Business > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > PRACTICE QUESTIONS FOR COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAM --THE FULL JOURNEY-- (All)
PRACTICE QUESTIONS FOR COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAM --THE FULL JOURNEY--
Document Content and Description Below
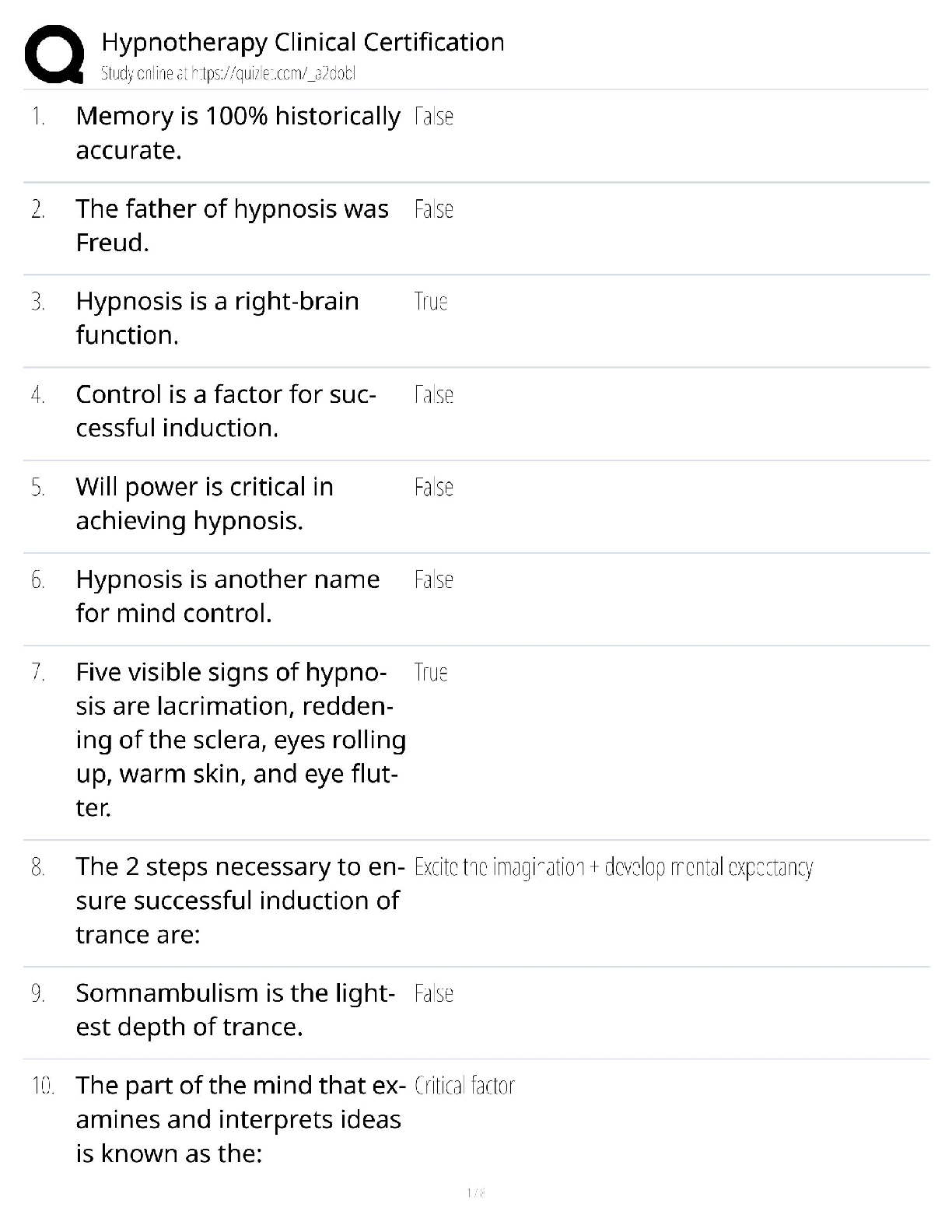
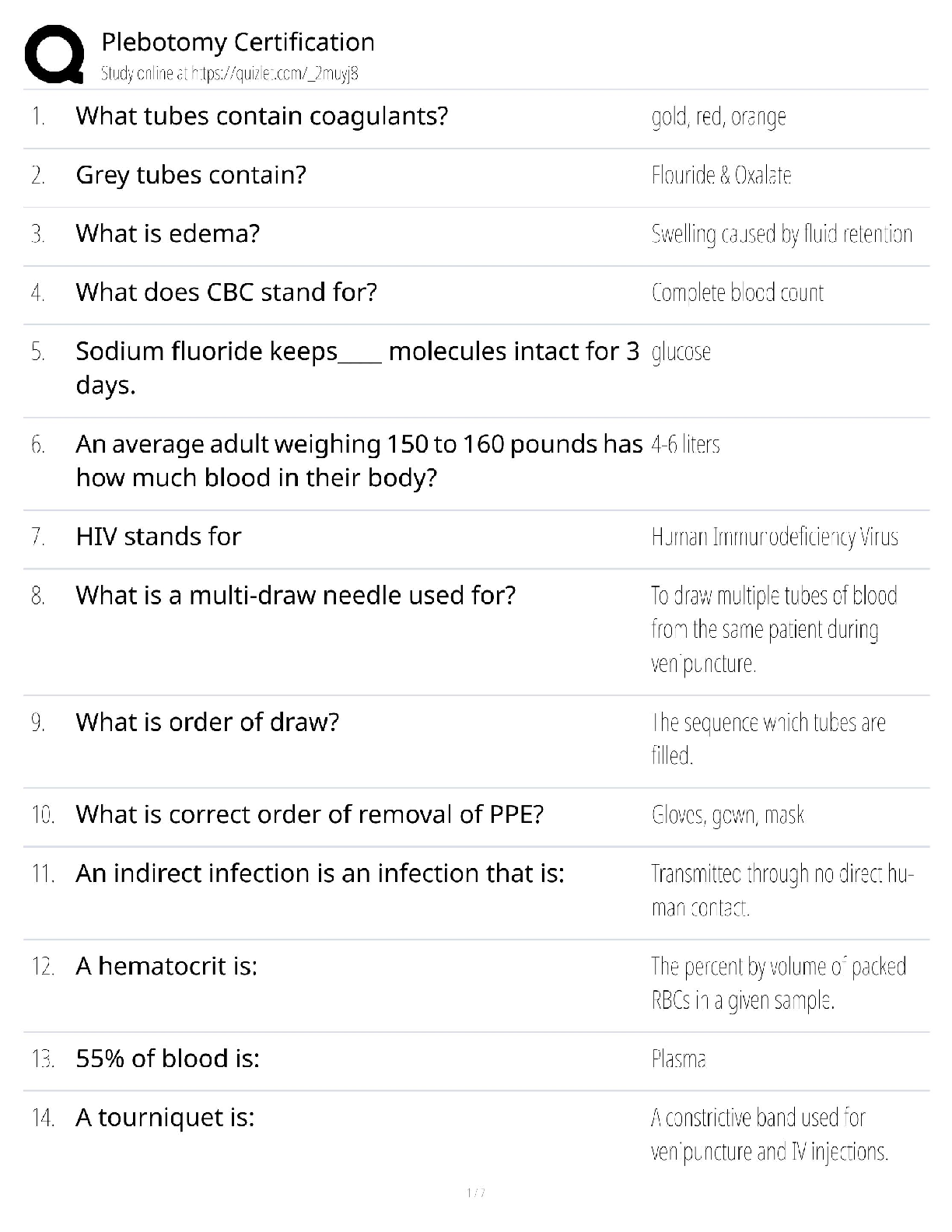
Which of the following is not one of the standards pertaining to the auditor’s fieldwork? a. The work is to be adequately planned and assistants, if any, are to be properly supervised. b. Due pro ... fessional care is to be exercised in the planning and performance of the audit and the preparation of the report. c. Sufficient competent evidential matter is to be obtained through inspection, observation, inquiries, and confirmations to afford a reasonable basis for an opinion regarding the financial statements under audit. d. A sufficient understanding of internal control is to be obtained to plan the audit and to determine the nature, timing, and extent of tests to be performed. 2. Financial statement assertions are established for account balances, Classes of transactions Disclosures a. Yes Yes b. Yes No c. No Yes d. No No 3. Which of the following is not a financial statement assertion relating to account balances? a. Completeness. b. Existence. c. Rights and obligations. d. Valuation and competence. 4. Which of the following is not an assertion relating to classes of transactions? a. Accuracy. b. Consistency. c. Cutoff. d. Occurrence. 5. In testing the existence assertion for an asset, an auditor ordinarily works from the a. Financial statements to the potentially unrecorded items. b. Potentially unrecorded items to the financial statements. c. Accounting records to the supporting evidence. d. Supporting evidence to the accounting records. 2 6. In determining whether transactions have been recorded, the direction of the audit testing should be from the a. General ledger balances. b. Adjusted trial balance. c. Original source documents. d. General journal entries. Audit Risk Model & Risk Assessment Procedures 7. Which of the following audit risk components may be assessed in nonquantitative terms? Control risk Detection risk Inherent risk a. Yes Yes No b. Yes No Yes c. Yes Yes Yes d. No Yes Yes 8. Inherent risk and control risk differ from detection risk in that they a. Arise from the misapplication of auditing procedures. b. May be assessed in either quantitative or non-quantitative terms. c. Exist independently of the financial statement audit. d. Can be changed at the auditor’s discretion. 9. The risk that an auditor will conclude, based on substantive tests, that a material misstatement does not exist in an account balance when, in fact, such misstatement does exist is referred to as a. Sampling risk. b. Detection risk. c. Nonsampling risk d. Inherent risk 10. On the basis of the audit evidence gathered and evaluated, an auditor decides to increase the assessed level of control risk from that originally planned. To achieve an overall audit risk level that is substantially the same as the planned audit risk level, the auditor would a. Decrease substantive testing. b. Decrease detection risk. c. Increase inherent risk. d. Increase materiality levels. 11. When an auditor increases the assessed level of control risk because certain control activities were determined to be ineffective, the auditor would most likely increase the a. Extent of tests of controls. b. Level of detection risk. c. Extent of tests of details. d. Level of inherent risk. 3 12. Relationship between control risk and detection risk is ordinarily a. Parallel. b. Inverse. c. Direct. d. Equal. 13. As the acceptable level of detection risk decreases, an auditor may a. Reduce substantive testing by relying on the assessments of inherent risk and control risk. b. Postpone the planned timing of substantive tests from interim dates to the yearend. c. Eliminate the assessed level of inherent risk from consideration as a planning factor. d. Lower the assessed level of control risk from the maximum level to below the maximum. 14. As the acceptable level of detection risk decreases, the assurance directly provided from a. Substantive tests should increase. b. Substantive tests should decrease. c. Tests of controls should increase. d. Tests of controls should decrease. 15. While assessing the risks of material misstatement auditors identify risks, relate risk to what could go wrong, consider the magnitude of risks and a. Assess the risk of misstatements due to illegal acts. b. Consider the complexity of the transactions involved. c. Consider the likelihood that the risks could result in material misstatement. d. Determine materiality levels. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 70 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 13, 2023
Number of pages
70
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 13, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
129