NAADAC Module Two Study Guide
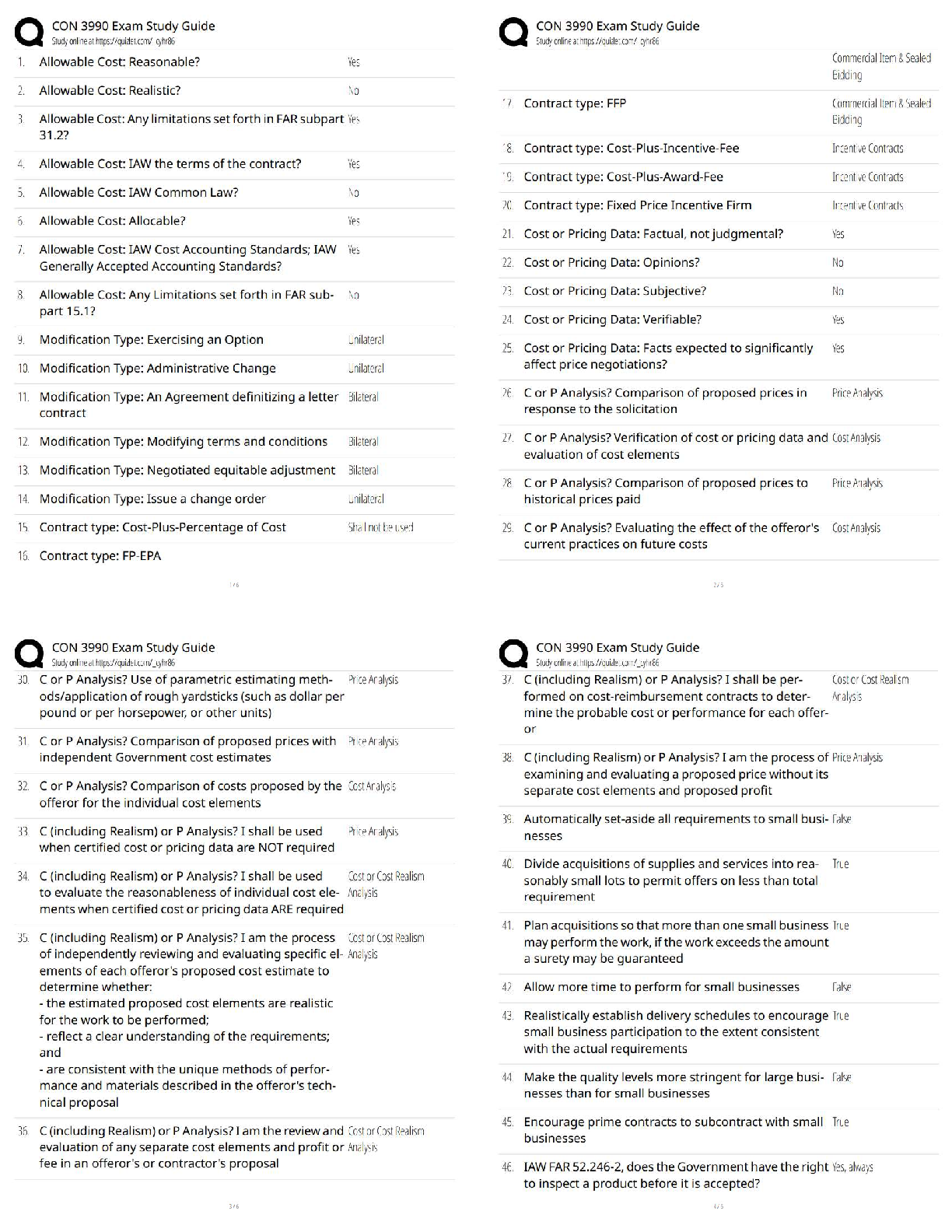
Updated Version. Questions with
accurate answers. Graded A+
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*What is the basis?* - ✔✔It is holistic in nature and we are all striving towards superiority
...
NAADAC Module Two Study Guide
Updated Version. Questions with
accurate answers. Graded A+
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*What is the basis?* - ✔✔It is holistic in nature and we are all striving towards superiority and
perfection, must learn how to deal with feelings of inferiority.
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*What is the method of counseling?* - ✔✔A method of counseling, which is also called individual
Psychology, where all behavior is believed to be purposive and goal directed
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*What is Fictional Finalism?* - ✔✔A component of Adlerian therapy is an imagined central goal that
gives a client purpose and guides his or her behavior.
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*Phenomenology*. - ✔✔To use Adlerian therapy effectively, an addiction counselor or other helping
professional must attempt to view the world from the perspective of the client through a process called
*phenomenology.*
ln other words, the client can only be understood in terms of his or her family, social and cultural
contexts, perceptions and private loqic.
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*Private Logic* - ✔✔*Private logic* is reality as we perceive it; it is subjective, and the behavior that
results from it can change if the client's perceptions change.
Addiction counselors and other helping professionals must recognize the client's perspective and work
to create change within it.
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*Lifestyle* - ✔✔A component of Adlerian therapy that refers to the client's chosen method of moving
through life.
Adlerian Psychology (Therapy)
*Social Interest* - ✔✔A component of Adlerian therapy that is an awareness of being a part 0f the
human community and how one interacts with the social world.
Behavior Therapy
*What is the basis?* - ✔✔A method of therapy that focuses on modifying the client's learned behaviors
that are negatively affecting their lives.
Behavior Therapy
*What is classical conditioning?* - ✔✔*Think Pavlov's dog*, where a particular response to a stimuli can
be elicited over time by association with another related stimuli, like ringing of the bell when food is
given to the dog.
Behavior Therapy
*Operant Conditioning* - ✔✔Think BF Skinner and his little girl, where behavior is reinforced and
learned based on the consequences of the behavior.
Behavior Therapy
*Social Learning Approach* - ✔✔Think the post toasties cereal joke - A method of behavior therapy
developed by Albert Bandura where *behavior is learned by observing the consequences of someone
else's experience.*
Behavior Therapy
*How is it applied?* - ✔✔Tokens for sobriety i.e. AA Chips
Cue Exposure Treatment
Aversion Therapy i.e. Antabuse - Schick Shadel
Cognitive Behavior Therapy
*What is the basis?* - ✔✔An method of counseling that focuses on simultaneously learning new
behaviors and restructuring automatic thoughts,.
Cognitive Behavior Therapy
*Where it does not work well* - ✔✔For the client who is unwilling to be engaged in therapy and do the
homework.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
*History and Original Intent* - ✔✔Modified form of CBT originally designed to treat suicide patients
who meet the diagnosis for *borderline personality disorder*.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
*What else is DBT used for?* - ✔✔Shown empirically to be useful for substance dependence,
depression, post- traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and eating disorders.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
*Main Principal* - ✔✔*Mindfulness* - Essential and core skill
*Interpersonal Effectiveness* - Similar to assertiveness training
*Distress Tolerance* - This involves accepting, finding meaning for, and tolerating distress
*Emotional Regulation* - Learning to regulate emotions
Family Systems Counseling
*Six Basic Family Roles* - ✔✔*Substance Abuser*
*Enabler*
*Hero*
*Scapegoat*
*Lost Child*
*Mascot* - Most likely to commit suicide
Family Systems Counseling
*Common Family Approaches* - ✔✔*Bowenian Family Therapy* triangulation, genograms
*Experiential/Humanistic Family Therapy* Focuses on the present, promoting choice, self-determination
and actualization
*Family Disease Model* Family disease
*Structural Family Therapy* enmeshment - boundaries
*Strategic Family Therapy* directives
Gestalt Therapy
*Basis* - ✔✔A method of counsering where a client gains awareness of his or her behavior and learns
how to accept personal responsibility for those behaviors
Gestalt Therapy
*Key Aspects* - ✔✔*Genuineness* must occur between the client and the therapist
*Projective Therapy* Think empty chair approach
Gestalt Therapy
*Other Key Tenets* - ✔✔*Existentialism* focuses on present day and stresses personal responsibility
for one's own destiny
*Unfinished Business* Unexpressed feelings from childhood that now interfere with healthy functioning
*Contact* process of interacting with nature and with other people without losing one's sense of
individuality
Medication Assisted Treatment
*Basis* - ✔✔The use of prescriptions to assist and support a client's ongoing counseling and recovery
Medication Assisted Treatment
*Types* - ✔✔*Sensitizers* Overly sensitizes Antabuse
*Antagonists* Block the effects Naltrexone
*Opioid Inverse Agonist* both opioid-like properties and can also be a blocker of opioids Buprenorphine
*Psychotropics* dual diagnosis anti-depressants
Person Centered Therapy
*Basis* - ✔✔The client, not the counselor directs the course of the treatment process
Person Centered Therapy
*Main Principals* - ✔✔*Humanism:* A philosophical movement that focuses on the innate nature
within all humans to achieve our potential and find meaning in our lives
*Congruence:* This is the most important of the three attitudes. lt is a condition where the counselor is
consistently *genuine or real*, the counselor is able to match his or her external behavior with inner
thoughts and feelings
*Unconditional Positive Regard:* A component of person- centered therapy where a counselor shows
the client constant acceptance and caring.
*Accurate Empathic Understanding:* The ability to
identify with and understand the subjective world of a client; also a component of person-centered
therapy
Psychoanalytical Theory
*Basis* - ✔✔A *deterministic method* of counseling where the mental dysfunction results from a
client's internal conflicts, processes and memories.
Psychoanalytical Theory
*Key Principles* - ✔✔*Unconscious Mind:* A part of the human psyche that functions outside of the
awareness of the individual
*Analysis of Resistance:* A component of psychoanalytical therapy where a client surfaces repressed
material from the unconscious mind up to the conscious mind,
*ld:* A component of psychoanalytical therapy that is the source of unconscious aggressive and sexual
urges
*Ego:* A component of psychoanalytical therapy that is the mediator between the id and superego
*Super Ego:* A component of psychoanalytical therapy that is the source of moral urges
*Defense Mechanism:* A technique employed by the ego when a conflict between the superego and id
causes anxiety, according to psychoanalytical therapy
Rational-emotive;behavior Therapy (REBT)
*Basis* - ✔✔A method of counseling that focuses on changing the problematic beliefs ol an individual as
a result of the events in his or her life
Rational-emotive;behavior Therapy (REBT)
*Key Principal* - ✔✔*Activating Events:* According to rational-emotive- behavior therapy, they are
events that occur in an individual's life that lead to a reaction (belief) about that event,
*Beliefs:* How a person feels or thinks about an activating event; a component of rational-emotive�behavior therapy.
*Consequences:* How an individual behaves based on his or her beliefs concerning an activating event;
a component of rational-emotive-behavior therapy
Rational-emotive;behavior Therapy (REBT)
*The A-B-C Theory* - ✔✔ABC Model of REBT
*A* = Activating Event
*B* = Beliefs
*C* = Emotional and Behavioral Consequences
ln therapy, the therapist also introduces *D (disputing intervention)*, *E (the effect of D)*, and *F (the
new feeling that results from E)*.
Reality Therapy/Control Theory
*Basis* - ✔✔A method of counseling that focuses on how a client perceives the external world and the
behaviors he or she exhibits to fit those perceptions and needs.
Reality Therapy/Control Theory
*Central Question of Reality Therapy* - ✔✔ls what you are choosing to do getting you what you want?
Reality Therapy/Control Theory
*Key Principal" - ✔✔*Success Identity:* A component of reality therapy/control theory where a person
feels he or she has seltworth, is powerful, and is able to love and be
Reality Therapy/Control Theory
*Total Behavior* - ✔✔Doing
Thinking
Feeling
Physiology
Reality Therapy/Control Theory
*Eight Basic Principles* - ✔✔1) develop a therapeutic relationship
2) focus on the client's current behavior
3) ask the client to evaluate the behavior
4) develop plans for change;
5) get a commitment from the client
6) do not accept any excuses
7) do not use punishment
8) never give up on the client
Solution-Focused Therapy
*Basis* - ✔✔What is possible in developing solutions, rather than attempting to understand the
problem.
Solution-Focused Therapy
*Key Principle* - ✔✔*Utilization:* A component sf solution- focused therapy where the counselor helps
the client utilize previous successes to motivate change
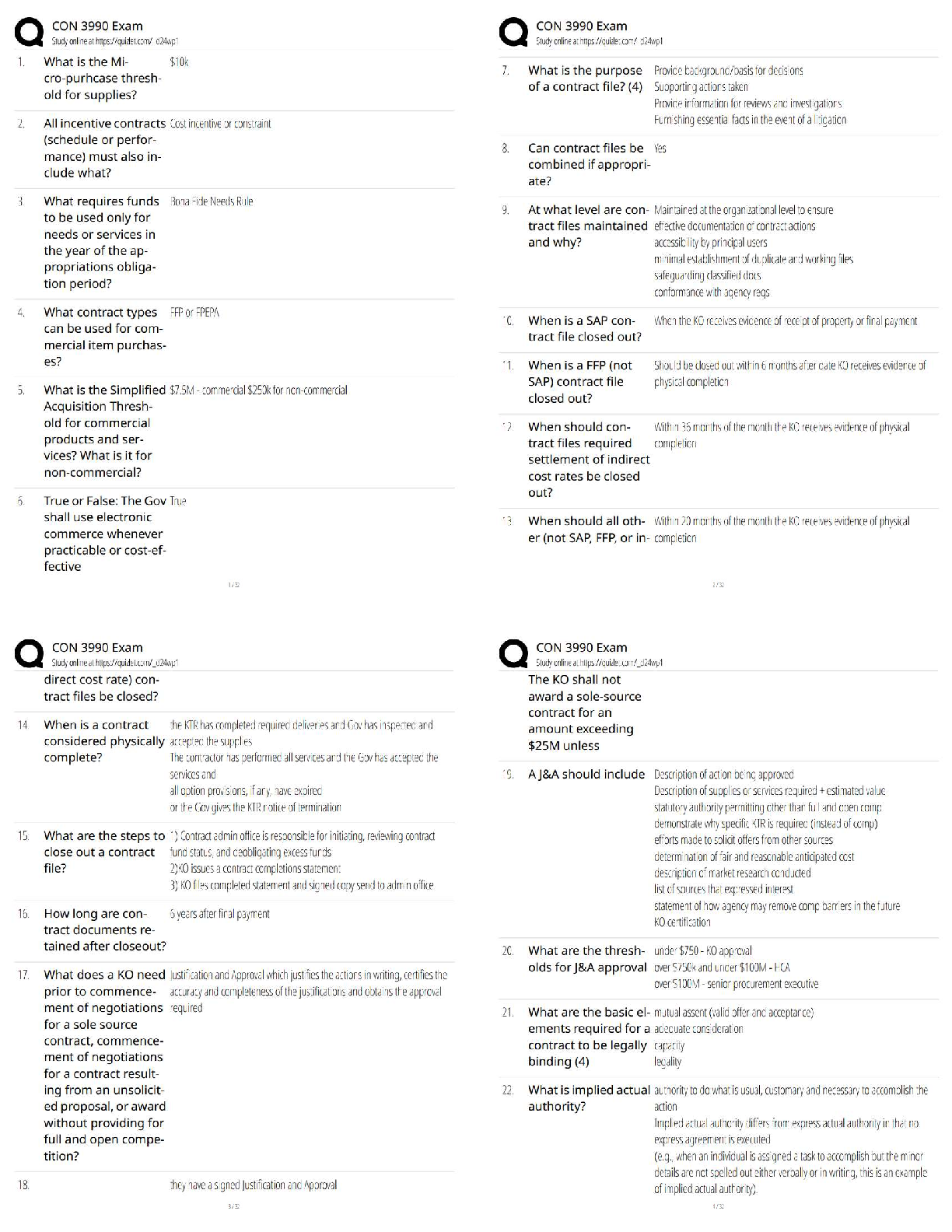
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Evaluation* - ✔✔A systematic and ongoing process in which a relationship is initially formed with the
evaluating counselor in the initiation of a two-phase process: *Screening* and *Assessment*
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Screening* - ✔✔The first phase of evaluation where the potential client is briefly interviewed to
determine if he or she is appropriate for that specific facility
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Intake* - ✔✔Generally the business end of services that must be finalized before treatment can begin
i.e. ROIs, Consent for services, clarification of fees, etc
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Assessment* - ✔✔The second phase of evaluation where the client is interviewed extensively to
determine the most effective treatment plan after he or she is admitted into the treatment program.
*Assessment of the client's history, experiences and mental status*
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Assessment generally has five major objectives* - ✔✔*1)* To identify those who have a condition
related to a psychoactive substance use disorder.
*2)* To assess the full range of difficulties currently experienced by the client. The addiction counselor
or other helping professional should rate the symptom severity, diagnose evident mental health
disorders and screen for related difficulties or challenges;
*3)* To plan appropriate treatment interventions for the client;
*4)* To involve the appropriate family members or significant others in the client's evaluation and
treatment;
*5)* To determine the methods for evaluating the effectiveness of the treatment interventions that will
be implemented.
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF)* - ✔✔Pre DSM5 for accessing for Axis V
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Individualized Treatment Plan* - ✔✔*Reflects the salient points of the assessment and outlines the
next steps for the client.*
lt is important for the *client to be involved* in this process as it fosters a sense of ownership and,
internal motivation to pursue the agreed upon goals,
Addiction Counseling Practices
*Treatment Plan Key Elements* - ✔✔Need
Goal Statement
Measurable Objective
Strategies and Interventions
Addiction Treatment Modalities
*Brief Therapy* - ✔✔Brief therapy does not point to any specific therapy or theoretical approach but
rather is a relative set of therapies that includes a shorter time period and fewer sessions than
"traditional" therapy.
Addiction Treatment Modalities
*Brief Therapy Parts* - ✔✔Induction Phase
Alliance (Pretreatment)
Refocus/Change
Termination/Homework
Continuation/Followup
Addiction Treatment Modalities
*Motivational Interviewing* - ✔✔non-directive approach to counseling that uses the internal
motivation of a client to evoke and sustain rapid change, instead of counselor interpretation and
discovery
Addiction Treatment Modalities
*Motivational Interviewing - OARS* - ✔✔O = Ask *Open*-ended questions
A = *Afflrm* the client for change
R = Listen *Reflectively*
S = Provide *Summaries*
Addressing Relapse
*True or False: Relapse is unpredictable* - ✔✔*False*
Relapse is usually preceded by clearly def
[Show More]