IC&RC MEGA STUDY. 100% Coverage.
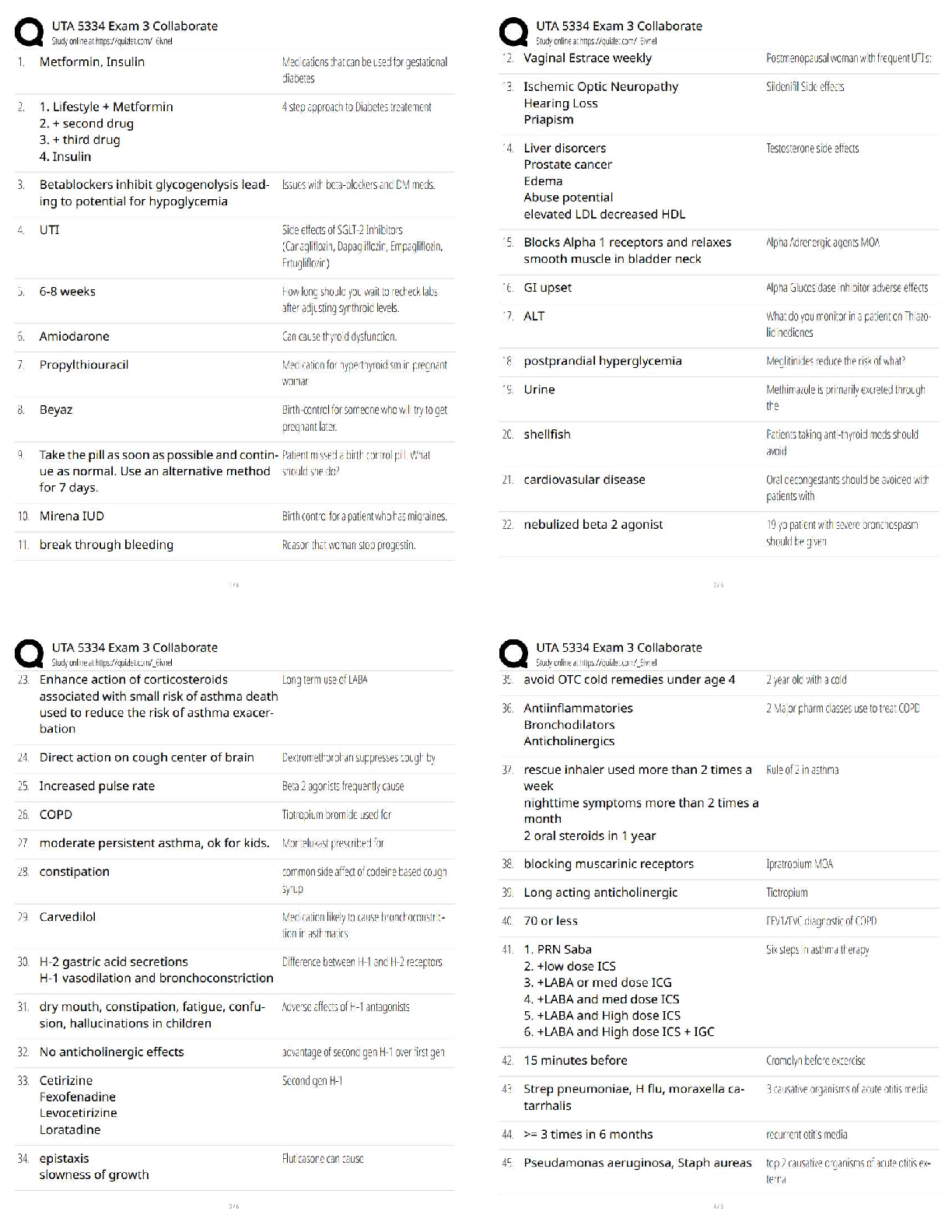
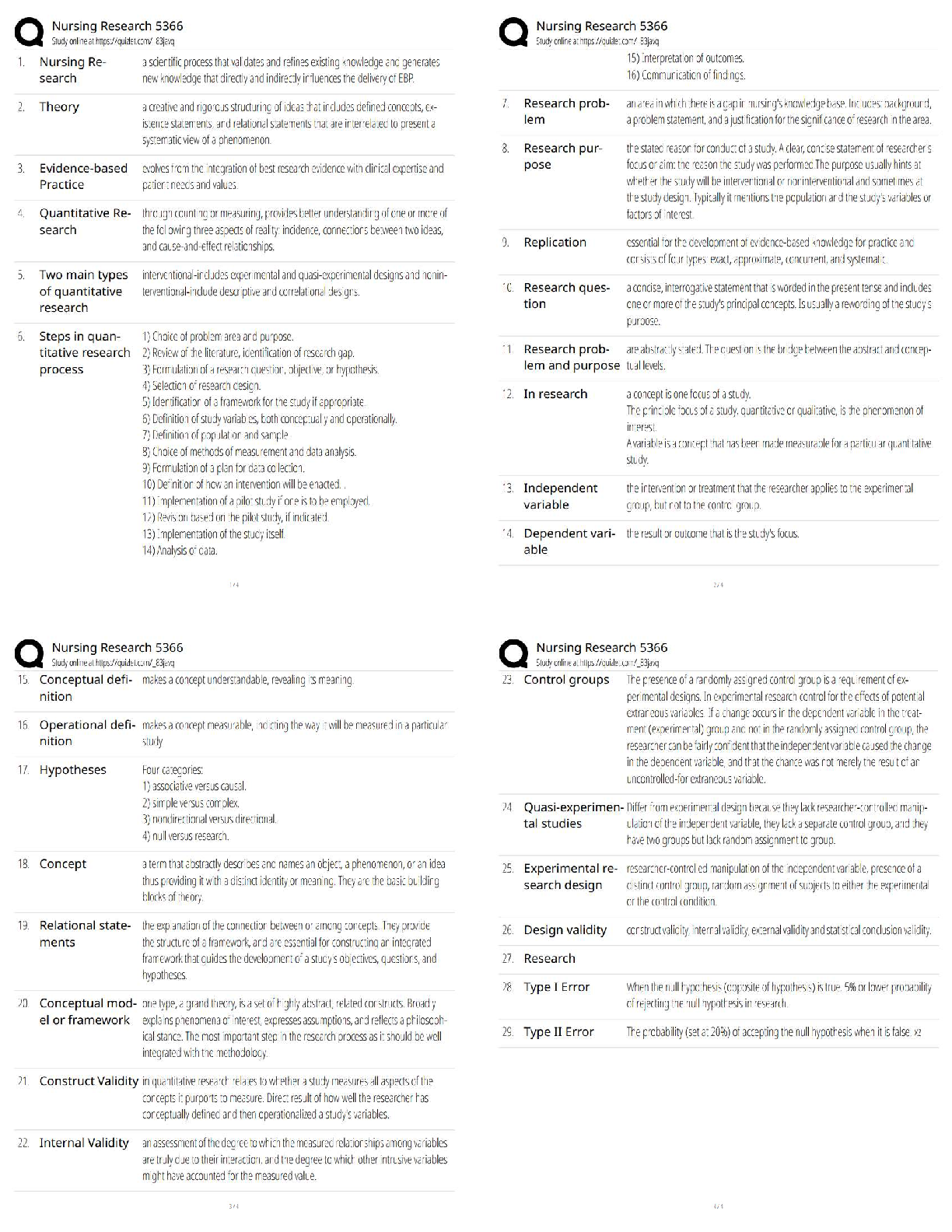
Guaranteed Mastery. Rated A
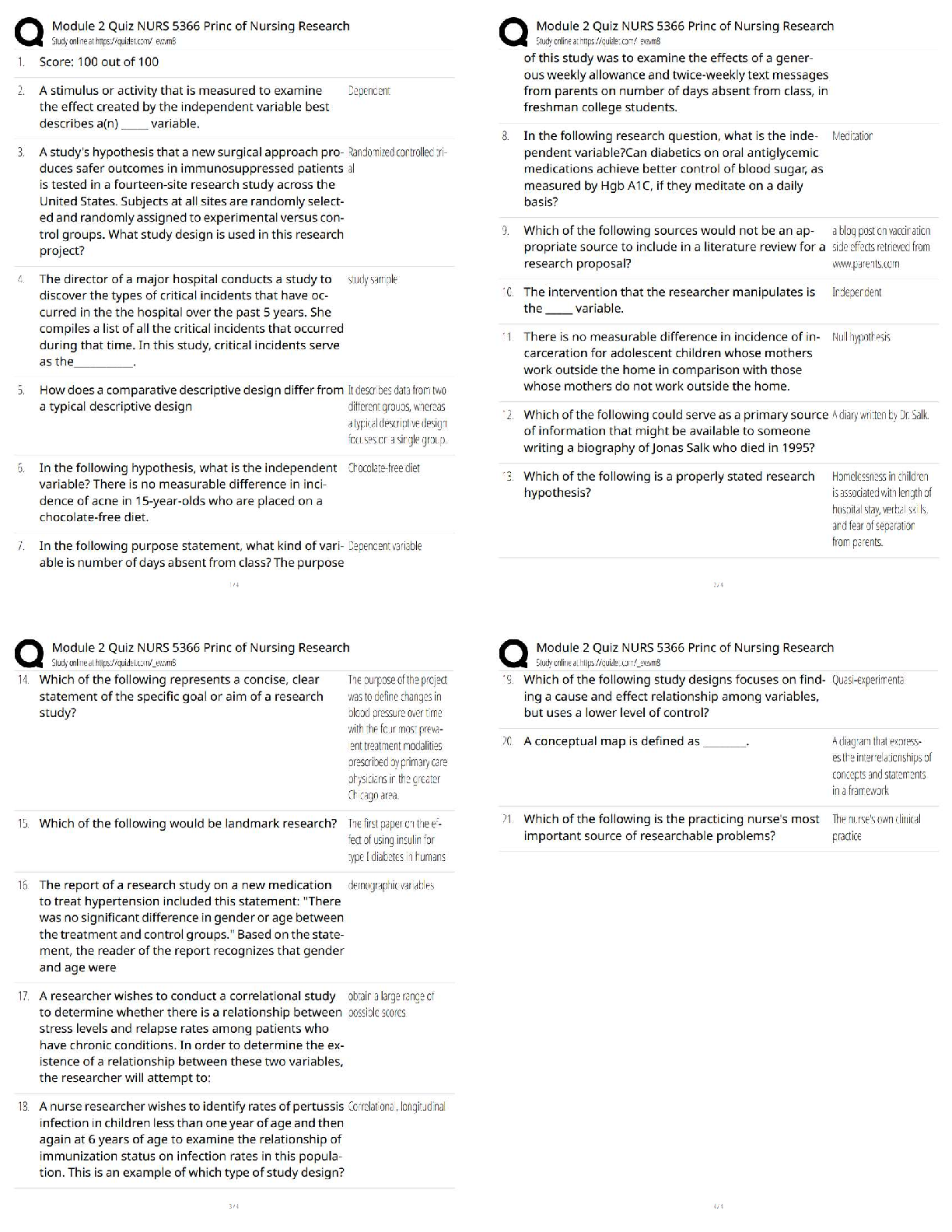
Stage 1: Experimentation - ✔✔is defined as the voluntary use of drugs without experiencing any
negative social or legal consequences. For many, experiment
...
IC&RC MEGA STUDY. 100% Coverage.
Guaranteed Mastery. Rated A
Stage 1: Experimentation - ✔✔is defined as the voluntary use of drugs without experiencing any
negative social or legal consequences. For many, experimenting may occur once or several times as a
way to "have fun" or even to help the individual cope with a problem. For many, experimentation can
occur without any desire to continue using the drug. For others, it can start to become a problem when
it moves into the next stage of addiction: regular use.
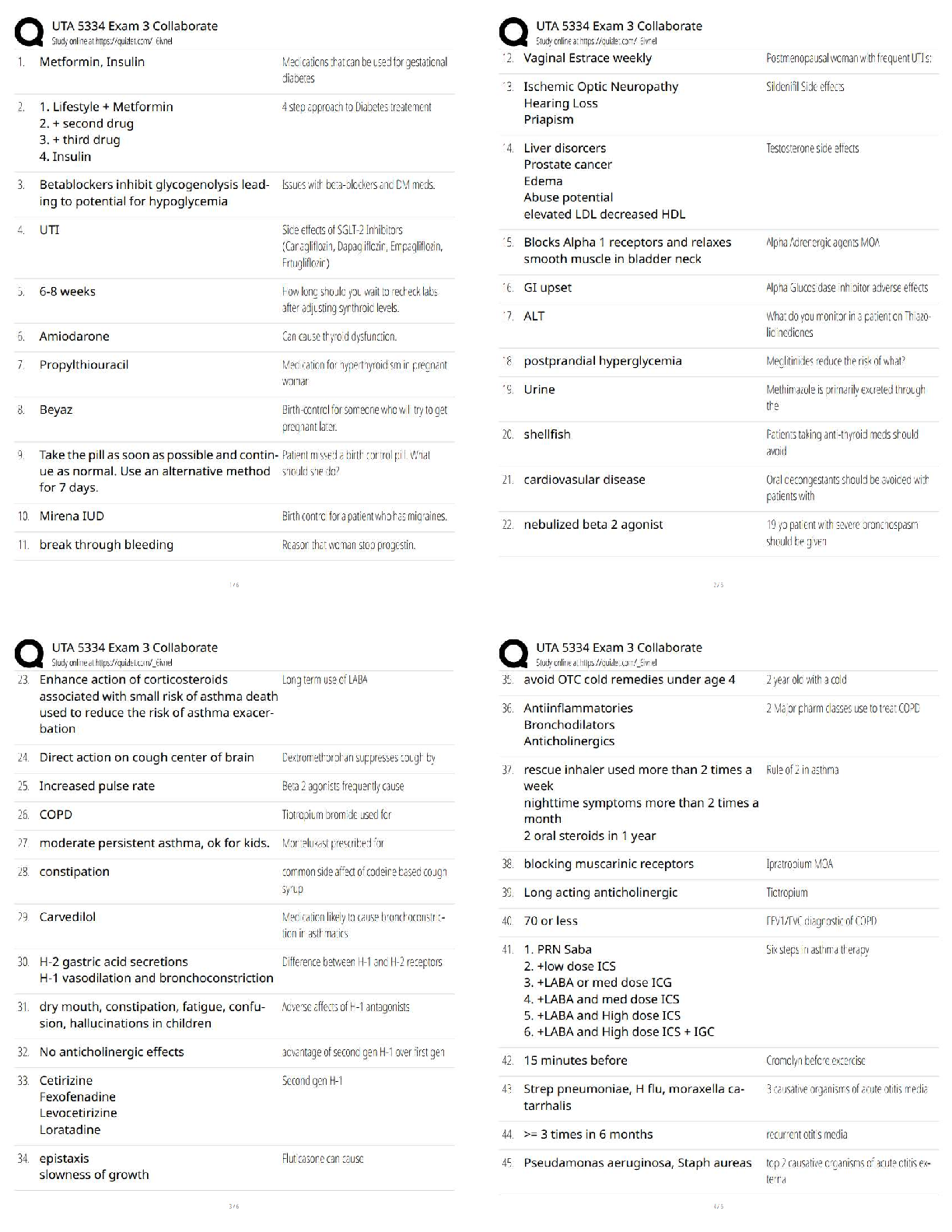
Stage 2: Regular Use - ✔✔Some people will be able to enter the stage of ------ --- without developing a
dependence or addiction. These people will be able to stop the drug use on their own. The problem with
regular use is that the risk for substance abuse greatly increases during this stage. It also increases risky
behaviors such as driving under the influence, unexplained violence, and symptoms of depression and
anxiety.
Stage 3: Risky Use/Abuse - ✔✔The line between regular use and risky use/abuse is a very thin one, but is
usually defined as continued use of drugs in spite of severe social and legal consequences. What might
have begun as a temporary form of escape can quickly lead to more serious problems. This is the stage
where the warning signs of addiction will begin to appear: craving, preoccupation with the drug, and
symptoms of depression, irritability and fatigue if the drug is not used.
Stage 4: Drug Addiction and Dependency - ✔✔Physical dependence on a drug is often intertwined with
addiction. Characteristics of dependence and drug addiction include withdrawal symptoms and
compulsive use of the drug despite severe negative consequences to his or her relationships, physical
and mental health, personal finances, job security and criminal record.
AUDIT - ✔✔The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) is a ten-question test developed by a
World Health Organization-sponsored collaborative project to determine if a person may be at risk for
alcohol abuse problems.
GATE - ✔✔GATE, a four-step process (Gather information, Access supervision, Take responsible action,
Extend the action) for addressing suicidal thoughts and behaviors in substance abuse treatment
CAGE AID - ✔✔is a commonly used, 5- question tool used to screen for drug and alcohol use.The CAGE
Assessment is a quick questionnaire to help determine if an alcohol assessment is needed. If a person
answers yes to two or more questions, a complete assessment is advised.
AUDIT (Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test) - ✔✔is a 10-item questionnaire that screens for
hazardous or harmful alcohol consumption. Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), the
test correctly classifies 95% of people into either alcoholics or non-alcoholics. The AUDIT is particularly
suitable for use in primary care settings and has been used with a variety of populations and cultural
groups. It should be administered by a health professional or paraprofessional.
CRAFFT - ✔✔is a short clinical assessment tool designed to screen for substance-related risks and
problems in adolescents. CRAFFT stands for the key words of the 6 items in the second section of the
assessment - Car, Relax, Alone, Forget, Friends, Trouble.
MAST - ✔✔is a simple, self scoring test that helps assess if you have a drinking. problem. Please answer
YES or NO to the following questions: MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST (MAST)
ASAM - ✔✔AMERICAN SOCIETY OF ADDICTION MEDICINE
SOAP - ✔✔subjective, objective, assessment, and plan
is a method of documentation employed by health care providers to write out notes in a patient's chart,
along with other common formats, such as the admission note.
MATRS - ✔✔Measurable—Can change or progress toward meeting the objectives be
documented/evaluated?
Attainable—Can the client take steps toward meeting the objectives?
Time-Limited—Is the time frame specified for the objectives?
Realistic—Can the client meet the objectives given their current situation?
Specific—Are specific activities included? Could the client understand what is expected?
SAMHSA - ✔✔Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
HIPAA - ✔✔Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996
ASI - ✔✔Addiction Severity Index
DSM - ✔✔Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
DAP - ✔✔Data, Assessment , Plan
DIG-FAST - ✔✔Is a tool Prompting the full evaluation of symptoms of mania
Distractibility
Impulsivity / Indiscretion (excessive involvement in pleasurable activities
Grandiosity - Inflated self-esteem
Flight of ideas / Racing thoughts
Activity increase / Increase goal-directed behavior (socially, sexually, at work, etc)
Sleep deficit (decreased need for sleep)
Talkativeness (pressured speech)
CSAT - ✔✔Center for Substance Abuse Treatment
TCI-JDS - ✔✔Texas University Drug Screen
CR - ✔✔Community Reinforcement
DOC - ✔✔Drug Of Choice
DOB - ✔✔Date Of Birth
BAC - ✔✔Blood Alcohol Content
Patient Screening - ✔✔Counselors must take a variety of factors into account when deciding to admit a
potential client for treatment. So it's crucial for counselors to use the right diagnostic criteria. They must
determine whether the individual's habits constitute abuse or recreational use.Eligibility requirements
differ between agencies and programs. Criteria usually examine the patient's age, gender, legal status,
income, and more. If a counselor deems an individual eligible for treatment, but he/she does not fit the
parameters of the program, the professional should be able to suggest an alternative location.
Patient Intake - ✔✔After the initial assessment, the counselor is required to fill out all the documents
and examine the technical aspects of admitting the patient. Patient Intake. Although this step is simpler
than the first, it can be stressful and time consuming depending on the volume of paperwork and
process of the treatment facility.Counselors must sign consent forms when gathering information from
or providing it to outside sources. The consent forms are a legal step that protects the confidentiality of
the patient. It is critical for the counselor to understand the process and guidelines fully for admittance.
Patient Orientation - ✔✔After screening and admitting, the patient will be added to the program and
oriented to the goals and nature of the treatment. Everyone must be given rules regarding conduct and
expectations. They should also be fully educated about the disciplinary actions they may be subject to
when rules are broken. Regulations vary between program types. For example, non-residential
treatment options will have service hours for each available treatment. Residential options will include
rules about leaving the campus and family visiting hours. All facilities include regulations about
treatment costs, insurance, and client rights. The counselor must examine each of these aspects to
properly educate incoming patients and protect them, as well as the establishment itself.
Patient Assessment - ✔✔Once the patient is admitted to a program and orientated about the specific
guidelines of the facility, he/she is assessed by the counselor. This procedure involves one-on-one
meetings between the counselor and patient. Assessment is one of the most vital parts of treatment
because it determines the path each patient will take. During the assessment, the counselor will identify
the strengths, weaknesses, and problems of each patient. The counselor will also evaluate the patient's
mental state to determine the best and most effective course of treatment.
Treatment Planning - ✔✔Once the patient is fully assessed and the best treatment types are
determined, treatment planning begins. This process takes broad ideas and turns them into specific
tactics and plans to fit the patient's needs. The counselor must determine the rank of the problems and
establish goals. Both long-term and short-term goals are set for every patient to take care of the most
severe problems and work toward rehabilitation. The counselor needs to properly explain treatment
goals and assessment results to every patient. Once the problems are uncovered and goals set, the
counselor works with the patient to identify treatment methods. It's important to give an approximate
timeline, if possible, and inform the patient about what his/her future at the facility includes. All
treatment language must be intelligible for the individual so he/she knows what every aspect truly
means.
Counseling - ✔✔Counseling is part of every good treatment facility. Different programs and locations
have different treatment types. Many offer individual and group treatment plans. In this step,
counselors work to assist patients and families in achieving objectives. They explore problems,
ramifications, feelings, attitudes, and more. The drug and alcohol counselor must select the proper
counseling type, apply techniques to assist the patient (or family/group), continue individualized
counseling, offer therapeutic advice, reach solutions, and implement the treatment plan.
Case Management - ✔✔This portion of treatment is a broad section. It refers to activities that bring
people, services, and agencies together in a predetermined framework of action. These methods are
necessary to establish the short-term and long-term goals of the patient. Global criteria for case
management includes coordinating client care services and explaining the care management activities to
the client. Again, it's imperative to help the patient understand the methods and goals of the program.
Crisis Intervention - ✔✔Even with the best treatment plans and facilities, drug and alcohol rehab isn't an
easy process. Every patient will likely experience acute emotional and physical distress at some point,
including recovery issues or drug relapse.
Patient Education - ✔✔Counselors must continue to provide information to their patients through the
duration of treatment. Both formal and informal processes are used to keep patients educated and up�to-date about treatments, discoveries, progress, and other relevant factors.
Referral - ✔✔In some cases, the needs cannot be met by the counselor or agency. When such a
situation arises, the counselor must provide relevant information and advice for the patient. The
counselor must identify which services the facility cannot meet and determine if supplemental
assistance can be offered without leaving or un-enrolling from the facility. The counselor can also take
advantage of community resources and support systems. One important part of the referral is to adhere
to applicable laws. Local, state, and federal regulations apply when it comes to patient confidentiality.
Record-Keeping and Reporting - ✔✔The results of treatment and assessments must be carefully
documented to track progress and develop plans for the patient's future. Reports, notes, discharge
summaries, and other types of information must be kept confidential but properly tracked.
Cross-Consultation - ✔✔The final function of a counselor is to communicate with other professionals.
Client treatment and services can benefit from in-house and outside resources. The goal of cross�consultation is to ensure the highest quality, most comprehensive care.
MAST - ✔✔Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test
AUDIT - ✔✔Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test
CAGE - ✔✔Cut-down, Annoyed, Guilt, Eye-opener
TWEAK - ✔✔Tolerance, Worried, Eye-opener, Amnesia, and K/Cut-down
DAST - ✔✔Drug Abuse Screening Test
SASSI - ✔✔Substance Abuse Subtle Screening Inventory
ASI - ✔✔Addiction Severity Index
MAT - ✔✔Medication Assisted Treatment
DSM IV - ✔✔Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Menatl Disorders, 4th Edition
ASAM - ✔✔American Society of Addiction Medicine
CBT - ✔✔Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
SBIRT - ✔✔Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment
SOAP - ✔✔Subjective, Objective, Assessment, and Plan
COD - ✔✔Co-Occurring Disorders
BDI - ✔✔Beck Depression Scale
CAADE - ✔✔California Association for Alcohol/Drug Educators
SAMHSA - ✔✔Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
CSAT - ✔✔Center for Substance Abuse Treatment
CAADAC - ✔✔California Association of Alcoholism and Drug Abuse
CATC - ✔✔Certified Addiction Treatment Counselor
NAADAC - ✔✔National Association of Alcoholism and Drug Abuse Counselors
IC&RC - ✔✔International Certification & Reciprocity Consortium
INCASE - ✔✔International Coalition of Addiction Studies Education
TAP - ✔✔Technical Assistance Publication
LGBT - ✔✔Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender
MI - ✔✔Motivational Interviewing
CTRS-CCDP - ✔✔Clinical Evaluation, Treatment Planning, Referral, Service Coordination, Counseling,
Client, Family, and Community Education, Documentation, Professional and Ethical Responsibilities (8
Performance Domains)
ATTC - ✔✔Addiction Technology Transfer Center
TIPs - ✔✔Treatment Improvement Protocols
CDADP - ✔✔California Department of Alcohol and Drug Programs
NIDA - ✔✔National Institute on Drug Abuse
EBPs - ✔✔Evidence-Based Practices
N-SSATS - ✔✔National Survey on Substance Abuse Treatment Services
SAPT - ✔✔Substance Abuse Prevention and Treatment
HIPAA - ✔✔Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
CAGE - ✔✔• The briefest and most widely used.
• Only four questions asked directly to the person.
• If someone answers yes to one of the questions then there is an indicator that their might be a
problem that needs to be further investigated.
• If they answer yes to two or more they are sent for further testing.
• Advantages-yes or no questions
• Disadvantages-not asking about time frame, self report, not in depth about environment, not in depth
MAST - ✔✔• Widely used
• Good reliability and validity
• Original had 25 self administered questions the one now has only 22.
• Advantages-it could be a reality check to someone taking it, not very time consuming, simple yes and
no
• Disadvantage-it doesn't ask you to explain, doesn't ask time frame
AUDIT - ✔✔• Ten items 1-3 frequency and quantity 4-6 alcohol dependence 7-10 how harmful alcohol
use.
• Advantages-you can use it in an interview, it's not that long, it's more specific
• Disadvantage-not specific enough, doesn't add in the times when drinking is more acceptable like
vacation etc., not valid
• Can be self report questionnaire or an interview
DAST - ✔✔Screen drugs other than alcohol
POSIT - ✔✔139 items on it
Used for substance use problems and social, behavioral, and learning problems
Disadvantages-too long, repetitious, lack of consistency
Advantages-more detailed
SASSI - ✔✔• Doesn't directly question about alcohol/drug use (not like the previous ones)
• Around 50 questions
• Asks questions about alcohol/drug use on one side and don't on the other
• Looking for defensiveness, looking at others, personal affect
• Disadvantages-could be hard to profile
DSM Axises - ✔✔o Axis I-Clinical syndromes
• Alcohol abuse, cannabis dependency
o Axis II-Personality disorders/mental retardation
• Not used very often in alcohol or chemical use
o Axis III-Medical Conditions
• Psuerosis of the liver
o Axis IV-Psychosocial/environmental stressors
• Losing kids because of substance abuse, lacks good social support system
o Axis V-Global assessment of functioning
• 0-100 how the person is functioning overall
Narcotics possible effects - ✔✔Euphoria, drowsiness, respiratory depression, constricted pupils, nausea
Narcotics effects of OD - ✔✔Slow/shallow breathing, clammy skin, convulsions, coma, and possible
death
Narcotics withdrawal syndrome - ✔✔Water eyes, runny nose, yawning, loss of appetite, irritability,
tremors, panic, cramps, nausea, chills, sweating.
Narcotics - ✔✔Heroin, Morphine, Hydrocodone, Hydro-morphone, Oxycodone, Codeine
Depressants - ✔✔Hydroxybutyric Acid, gamma, Benzodiazepines etc.
Depressant effects - ✔✔slurred speech, disorientation, drunken behavior without odor of alc., imparired
membory of events, interacts with alc.
Depressant overdose - ✔✔shallow respiration, clammy skin, dilated pupils, weak and rapid pulse, coma,
and possible death.
Depressant withdrawal - ✔✔Anxiety, insomnia, tremors, delirium, convulsions, possible death.
Stimulants - ✔✔Cocaine half life=one hour, Amphetamine=6-12 hours, Methylphenidate=2 hours
Stimulant effects - ✔✔Increased alertness, excitation, euphoria, increased pulse rate, increased blood
pressure, insomnia, and loss of appetite, dialated pupils.
Stimulant OD - ✔✔Agitation, increased body temperature, hallucinations, convulsions, and possible
death
Stimulant withdrawal - ✔✔Apathy, long periods of sleep, irritability, depression (possible with suicidal
potential), and disorientation, increased appetite, anhedonia (absence of pleasure) and craving.
Hallucinogens - ✔✔MDMA and Analogs, LSD, Phencyclidine,
Hallucinogen signs and symptoms - ✔✔Increased reflexes, tremors, weakness, flushing and chills,
seizures, inappropriate mood, elation, hallucinations, bizarre behafvior, diorientation, confusion,
delusions, and impaired judgement.
Hallucinogen OD - ✔✔Increased body temp, electorlyte imbalance, cardiac arrest, unable to direct
movement, feel pain, or remember.
Hallucinogen withdrawal - ✔✔Muscle aches, drowsiness, depression, acne, and drug seeking behavior.
Cannabis effects - ✔✔Euphoria, relaxed inhibitions, increased appetitie, disorientation,
Cannabis problems - ✔✔impairment of ability to learn. Medical effects wth prolonged use include
respiratory problems, possible impaired immune function and possible reproductive problems
includinglow birth weight infants.
Cannabis withdrawal - ✔✔Rare. Appear limited to some heavy users. Possible irritability, restlessness,
craving, loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, muscle twitching, overt aggression and depression.
Anabolic Steroids effects - ✔✔Virilization, edema, testicular atrophy, gyneco-mastia, acne aggressive
behavior
Anabolic Steroids withdrawal - ✔✔Possible depression
Inhalants effects - ✔✔flushing, hypotension, headache, cardiac depressants leading to "sudden sniffing
death.
Inhalants signs and symptoms - ✔✔possible asphyxiation and frostbite of nose, lips, or larynx if inhaled
from a tank, loss of motor control, nausea, ataxia, muscle weakness, dysarthia, nystagmus, diminished
reflexes.
Inhalants withdrawal - ✔✔Agitation -pyschological but no known physical symptoms
Alcohol common problems - ✔✔Tolorance, Dependence, Depression, neurologic deficits, hypertension,
liver and heart disease.
Alcohol OD - ✔✔Vomiting, respiratory depression, loss of consciousness, possible death.
Alcohol Withdrawal - ✔✔Trembling, autonomic hyperactivity, Anxiety, insomnia, vitamin deficiency,
confusion, hallucination, and convulsions.
Alcohol acute effects - ✔✔low doses: eupohoria, mild stimulation, relaxation, and lowered inhibitions.
high doses: drowsiness, slurred speech, nausea, emotional volatility, loss of coordination, visual
dostortions, impaired memory, sexual dysfunctions, loss of consciousness/increased risk or injuries,
violence, fetal damage.
Sedative Hypnotics desired effects - ✔✔Similar to alcohol. Reduction of anxity; possible elation,
secondary to decrease alertness and judgment.
Sedative Hypnotics acute effects - ✔✔Sedation, impaired judgement, impaired operation of vehicles,
respiratory and cardiac depression with overdose (much less likely with benzoidiazepines alone).
Sedative Hypnotics interaction with alcohol - ✔✔Potentiation of effects, especially respiratory
depression, Some degree of cross tolorance.
Sedative Hypnotics common problems - ✔✔Tolerance, dependence, addiction, elderly falls, respiratory
dpression
Sedative Hypnotics withdrawal - ✔✔Similar to alcoho, but may have slower onset. Severity and time of
onset vary wtih half life of drug. Mild: anxiety, restlessness, nausea, vomiting, insomnia, hpertention,
tachycardia, agitation, tremors, sensory, hypersensitivity, dizziness, confusion, fatigue. Severe:
Autonomic hyperactivity, vital sign instability, elevated temp, delusions, hallucinations, mania, delirium,
catatonia, seizures, tremulousness, altered perceptions, w/d seizures possibly leading to death.
Sedative Hypnotics Medical uses - ✔✔Sleep, anxiety, muscle relaxation, alcohol, and sedative/hypnotic
w/d, control of seizures includes Benzodiazepines, barbiturates, and others.
Sedative Hypnotics physica/mental exam - ✔✔Slurred speech, ataxia, stupor, coma, and for nonbenzo's
respiratory depression. confulsion, impaired judgement, delirium.
Cocaine action - ✔✔affects dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin levels. Blocks re-uptake of
dopamine, prolonging dopamine effects. Depleats it with prolonged use. Toxic effects on cardiac,
respiratory, and cns.
Amphetamines and Methylphenidate action (stimulant) - ✔✔Direct neuron release of dopamine and
norepinepherine and blockade of catecholamine re-uptake produce euphoric effects. Various toxic
effets on the sympathetic nervous system.
Stimulant physical and mental status - ✔✔pupils dialated, dry mouth, cardiac arrhythmias, twitching,
tremors, convulsions, stroke, coma, confusion, disinhibited behaivor, parnaoid thoughts, hallucinations,
hyper vigilance, elevation and or depression, suciadal behavior, impaired judgement.
Opiates Action - ✔✔Bind to opiate receptors in the cns where they block normally occuring opiate-like
substances.
Opiate acute effects - ✔✔sedation, decreased judgement, decreased ability to operate vehicles,
posssible respiratory depression if oding.
Opiate W/D - ✔✔Drug craving, dysphoria, anxiety, yawning, perpiration, sleep difficulties, fever, chills,
gooseflesh, abdominal cramps, nausea, diarrhea, muscle cramps, bone pain tears.
Opiate problems - ✔✔Rapid acquired tolerance, dependence, respiratory dpression, cellulitis, sepsis,
endocarditis, @ risk for HIV, and legal problems.
Opiate physical/mental exam - ✔✔Pupil constricted, relexes absent or diminished, pulmonary edema,
convulsions. Euphoria, sedation, possible normal mood, possible stupor.
Opiate users - ✔✔rate of relapse goes down by 60% 6 months to 1 year after stopping
methodone/suboxonel maintenance.
Medical Marijuana - ✔✔FDA has not cleared it. The ill affects of smoking far out weigh the medical
affects.
THC - ✔✔Fat soluable-stored in fat-time released, hard to recognize withdrawal.
Cannabis signs and symptoms - ✔✔Red eyes, mild dilation of pupils, mild tremor, decreased
coordination, decreased strength, less ability to perform complex motor tasks and dry mouth, feelings of
depersonalization, anxiety, panic, memory problems, alterationin mood disorganization, hallucinations,
paranoid thoughts.
Hallucination LSD acute effects - ✔✔panic attacks, increased b/p, heart palpitiations, tremors, nausea,
muscle weakness, increased body temp, ataxia, accidental dealth (believing one can fly).
Hallucination MDMA acute effects - ✔✔Nausea, jaw and teeth clenching, muscle tension, blurred vision,
panice attacks, confusion, depression, anxiety, paranoid psychosis, hyperthermia, and cardiac arrest.
Phencyclidine (PCP) Action - ✔✔Behvior effects believed to be meediated through the N-Methyl-D�Aspartate (ND) excitatory amino acid receptor-channel complex in the brain.
PCP acute effects - ✔✔visual illusions, hallucinations, and distroted perceptions, feelings of stregth,
power, and invulnerability, depresonalization, distorted body image.
PCP common problems - ✔✔Psychotic reactions, bizarre behavior, ooutbursts of hostililty and violence,
feelings of anxiety, doom or impending death, gross impairment of coordination, nystagmus,
hypersalivation, vomiting, fever. With longterm use: Persistent cognitive and memory problems speech
difficulties, mood d/o, loss of puposive activities and weight loss.
PCP w/d - ✔✔Limited reports of w/d effects. Depression, drug craving, increased appetitie and
increased need for sleep
PCP signs and symptoms - ✔✔Red eyes, muscle rigidity, increased reflexes, repetitive movements,
flushing, salivation, sweating, nausea, vomiting, possible coma, seizures, stroke. Abnormal appearance
and behavior, diorientation, inappropriateeffect, memory problems, depression, elation, suicidal or
homicidal behavior, and impaired judgement.
behavioral view of etiology - ✔✔suggests the influence of both positive and negative reinforcement as
causal factors for continued drug use.
pleasure pathway in the brain - ✔✔mesolimbic dopamine system
GABA transmitters - ✔✔located in the mesolimbic system stimulated by certain drugs
Alcohol flush syndrome - ✔✔causes an individual to feel sick after consuming alcohol because of a lack
of the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase.
aldehyde dehydrogenase - ✔✔breaks down acetaldehyde, a by-product of alcohol .
The treatment and recovery continuum of care - ✔✔identification, assessment, stabilization,
rehabilitation, relapse prevention and substance substitution (if necessary)
identification - ✔✔can be through self, court order, a condition of probation or parole, or intervention.
screening process helps determine the likelihood of a problem with drugs or alcohol
assessment - ✔✔the collection of data from the individual and corroborative sources to determine the
extent of the individual's problem and their strengths, weaknesses, and needs.
stabilization - ✔✔includes the need for detoxification at an appropriate medical facility if needed.
rehabilitation/treatment programs - ✔✔depends upon assessment and diagnosis and can range from
providing education, an intensive outpatient program to an inpatient residential program.
relapse prevention program - ✔✔a process whereby indentification of individualized triggers and a plan
to confront those triggers is developed
Stages of family response to drug and alcohol abuse - ✔✔denial, attempts to eliminate the problem,
disorganization and chaos, reorganization in spite of the problem, efforts to escape, family
reorganization.
Dysfunctional family roles - ✔✔family hero, mascot, scapegoat, lost child
pancreatitis - ✔✔this occurs when swelling of the pancreatic duct causes a backup of digestive juices
causing irritation and swelling of the pancreas.
acute fatty liver - ✔✔this occurs when fat deposits build up in the normal liver cells and can develop in
anyone who has been drinking heavily even for a short period of time.
acoholic hepatitis - ✔✔occurs after a heavy or extended bout of alcohol use and can occur in non�alcohol dependent persons. An inflammation of the liver where metabolism is disrupted, jaundice,
yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
cirrhosis - ✔✔permanent, widespread destruction of liver cells, which are replaced with nonfunctioning
scar tissue. irreversible and fatal if alcohol continues to be used.
alcoholic heart muscle disease or AHMD - ✔✔a serious condition in which the heart does not pump the
amount of blood needed to meet the demands of the body.
Beriberi heart disease - ✔✔a reduction of vitamin B-1 that over time cause a normal heart to fail to keep
up with an abnormally high metabolic need of the body.
Alcoholic dementia - ✔✔an overall decline of intellect
Wernicke's disease - ✔✔associated with Vitamin B1 deficiency and may be corrected nutritionally
Korsakoff's psychosis - ✔✔apparently irreversible condition characterized by the individual's inability to
learn new information and remember recent events.
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome - ✔✔combined condition of Wernicke's encephalopathy and Korsakoff's
syndrome - symptoms include nystagmus (abnormal eye movement), problems with gait, memory,
confabulation, low Bi, low blood pressure, tremor. Often called wet brain.
dependence - ✔✔a condition where, after using drugs, an individual finds it difficult or impossible to
control use. Dependence usually involves a physical and or psychological need for the drug in order to
function normally and it usually involves tolerance and withdrawal.
Physical dependence - ✔✔a state of functional adaptation to a drug in which the presence of a foreign
chemical becomes normal and necessary, and the absence of the drug would present an abnormal state.
Psychological dependence - ✔✔when the individual has a strong desire to continue to use the drug for
emotional reasons and is related to the rewarding effects of the drug. There are no physical withdrawal
symptoms with the discontinuation of use.
Cross-dependence - ✔✔this is evident when a person who is physically dependent on one drug can
lessen or prevent withdrawal symptoms by using other drugs from the same or similar classification.
Tolerance - ✔✔an altered physiological state that develops after repeated drug use when the body
becomes accustomed and adapts to the presence of the drug and functions normally. Evidence of this is
when the drug has less of an effect when using the same dose, or when a larger dose must be used to
get the desired effect.
Pharmacodynamic tolerance - ✔✔when the nerve cells become less sensitive to the effects of the drug
over time and repeated use
metabolic tolerance - ✔✔when the liver adapts to the presence of a drug over time and may produce
more of the enzyme needed to break down the drug.
behavioral tolerance - ✔✔when after a period of time and repeated drug use, the users are able to
modify their behavior in hopes that others will not notice they are intoxicated
reverse tolerance - ✔✔when the individual can become more sensitive to the drug's effects rather than
less sensitive. Also known as the kindling effect.
half-life - ✔✔the length of time a drug remains in the body and continues to affect the user.
effective dose - ✔✔the amount of a drug necessary to get the desired effect in about 50 percent of
those who use the drug
therapeutic index - ✔✔the dose determined to be safe for use and get the desired effect; determined by
dividing the lethal dose by the effective dose
potency - ✔✔the amount of a drug necessary to produce the desired effect.
drug interaction classifications - ✔✔addititive, synergistic, antagonistic
additive effects - ✔✔two or more drugs are used at the same time and the results are equal to the sum
of the actions of the drugs used.
synergistic interactions - ✔✔when two or more drugs are used at the same time, and the results are
greater that the sum of the actions of the drugs used.
antagonistic interactions - ✔✔occur when two or more drugs are used at the same time, and the results
are less than the sum of the actions of the drugs or the drugs cancel out the effects of each other.
Routes of administration - ✔✔how a person takes substances into the body
oral administration - ✔✔taken by mouth and swallowed into the stomach.
injected - ✔✔using a needle and syringe
subcutaneously - ✔✔skin-popping, injecting in the fatty layer just under the external skin.
intramuscularly - ✔✔injected into the large muscles
intravenously - ✔✔injected directly into a vein
inhalation - ✔✔substances can be inhaled into the lungs by smoking or huffing
snorting - ✔✔drugs can be inhaled into the nose and absorbed through the mucous membranes.
transdermal - ✔✔the drug is absorbed through the skin from a patch.
buccal administration - ✔✔the drug is absorbed through the mucous membranes in the mouth.
rectal administration - ✔✔Drugs are administered by inserting them into he body through the rectum
and are absorbed through the intestinal lining.
neorotransmitters - ✔✔GABA, norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, acetylcholine.
GABA - ✔✔relates to inhibitory factors and slows communication.
Norepinephrine - ✔✔associated with arousal reactions and moods.
Dopamine - ✔✔associated with feeling of pleasure.
Serotonin - ✔✔associated with feelings of anxiety, depression and aggressiveness.
Acetylcholine - ✔✔associated with arousal reactions or inhibitory factors.
Pleasure/reward center of the brain - ✔✔made up of the ventral tegmental area (VTA), nucleus
accumbens and other structures of the brain.
Fat-soluble drugs - ✔✔These store in the fatty areas of the body and can have longer lasting traces in
the body that water-soluble drugs do not.
Abuse potential - ✔✔generally related to the drug's speed of action and how long the effects last.
Contolled Substance Act - ✔✔Law which places drugs in 1 of 5 schedule categories, depending on their
abuse potential, potential for dependence/addiction, and currently accepted medical use.
Schedule I - ✔✔Any drug included here has a high level of abuse/dependence. Also, there is no accepted
medical use. Include are heroin, LSD and marijuana.
Schedule II - ✔✔Drugs in this category are essentially similar to Schedule I, but with an accepted medical
use. There are restrictions on manufacture and distribution via production quotas and import/export
controls. Non-refillable meds. Include methadone, morphine, methamphetamine and cocaine.
Schedule III - ✔✔Drugs in this category are considered to be at moderate or low risk for physical
dependence, and with current reasons for medical use. Includes anabolic steroids, most barbituates and
ketamine.
Schedule IV - ✔✔Drugs in this category are considered to be at low risk for physical dependence but
moderate risk for psychological dependence and have a currently accepted medical use. Includes Xanax,
Barbital and chloral hydrate.
Schedule V - ✔✔Drugs in this category are considered to be at low risk for either physical dependence or
psychological dependence, and with current indications for medical use. Includes medical mixtures using
small amounts of opium or codeine.
Depressants/Sedative-hypnotics - ✔✔These drugs are central nervous system depressants. Include but
are not limited to: alcohol, benzodiazepines and barbituates. In general these drugs bind to GABA
receptors resulting in sedation.
Stimulants - ✔✔Drugs in this class increase cental nervous system activity. Includes cocaine,
amphetamines, methamphetamines, and methylphenidate.
Hallucinogens/Dissociatives - ✔✔These drugs change sensory perception and have the ability to alter
reality and produce hallucination-like effects. Includes naturally occuring and synthetic drugs such as:
LSD, mescaline, psylocybin, psilocin, MDMA, PCP and ketamine.
Cannabinoids/cannabinols - ✔✔Includes marijuana, hashish and THC
Inhalants - ✔✔Chemicals that can be legally purchased and that are normally used for non-recreational
purposes. Includes industrial solvents and aerosol sprays and include, but are not limited to: gasoline,
kerosene, airplane glue, acetone, lighter fluid, metallic paints, correction flids, amyl, butyl and isobutyl
nitrite and nitrous oxide.
Anabolic steroids - ✔✔Synthetic illicit drugs that are used to increase muscle mass and improve athletic
performance. Include Depo-testosterone, Durabolin, Danocrine, and Halotestin. Some are approved for
veterinary medicine and sold illicitly for human use.
Stacking - ✔✔combining oral and injectable steroids.
Symptoms of Depressant intoxication - ✔✔decreased inhibition, slowed reaction times, memory
impairment, possible decrease in respirations, slurred speech, ataxia,
Symptoms of Stimulant intoxication - ✔✔increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure and
temperature, decreased respiration. dilated pupils, dry mouth, cardiac arrhythmias, twitching tremors,
impaired judgment, confusion, disinhibited behavior, paranoid thoughts, hypervigilance, hallucinations,
elation.
Symptoms of PCP adverse reactions - ✔✔psychotic reactions, bizarre behavior, outbursts of hostility and
violence, severe anxiety, doom or impending death.
Adverse Ketamine reacation - ✔✔Completed sensory detachment, explained as a near-death
experience, paranoia, boredom and possible coma.
Symptoms of cannabinoid intoxication - ✔✔slowed reaction time, altered perceptions, panic, anxiety,
nausea, dizziness, depersonalization, paranoid thoughts, trouble expressing thoughts. May cause
increases in respiration and heart rate and a slight increase in body temperature. Red eyes, mild dilation,
mild tremors, decreased coordination, decreased strength, less ability to perform complex motor tasks
and dry mouth.
Symptoms of Inhalant intoxication - ✔✔reduction of inhibition and euphoria, dizziness, slurred speech,
unsteady gait and drowsiness. Nystagmus may be noted, altered consciousness and enhanced sexual
pleasure.
Nystagmus - ✔✔the constant involuntary movement of the eyes.
Ataxia - ✔✔impaired gait
Whether we see drug use as a problem depends on all of the following: - ✔✔Reason one takes a drug
Quantity consumed and the manner by which one takes the drug
When and where the drug is used
The age of the individual taking the drug
In reference to psychoactive drug use, it is important to recognize that: - ✔✔History and expectations
influence how one is affected by a drug.
Type I error - ✔✔alpha error - null hypothesis is rejected as false or unproven when it is actually true.
The highest rates of illicit drug use are in what age group? - ✔✔18 to 25
Drug use is positively correlated with? - ✔✔rejection of traditional cultural systems
No Wrong Door - ✔✔Treatment is available at every point of someone trying to get help in any stage of
substance abuse.
The first of the pharmacological revolution was associated with the development of? - ✔✔vaccines
The age group that is least likely to have used alcohol in the previous 30 days is? - ✔✔12 to 17
Which of the following is an example of behavioral toxicity? - ✔✔driving inattentively after smoking
marijuana
An experiment in which rats were allowed to self-inject drugs showed that the rats? - ✔✔were more
likely to die form cocaine than heroin
Which drug is most clearly linked to violent crime? - ✔✔alcohol
Alcohol use is associated with? - ✔✔3/5 of all murders
40% of all assaults
1/3 of forcible rape and child molestation
50% committing violent crime
The number of people in the US arrested for drug-law violations each year is? - ✔✔1,000,000
About 1/2 of the emergency room episodes and 3/4 of the drug related deaths are associated with? -
✔✔multiple drug episodes
All of the following are types of prevention: - ✔✔primary prevention
secondary prevention
tertiary prevention
All of the following are key elements of the social influence model: - ✔✔training refusal skills
countering advertising
use of teen leaders
Type II errors - ✔✔beta error- null hypothesis is not rejected when it is actually false. Often result of too
small of sample size.
Tertiary prevention programs are those aimed mainly at? - ✔✔people who have been treated for
substance abuse or has stopped the substance abuse without assistance
Secondary prevention programs are those aimed mainly at? - ✔✔People who have tried the drug in
question or a variety of other substances
Naltrexone-synthetic opioid antagonist - ✔✔blocks opioids from binding to receptors
reduces craving for alcohol
was approved by the FDA in 1994 for the treatment of alcoholism
Disulfiram: Trade name Antabuse - ✔✔Tablet by mouth once daily - may be crushed. 250mg or 500 mg.
Typically begins about 10 to 30 min after alcohol is ingested.
May occur for up to 14 days after last dose.
Inhibits the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase
Alcoholics Anonymous believes that alcoholism - ✔✔Is a disease and the only cure is total abstinence.
Some critics say it gives alcoholics an "excuse".
The process by which alcohol concentration is increased to more than 15%? - ✔✔distillation
In most commercial beers today, alcohol content is a little over? - ✔✔4%
Alcohol WD symptoms 6-24 hours after last drink. - ✔✔tremors, nausea, anxiety, irritablility
insomnia, feelings of unreality
convulsions
hallucinations
Thirty years ago, when people spoke of addiction they were most likely thinking of? - ✔✔Heroin
The three basic processes related to the concept of addiction are? - ✔✔tolerance, physical dependence,
reinforcement
Tolerance refers to? - ✔✔The diminishing effect of a drug as a result of repeated exposure to the same
dose of the drug.
Withdrawal syndrome refers to? - ✔✔A set of consistent symptoms that appear when drug usage stops.
The driving force behind narcotic addiction? - ✔✔The reinforcing effect of a drug on the brain rather
than fear of withdrawal.
In relation to physical dependence, psychological dependence is? - ✔✔A greater problem, since many
addicts have gone through withdrawal will later relapse.
ANOVA - ✔✔Factorial analysis of variance - used in the study of 2 or more variables. Most common is
the 2x2 where there are 2 independent variables with each having 2 distinct values.
Chemicals released from neurons (nerve cells) are called? - ✔✔neurotransmitters
The neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junctions in the somatic system is? - ✔✔acetylcholine -
patients who die from Alzheimer has less than normal amount
the basal ganglia is important for - ✔✔maintaining proper muscle tone
Clonidine (Catapres) - ✔✔Used for opioid detoxification.
Advantages of Clonidine over Methadone - ✔✔Does not produce opioid intoxication and is not
reinforcing.
Not classified as having abuse potential
detox occurs w/o opioids
no special licensing is required.
Buprenorphine forms? - ✔✔Buprenex-injectable form
Subutex-oral form (starting treatment)
Suboxone-buprenorphine and nalxone(intedend for persons dependent on opioids who have already
started and are continuing medication therapy.)
Stimulants can produce at moderate doses? - ✔✔Wakefulness and a sense of well-being. Cocaine and
amphetamines (methamphetamine) are the most frequently abused CNS stimulants.
Opiates can produce at low doses? - ✔✔a relaxed dreamlike state
Major tranquilizers are now referred to as? - ✔✔antipsychotics
The safety margin of a drug is measured by the: - ✔✔difference between the effective dose level and
the lowest toxic dose
Drug absorption is most rapid when the intramuscular injection is given into the? - ✔✔deltoid muscle
The fastest method by which the drug is delivered to the brain is? - ✔✔inhalation
The reduced effect of a drug that may result from more rapid metabolism or excretion of the drug is
referred to as? - ✔✔drug disposition tolerance
Speedball is generally the combination of? - ✔✔heroin and cocaine
In the 1960s, cocaine became popular again because? - ✔✔amphetamines became harder to obtain
In South America, a popular way to use cocaine is? - ✔✔coca paste
Crack? - ✔✔cocaine mixed with baking soda
Cocaine's behavior effects are believed to depend on blocking the reuptake of? - ✔✔dopamine and
serotonin
A smokeable form of methamphetamine is referred to as? - ✔✔ice
The current drug of choice for treating attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is? -
✔✔methylphenidate(Ritalin) and dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine) - CNS stimulant most commonly
abused along with opioids and CNS depressants.
The most widely-used sedative-hypnotic drug is? - ✔✔alcohol
Nonbarbiturate paraldehyde is not used because? - ✔✔has a noxious taste and odor
Drugs used to induce sleep are called - ✔✔hypnotics
A popular sedative that was introduced in 1960? - ✔✔Chlordiazepoxide(Librium)- benzodiazepine
Meprobramate - ✔✔Anti-anxiety drug became very popular in the 1950's. Miltown, Equanil, Meprin -
sedative and tranquilizer used to treat muscle tension and anxiety.
Quaalude and Sopor were brand names for - ✔✔methaqualone- Schedule 1 drug
Benzodiazepines - ✔✔Combined sales of the make them easily the most widely prescribed drug class.
Flumazenil (Romazicon) acts at the receptor and reverses the sedative and overdose effects, but not
alcohol or other sedative-hypnotics.
The DSM-IV now refers to neurosis as? - ✔✔anxiety disorder
Bipolar depression is a mood disorder? - ✔✔characterized by manic-depressive
General paresis refers to? - ✔✔a syphilitic infection of the nervous system
1933 to help schizophrenic patients, Sakel used what? - ✔✔insulin
Ugo Cerletti introduced electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) to treat? - ✔✔schizophrenia
Phenothiazines are now referred to as? - ✔✔Antipsychotics
Indivdiuals who use antipsychotic drugs may? - ✔✔exhibit photosensitivity and jaundice
More than half of the prescribed antidepressants are prescribed by? - ✔✔non-psychiatrists
Lithium was demonstrated to be effective on - ✔✔manic patients
About how many homeless people in the US have some form of mental illness? - ✔✔33%
"The way to tell whether a man is having drinking problems is to ask..." - ✔✔The BEST answer is
"whether he has tried several times without success to reduce his drinking."
What is the misconception of dependence potential for all psychoactive drugs? - ✔✔They are all not
rated as "high". i.e. alcohol, marijuana, or hallucinogens they are moderate.
When 2 or more psychoactive drugs are consumed together, the most serious risk from their
"interaction" is? - ✔✔Respiration-Breathing, which can slow down to the point of starving the brain of
oxygen. Blood pressure or circulation may also be at risk.
BAC and metabolism in a standard drink has ½ ounce of ethanol, and the body eliminates ¼ ounce of
ethanol per hour or 10-30 mg(.01-.03) - ✔✔"If you drink faster than one drink every two hours, your
BAC will climb."
Overall, the dependence risk from alcohol use? - ✔✔It is neither low nor high but moderate.
When US deaths are classified and ranked according to the contributions of alcohol and other drugs,
TOBACCO causes the most deaths, followed by alcohol, and then all other drugs. - ✔✔Some of the "all
other drugs" are cocaine, heroin, and tranquilizers.
Alcohol ranks SECOND after WHAT? - ✔✔tobacco and before drugs in annual deaths - after tobacco and
other drugs
analgesics - ✔✔Drugs used to relieve or eliminate pain
acetylsalicylic acid - ✔✔the chemical known as aspirin
antipyretic - ✔✔fever reducing
NSAID - ✔✔nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen
chlorpheniramine maleate - ✔✔a common antihistamine in cold products
dextromethorphan - ✔✔an OTC antitussive (cough control) ingredient
Antihistamines - ✔✔OTC sleep aids are based
[Show More]
.png)
.png)



.png)