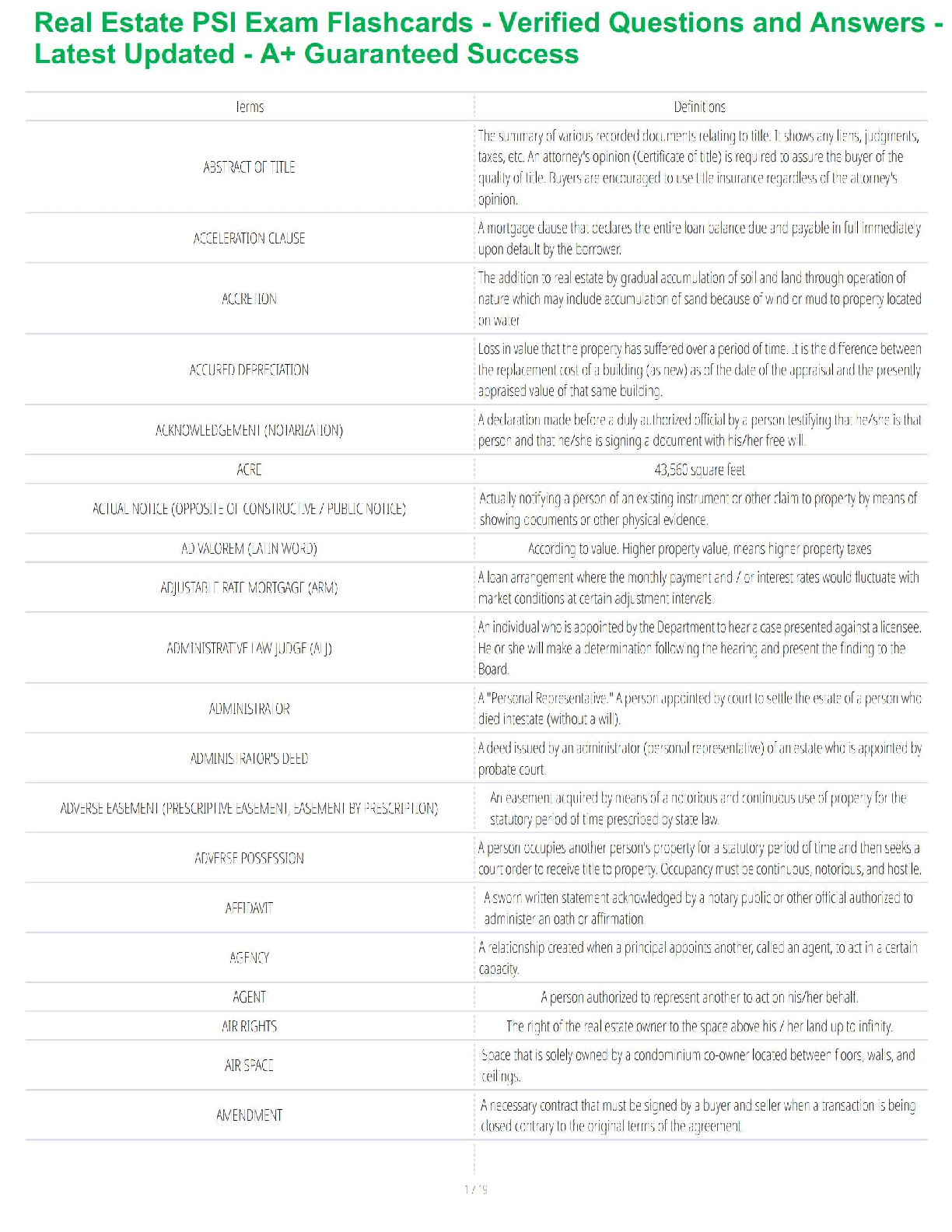
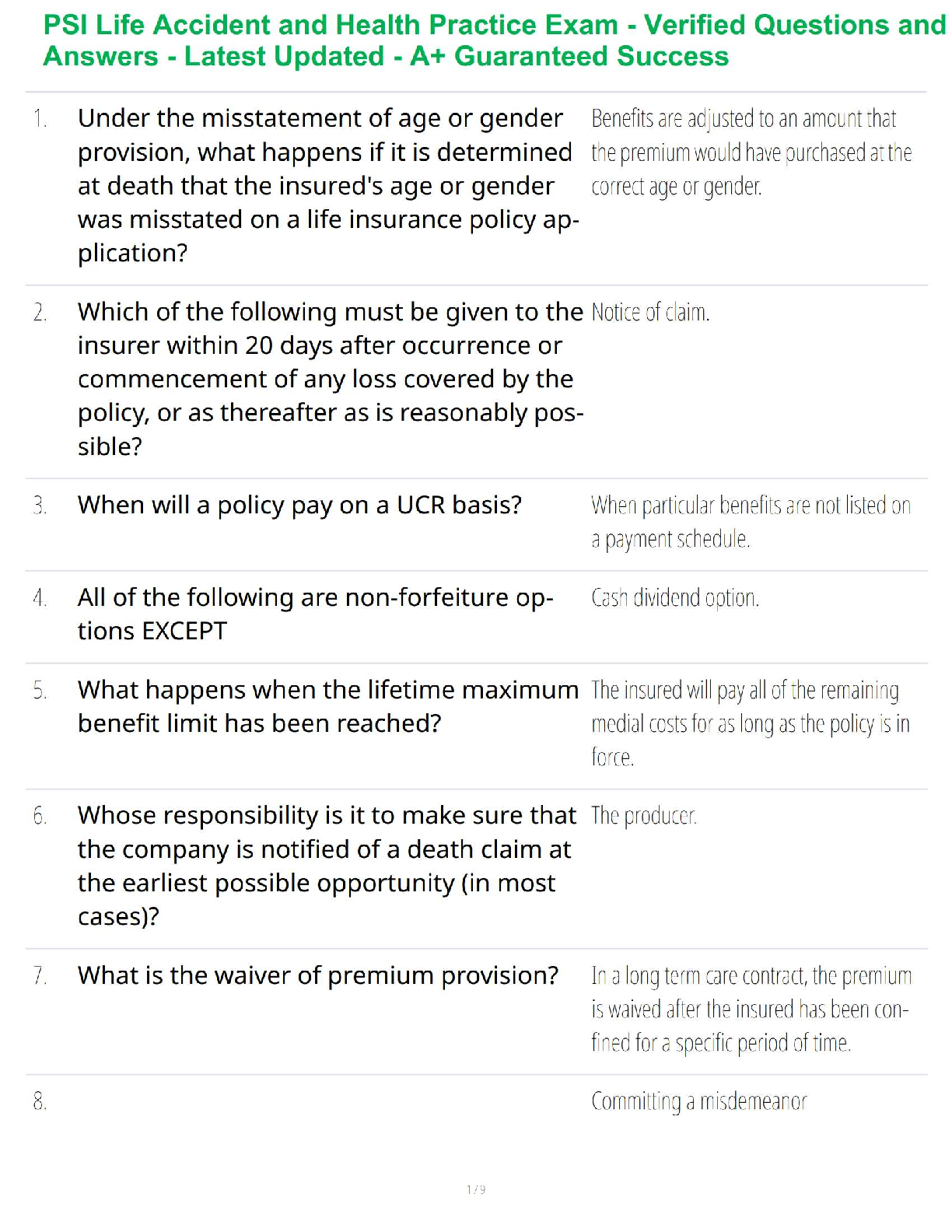
ENT practice questions & Answers.
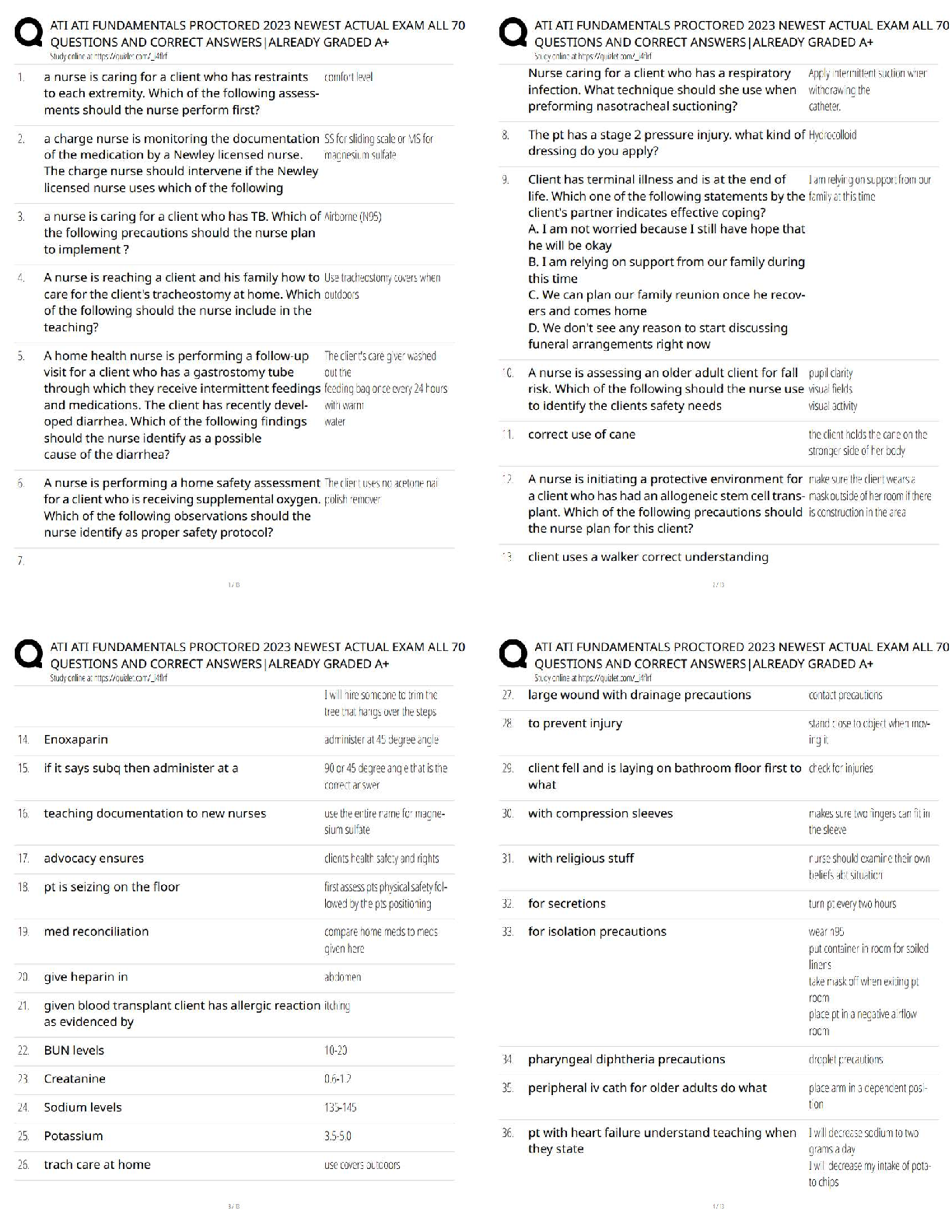
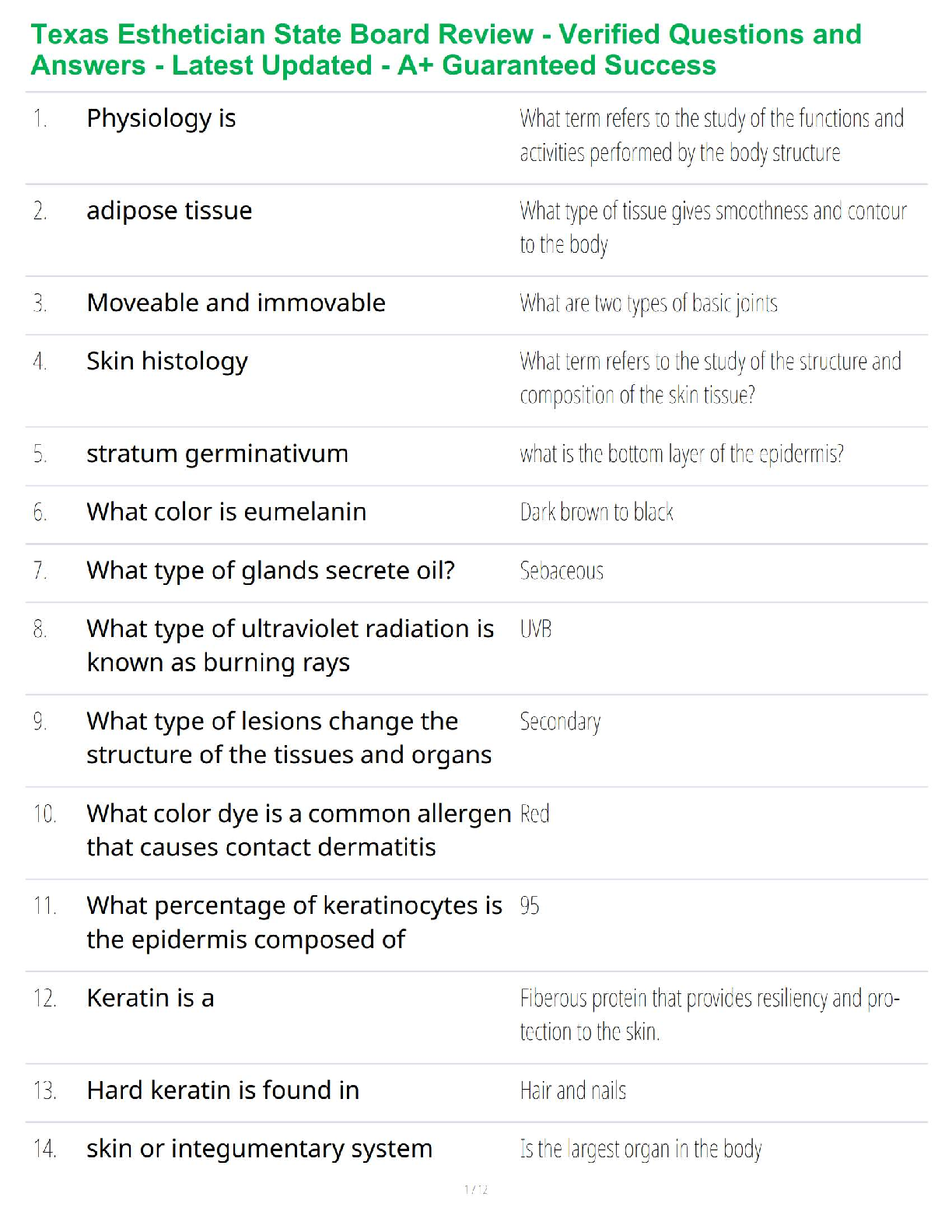
100% Accurate, rated A+.
Abscessed teeth can rupture the medial mandibular cortex into the sublingual space. This can cause the
tongue to be pushed up and back. The biggest danger i
...
ENT practice questions & Answers.
100% Accurate, rated A+.
Abscessed teeth can rupture the medial mandibular cortex into the sublingual space. This can cause the
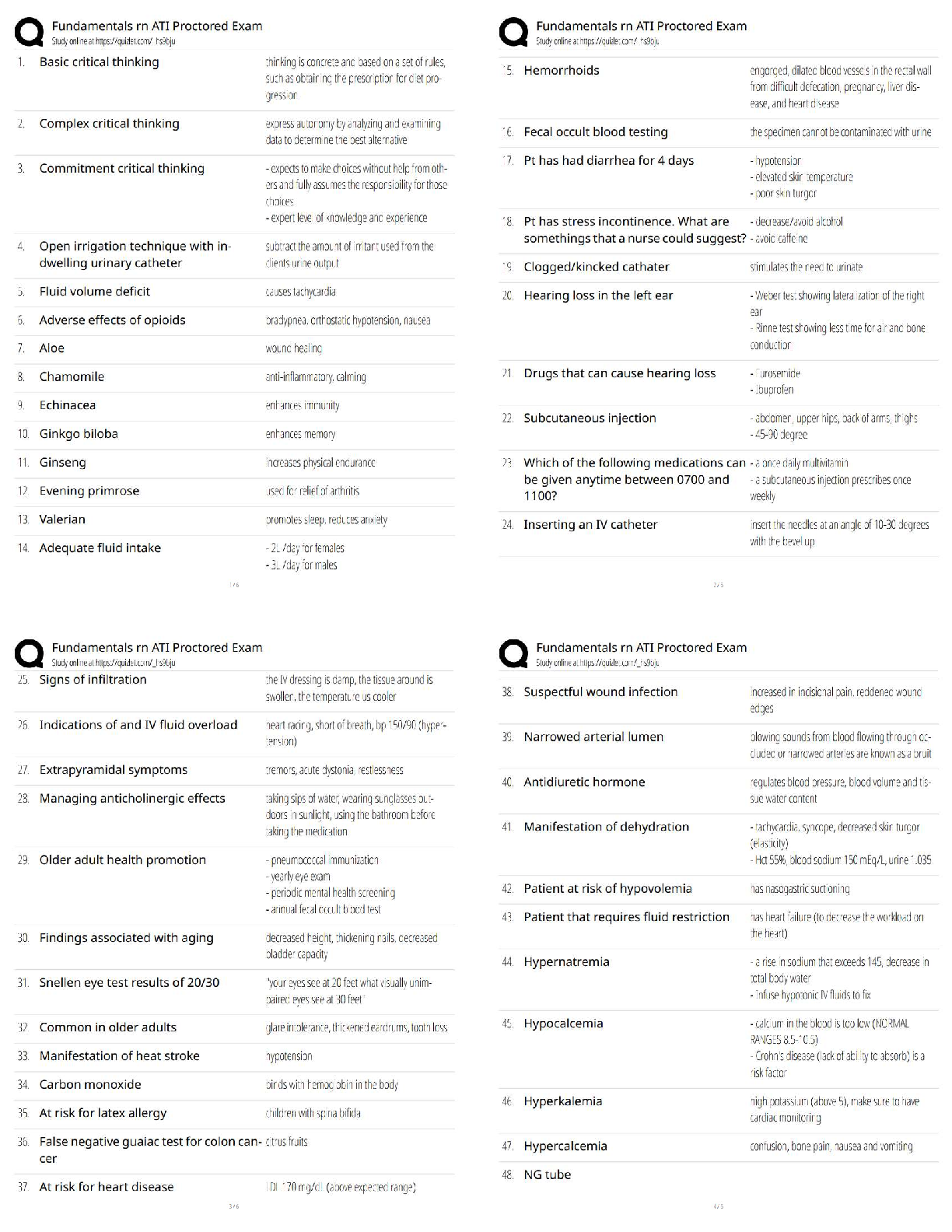
tongue to be pushed up and back. The biggest danger in this is loss of... - ✔✔-Airway
The easiest way to ensure that the airway isn't lost in this isutation is to perform... - ✔✔-A tracheotomy
Immunocompromised patients, especially patients with diabetes, can get a devastating fungal infection
of the sinuses called... - ✔✔-mucormycosis
Necrotizing otitis externa is a Pseudomonas infection of ????? and ????? which can lead to fatal
complications - ✔✔-EOC, skull base, temporal bone
Often ???? tissue is seen at the junction of the bony-cartilaginous junction in the external auditory canal
in patients with mecrotising otitis externa - ✔✔-granulation
The most common cause of a nosebleed in children is injury to vessels in.... - ✔✔-Kisselbach's plexus
A posterior nosebleed in an adolsecent make is considered to be a ???? until proven otherwise. - ✔✔-
Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
Two topical vasocontrictors often used in the nose are... - ✔✔-Oxymetazoline, phenylephrine
The 3 most common organisms causing acute otitis media are... - ✔✔-S. pneumonieae, H. influenza,
Moraxella
The first-line antibiotic therapy for acute otitis media in children is - ✔✔-Amoxicillin
Children with persistent otitis media with effusion for ??? months and evidence of hearing loss are
candidates for PE tube placement. - ✔✔-Three
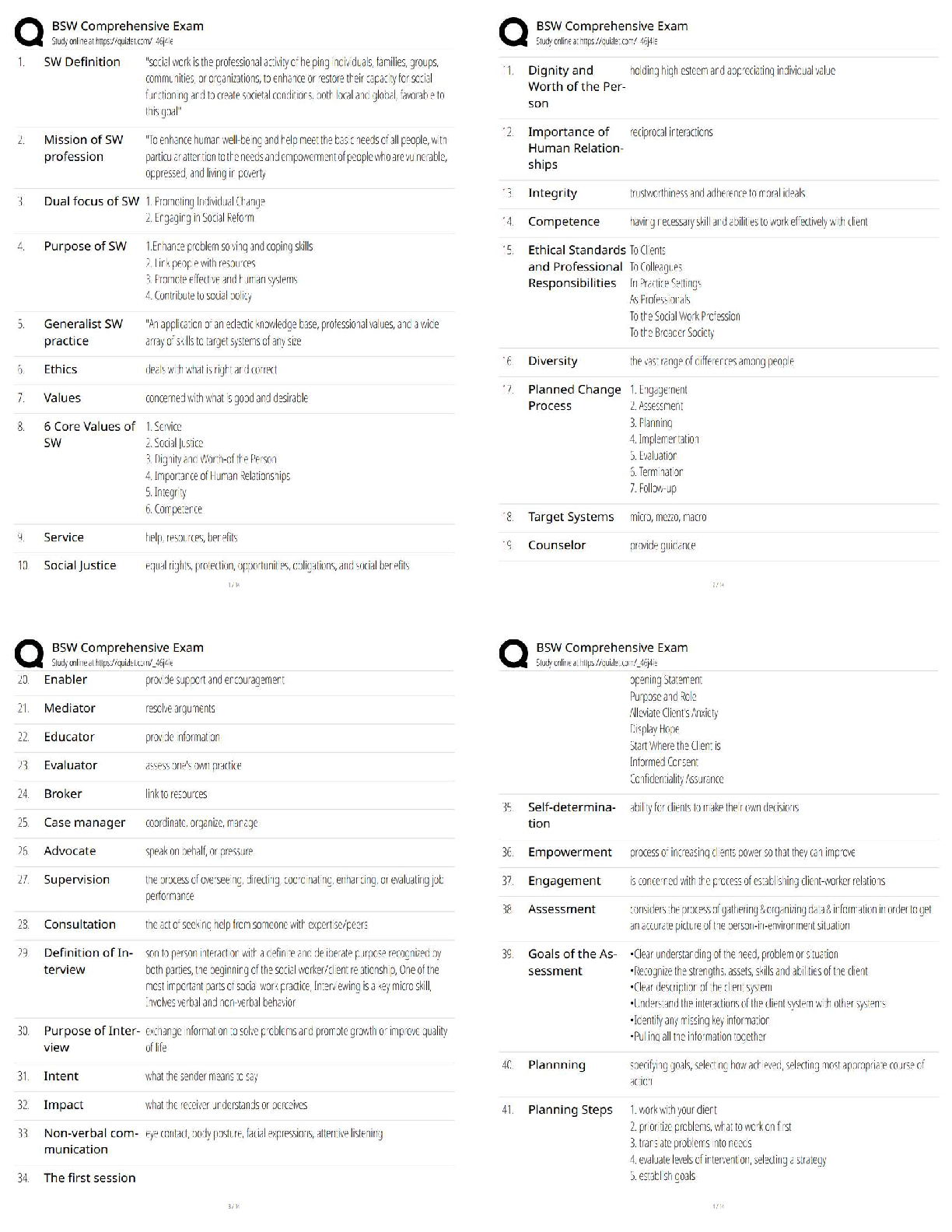
Ear drainage in patients with PE tubes in place should be treated with - ✔✔-Ototopical fluoroquinolone
drops
The presence of bilateral fluid in the ears may cause up to ???? dB conductive hearing loss. - ✔✔-30-
40dB
It is important to examin the ???? in any adult with unilateral otitis media with effusion. - ✔✔-
Nasopharynx
In a patient with acute otitis media, in addition to being opaue and bulging, the ear drum has ????
mobility on pneumatic otoscopy. - ✔✔-Decreased
The collection of trabeculated bony cavities lined with mucose and connected with the middle ear is
called the... - ✔✔-mastoid air cells
The pars flaccida (superior portion) of the eardrum can become ??? when there is chronic megative
pressure in the middle ear. - ✔✔-retracted
The outside of the TM, including the pars flaccida, is line with... - ✔✔-Squamous epithelium
???? is suspected in a child presenting with gever, ear pain, a protruding auricle, and fluctuance behind
the ear. - ✔✔-Acute mastoiditis
In patients with chonic eustachian tube dysfunction, desquamated debris, consisting mainly of keratin,
cllects in the retracted pars flaccida. Over time, this can gow and become a - ✔✔-cholesteatoma
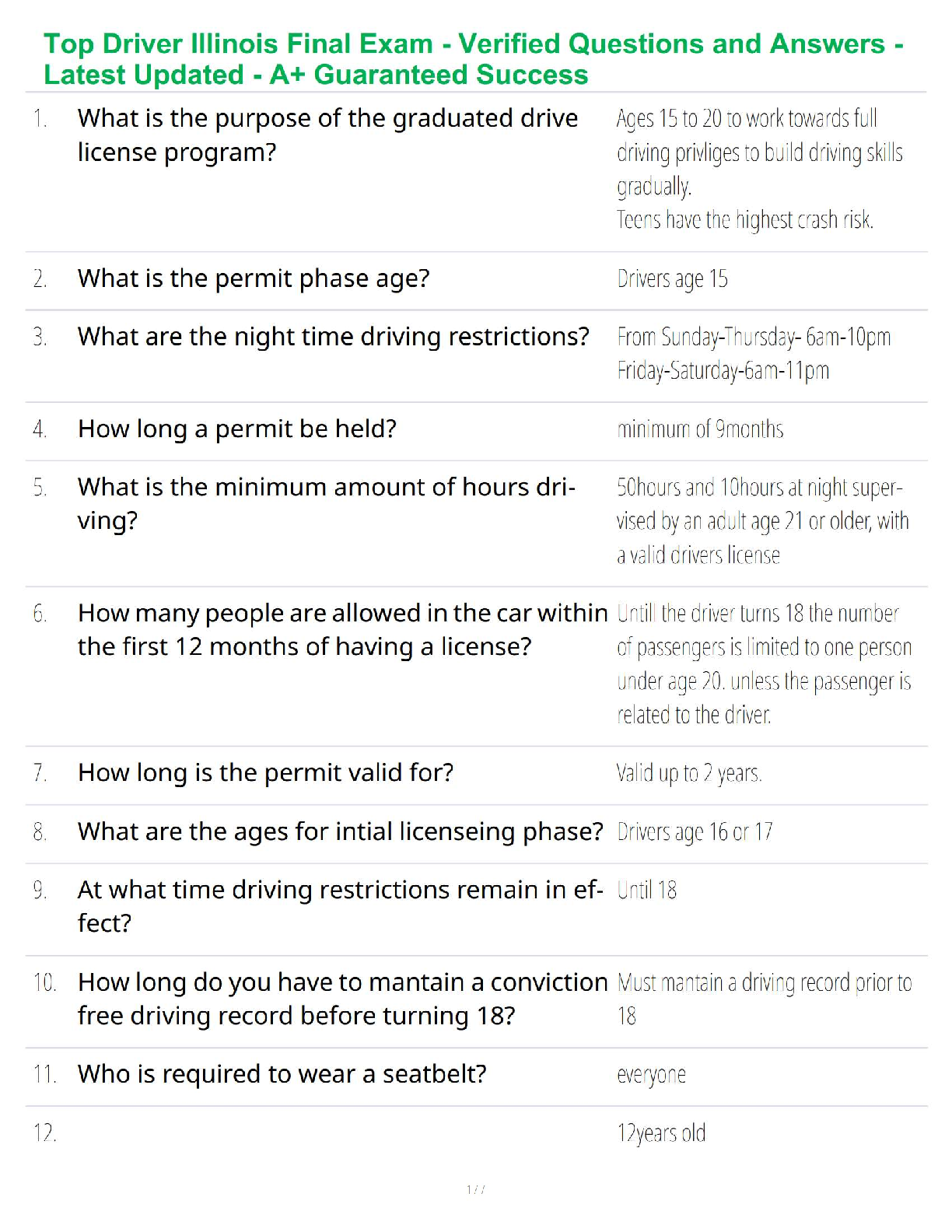
If a patient presents with a draining ear, appropriate therapy includes drops, and - ✔✔-oral antibiotics
???? is the furm submucosal scarring that can appear as a chalky white patch on the eardrum. - ✔✔-
Tympanosclerosis
If ear drainage persists depsite medical therapy, the patient requires referral to an otolaryngologist to
rule out - ✔✔-Cholesteatoma
The most common cause of conductive hearing loss in children is - ✔✔-Fluid in the middle ear (otitis
media)
The magnitude of a heraing loss is documented in the - ✔✔-Audiogram
The two major types of hearing loss are... - ✔✔-Conductive and sensorineural
Conductive hearing loss is present when air and bone conduction thresholds are... - ✔✔-similar,
approximate
Conductive hearing loss is present when there is a difference between ?? and ?? conduction thresholds.
- ✔✔-Air and bone
Noise-induced hearing loss often produces a high frequency ??? in the audiogram. - ✔✔-notch
Otitis media with effusion produces a ???? tympanogram - ✔✔-Flat (type B)
Presbycusis produces a hearing loss that slopes to the ??? side of the audiogram - ✔✔-right side,
downward (Type C)
A patient with an asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss must be evaluated for the potential of having
an... - ✔✔-acoustic neuroma
Dizziness associated with an illusion of motion - ✔✔-Vertigo
Sudden vertigo that develops without ear symptoms and last for 24-48 hous is most likely - ✔✔-
Vestibular neuronitis or labyrinthitis
Vertigo precipitated by postional changes, lasting 10-60 seconds, and unassociated with serious illness -
✔✔-Benign paroxysmal postional vertigo (BPPV)
Peripheral facial paralysis can be due to... - ✔✔-Tumor of parotid or skull base
infection
trauma
Facial paralysis with out an identified etiology - ✔✔-Bell's Pals
[Show More]