Engineering > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NETA PT Exam Flash Cards, Questions with Accurate Answers, Graded A+ (All)
NETA PT Exam Flash Cards, Questions with Accurate Answers, Graded A+
Document Content and Description Below
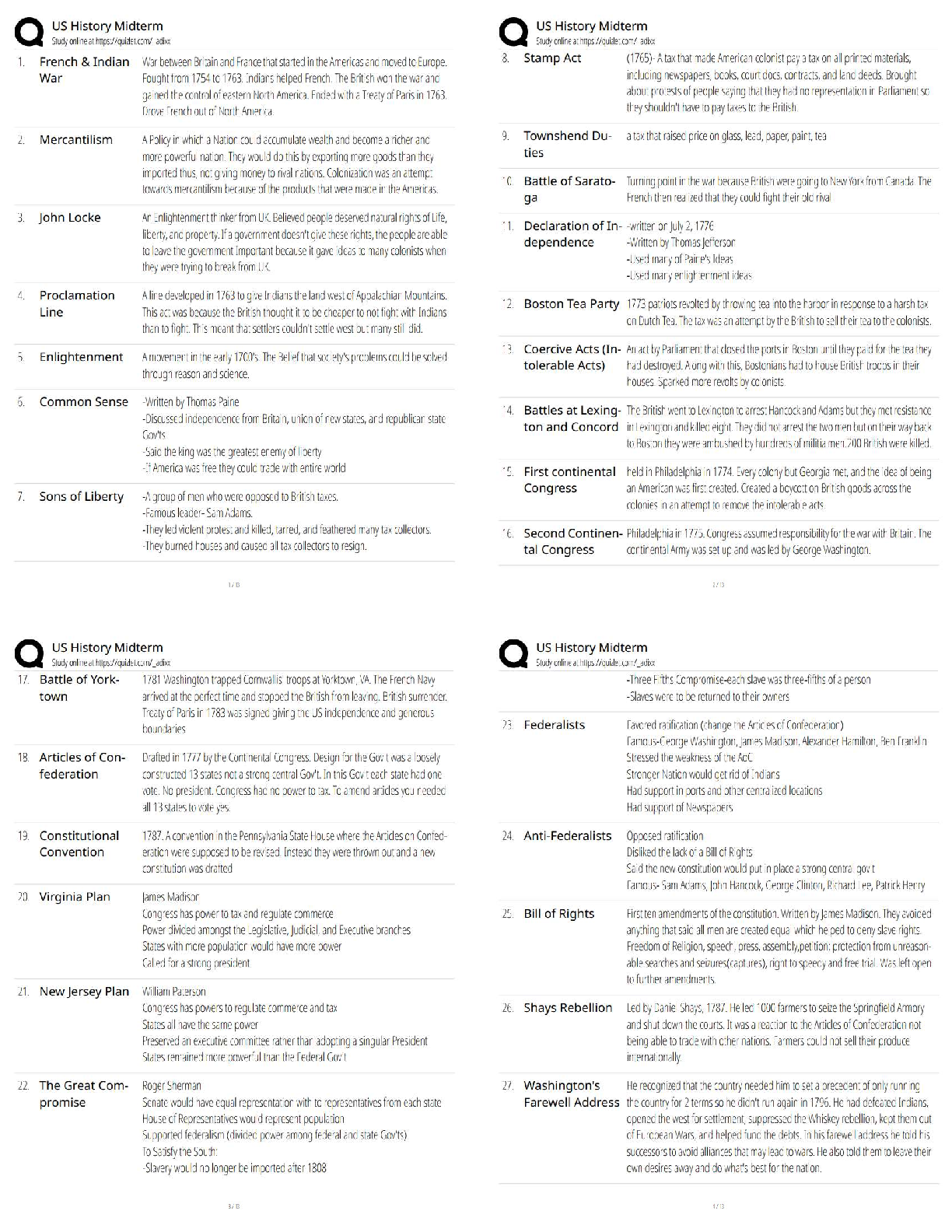
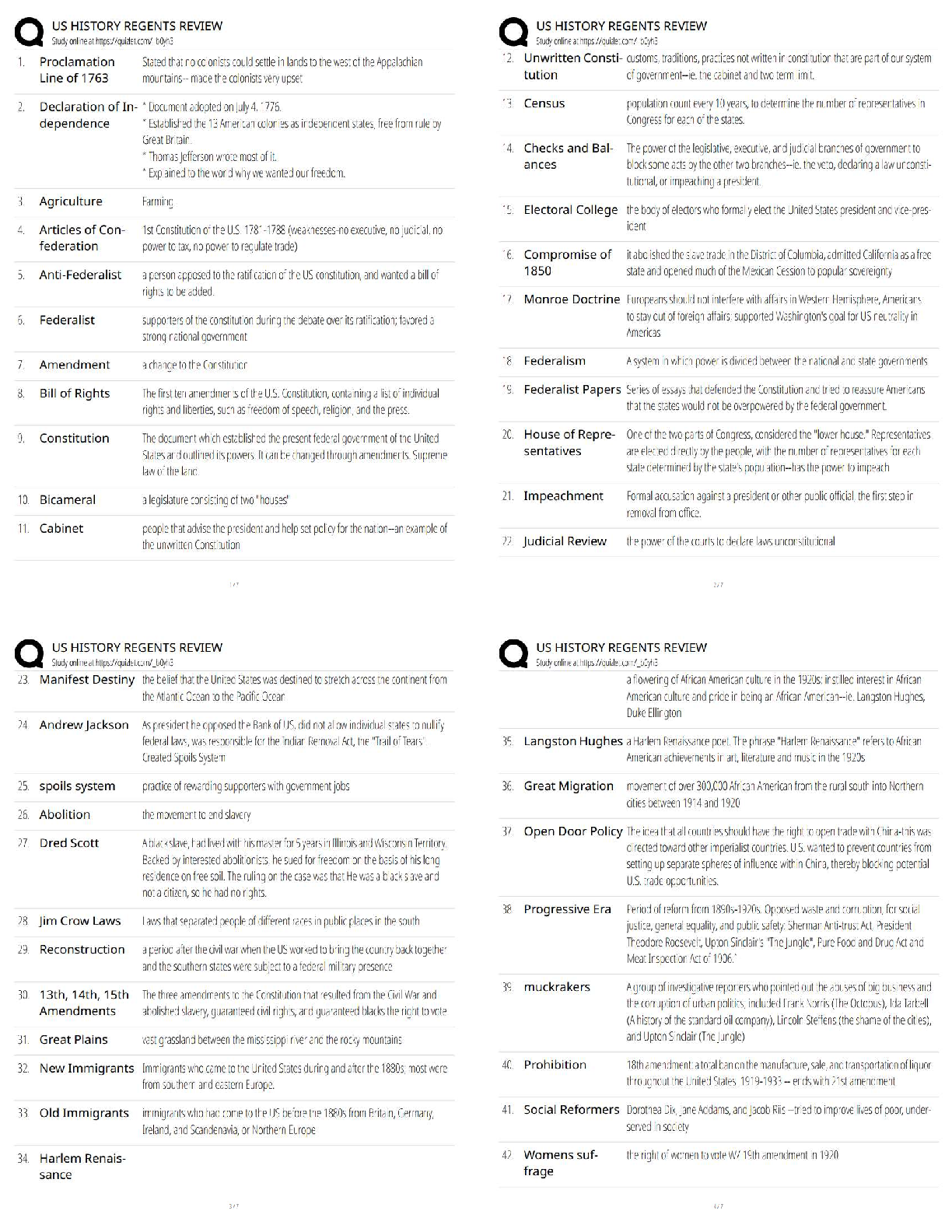
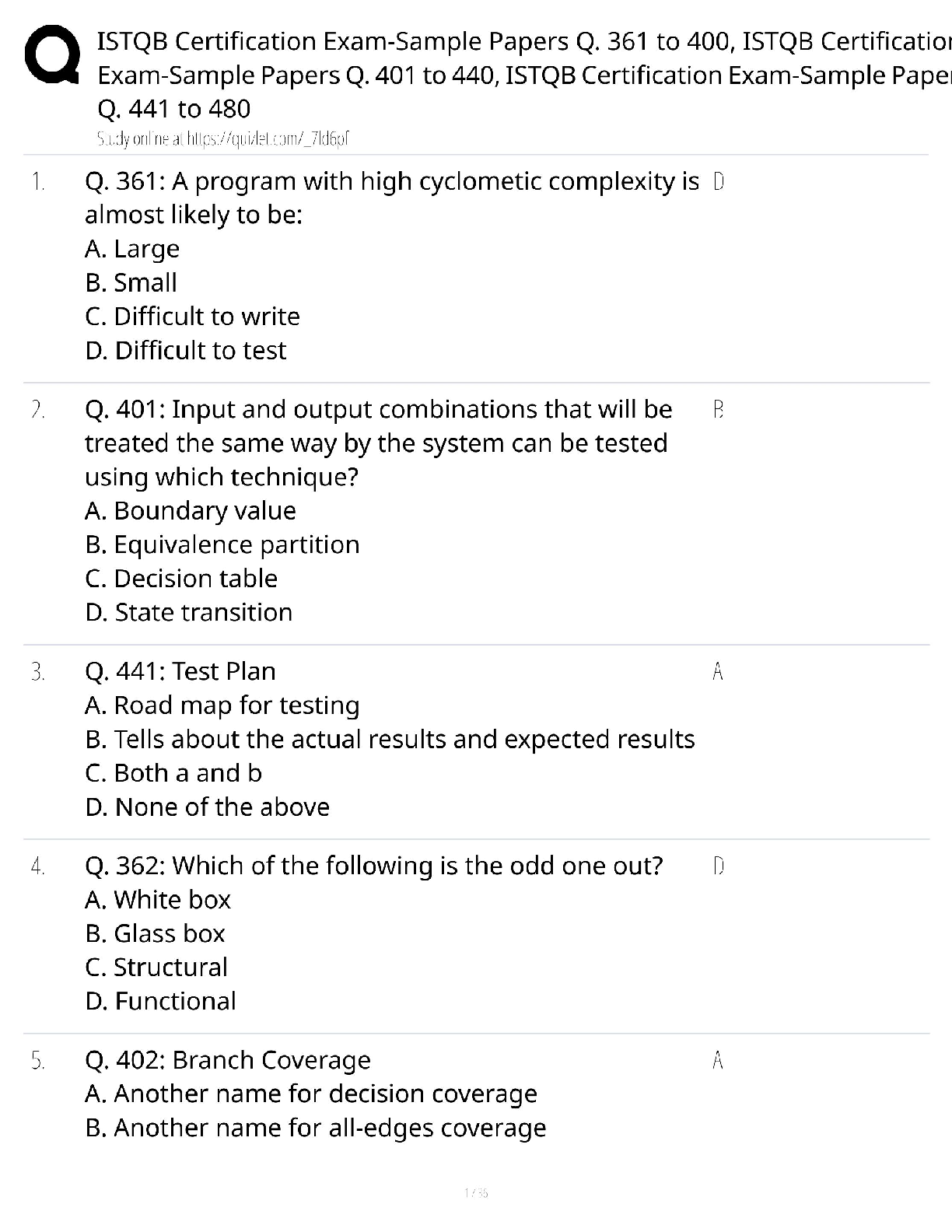
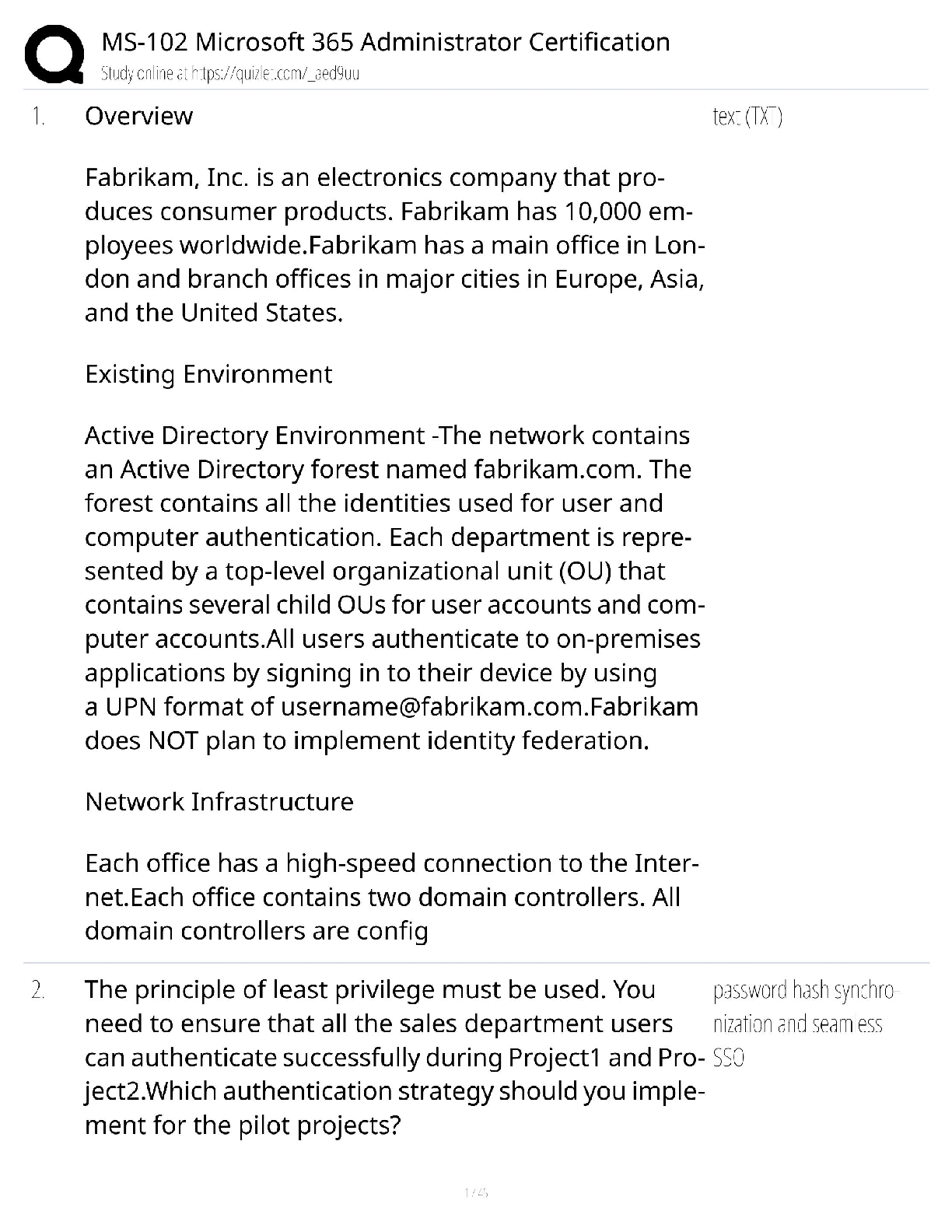
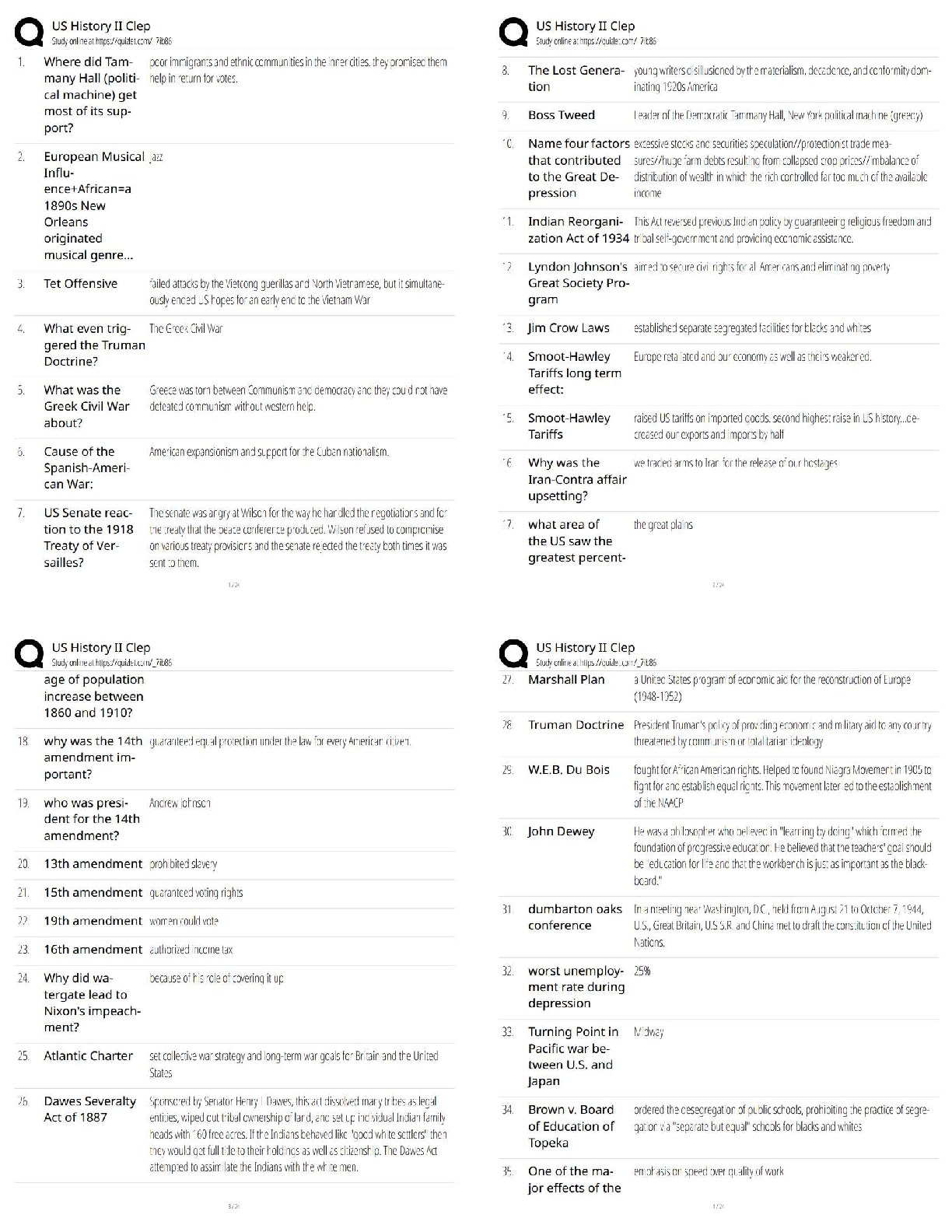
NETA PT Exam Flash Cards, Questions with Accurate Answers, Graded A+ origin - ✔✔-musculotendinous attachment located at the more stable end of the body segment which tends to be located proxi ... mally insertion - ✔✔-musculotendinous attachement located at the moving end of the body segment, located distally kinetic chain - ✔✔-series of interconnected segments and joints throughout the body skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems - ✔✔-proper movement throughout the kinetic chain requires the ____, ____, and ____ systems imparing - ✔✔-If any of the systems or components are disrupted, the remainder of the kinetic chain will be affected _______ function and optimal movement kinesiology - ✔✔-the study of human movement open kinetic chain excercises - ✔✔-Tend to be single-joint movements. The distal end (hand or foot) of the moving body segment is 'open' in free space. closed kinetic chain excercises - ✔✔-Tend to be a mulitple-joint movements. The distal end (hand or foot) of the moving body segment is in a fixed position and remains in constant contact with the surface, usually the ground. The Shoulder Complex - ✔✔-includes the humerus, scapula, and clavical bones and the muscles that control movement through the glenohumeral and scapulothoracic joints. middle deltoid and supraspinatus - ✔✔-muscles involved in shoulder abduction latissimus dorsi assisted by teres major - ✔✔-muscles involved in shoulder adduction shoulder abduction - ✔✔-movement in the frontal plane of motion of the arm away from the midline of the body. ROM 0-180 degrees. shoulder adduction - ✔✔-movement in the frontal plane of motion of the arm toward the midline of the body. ROM 0-50 degrees. horizontal adduction - ✔✔-movement in the transverse plane of the arm toward/across the midline of the body. ROM is 0-50 degrees (looks like a flye) pectoralis major - ✔✔-muscles involved in horizontal adduction horizontal abduction - ✔✔-movement in the transverse plane of the arm away from the midline of the body. ROM is 0-125 degrees (looks like a reverse flye) shoulder flexion - ✔✔-movement in the sagital plane raising the arm forward. ROM 0-180 degrees (looks like a front raise) anterior deltoid - ✔✔-muscles involved in a shoulder flexion shoulder extension - ✔✔-movement in the sagital plane of the arm back to the anatomical position and posterior to the body ROM 0-50 degrees (swimmer or lowering portion of front raise) external rotation - ✔✔-rotation around the long axis of the humerus away from the body. ROM 0-80 degrees (transverse plane) infraspinatus and teres minor - ✔✔-muscles involved in external rotation internal rotation - ✔✔-rotation around the long axis of the humerus toward the body. ROM 0-80 degrees. (transverse plane) (second part of front hand tennis swing) subscapularis - ✔✔-muscles involved in internal rotation pectoralis minor and serratus anterior - ✔✔-muscles involved in protraction of the scapula (abduction of the scapula) rhomboids and middle trapezius - ✔✔-muscles involved in retraction of the scapula (adduction of the scapula) upper trapezius and levator scapula - ✔✔-muscles involved in scapular elevation (raising the scapula) lower trapezius - ✔✔-muscles involved in scapular depression (lowering the scapula) fossa - ✔✔-a broad shallow area of a bone tubercle - ✔✔-a relatively small projection or bump on a bone process - ✔✔-relatively large or prominent bump on a bone shoulder flexion - ✔✔-action of the anterior deltoid shoulder abduction - ✔✔-action of the middle deltoid shoulder horizontal abduction and extension - ✔✔-action of the posterior deltoid recommended excercises for the deltoid - ✔✔-shoulder press (mid, anterior) lateral raise (mid) scaption (mid, anterior) reverse flye (posterior) SITS - ✔✔-the four rotator cuff muscles consisting of the (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis) that stabilize the glenohumeral joint action of the supraspinatus - ✔✔-shoulder abduction (first 30 degrees) Glenohumeral stabilization lateral raise and scaption - ✔✔-recommended exercises for the supraspinatus action of the infraspinatus and teres minor - ✔✔-Shoulder external rotation glenohumeral stabilization recommended exercises for the infraspinatus and teres minor - ✔✔-external rotation w/cable or tubing external rotation side-lying w/dumbell action of the subscapularis - ✔✔-shoulder internal rotation; glenohumeral stabilization recommended excercises for the subscapularis - ✔✔-internal rotation w/cable or tubing internal rotation side-lying w/dumbell action of the teres major and latissimus dorsi - ✔✔-responsible for shoulder adduction; shoulder extension recommended excercises for the teres major - ✔✔-seated narrow row, dumbbell one arm row, lat pulldown teres major - ✔✔-works synergistically with the latissimus dorsi in many rowing and pulling movements action of the pectoralis major - ✔✔-shoulder horizontal adduction; shoulder flexion; shoulder internal rotation recommended excercises for the pectoralis major - ✔✔-bench press, chest press (machine or dumbbells), push-up, cable chest flye action of the pectoralis minor - ✔✔-scapular protraction; scapular depression recommended exercises for the pectoralis minor - ✔✔-push-up plus (protraction at end ROM) rarely needed to isolate pec minor serratus anterior - ✔✔-scapular protraction; scapular stabilization and upward rotation recommended excercises for the serratus anterior - ✔✔-push-up plus (protraction at end ROM) rarely necessary to isolate shoulder impingement - ✔✔-overuse injury to the rotator cuff specifically the supraspinatus muscle related to repetitive overhead movements, which results in pain, inflammation, and decreased ROM causes of shoulder impingement syndrome - ✔✔-anomaly in the shape of the acromion, poor posture, posterior shoulder weakness, lack of scapular stability or mobility-all contributing to a decreased subacromial space retraction - ✔✔-adduction of the scapula is called rhomboids; middle trapezius - ✔✔-muscles involved in retraction extension - ✔✔-movement back to the anatomical position and continued posteriorly from a position of spinal flexion ROM 0-30degrees erector spinae - ✔✔-muscles involved in spinal extension action of the upper trapezius - ✔✔-scapular elevation and upward rotation action of the middle trapezius and rhomboids - ✔✔-scapular retraction action of the lower trapezius - ✔✔-scapular depression and downward rotation exercises for trapezius - ✔✔-shrugs; shoulder press(upper) seated narrow row (middle) front lat pull down (lower) scapular retraction; scapular downward rotation - ✔✔-action of the rhomboids excercises for the rhomboids - ✔✔-seated narrow row; seated wide row; front lat pulldown; pull-up; assisted pull-up exercises for latissimus dorsi - ✔✔-seated narrow row; front lat pulldown; pull up; assisted pull up; one arm row (cable or dumbbell) action of the erector spinae - ✔✔-spinal extension; spinal stabilization recommended exercises for erector spinae - ✔✔-back extension machine; roman chair back extension; back extension prone on stability ball; bird-dog elbow flexion - ✔✔-decreasing the joint angle; ROM 0-145 degrees; sagittal plane (bicep curl) biceps brachii - ✔✔-muscles involved in elbow flexion elbow extension - ✔✔-increasing the joint angle; returning the arm position to the anatomical positions; ROM 0 degrees; sagittal plane (extension in bicep curl) elbow flexion - ✔✔-action of the bicep brachii bicep brachii excercises - ✔✔-dumbell biceps curl; barbell biceps curl; preacher curl long head of the triceps - ✔✔-infraglenoid tubercle of scapula elbow extension - ✔✔-action of the triceps triceps exercises - ✔✔-cable triceps pushdown; supine dumbbell elbow extension core - ✔✔-muscle that control the position and stability of the lumbar and thoracic spine and pelvis; where all movement of the body originates; efficient function needed to optimize kinetic chain spinal flexion - ✔✔-forward movement of the torso; ROM 0-120 degrees; sagittal plane spinal extension - ✔✔-movement back to the anatomical position and continued posteriorly from a position of spinal flexion; ROM 0-30 degrees; sagittal plane rectus abdominus - ✔✔-muscle involved in spinal flexion erector spinae - ✔✔-muscles involved in spinal extension spinal rotation - ✔✔-side-to-side twisting movement of the torso through the axial spine; ROM 0-40 degrees; transverse plane lateral flexion - ✔✔-side-to-side bending movement of the torso; ROM 0-35 degrees; frontal plane internal and external obliques - ✔✔-muscles involved in spinal rotation internal and external obliques - ✔✔-muscles involved in lateral flexion spinal stabilization; abdominal compression - ✔✔-action of the transverse abdominus transverse abdominus exercises - ✔✔-"drawing-in" Manuever; abdominal "bracing" action of the internal obliques - ✔✔-spinal stabilization; spinal rotation; spinal flexion/lateral flexion internal obliques exercises - ✔✔-prone planks; oblique crunches; stability ball crunches; wood chops (downward rotation) action of the external obliques - ✔✔-spinal stabilization; spinal rotation; spinal flexion/lateral flexion external obliques exercises - ✔✔-prone planks; oblique crunches; stability ball crunches; hay bailers (upward rotation) action of the rectus abdomins - ✔✔-spinal stabilization; spinal flexion exercises for rectus abdominis - ✔✔-prone planks; abdominal crunches; stability ball crunches hip flexion - ✔✔-movement of the hip lifting the leg forward; ROM 0-110; sagittal plane hip extension - ✔✔-movement of the hip returning to the anatomical position and continuing to the body; ROM 0-30; sagittal plane Iliopsoas(psoas maj,psoas minor, iliacus) - ✔✔-muscles involved in hip flexion gluteus maximus; hamstrings - ✔✔-muscles involved in hip extension hip abduction - ✔✔-movement of the hip lifting the leg away from the midline of the body; ROM 0-45; frontal plane hip adduction - ✔✔-movement of the hip returning the leg to the anatomical position and continuing across the midline of the body; ROM 0-25; frontal plane gluteus medius; gluteus mimimus - ✔✔-muscles involved in hip abduction muscles involved in hip adduction - ✔✔-adductor magnus; adductor longus; adductor brevis; pectineus; gracilis hip extension - ✔✔-action of the gluteus maximus gluteus maximus exercises - ✔✔-barbell squat; stability ball/wall squat; leg press; lunge; straight-leg deadlift gluteus medius insertion - ✔✔-greater trochanter of the femur gluteus medius action - ✔✔-hip abduction; stabilization of pelvis and leg during single leg stance gluteus medius exercises - ✔✔-standing hip abduction w/cable column; lateral stepping w/resistance tubing; seated hip abduction machine iliopsoas(ilicusm psoas major/minor) action - ✔✔-hip flexion iliopsoas excercises - ✔✔-supine straight leg raise; hip flexion on multi-hip machine hip adduction - ✔✔-adductor action adductor exercises - ✔✔-hip adduction machine roles of a fitness professional - ✔✔-facilitator, instr [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

NETA EXAM Practice BUNDLE, VERIFIED.
NETA Practice test questions & Answers, 100% Accurate, rated A+. 19 VERSIONS. FULL CEOVERAGE, RATED A+
By Topmark 2 years ago
$38
19
Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2023
Number of pages
38
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
144