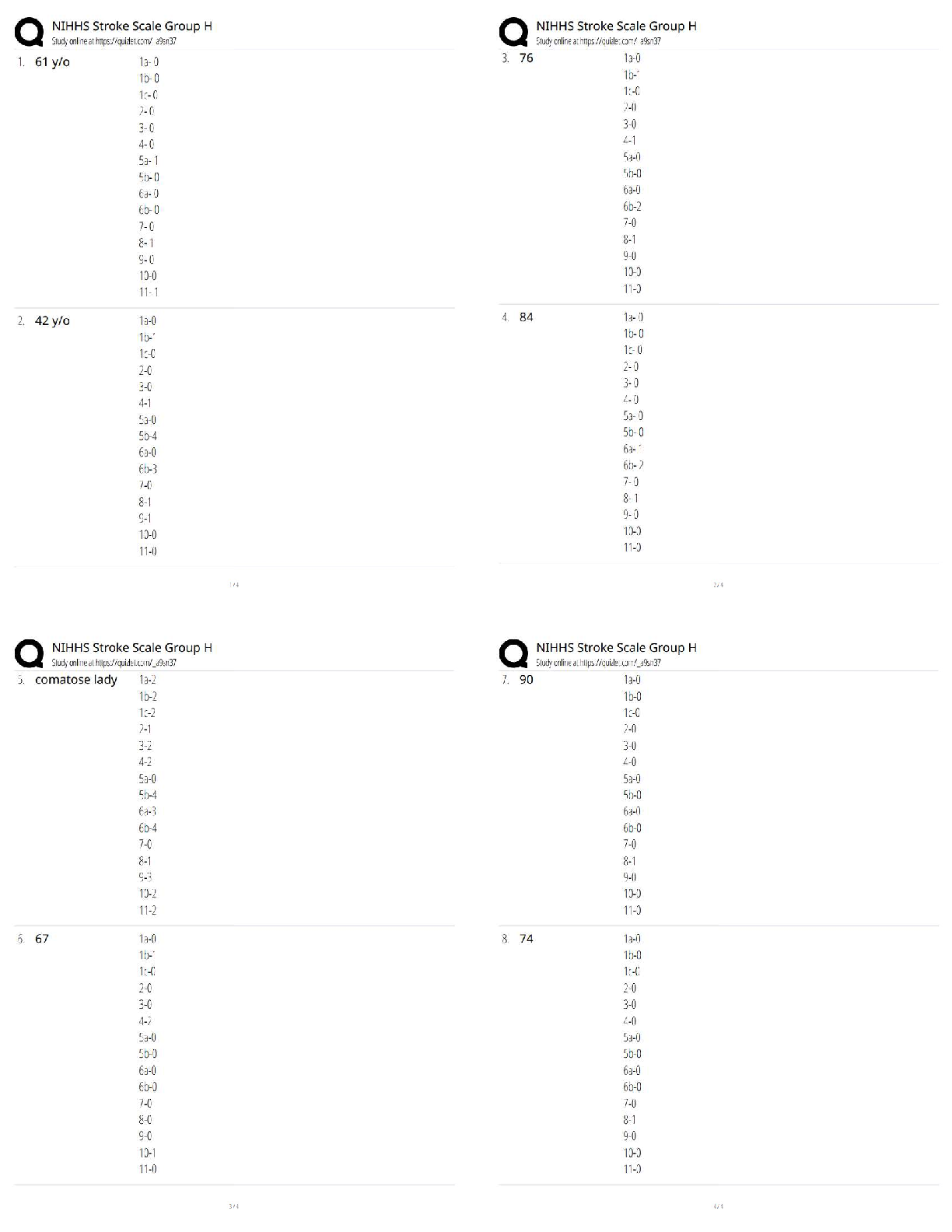
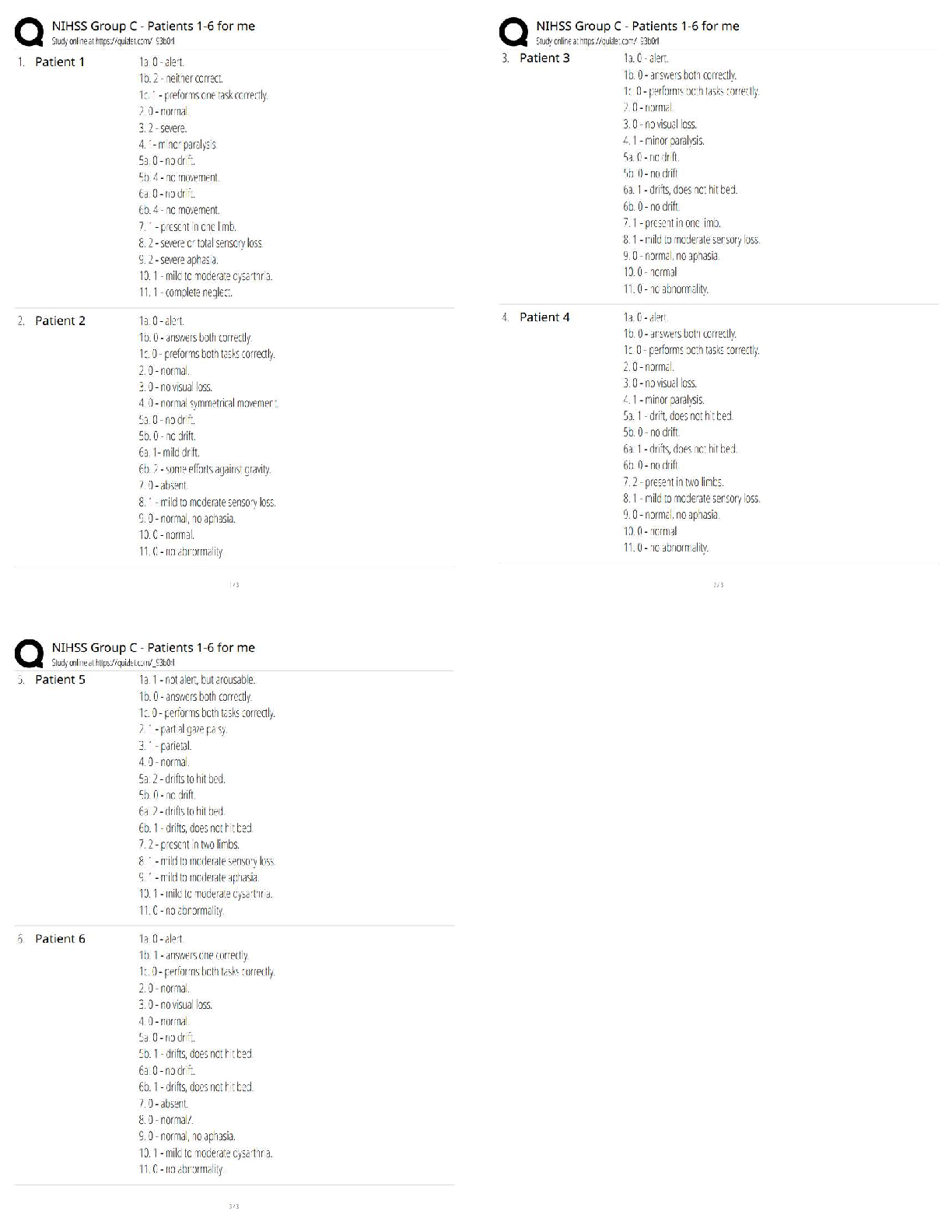
APES Exam: Study guide Questions and answers, 100% Accurate. Rated A+
Document Content and Description Below
APES Exam: Study guide Questions and
answers, 100% Accurate. Rated A+
Ecological Footprint - ✔✔-Amount of biologically productive land and water needed to supply a
population with the renewab
...
le resources it uses and to absorb or dispose of the wastes from such
resource use. It is a measure of the average environmental impact of populations in different countries
and areas
Ecological Tipping Point - ✔✔-Threshold level at which an environmental problem causes a fundamental
and irreversible shift in the behavior of a system.
Ecology - ✔✔-Biological science that studies the relationships between living organisms and their
environment; study of the structure and functions of nature.
Natural Capital - ✔✔-Natural resources and natural services that keep us and other species alive and
support our economies.
Per Capita - ✔✔-Annual gross domestic product (GDP) of a country divided by its total population at
midyear. It gives the average slice of the economic (or environmental) pie per person.
Ecosystem Services - ✔✔-Natural services or natural capital that support life on the earth and are
essential to the quality of human life and the functioning of the world's economies.
Perpetual Resource - ✔✔-has a never-ending supply. Some examples of perpetual resources include
solar energy, tidal energy, and wind energy
Environmental Wisdom Worldview - ✔✔-Set of assumptions and beliefs about how people think the
world works, what they think their role in the world should be, and what they believe is right and wrong
environmental behavior (environmental ethics).
Planetary Management Worldview - ✔✔-Worldview holding that humans are separate from nature, that
nature exists mainly to meet our needs and increasing wants, and that we can use our ingenuity and
technology to manage the earth's life-support systems, mostly for our benefit. It assumes that economic
growth is unlimited.
Stewardship Worldview - ✔✔-Worldview holding that we can manage the earth for our benefit but that
we have an ethical responsibility to be caring and responsible managers, or stewards, of the earth. It
calls for encouraging environmentally beneficial forms of economic growth and discouraging
environmentally harmful forms.
Sustainability - ✔✔-Ability of earth's various systems, including human cultural systems and economies,
to survive and adapt to changing environmental conditions indefinitely.
scientific principles of sustainability - ✔✔-To live more sustainably we need to rely on solar energy,
preserve biodiversity, and recycle the chemicals that we use. These three principles of sustainability are
scientific lessons from nature based on observing how life on the earth has survived and thrived for 3.5
billion years
First Law of Thermodynamics - ✔✔-Whenever energy is converted from one form to another in a
physical or chemical change, no energy is created or destroyed, but energy can be changed from one
form to another; you cannot get more energy out of something than you put in; in terms of energy
quantity, you cannot get something for nothing. This law does not apply to nuclear changes, in which
large amounts of energy can be produced from small amounts of matter.
Second Law of Thermodynamics - ✔✔-Whenever energy is converted from one form to another in a
physical or chemical change, no energy is created or destroyed, but energy can be changed from one
form to another; you cannot get more energy out of something than you put in; in terms of energy
quantity, you cannot get something for nothing. This law does not apply to nuclear changes, in which
large amounts of energy can be produced from small amounts of matter. It asserts that a natural
process runs only in one sense, and is not reversible.
Negative Feedback Loop - ✔✔-Feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction
from which is it moving.
Positive Feedback Loop - ✔✔-Feedback loop that causes a system to change further in the same
direction
Law of Conservation of Matter - ✔✔-In any physical or chemical change, matter is neither created nor
destroyed but merely changed from one form to another; in physical and chemical changes, existing
atoms are rearranged into different spatial patterns (physical changes) or different combinations
(chemical changes).
Electromagnetic Radiation - ✔✔-Forms of kinetic energy traveling as electromagnetic waves. Examples
include radio waves, TV waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays,
and gamma rays.
Ph - ✔✔-Numeric value that indicates the relative acidity or alkalinity of a substance on a scale of 0 to
14, with the neutral point at 7. Acid solutions have pH values lower than 7; basic or alkaline solutions
have pH values greater than 7.
High-Quality energy - ✔✔-energy that is concentrated and has great ability to perform useful work; e.g.
heat and energy in electricity, coal, oil, gasoline, sunlight, nuclei of uranium-235
low quality energy - ✔✔-energy that is dispersed and has little ability to do useful work; e.g. low�temperature heat
Ions - ✔✔-Atom or group of atoms with one or more positive (+) or negative (−) electrical charges.
Examples are Na+ and Cl-.
Isotopes - ✔✔-Two or more forms of a chemical element that have the same number of protons but
different mass numbers because they have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei.
Species - ✔✔-Group of similar organisms, and for sexually reproducing organisms, they are a set of
individuals that can mate and produce fertile offspring. Every organism is a member of a certain species.
Population - ✔✔-Group of individual organisms of the same species living in a particular area.
Community - ✔✔-Populations of all species living and interacting in an area at a particular time.
Ecosystems - ✔✔-One or more communities of different species interacting with one another and with
the chemical and physical factors making up their nonliving environment.
Biosphere - ✔✔-Zone of the earth where life is found. It consists of parts of the atmosphere (the
troposphere), hydrosphere (mostly surface water and groundwater), and lithosphere (mostly soil and
surface rocks and sediments on the bottoms of oceans and other bodies of water) where life is found.
Atmosphere - ✔✔-Whole mass of air surrounding the earth.
Troposphere - ✔✔-Innermost layer of the atmosphere. It contains about 75% of the mass of earth's air
and extends about 17 kilometers (11 miles) above sea level.
Stratosphere - ✔✔-Second layer of the atmosphere, extending about 17-48 kilometers (11-30 miles)
above the earth's surface. It contains small amounts of gaseous ozone , which filters out about 95% of
the incoming harmful ultraviolet radiation emitted by the sun.
Hydrosphere - ✔✔-Earth's liquid water (oceans, lakes, other bodies of surface water, and underground
water), frozen water (polar ice caps, floating ice caps, and ice in soil, known as permafrost), and water
vapor in the atmosphere. See also hydrologic cycle.
Abiotic - ✔✔-Nonliving
Biotic - ✔✔-Living
Aerobic Respiration - ✔✔-Complex process that occurs in the cells of most living organisms, in which
nutrient organic molecules such as glucose combine with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide , water , and
energy.
Anaerobic Respiration (Fermentation) - ✔✔-Form of cellular respiration in which some decomposers get
the energy they need through the breakdown of glucose (or other nutrients) in the absence of oxygen.
Autotrophs/Producers - ✔✔-Organism that uses solar energy (green plants) or chemical energy (some
bacteria) to manufacture the organic compounds it needs as nutrients from simple inorganic
compounds obtained from its environment.
Photosynthesis - ✔✔-Complex process that takes place in cells of green plants. Radiant energy from the
sun is used to combine carbon dioxide and water to produce oxygen , carbohydrates (such as glucose, ),
and other nutrient molecules.
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) - ✔✔-Rate at which an ecosystem's producers capture and store a
given amount of chemical energy as biomass in a given length of time.
Heterotrophs/Consumers - ✔✔-Organism that cannot synthesize the organic nutrients it needs and gets
its organic nutrients by feeding on the tissues of producers or of other consumers; generally divided into
primary consumers(herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), tertiary(higher-level) consumers,
omnivores, and detritivores(decomposers and detritus feeders).
Carnivores - ✔✔-Animal that feeds on other animals.
Omnivores - ✔✔-Animal that can use both plants and other animals as food sources.
Herbivores (Primary Consumers) - ✔✔-Organism that feeds on some or all parts of plants (herbivore) or
on other producers.
Decomposer - ✔✔-Organism that digests parts of dead organisms, and cast-off fragments and wastes of
living organisms by breaking down the complex organic molecules in those materials into simpler
inorganic compounds and then absorbing the soluble nutrients. Producers return most of these
chemicals to the soil and water for reuse. Decomposers consist of various bacteria and fungi.
Detritivores - ✔✔-Consumer organism that feeds on detritus, parts of dead organisms, and cast-off
fragments and wastes of living organisms. Examples include earthworms, termites, and crabs.
Food Chain - ✔✔-Series of organisms in which each eats or decomposes the preceding one. Shows how
each living thing gets food, and how nutrients and energy are passed from creature to creature
Food Web - ✔✔-Complex network of many interconnected food chains and feeding relationships.
Trophic Level - ✔✔-each of several hierarchical levels in an ecosystem, comprising organisms that share
the same function in the food chain and the same nutritional relationship to the primary sources of
energy.
Pyramid of Energy Flow - ✔✔-Diagram representing the flow of energy through each trophic level in a
food chain or food web. With each energy transfer, only a small part (typically 10%) of the usable energy
entering one trophic level is transferred to the organisms at the next trophic level.
Biogeochemical Cycles - ✔✔-pathway by which a chemical substance moves through both the biotic
(biosphere) and abiotic (lithosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) components of Earth.
Carbon Cycle - ✔✔-the series of processes by which carbon compounds are interconverted in the
environment, chiefly involving the incorporation of carbon dioxide into living tissue by photosynthesis
and its return to the atmosphere through respiration, the decay of dead organisms, and the burning of
fossil fuels
Greenhouse Gases - ✔✔-a gas that contributes to the greenhouse effect by absorbing infrared radiation,
e.g., carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons.
Hydrologic Cycle - ✔✔-Biogeochemical cycle that collects, purifies, and distributes the earth's fixed
supply of water from the environment to living organisms and then back to the environment
Nitrogen Cycle - ✔✔-Cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms from the environment to
organisms and then back to the environment
Phosphorus Cycle - ✔✔-Cyclic movement of phosphorus in different chemical forms from the
environment to organisms and then back to the environment
Sulfur Cycle - ✔✔-Cyclic movement of sulfur in various chemical forms from the environment to
organisms and then back to the environment.
Adaptation - ✔✔-a change or the process of change by which an organism or species becomes better
suited to its environment.
Background Extinction - ✔✔-refers to the standard rate of extinction in earth's geological and biological
history before humans became a primary contributor to extinctions.
Mass Extinction - ✔✔-The extinction of a large number of species within a relatively short period of
geological time, thought to be due to factors such as a catastrophic global event or widespread
environmental change that occurs too rapidly for most species to a
[Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages











.png)

















.png)