*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NURSING 21: NCLEX-RN EXAM TEST BANK RATIONALE (UPDATED) A Guide. (All)
NURSING 21: NCLEX-RN EXAM TEST BANK RATIONALE (UPDATED) A Guide.
Document Content and Description Below
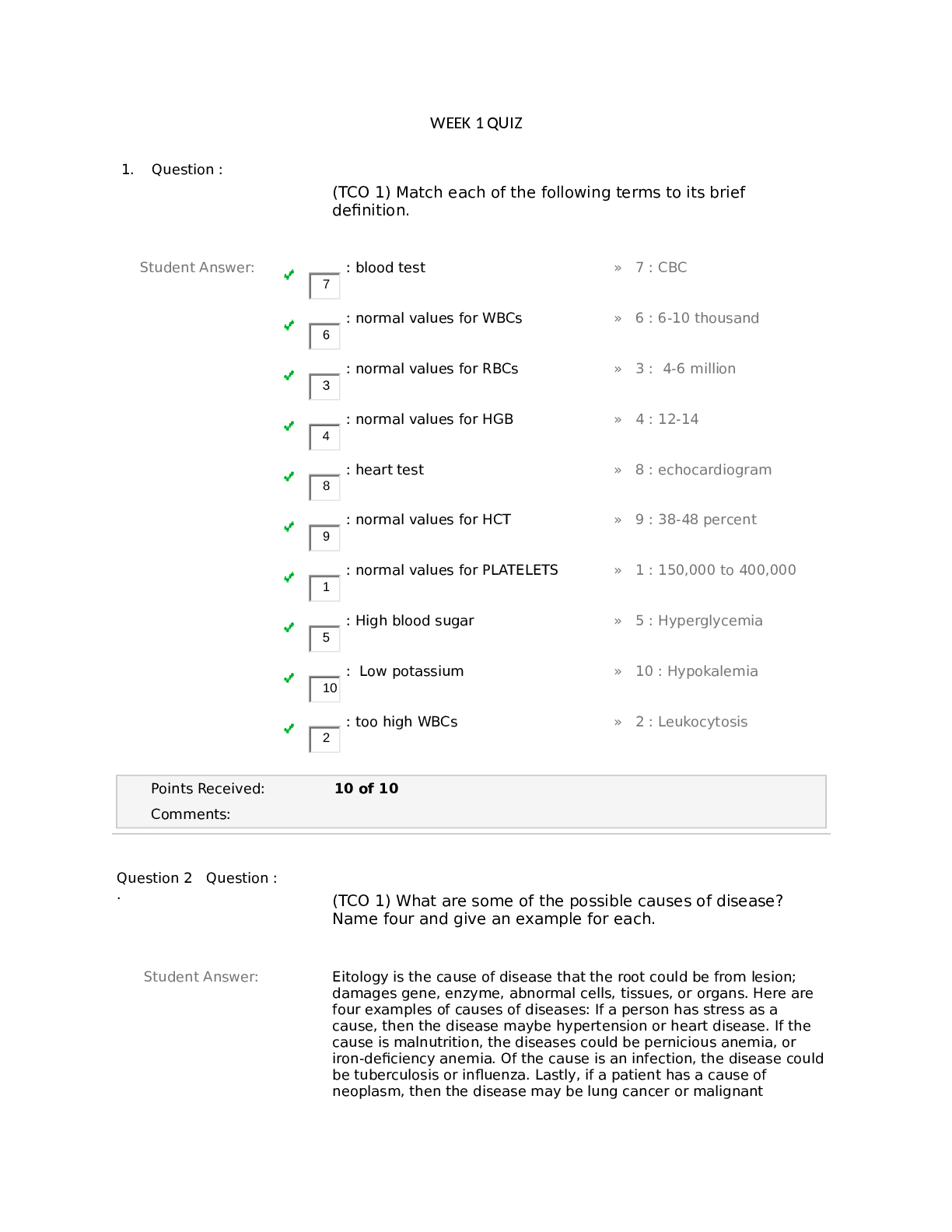
NURSING 21 NCLEX-RN EXAM TEST BANK 1001 Which electrolyte abnormalities would the nurse expect to occur while working with a client who just sustained partial- and full-thickness burns? 1) Decreased s ... odium and increased potassium 2) Increased calcium and decreased potassium 3) Decreased magnesium and increased sodium 4) Increased sodium and decreased potassium 1002 The nurse provides teaching to a client after the removal of a short leg cast. The nurse should include which of the following in discussions with the client? 1) Wash the skin with undiluted hydrogen peroxide. 2) Vigorously scrub the legs to remove dead skin. 3) Gently wash and lubricate the leg. 4) Avoid touching the leg for 2 weeks. 1003 Which of the following nursing diagnoses would be the priority for a client with Paget’s disease? 1) Risk for noncompliance 2) Disturbed sleep pattern 3) Impaired physical mobility 4) Disturbed body image 1004 A client with a right arm cast for fractured humerus states, “I haven’t been able to extend the fingers on my right hand since this morning.” What action should the nurse take next? 1) Assess neurovascular status. 2) Ask the client to massage the fingers. 3) Encourage the client to take the prescribed analgesics as ordered. 4) Elevate the right arm on a pillow to reduce edema. 1005 A client with an open fracture is at risk for developing osteomyelitis. Which of the following classic symptoms would the nurse assess for to detect development of this complication? 1) Low bone density 2) Elevated temperature 3) Acute respiratory distress 4) Shortening of the affected extremity 1006 An obese client with degenerative joint disease is being managed pharmacologically with aspirin therapy. The nurse knows that additional client teaching is necessary when the client makes which of the following statements? 1) “I take my aspirin only when I have extreme pain and stiffness.” 2) “I use heat sometimes to help decrease my pain and joint stiffness.” 3) “I frequently examine my stools for bleeding.” 4) “I started an exercise program to lose weight.” CRRECT ANSWER: 1 RATIONALE: Aspirin therapy for this condition is continuous and is effective only after a therapeutic level is reached. It should not be taken intermittently (option 1). The other options are correct statements about self-care measures when taking aspirin for degenerative joint disease. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Evaluation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of appropriate self-management techniques for degenerative joint disease. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1007 A client underwent a lumbar laminectomy today. Which nursing diagnosis has highest priority for this client? 1) Disturbed body image disturbance 2) Social isolation 3) Ineffective role performance 4) Impaired physical mobility CORRECT ANSWER: 4 RATIONALE: Immediately after surgery, the client will be inclined not to move because of pain and fear of disturbing the operative site. Minimal scarring results from this surgery, so body image disturbance is not likely to be appropriate (option 1). The psychosocial diagnoses in options 2 and 3 have less priority than option 4 because option 4 is a physiological concern. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Analysis CONTENT AREA: Fundamentals STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of priority nursing diagnoses following musculoskeletal surgery. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1008 A client had a left above-the-knee amputation today. For the first 24 hours postoperatively, the nurse makes it a priority to do which of the following to properly manage the surgical site? 1) Elevate the residual limb on a pillow. 2) Loosen the stump dressing every 4 hours. 3) Maintain the residual limb in a dependent position. 4) Change dressings as often as needed. CORRECT ANSWER: 1 RATIONALE: Elevating the limb on a pillow facilitates venous return, decreases swelling, and promotes comfort. The stump dressing is usually a compression type to mold the stump and to decrease the edema associated with inflammation, so option 2 is an inappropriate intervention. The other options are also inappropriate because option 3 increases risk of edema and option 4 is done as ordered. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of postoperative stump care and positioning. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1010 A truck driver presents to the primary care provider with complaints of persistent back pain. The nurse explains that which client activity documented during the nursing history may contribute to further back injury? 1) Lifting objects close to the body 2) Shifting positions often when sitting for prolonged periods 3) Providing back support with a pillow when sitting 4) Prolonged standing or sitting CORRECT ANSWER: 4 RATIONALE: Prolonged sitting or standing aggravates back injury because of the additional stress placed on the structures supporting the back. Lifting objects close to the body, shifting positions frequently, and providing back support are appropriate actions to maintain good body mechanics. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Assessment CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of risk factors and aggravating factors of low back pain. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1011 A client underwent a lumbar laminectomy. Which of the following activities would be best 4 hours postoperatively? 1) Sitting up in a chair to watch television 2) Sitting at the side of the bed 3) Lying in bed in good alignment with the head of bed flat 4) Using the side-rails for support to get out of bed CORRECT ANSWER: 3 RATIONALE: The physician orders the client’s activity after a laminectomy. After a laminectomy procedure, a client should be assisted to logroll from side to side. The principle is to maintain the alignment of the vertebral column at all times. Clients with lumbar laminectomy should be kept flat or with head of bed slightly elevated to minimize stress on the suture line. Using the side-rails to get out of bed causes shifting of the vertebral column. Sitting up in a chair or on the side of the bed is usually done the evening of the surgery or the first day following surgery, and it is for brief periods only. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Safe Effective Care Environment: Safety and Infection Control INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of activity levels after surgery that will not cause harm to the surgical area following laminectomy. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1012 The nurse provides teaching to a 50-year-old male Caucasian client with chronic low back pain. The client weighs 200 pounds, works as a truck driver, sits for prolonged periods, and seldom participates in exercise activities. The client smokes one pack of cigarettes and drinks six cans of beer per day. What risk factors should the nurse include in the discussion? 1) Lack of exercise, obesity, sitting for long periods, smoking, sedentary occupation 2) Degenerative disk disease, gender, race, smoking 3) Degenerative disk disease, race, alcohol use, smoking, inactivity 4) Age, obesity, lack of exercise, genetic factors CORRECT ANSWER: 1 RATIONALE: Smoking has been found to contribute to disc deterioration. Lack of exercise predisposes the muscles of the back to strain. The extra weight of obese individuals imposes more strain on the back and also interferes in maintaining good body mechanics in lifting. Occupations that require prolonged sitting or standing predispose those individuals to exacerbation of back pain. Option 1 is the only answer that accurately reflects risk factors associated with chronic low back pain for the client described in the question. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Planning CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of factors that aggravate low back pain. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1013 The nurse is teaching a postmenopausal client about the use of calcium to prevent the effects of osteoporosis. The client asks: “Why do I have to take Vitamin D with my calcium?” Which of the following is the nurse’s best response? 1) “Vitamin D prevents osteoporosis.” 2) “Vitamin D increases intestinal absorption of calcium.” 3) “You are most likely to be deficient in Vitamin D.” 4) “Calcium and Vitamin D supplementation is the only way to prevent osteoporosis.” CORRECT ANSWER: 2 RATIONALE: A combination of calcium and Vitamin D is recommended for the prevention of osteoporosis. Vitamin D increases the intestinal absorption of calcium and mobilizes calcium and phosphorus into the bone. Vitamin D alone does not prevent osteoporosis (option 2). Whereas some elderly might be deficient in Vitamin D, a postmenopausal state does not necessarily cause the deficiency (option 3). There are other interventions for the prevention of osteoporosis, including lifestyle modifications (e.g., smoking cessation), which makes option 4 inaccurate. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Health Promotion and Maintenance INTEGRATED PROCESS: Communication and Documentation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of risk factors for and prevention of osteoporosis. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1014 The nurse is caring for a client with a week-old cast. The client asks why the nurse palpates the casted area when doing the assessment. Which of the following is the most appropriate response by the nurse? 1) “I am making sure that the cast has dried.” 2) “I am evaluating the strength of the cast.” 3) “I am feeling for hot spots that might indicate infection.” 4) “I am making sure that the cast is not too tight.” CORRECT ANSWER: 3 RATIONALE: A complication of cast application is skin breakdown underneath the cast. If this occurs, infection can set in and can cause the area over the breakdown to be warmer than other areas. A bad odor coming from the area may also be noted. Option 1 is inaccurate because generally plaster casts dry in 48 hours or less and erglass casts in 30 minutes to 1 hour. If a cast is too tight, symptoms associated with neurovascular compromise will be noted, which include pain, paresthesia, pallor, diminished pulse distal to the cast, and paralysis (option 4). COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Communication and Documentation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of various complications of casts. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1015 A client is placed on continuous passive motion (CPM) machine postoperatively after a total knee replacement. The nurse observes that the client’s knee is externally rotating during flexion. What should the nurse do next? 1d, loss of the limb may occur. The nurse needs to ensure that the leg is not above heart level so no further damage occurs. The physician needs to be notified immediately so medical interventions can be instituted before irreversible tissue and nerve damage occurs. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of adverse neurovascular changes to a client in a cast. Recall principles of gravity and blood flow to aid in answering the question. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1017 A nurse receives a client from the emergency department in Buck’s traction following a fracture of the right femur. The nurse documents which of the following as a priority in the client medical record? 1) Status of skin underneath the traction and over bony prominences 2) Type of pin, wire, or tongs used 3) The effectiveness of pain medication given in the field 4) Medications given in the emergency department CORRECT ANSWER: 1 RATIONALE: It is essential to monitor the condition of the skin under traction, as well as bony prominences, because these areas are at risk for breakdown due to continuous friction and pressure from the skin traction device. Option 2 is incorrect because Buck’s traction is a type of skintraction. Skeletal tractions use pins, wires, or tongs to aid in realignment. Option 3 is appropriate, but the most essential assessment to be documented for a client with skin traction is the condition of the skin underneath the straps. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Communication and Documentation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The critical word in the question is priority, which tells you that all or more than one options are correct and that the most essential one is the correct answer. Use nursing knowledge about skin traction and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1018 The nurse planning for the care of a client admitted with balanced suspension traction explains to the family that an advantage of balanced suspension is which of the following? 1) It eliminates the risk for skin breakdown. 2) It allows the client to raise the buttocks off the bed for bedpan use and skin care. 3) It is more effective in reducing hip contracture. 4) It requires only one weight to maintain traction. CORRECT ANSWER: 2 RATIONALE: Balanced suspension allows for ease with bedpan use and skin care without disturbing the line of traction. In this type of traction, the client’s injured extremity is lifted off the bed and a straight pull is accomplished by the application of several forces and several weights. Skin breakdown is not eliminated with this type of traction because any immobile client can be at risk. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of Buck’s traction as a skin traction and the need to assess the underlying skin. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1019 A client is taking colchicine for gout. The client complains of weakness, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea for the past 2 days. The nurse interprets these complaints indicating which of the following? 1) Therapeutic effects of the medication 2) Signs of toxicity 3) Expected side effects 4) An allergic response CORRECT ANSWER: 2 RATIONALE: Colchicine is used in treating the acute attack of gout. The symptoms described are signs of toxicity. The client should be instructed to stop the medication and be seen for follow-up treatment. The expected effect of colchicine is to diminish the joint pain associated with the acute attack. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Analysis CONTENT AREA: Adult Health: Musculoskeletal STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of actions and adverse effects of colchicines in the client with gout. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1020 An 87-year-old client sustained a right hip fracture. The client asks the nurse about the length of time needed for the fracture to heal. The nurse’s response includes consideration of which client factor that influences the rate of bone healing? 1) Frequency of physical therapy 2) Age of the client 3) Weight of the client 4) Early ambulation 1022 A child is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of osteomyelitis. Which of the following would the nurse likely find when gathering the nursing history? 1) History of an upper respiratory infection 2) History of gastroenteritis 3) History of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease 4) History of congenital hip dysplasia CORRECT ANSWER: 1 RATIONALE: The history of a child with osteomyelitis may include a recent upper respiratory infection (which may include an ear infection or sinus infection), skin infection, or blunt trauma to a bone. Gastroenteritis would not be found in the recent history of this child that would lead to this illness. LCPD and CHD do not lead to osteomyelitis. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Assessment CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is the knowledge of risk factors for osteomyelitis. Use nursing knowledge and the process of elimination to make a selection. 1023 Two hours after a child had a cast applied for a fractured radius, the nursing assessment reveals swelling in the hand, which is elevated higher than the heart. Ice has been applied continuously. The child does not complain of pain but does complain of numbness and tingling. Which should the nurse do first? 1) Medicate for pain. 2) Elevate the injured extremity even higher. 3) Call the physician. 4) Provide the child with diversional activities. CORRECT ANSWER: 3 RATIONALE: A very swollen hand despite application of ice and elevation is a grave concern, especially with the child complaining of numbness. Such swelling can lead to compartment syndrome, which can lead to neurological damage. This is a medical emergency, and the physician should be called immediately. The nurse can then provide diversional activities while waiting for definitive orders. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is recognition of a complication, compartment syndrome, that can lead to neurological damage. The correct answer is the one that provides for definitive treatment of the problem, which in this case is in the practice realm of the physician. 1024 The pediatric nurse interprets that which of the following infants is the least likely to be diagnosed with developmental dysplasia of the hip? 1) The infant with a family history of developmental dysplasia of the hip 2) The infant who weighs over 10 pounds 3) The infant carried on the mother’s hips 4) The infant who had breech position while in the uterus CORRECT ANSWER: 3 RATIONALE: The infant who is carried with the hips abducted is at decreased risk for developing developmental dysplasia of the hip. Options 1, 2, and 4 are all factors that would possibly increase the incidence of this defect. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Analysis CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: The core issue of the question is recognition of which situation allows the infant to keep the hips abducted. Evaluate each option according to this criteria to make a selection. 1025 Which of the following interventions would be essential for the nurse to implement to promote a stable respiratory status in the adolescent who recently had a spinal fusion for scoliosis? 1) Logrolling and repositioning every 4 hours 2) Coughing and deep-breathing every 2 hours during the day 3) Assessing pain status and ensuring adequate pain relief 4) Encouraging use of incentive spirometry every 4 hours while awake CORRECT ANSWER: 3 RATIONALE: Pain must be managed properly in the child after spinal fusion in order for the client to participate in respiratory exercises. Logrolling and repositioning, as well as coughing, deep-breathing, and use of incentive spirometry should be done every 2 hours around the clock with this postoperative client. Providing adequate pain relief will enable the client to carry out these important activities. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEE CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Assessment CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: The issue of the question is the ability of the nurse to analyze assessment data and compare it to typical data of childhood musculoskeletal problems. Note that the temperature is elevated to help choose the option related to infection. 1027 The nurse is preparing to help a client get up from a chair using crutches. Place in order the steps that the nurse outlines to the client to do this procedure correctly. Click and drag the options below to move them up or down. 1) Place unaffected leg slightly under or at the edge of the chair. 2) Grasp the arm of the chair using the hand on the unaffected side. 3) Grasp the crutches by the horizontal hand bars using the hand on the affected side. 4) Move forward to the edge of the chair. 5) Assume a tripod position. 6) Push down on the crutches and the chair armrest while raising the body out of the chair. CORRECT ANSWER: 4, 1, 3, 2, 6, 5 RATIONALE: The proper procedure is as follows:<BR /> 1. Move forward to the edge of the chair.<BR /> 2. Place unaffected leg slightly under or at the edge of the chair (this position helps the client to stand up from the chair and achieve balance, since the unaffected leg is supported against the edge of the chair).<BR /> 3. Grasp the crutches by the horizontal hand bars using the hand on the affected side.<BR /> 4. Grasp the arm of the chair using the hand on the unaffected side (the body weight is placed on the crutches and the hand on the armrest to support the unaffected leg when the client rises to stand).<BR /> 5. Push down on the crutches and the chair armrest while raising the body out of the chair.<BR /> 6. Assume a tripod position (crutches out laterally in front of feet, approximately 6 inches, with feet slightly apart, creating a wide base of support) for balance before moving. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: Visualize the procedure and think about principles of joint support and balance to complete the ordered steps. 1028 The mother of a newborn is upset that her baby has congenital clubfoot. She asks the nurse what she did to cause her baby's deformity. Which of the following answers is the most appropriate? Select all that apply. 1) Abnormal uterine positioning could have caused this deformity 2) A lack of good nutrition during pregnancy could have caused this defect 3) Having the baby before the due date could have caused this problem 4) There are no known etiologies of this defect 5) Neuromuscular and vascular problems may have caused the problem CORRECT ANSWER: 1, 5 RATIONALE: The exact cause of clubfoot is unknown, though several possible etiologies exist. Abnormal intrauterine position may cause the deformity, along with neuromuscular or vascular problems. A positive family history increases the chance of this deformity. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: Knowledge of the etiology of clubfoot will help to determine the correct response. Consider which response, in addition to being accurate, would be most comforting for the mother. 1029 Which of the following are appropriate nursing interventions to include in the initial postoperative care of a child who has had surgery for clubfoot? Select all that apply. 1) Apply ice bags to the foot; keep the ankle and foot elevated on a pillow 2) Check for drainage or bleeding; observe for swelling around the cast edges 3) Administer pain medications routinely and maintain nasogastric intubation 4) Perform neurovascular status checks every 2 hours and provide diversional activities 5) Cover the surgical extremity with warm blankets CORRECT ANSWER: 1, 2, 4 RATIONALE: The postoperative care of the child undergoing repair of clubfoot includes elevation, application of ice, assessment for neurovascular status, bleeding and swelling, and pain. Nasogastric intubation is usually not needed and warm blankets are not indicated. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Planning CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: Knowledge of the postsurgical care of the infant with clubfoot will aid in choosing the correct answer. 1030 Which of the following does the nurse expect to find during assessment of a 5-year-old client who has developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)? 1) Asymmetry of gluteal and thigh fat folds 2) Positive Ortolani-Barlow maneuver 3) Telescoping of the femoral head into the pelvis 4) Limited abduction of the affected hip CORRECT ANSWER: 3 RATIONALE: All symptoms listed are clinical manifestations of developmental dysplasia of the hip, although the only one that would be found in a 5-year-old would be the telescoping of the femoral head into the pelvis. Other clinical signs in an older child would be lordosis, and a waddling gait with a marked limp. A positive Ortolani-Barlow maneuver is found in the infant younger than 2 to 3 months of age. Limited abduction is the sign most often used for an infant older than three months, along with asymmetry of thigh and gluteal folds. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Application CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Assessment CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: Knowledge of the assessment findings for a child with DDH will aid in choosing the correct answer. 1031 A 14-year-old boy is diagnosed with slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE). He asks the nurse what caused this condition. Which of the following best answers his question? 1) SCFE is a result of an injury to the hip 2) SCFE may be caused by an endocrine disorder 3) SCFE may be caused by an abnormality of the muscles 4) SCFE is caused by abnormal intrauterine position CORRECT ANSWER: 2 RATIONALE: The exact cause of SCFE is unknown. Predisposing factors include obesity, a growth spurt resulting in a tall and thin stature, and endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism and hypogonadism. There may be a genetic predisposition to this disorder. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Physiological Integrity: Physiological Adaptation INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Implementation CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: Knowledge of the possible etiology of SCFE will aid in choosing the correct answer. 1032 An adolescent is wearing a cast following a spinal fusion for scoliosis. The nurse would include which of the following interventions to address the nursing diagnosis of disturbed body image related to wearing a cast after spinal fusion? Select all that apply. 1) Encourage independence in daily activities 2) Encourage the adolescent to participate in community activities 3) Provide contact with a peer who has undergone the same treatment 4) Teach cast care as appropriate 5) Suggest the client change hairstyle or buy new clothes as a coping mechanism CORRECT ANSWER: 1, 2, 3 RATIONALE: All are appropriate interventions for the child who has undergone a spinal fusion, although only the first three are appropriate interventions directly aimed at the client experiencing an altered body image. Teaching cast care is important, but would be appropriate under the nursing diagnosis of knowledge deficit. The nurse would assist with coping, but this does not necessarily involve new hairstyle or clothes. COGNITIVE LEVEL: Analysis CLIENT NEED: Psychosocial Integrity INTEGRATED PROCESS: Nursing Process: Planning CONTENT AREA: Child Health STRATEGY: Knowledge of the interventions aimed at helping the adolescent in a cast with body image difficulties will help to choose the correct answers. 1033 Which of the following instructions would be appropriate for the nurse to include in the discharge teaching of an adolescent following a spinal fusion? 1) No sittins; it's just too dangerous for you. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 255 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

ALL NURSING EXAMINATONS REVISIONS TEST PAPERS COMBINED
NSG 6430 Final Exam : South University Question 1 (2.5 points) The nurse practitioner knows that a highly valuable assessment tool for evaluating urinary incontinence and contributing factors in daily...
By darrelmay002 2 years ago
$60
15
Reviews( 0 )
$8.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 20, 2023
Number of pages
255
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 20, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
225