PROGRESSION FIELD TECH II – IV CONVECTIONAL > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Progression: Field Tech IV – V Questions and Answers 100% Pass (All)
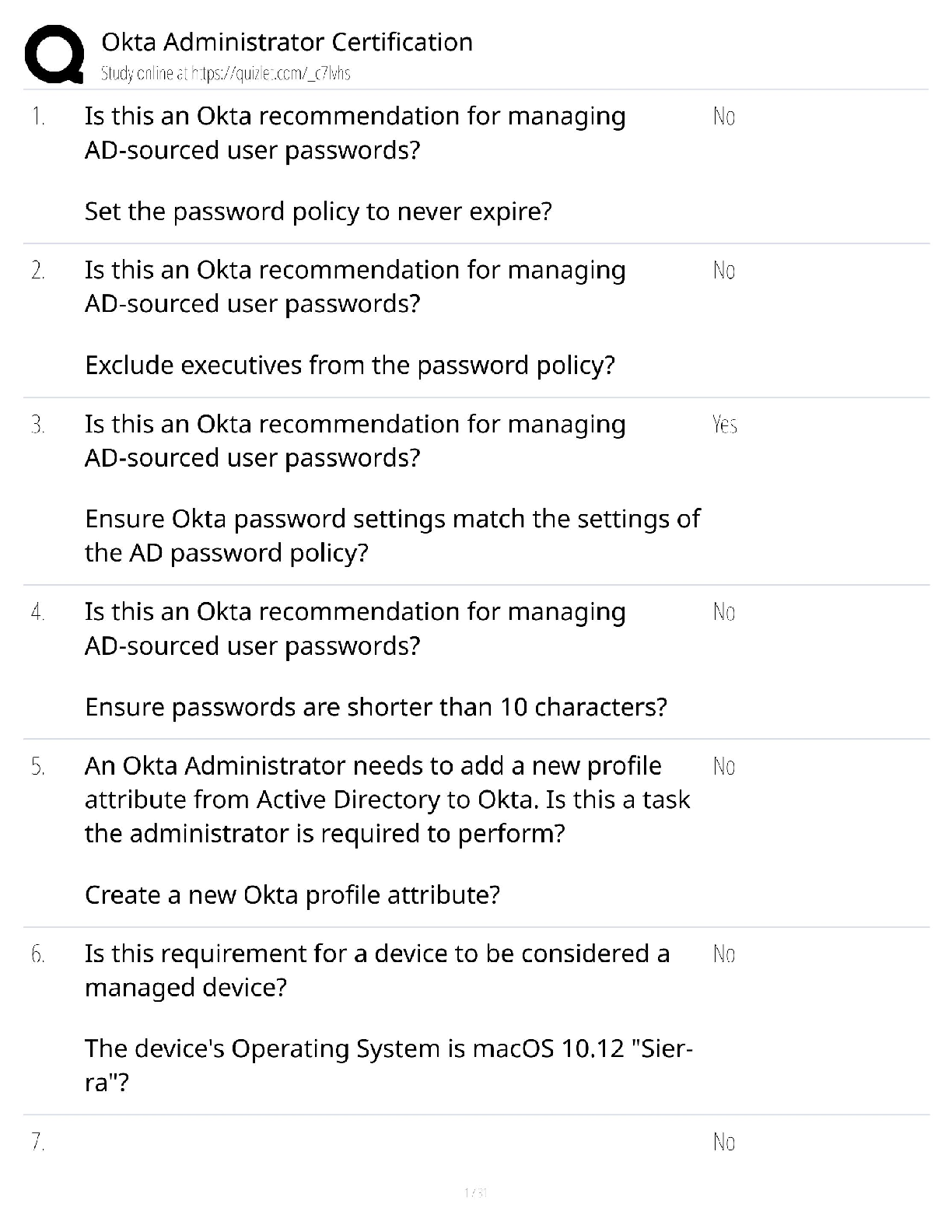
Progression: Field Tech IV – V Questions and Answers 100% Pass
Document Content and Description Below
Progression: Field Tech IV – V Questions and Answers 100% Pass Baseband signaling ✔✔is predominant in Ethernet networks. two ways we can use a flow of energy to carry data ✔✔Analog and di ... gital Simplex ✔✔A signal may flow in only one direction. A commercial radio station uses simplex communication, because listeners cannot transmit radio signals back to the station. Half-duplex ✔✔Signals may flow in either direction, but not simultaneously. For example, a two-way radio allows only one user to speak at any one time. Full-duplex ✔✔Signals may flow in both directions simultaneously. A telephone is the best example of full-duplex communication. One wire brings a signal from the telephone company to your home, and a second wire carries a separate signal from your home back to the telephone company. Thus, you can both hear and speak simultaneously. Synchronous ✔✔The communicating parties or endpoints use time to organize communication. In a data network, two communicating computers use each clock "tick" to detect whether a digital bit is a 1 or 0. For example, as each time interval passes, a computer checks the network cable to see whether the voltage is high (binary 1) or low (binary 0). Because the timing determines the meaning of the signal, it is essential that the endpoints are synchronized to the same clock before sending signals. Asynchronous ✔✔Bits are not transmitted on any strict timetable. For example, a computer modem typically uses 8 bits to represent one character or letter. To indicate the start of each character, the sending modem transmits a "start" bit to alert the receiving end to the incoming signal. After the final bit of the eighth character is transmitted, the sending modem transmits a "stop" bit to indicate the end of the character. This process is repeated for each character the modem transmits. Thus, the receiving modem must stay synchronized to the signal only for the length of time it takes to transmit 8 bits. If the sending and receiving clocks are slightly out of synchronization, these short data transfers will still be successful. Which of the following is most typical of a broadband network? ✔✔Multiple analog channels Data bus size ✔✔The size of the bus refers to the number of data bits a CPU can work on in a single instruction. Clock speed ✔✔The clock speed indicates how many instructions per second the processor can execute. Each "tick" of the clock is called a cycle, thus clock speed is measured in cycles per second. A single cycle per second is called 1 hertz (Hz), 1,000 Hz is 1 kilohertz (kHz), 1 million Hz is 1 megahertz (MHz), and 1 billion Hz is 1 gigahertz (GHz). A CPU that runs at 400,000,000 cycles per second is a 400- MHz processor. storage ✔✔used to describe media that hold data for longer periods, even when the power goes off. What components are common to all computer syste [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 49 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

Progression: Field Tech Bundled Exams Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions
Progression: Field Tech Bundled Exams Questions and Answers with Verified Solutions
By Nutmegs 2 years ago
$25
18
Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 25, 2023
Number of pages
49
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 25, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
115








.png)