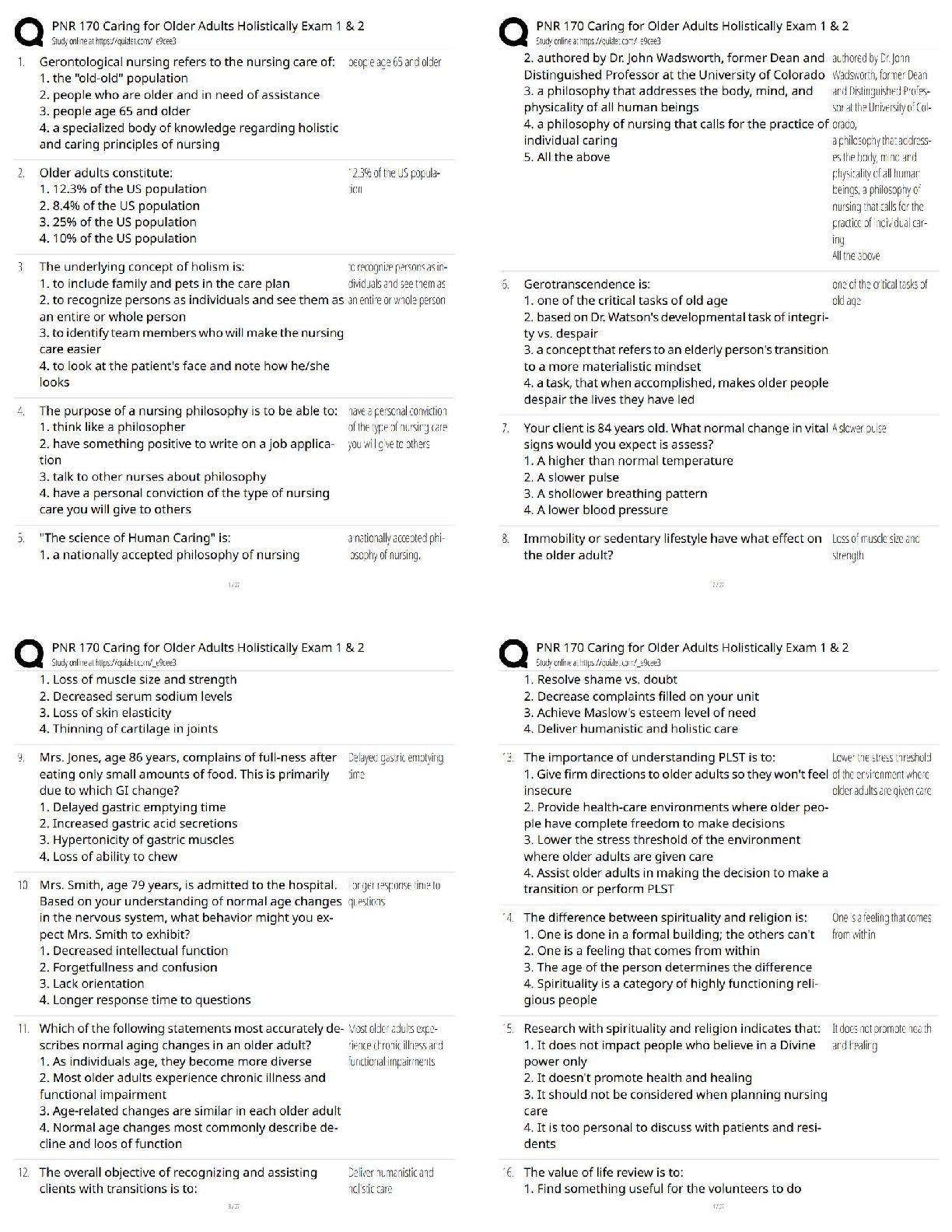
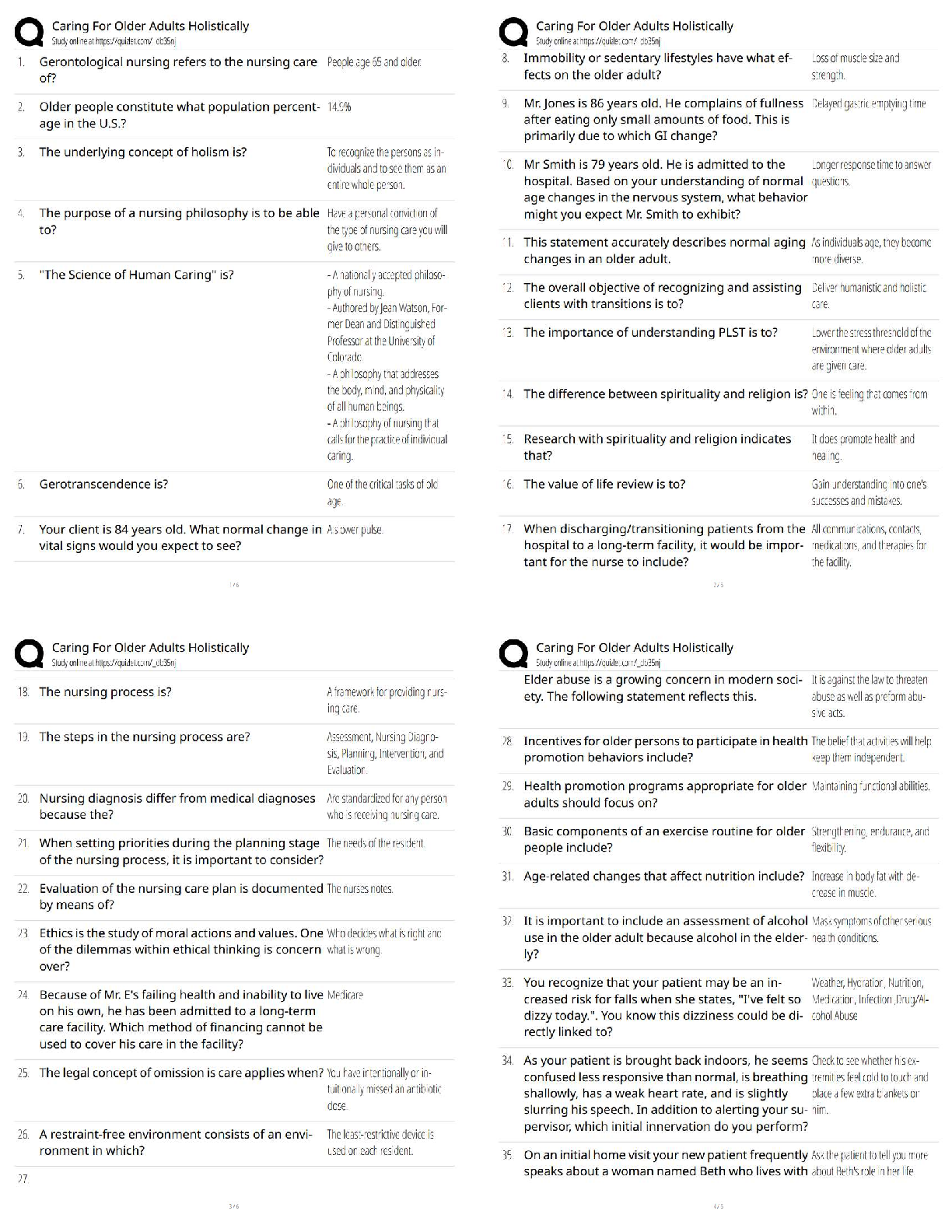
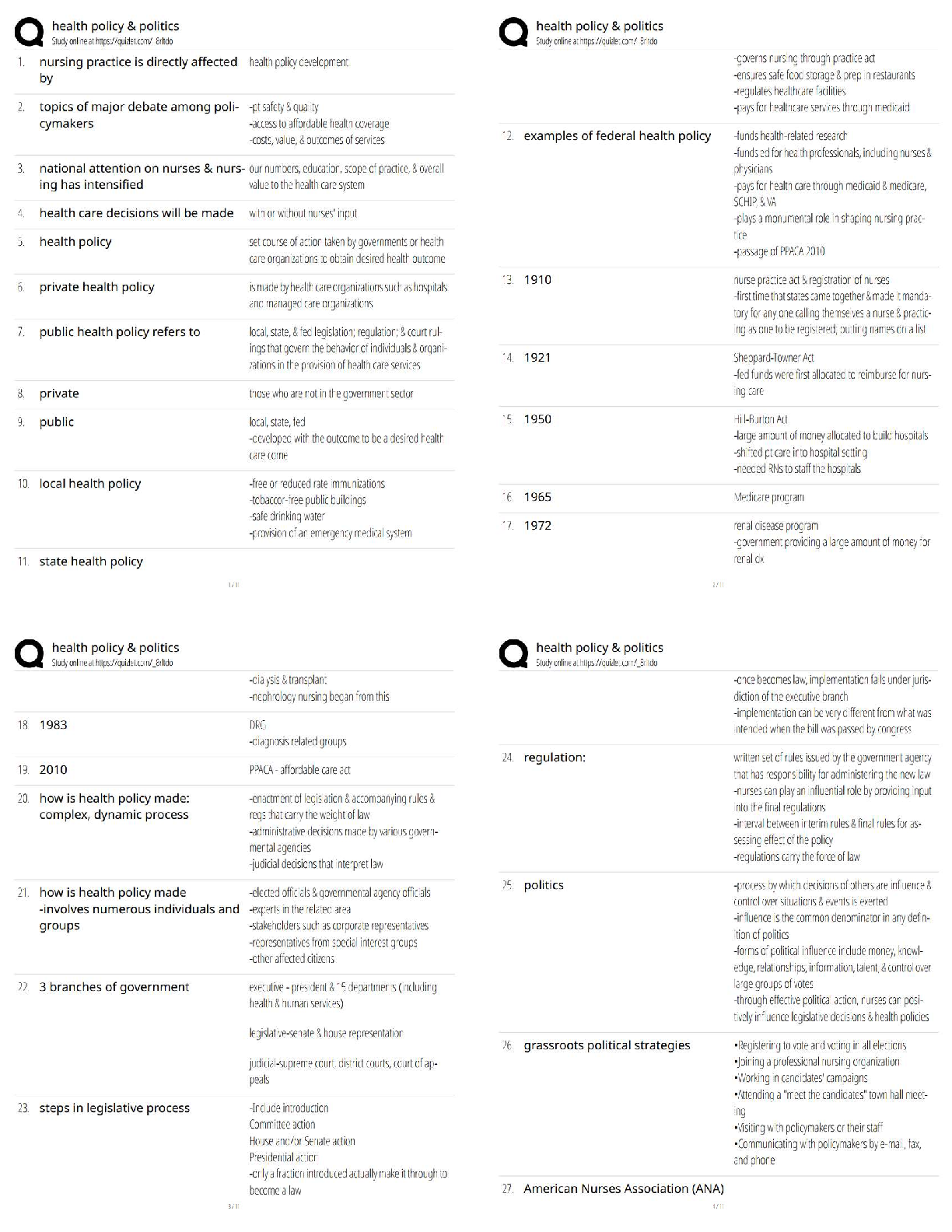
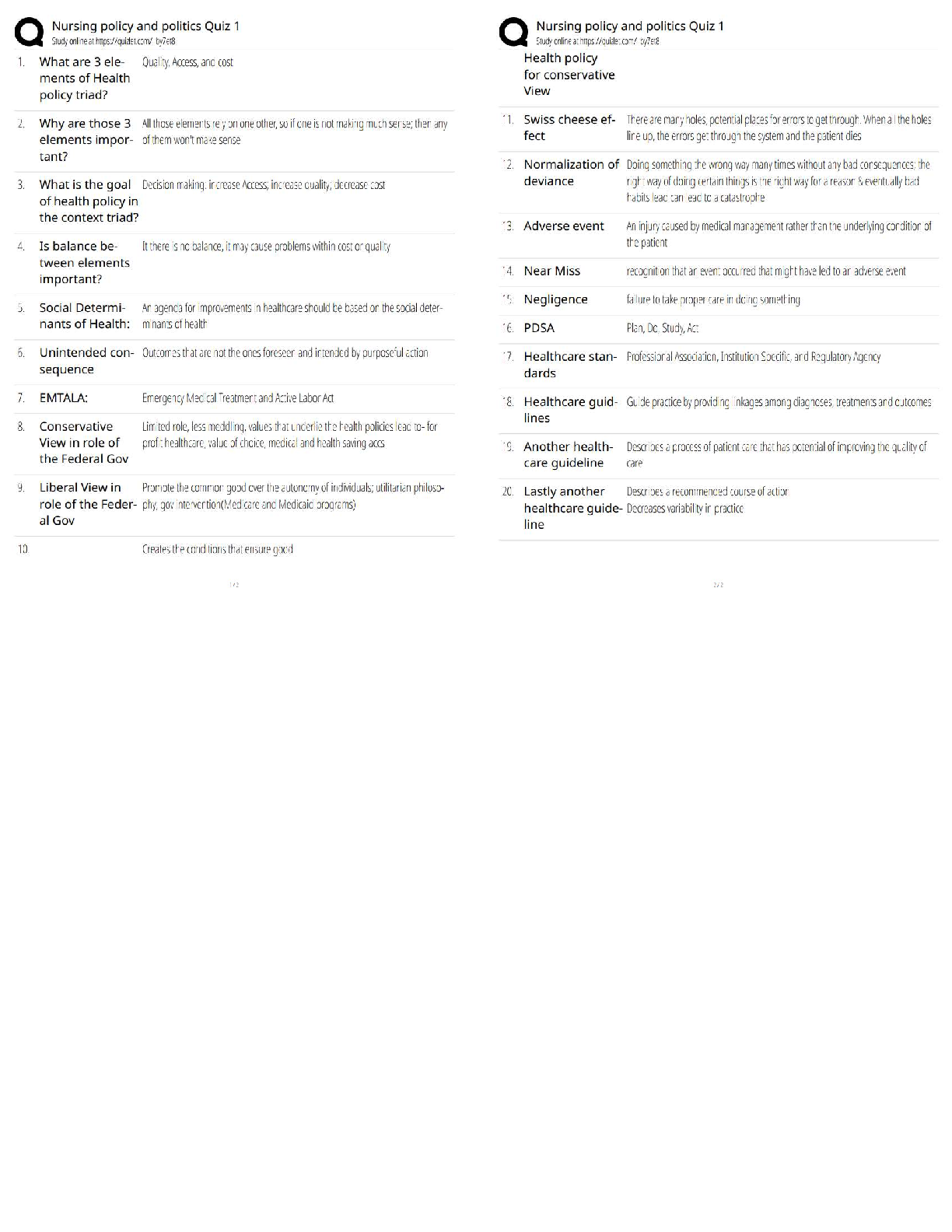
HLTH 101 Exam Preview. All sections
coverage, rated A+. verified.
Lalonde Report - ✔✔-- Health care services are not the primary means of improving health, nor can we
rely on improved living conditions and conventio
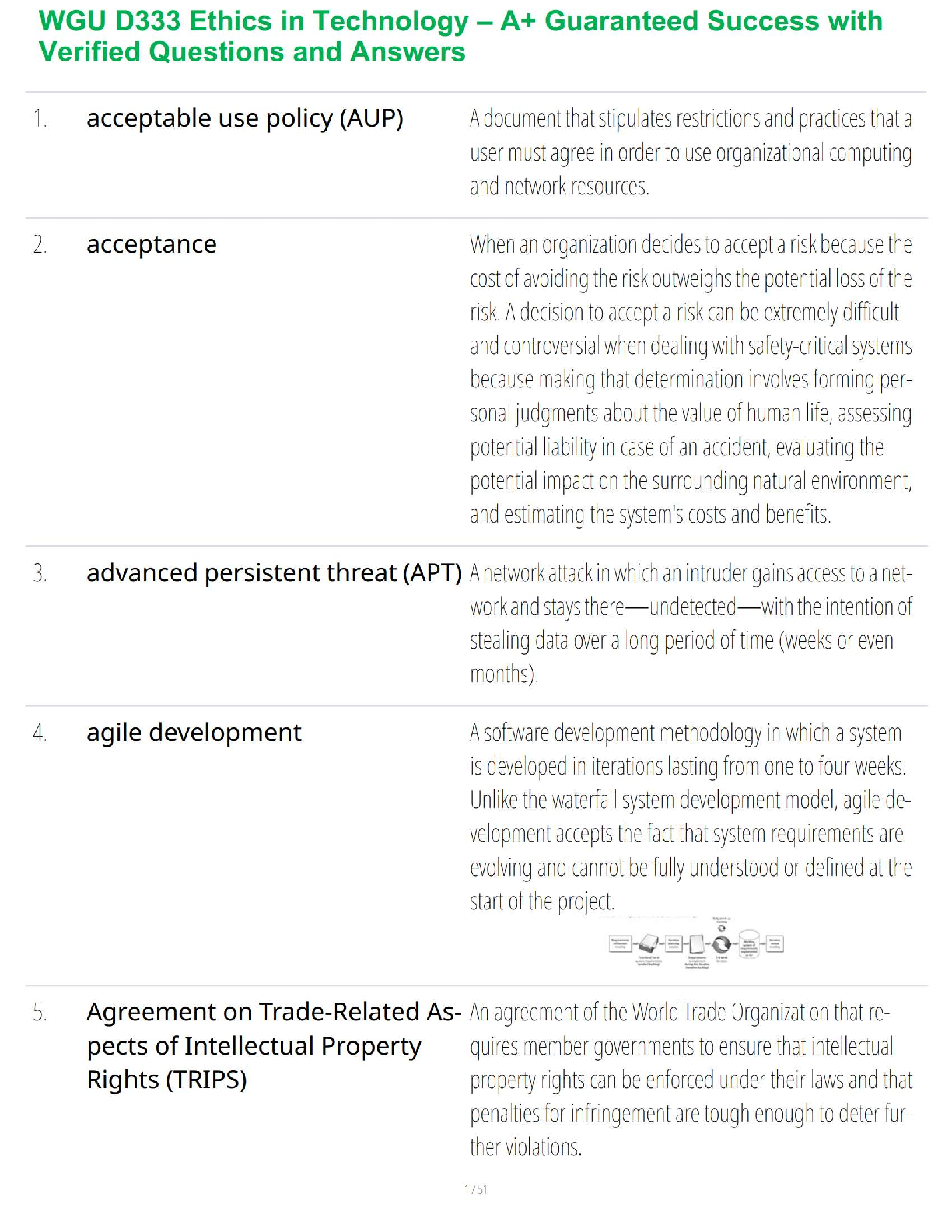
...
HLTH 101 Exam Preview. All sections
coverage, rated A+. verified.
Lalonde Report - ✔✔-- Health care services are not the primary means of improving health, nor can we
rely on improved living conditions and conventional public health measures to enhance health.
- Example: Canadians must become more active individually and collectively in maintaining and
enhancing health by adopting healthy lifestyles and protecting air and water quality.
- Two main health objectives: the health care system and promotion of good health.
Health Gradient - ✔✔-As income (and other social determinants such as education or job quality) rises,
so does health and life expectancy
Health Inequities - ✔✔-Differences in population health that are avoidable, such as the gap between the
health of the richest and the health of the poorest
Neoliberalism - ✔✔-Does not support public health because:
- aligns with conventional view of health that sees health outcomes as a mix of genetics and lifestyle
determinants of health
- does not support the strong government action and intervention needed for public health to work
- tax cuts mean that there is not enough government money to fund public health
- it tends to increase the income gap between the riches and poorest
Chronic stress - ✔✔-- Occurs when pressure are relentless and those affected do not have the power or
resources to control them
- Results in a prolonged activation of stress pathways, including stress hormones, affecting memory,
immune function, heart rate variability, glucose processing, blood pressure, and other bodily functions
- Has the biggest effect on those in high demand/low control jobs
Social determinants of health - ✔✔-- Income and social status
- Social support networks
- Education and literacy
- Employment/working conditions
- Social environment
- Physical environment
- Healthy childhood development
- Gender
The Epp Report - ✔✔-Emphasizes a new vision for health embracing physical, mental, and social well�being which introduces a health promotion framework:
- Challenge 1: to reduce inequities in health between high and low income Canada
- Challenge 2: prevent injury and disease
Friedrich Engels - ✔✔-- Showed that the death rates of poor people in urban centres were much higher
than the death rates of poor people in rural centres
- Social and economic change can substantially affect health and longevity and that living/working
conditions are the major determinants of human health and well being
- "Health harming behaviour" amongst the working class was a product of the conditions under which
people live, not their character flaws or bad choices
Rudolf Virchow - ✔✔-Noticed poor health in Upper Silesia and determined it was due to poor living
conditions. He claims medicine cannot help improve health as much as economic, political, and social
reform.
Thomas McKeown - ✔✔-Believed that vaccinations made no help to health, but his views have been
disregarded.
He thought that deaths from diseases such as TB, measles, etc. fell sharply after 1850 because of
changes in social and environmental factors, especially better nutrition, not health care.
Social patterning of behaviour - ✔✔-Refers to the usually unconscious determination of behaviour by
contextual factors including the social norms of one's workplace and social position
Healthy lifestyle - ✔✔-- appears to have the greatest positive health effects on those already living in
high economic and social circumstances
- appears to have little measurable impact on the health of lower-income people
- is difficult to achieve and maintain for those who live in poverty
Emile Durkheim - ✔✔-Believes that society dictates our behaviour and understanding because social
structures dictate our opportunity and restraints
KFL&A Affordability of Healthy Eating - ✔✔-Shows that:
- social assistance rates are too low for individuals and families to meet the average cost of basic needs
and are set below absolute poverty lines
- it is reasonable to expect people on social assistance might feel deprived of a lifestyle that would
consider normal or typical for Canadians
The cost of poverty - ✔✔-Showed that there are significant institutional barriers that keep people
trapped in poverty
Basic Income Guarantee - ✔✔-Would reduce or largely eliminate poverty in Canada bye expanding to
the working age population the universal income security measures already in place for Canadian
seniors and children
"Physicians are the natural attorneys of the poor" - ✔✔-Rudolph Virchow meant that physicians see
firsthand the devastating effects of poverty because poverty very often leads to poor health; thus
physicians should advocate for improved living conditions for the poor and for the political conditions
that would empower the poor to have a stronger voice and more cool over their lives
Pathways to Education - ✔✔-Is a program developed for kids at risk of dropping out of high school has
been shown to be an effective intervention to reduce the intergenerational cost of poverty. It will have a
long term payoff of about $12 for ever dollar invested because graduates of the program will pay higher
income taxes than those who drop out
Ryan Meili - ✔✔-
Alan Davidson on animal studies - ✔✔-The contexts of animal's infancies can strongly override their
genetic predispositions
The Barker Hypothesis - ✔✔-Contends that early development has lifelong implications of health and
life expectancy
- early life experiences (in utero and early infancy) have latent health effects
- suggests that low birth rate can result in negative health outcomes in adulthood
- is compatible with the Theory of Epigenetic Adaptation (early life experiences regulate gene
expression)
Pathway effects of poverty on health - ✔✔-Suggest the importance of addressing poverty in early
childhood to improve population health in the future. Refers to a situation that "sets the stage" for
subsequent developments.
- Early life conditions that affect success at school, which then affects future job prospects, income,
housing, and other social determinants of
[Show More]