Chemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NFS 5130 Food Chemistry - Wayne State University Exam Maximum Points = 100 (All)
NFS 5130 Food Chemistry - Wayne State University Exam Maximum Points = 100
Document Content and Description Below
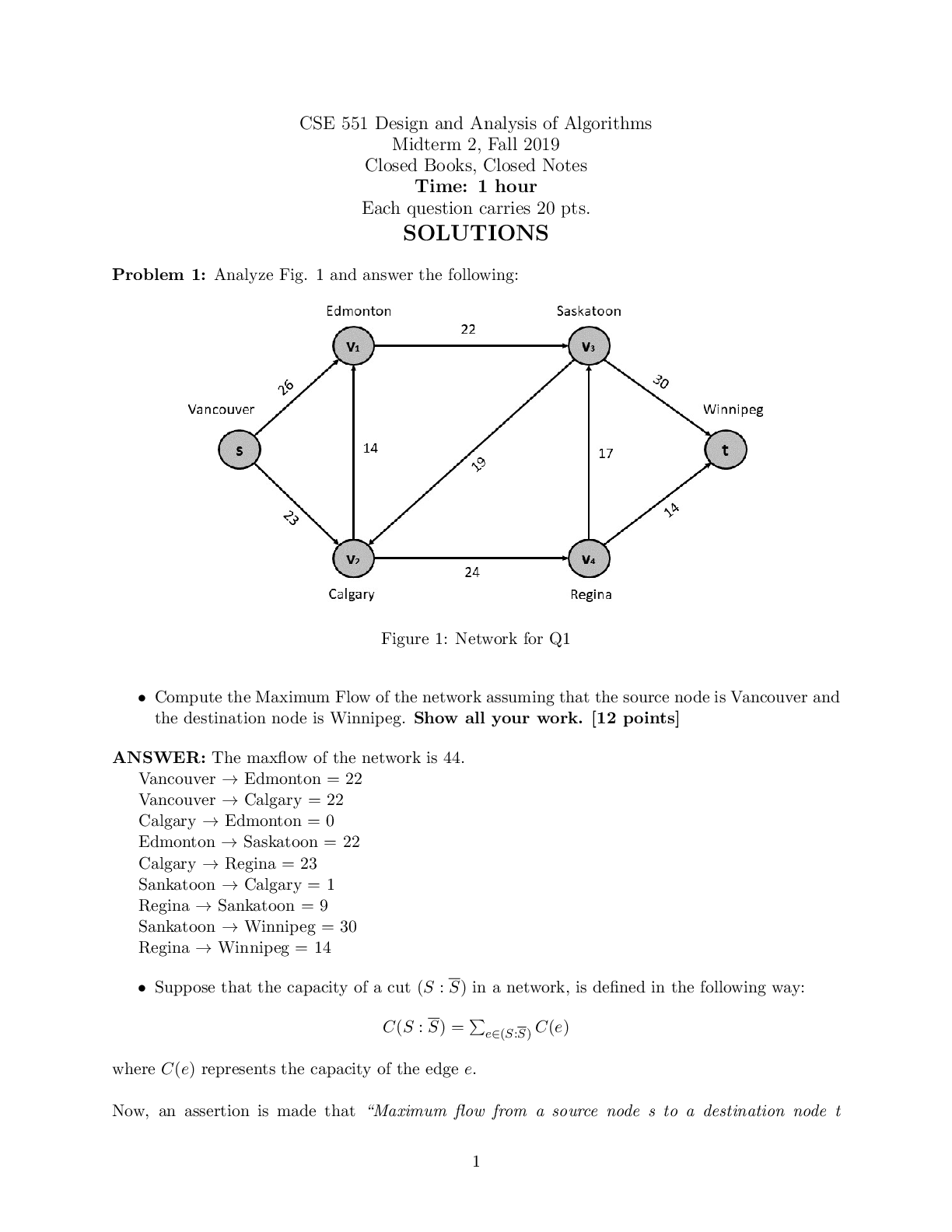
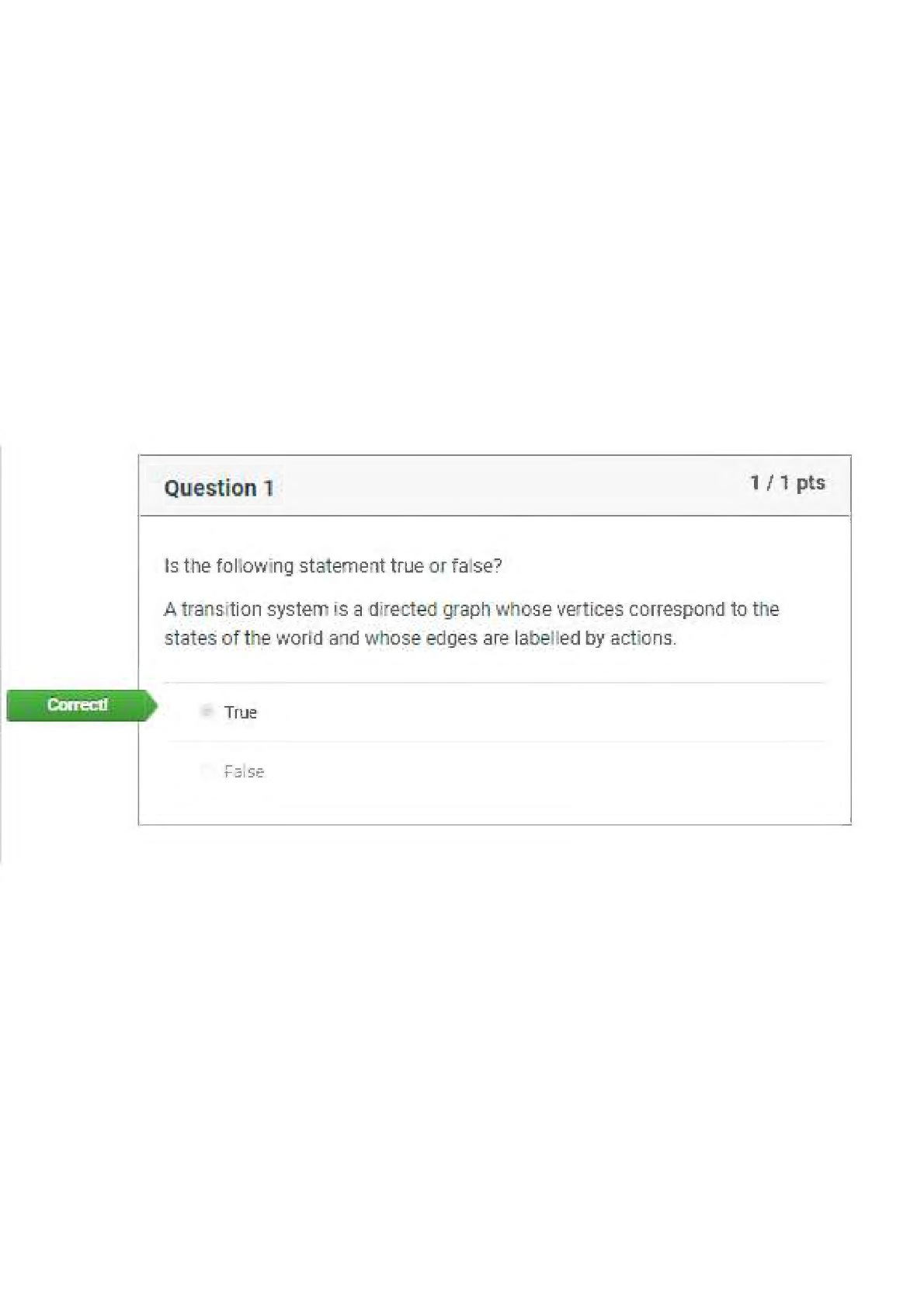
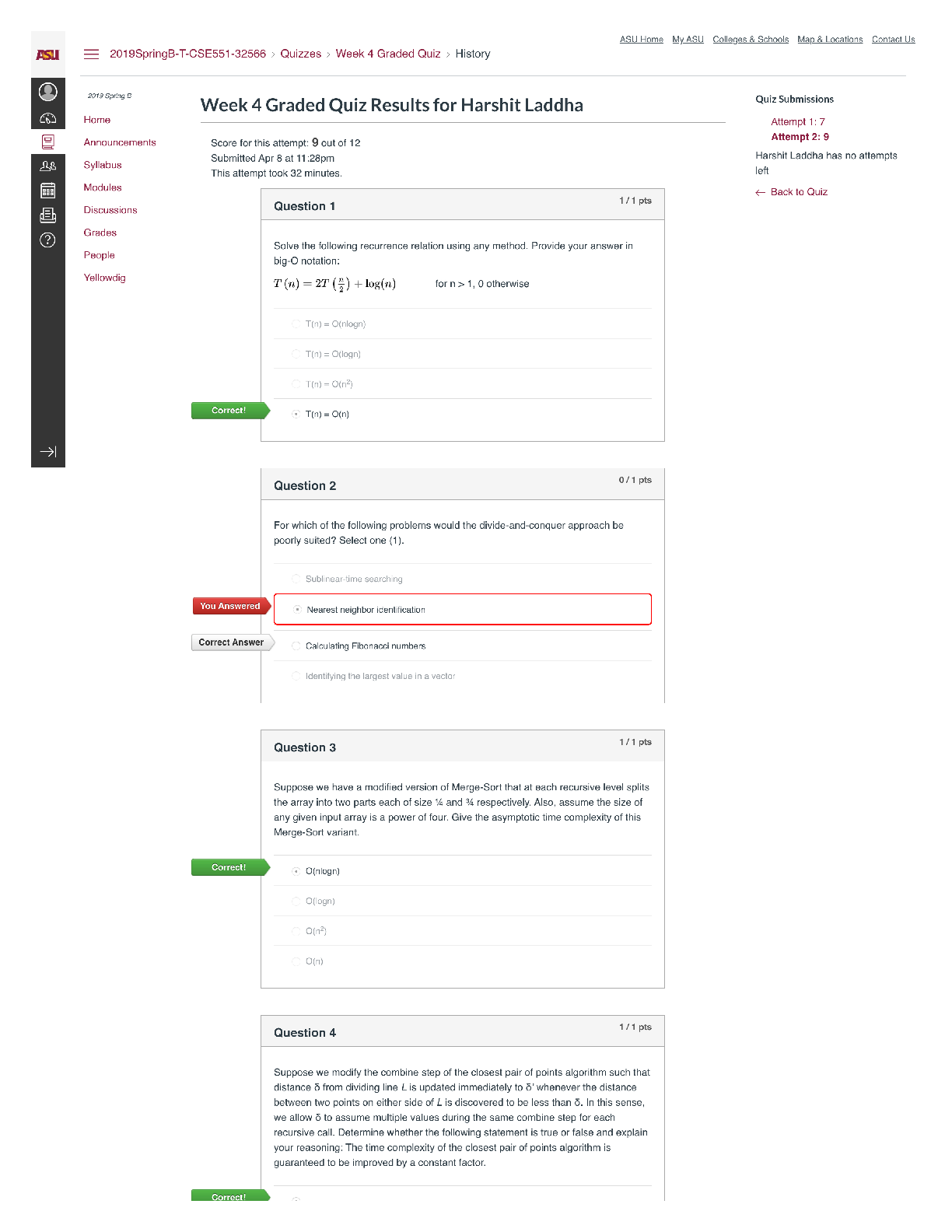
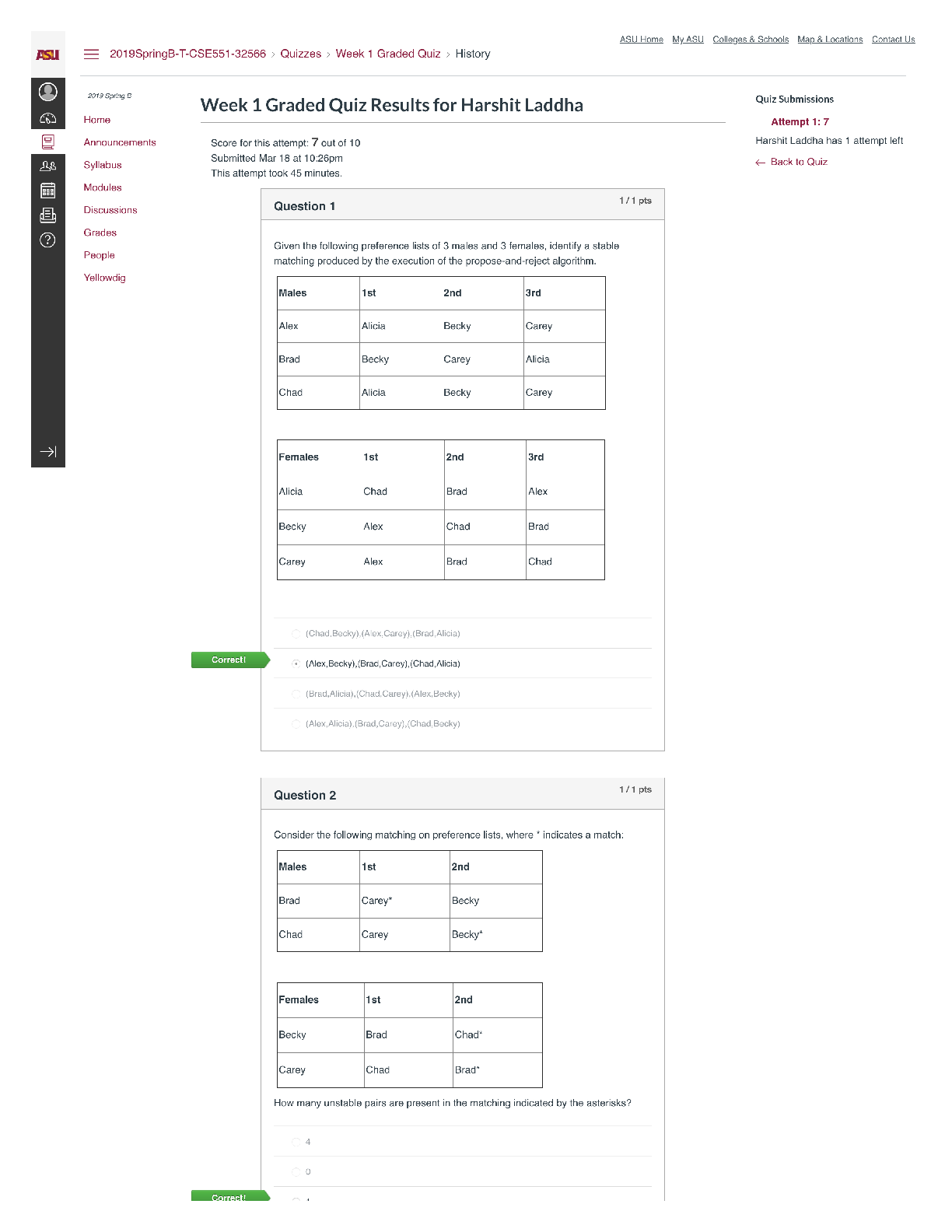
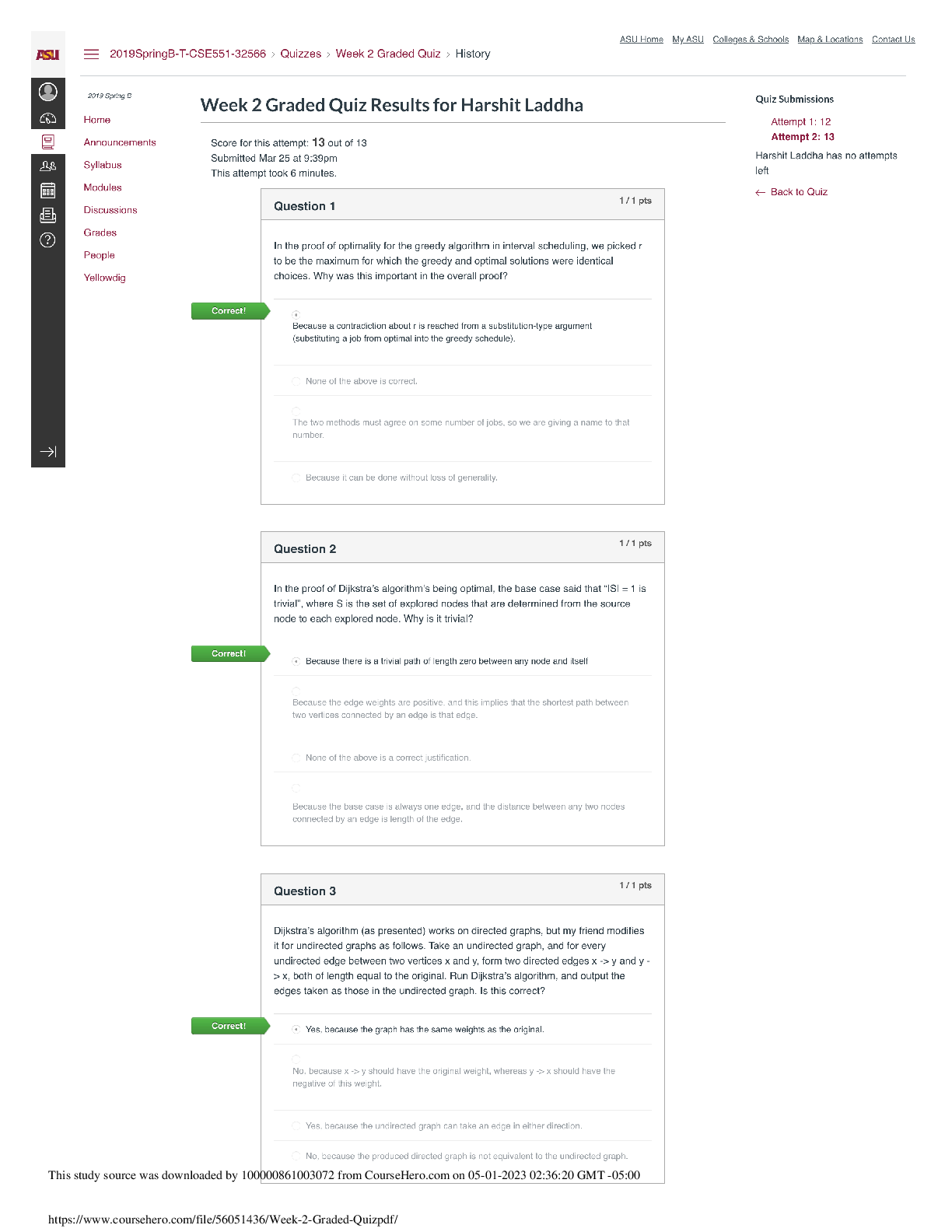
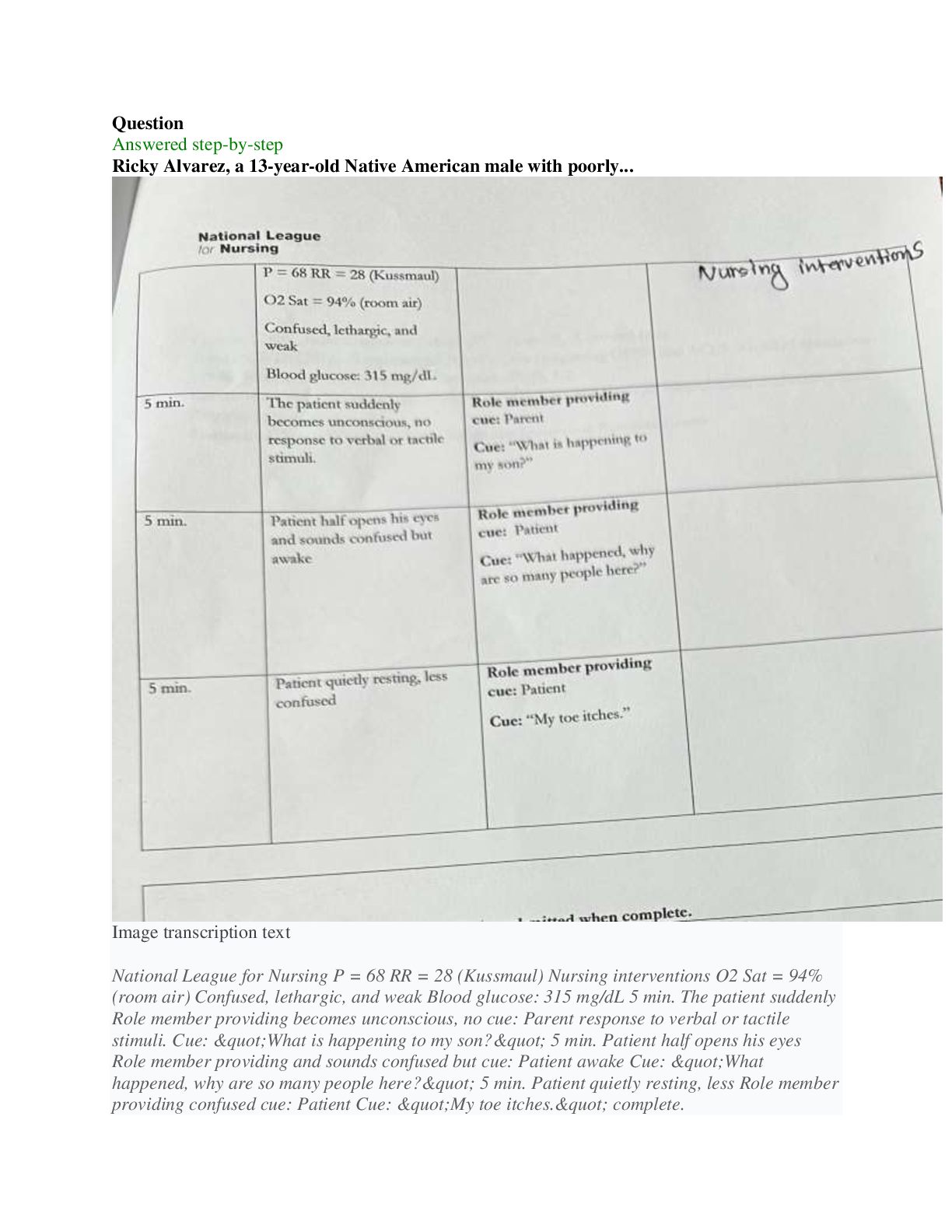
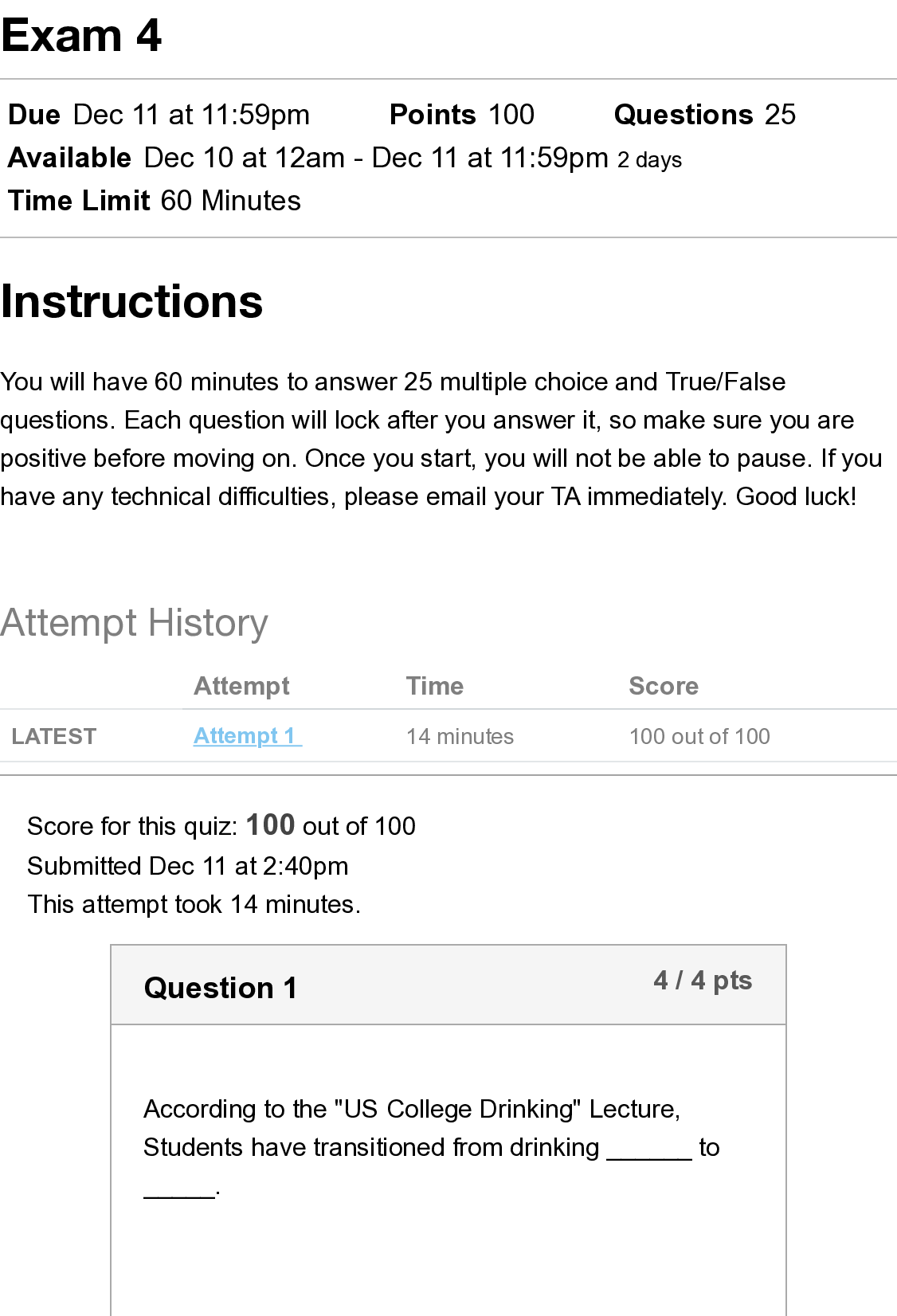
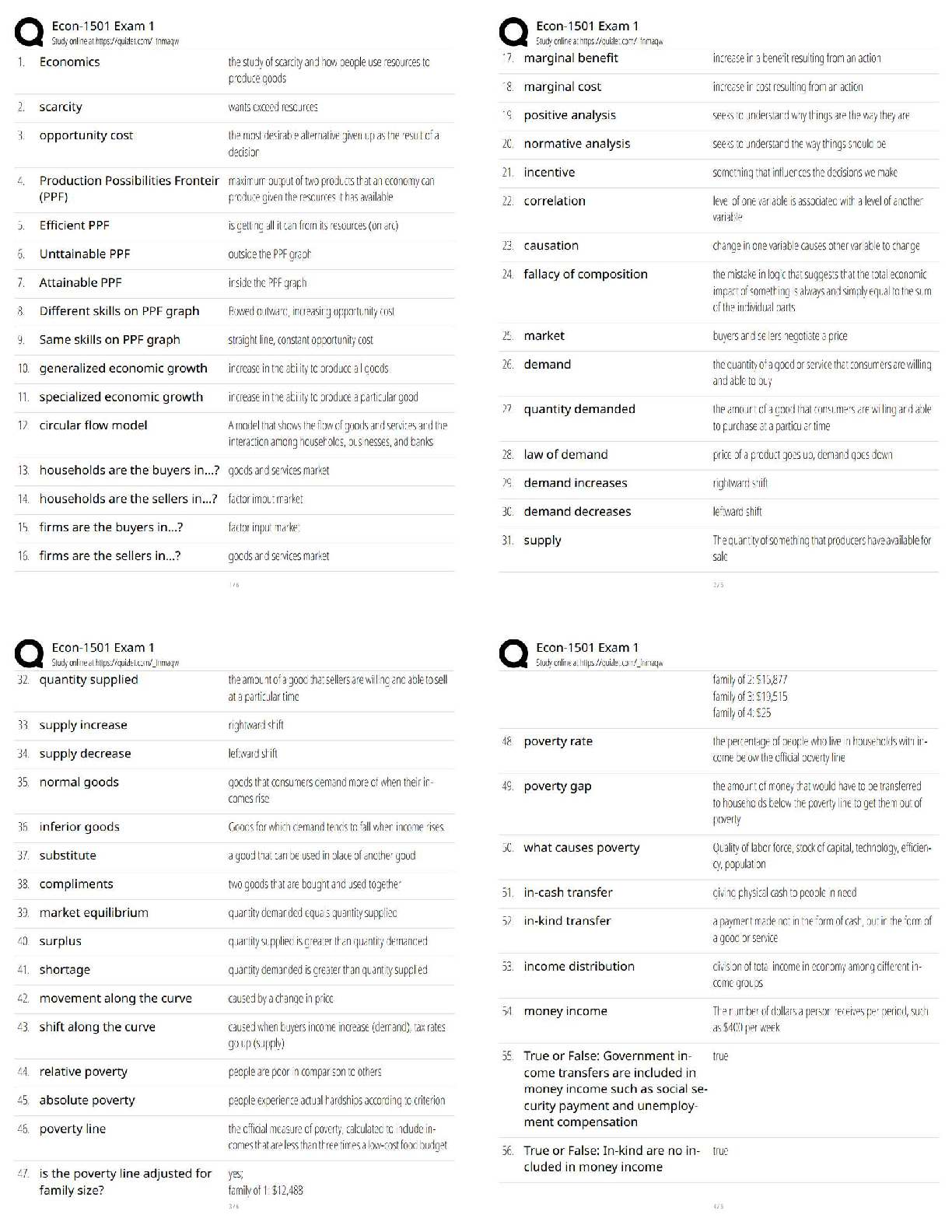
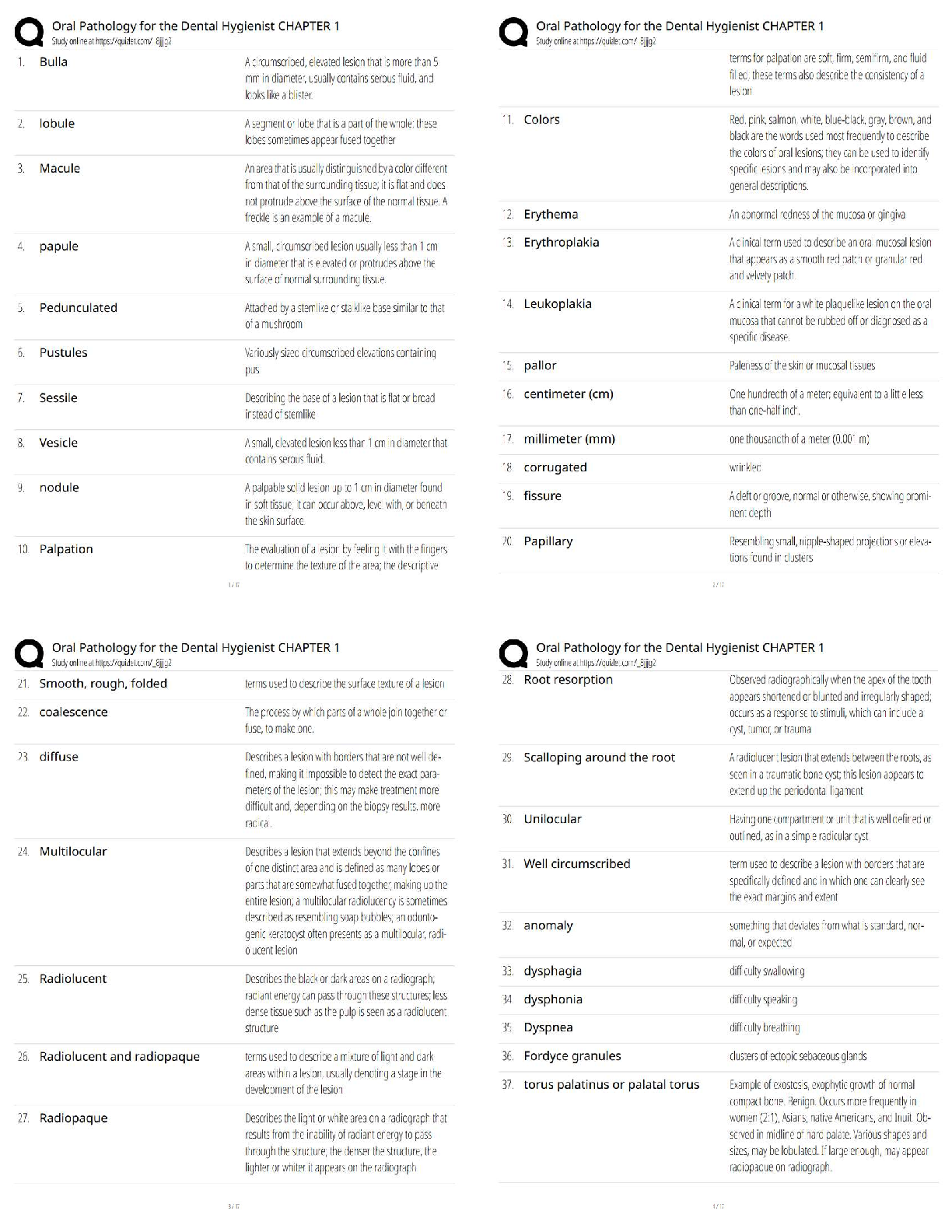
NFS 5130 2010 Exam Maximum Points = 100 Question 1: Select the most appropriate answer (1 x 40 points) 1. The secondary structure of a protein is a. the sequence of amino acids in the protein b ... . the coiling of the amino acid backbone c. due to the S-S bonding in the protein d. due to the electrostatic interactions in the helix 2. The following covalent bonds are involved in the formation of tertiary structure of proteins. a. Electrostatic interactions b. disulfide –S-S linkages c. H-bonding d. all of the above 3. The red color in water melon is due to the presence of a. Isothiocyanates b. Lycopenes c. Lutein d. Anthocyanins 4. The following food is high in allyl sulfides a. Tomatoes b. Onion c. Mangoes d. Grapes 5. The following is a food rich in flavonoids a. Tomatoes b. Onion c. Mangoes d. Grapes 6. Broccoli is a rich source of: a. Isothiocyanates b. Lycopenes c. Lutein d. Anthocyanins 7. The nitrite burn, sometimes observed during curing of meats is due to the formation of a. Methmyoglobin b. Nitrosylmyoglobin c. Nitrimyoglobin d. Oxygenated myoglobin 8. The following is an uncertified colorant a. Lycopene b. Annatto c. Resveratrol d. Chlorophyll 1 1 NFS 5130 2010 Exam (YELLOW) April 5, 9. Margarine is an example of the following dispersion type a. gel b. emulsion c. foam d. sol 10. A foam is a type of dispersion which may be described as a. liquid in solid b. gas in liquid c. solid in gas d. liquid in liquid 11. The following is an example of a w/o emulsion a. butter b. milk c. sausage d. gravy 12. A true solution has particles in the range of a. 0.01-0.1 nm b. 0.1-1nm c. 1-10 nm d. 10-100 nm 13. The following statement is not true with respect to Foams a. Foams contain air in a continuous liquid medium b. Foams are less stable than emulsions c. Foams have smaller particles than emulsions d. Solidifying a foam makes it very stable. 14. The following amino acid sequence, where N=nonpolar amino acid and P=Polar amino acid, would promote a helical structure a. N-P-N-P-N-P-N-P-N-P b. N-N-P-N-N-P-N-N-P-N-N-P-N-N-P c. N-N-P-P-N-N-P-P-N-N-P-N-N-P-N-N-P d. N-P-N-P-P-P-N-P-N-P-N-N-P-P 15. Trypsin is a monomeric protein. It has a. A primary and secondary structure b. A primary and tertiary structure c. A primary, secondary and tertiary structure d. A primary, secondary, teriary and quarternary structure 16. Protein ‘X’ has a cylindrical shape. This can be attributed to an increase in the number of the following type of amino acids: a. Hydrophobic b. Aromatic c. Hydrophilic d. Aliphatic 17. The sequence of a proteins can be determined by treating the protein with a. Amylase 2 2 NFS 5130 2010 Exam (YELLOW) April 5, b. Phenylisothiocyanate c. Hydrogen chloride d. Benzene degradation 18. In an alpha helical structure, the C=O group of amino acid (n) is hydrogen bonded to the NH group of the amino acid a. n +4 b. n + 13 c. n + 10 d. n + 8 19. _______________ is the most stable of the following structures: a. alpha helix b. pi helix c. random coil d. C 10 helix 20. The tertiary structure of a protein is formed to a. Decrease free energy to a minimum b. Increase free energy to a maximum c. Decrease stability to a minimum d. Decrease electrostatic interactions to a minimum 21. Cereal proteins tend to form oligomers in order to a. Increase their effective molecular weight b. Increase their solubility c. Increase their viscosity d. Increase their free energy 22. A bond connecting two amino acids is called a. ionic bond b. hydrogen bond c. peptide bond d. glycosidic bond 23. Aroma substances are usually a. detected by gas chromatography b. detected by HPLC c. water soluble compounds d. present in higher concentrations than taste substances 24. A compound is perceived as bitter if a. it can H-bond to the taste receptor b. it has vicinal electronegative atoms c. it has strong hydrophobic interaction with the taste receptor d. a and b e. all of the above 25. Sweet sensation has been explained by the Shallenberger model. A sensory panel evaluated 3 compounds, A, B and C and rated them as being intensely sweet, sweet and not sweet respectively. Based on the model, you would expect that 3 3 NFS 5130 2010 Exam (YELLOW) April 5, a. A H- Bonds strongly with the receptor b. A H- bonds and interacts at the gama site of the receptor c. C has a hydrophobic interaction with the receptor on gamma site d. B does not H-bond with the receptor. 26. _________ is an example of a bitter compound a. vitamin C b. tartaric acid c. caffeine d. acetic acid 27. ___________ is used as for flavor encapsulation a. gum arabic b. maltodextrins c. monosodium glutamate d. a + b e. a + c 28. Analysis of flavor compounds is complex because a. The molecules are present in low concentrations b. Most foods have character impact compounds which dominate the flavor of the food c. Compounds have low boiling points d. A and B e. A and C 29. Two flavor compounds A and B were shown to have detection threshold values of 100 and 1000 mg/L respectively. This implies that a. Compound A is very pure b. Compound B is very pure c. Compound A will be detected at lower concentrations than B d. Compound A will be detected at higher concentrations than B 30. In addition a sensory panel found the flavor threshold for compound A to be 100 mg/ml. This implies that a. Flavor panelist were well trained b. Only half the flavor panelists could detect compound A at 100mg/L c. All the flavor panelists could detect compound A at 100mg/L d. There was an error in measurement of the detection threshold for compound A. 31. A food product containing five flavor compounds A,B,C,D, E had odor potencies of 1000, 500, 250, 100 and 5 OU. This implies that a. Compound A is present in that food in the greatest amount b. Compound E is present in that food in the greatest amount c. Compound A has the greatest flavor threshold 4 4 NFS 5130 2010 Exam (YELLOW) April 5, d. Compound E has the greatest flavor threshold e. None of the above 32. In the food product described above, the flavor molecule which contributes least to its flavor is a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 33. Of the following, __________ will not provide a salty sensation a. Li F b. NaCl c. Li Cl d. CsCl 34. The pH of four different food products W, X, Y, Z was determined to be 8, 6, 4 and 2 respectively. When consumed, it is expected that a. Z will be extremely bitter b. Z will be extremely sour c. W will be extremely bitter d. W will be extremely sour 35. The dominant acid in Italian salad dressing is a. Lactic acid b. Tartaric acid c. Acetic acid d. Citric acid 36. In an alpha helix the H- Bonds between ‘O’ and NH are a. Parallel to the helical axis b. Perpendicular to the helical axis c. Pointing outwards from the helix d. Pointing into the core of the helix 37. The amino acid proline a. favors the formation of a C10 helix b. favors the formation of a parallel beta sheet c. favors the formation of an anti-parallel beta sheet d. favors the formation of a beta turn 38. In a parallel B- sheet structure, the a. sheets are stacked on top of each other b. H- bonds are shorter than those in the ant-parallel b-sheets c. H- Bonds are longer than those in the ant-parallel b-sheets d. S-S bonds are stronger than those in the ant-parallel b-sheets 39. In an a-helix, the loop contains 13 atoms. This happens due to a. H-Bonding between carbonyl C and the 13th N atom b. H- Bonding between the carbonyl O and the 13th N atom c. H- Bonding between the carbonyl O and the 13th H atom d. H-Bonding between carbonyl C and the 13th H atom 5 5 NFS 5130 2010 Exam (YELLOW) April 5, 40. In a molecular model for protein structure, the flat arrows depict, a. Random coil b. Alpha helix c. Pi helix d. Beta sheet Question 2: Indicate if the following statements are True (A) or False (B) (1 x 15 points) 41 Emulsions breakdown by the process of creaming. T 42 In an emulsion, a surfactant forms miscells at a concentration greater than its CMC. T 43 The forces responsible for tertiary structure of protein include H- bonds and Van der Waals interactions. F 44 Protein structure is coded for in the DNA. T 45 Proteins are emulsifiers of choice in food systems because they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic groups. T 46 Proteins are less surface active than soap-like detergents. T 47 Molecules in the interior of a phase are attracted equally from all directions while those on the surface have a net force of attraction directed towards the interior of the phase to which they belong. This decreases the number of molecules on the surface leading to increase in surface tension. T 48 Factors that stabilize emulsions include low rate of droplet encounter, and high viscosity of continuous phase, both of which are achieved by gum Arabic. T 49 Laplace pressure is defined as the difference in pressure at the concave and convex sides of a curved surface. T 50 The tetrapyrrole derivative, heme has iron in the center bound to the histidine of the pyrrole ring, 4 N atoms of the globin and a free binding site to which different ligands attach, imparting different colors to the whole complex. F 51 Colors are added to foods because naturally occurring pigments are unstable and cannot withstand the processing conditions T 52 The Delaney clause of the Food, Drug and Cosmetic act does not apply to color additives sanctioned before 1958. T 6 6 NFS 5130 2010 Exam (YELLOW) April 5, 53 Anthocyanins are color pigments belonging to the isoprenoid derivative family. F 54 F,D & C lakes are water insoluble colors extended on a substratum with a color content of more than 40 percent. F 55 Emulsifiers prevent creaming, flocculation and coalescence from occurring. T 56 Color of meat depends on the oxidation state of Fe, ligands bound to heme and the state of the globin protein. T Question 3: Circle the most appropriate answer: (2x 8 points) 7 7 A B C NFS 5130 2010 Exam (YELLOW) April 5, 8 8 D 57. Of the structures shown above, the following is an aliphatic amino acid a. A b. B c. C d. D 58. Of the structures shown above, the following are polar in nature a. A and B b. B and C c. C and D d. B and D 59. Of the structures shown above, the following will be less soluble in water a. A and B b. A and C c. C d. B 60. A protein will assume a predominantly random coiled structure if it is high in the following amino acids: a. A and B b. A and C c. D d. C and D 61. Of the structures shown above, the following will stabilize tertiary structure by forming strong covalent bonds a. A b. B c. C d. D 62. Of the structures shown above, the following will readily absorb UV light a. A b. B c. A and B d. B and C 63. Of the structures shown above, the following will not have an isoelectric point close to a pH=7 a. A and B b. A c. C d. A and C 64. Of the structures shown above, the following will give a basic solution when dissolved in water a. A b. B c. D d. None of the above Question 4: Complete the table below: (2 x 9 points) Name State of Fe Color of Complex Name of Ligand Nitric oxide myoglobin 2+ PINK :NO Reduced myoglobin 2+ PURPLE H20 cyanometmyoglo bin 3+ RED -CN Question 5: Using the table below, Points) (1x10 a. name the continuous phase for each type dispersion type b. name the dispersed phase for each dispersion type DispersionType ContinuousPhase DispersedPhase 1 Foam LIQUID GAS 2 Sol LIQUID SOLID 3 Gel SOLID LIQUID 4 Emulsion LIQUID LIQUID 5 Smoke GAS SOLID [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 10 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 31, 2023
Number of pages
10
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 31, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
142