Earth Science > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > IB ESS TOPIC 7, Exam Questions section and answers, 100% accurate, (All)
IB ESS TOPIC 7, Exam Questions section and answers, 100% accurate,
Document Content and Description Below
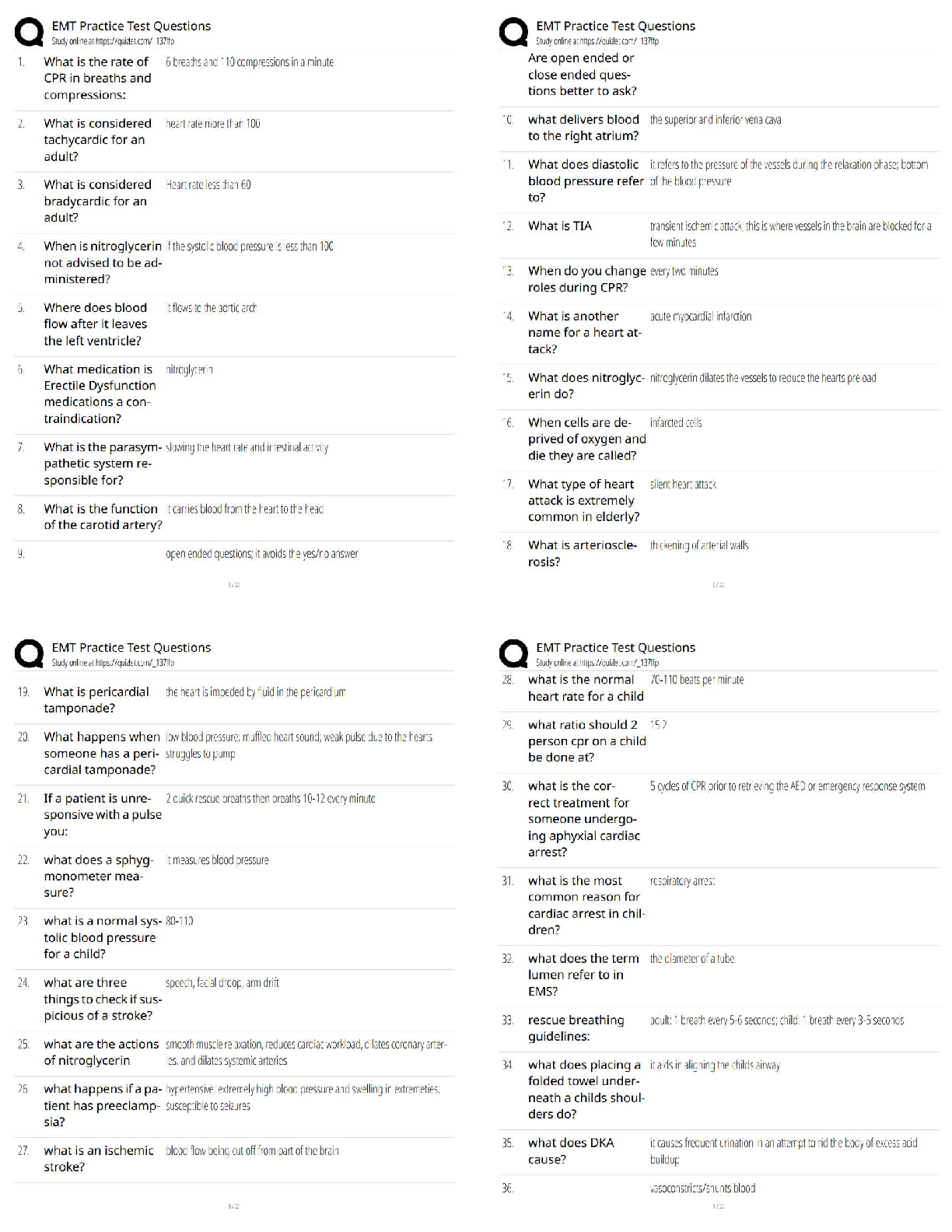
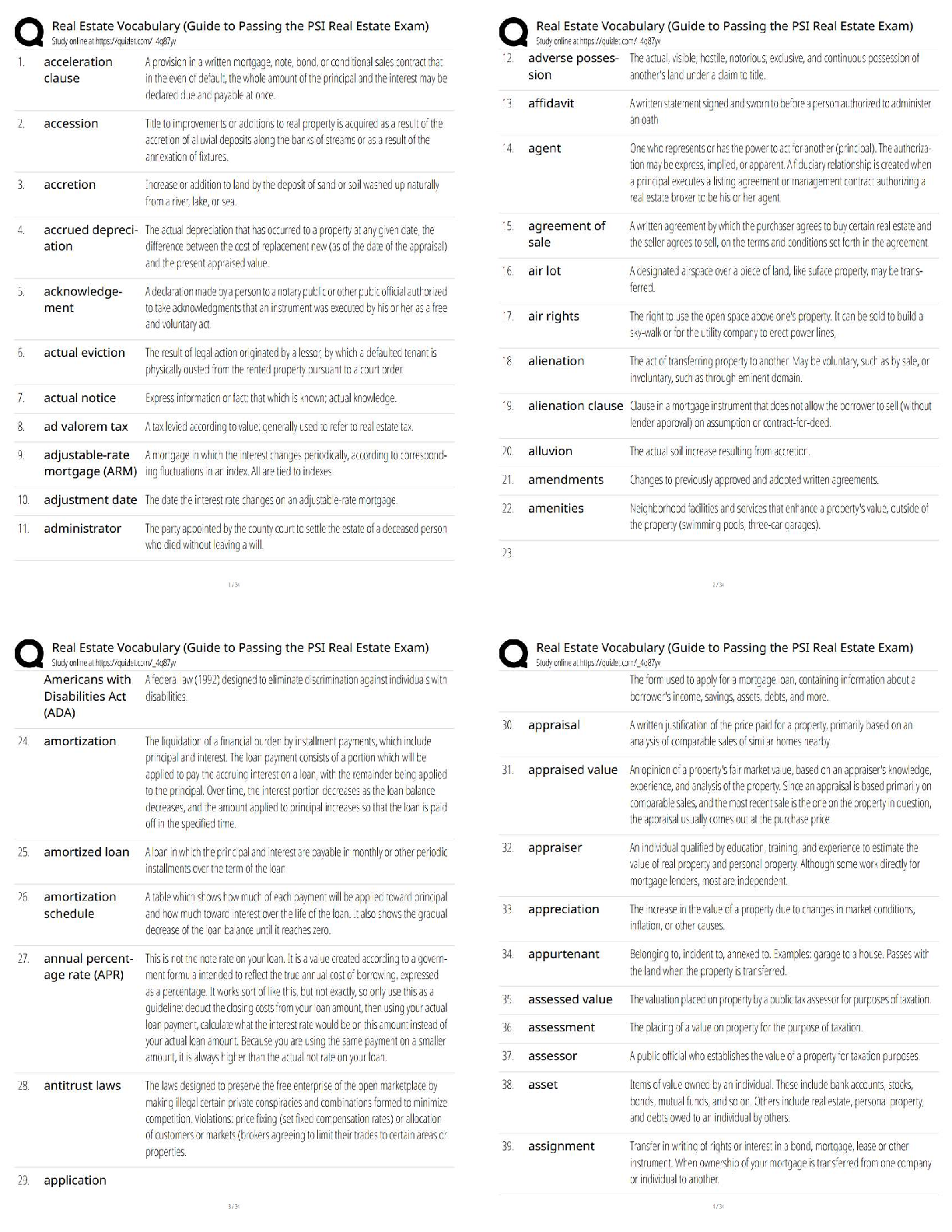
IB ESS TOPIC 7, Exam Questions section and answers, 100% accurate, Renewable - ✔✔-Natural resources that have a sustainable yield or harvest equal to or less than their natural productivity ... Non-Renewable - ✔✔-natural resources that cannot be replenished within a timescale of the same order as that at which they are taken from the environment and used (e.g. fossil fuels) Fossil fuels - ✔✔-non-renewable resources including oil, coal, natural gas and shale gas Oil - ✔✔-Advantages - cheap, versatile raw material - easy to transport - found in geological structures - reserves could last for another 40 years with present rates of C/P Disadvantages - oil spills - damages coastlines, fish stocks and sea communities - finite resource, non-renewable - burning contributes to global warming through release of CO2 Hydroelectric Power - ✔✔-Advantages: - renewable, harnesses fast-flowing water with a sufficient volume - clean: does not emit greenhouse gases - stations are often associated with aluminium smelters to use up excess energy Disadvantages: - Plants/stations expensive to build - few places have a sufficient water - plants must run at full capacity to make money - may affect routes of migratory fish and mammals - increased evaporation behind the dam and deposition of silt - diseases: schistosomiasis can be spread by the stagnant water - fish yields downstream can be adversely affected by the trapping of sediments behind the dam Solar Power - ✔✔-Advantages: - no finite resources are involved - less environmental damage caused - no atmospheric pollution given off - energy from sun is clean, renewable, so abundant that amount of energy received by Earth in 30 mins from sun = all power used by humans in 1 year - suitable for small-scale and large-scale production Disadvantages: - affected by clouds, seasons, day length, cannot be guaranteed to work in all locations - high costs make it difficult for industry to achieve its full potential - currently does not make a significant contribution to energy efficiency - each unit of electricity generated costs between 4 and 10 times as much as that derived from fossil fuels Coal - ✔✔-Advantages: - responsible for development of western industrial growth - thick, level, continuous seams are most competitive and use machinery - used for production of electricity in the thermal power stations and the smelting industry (e.g. iron and steel) Disadvantages: - dirty, bulky, costly and difficult to transport - inefficiencies in early forms of transport and machinery meant industries had to be located on coalfields - open-cast mining causes serious visual and noise pollution - burning coal contributes to acid rain, global warming " Energy Security - ✔✔-- adequate, affordable and reliable supply of energy - poverty affects this - lack of energy can impact negatively on social and economic development, may lead to conflict Energy Conservation - ✔✔-- efforts to reduce energy consumption - e.g. wearing extra clothing or using a blanket rather than a heater is conserving - e.g. double or triple glazing windows, cavity wall and loft insulation, switching off lights Energy Efficiency - ✔✔-- attempts to improve products and services so that less energy is required to function - e.g. fluorescent lights and LED lights reduce amount of energy needed to provide light for an area - many modern appliances (fridges, washing machines) require less energy compared with older models Atmospheric Circulatory Systems - ✔✔-- winds from low altitudes tend to be warm, winds from high altitudes are cold - winds blowing over oceans are moist whereas winds blowing over land are dry - winds can have seasonal influences e.g. Asian monsoon greenhouse gases - ✔✔-atmospheric gases that absorb infrared radiation, causing world temperatures to rise Impacts of climate change - ✔✔-1. biomes shifting 2. change in location of crop-growing areas 3. changed weather patterns 4. coastal inundation (due to thermal expansion of oceans from melting ice caps) 5. human health (spread of tropical diseases) Forms of GHGs - ✔✔-water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, CFCs, ozone and nitrogen oxides CO2 sources - ✔✔-respiration, breakdown of organic matter, volcanic vents, burning fossil fuels + organic materials, and forest fires Methane sources - ✔✔-wetlands, bogs, stagnant water bodies, rice paddies tundra soils, breakdown of organic material, volcanic vents, livestock, landfill sites, m [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 8 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 16, 2023
Number of pages
8
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 16, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
113