NURS 8022 Advanced Pathophysiology Exam #2 Study Guide MODULE 3: Hematology Readings: Ch. 27-29; article – interpretation of iron studies Blood NOT ON STUDY GUIDE • Volume: 6 quarts or 5.5 L • Consists of fluid, cells,
...
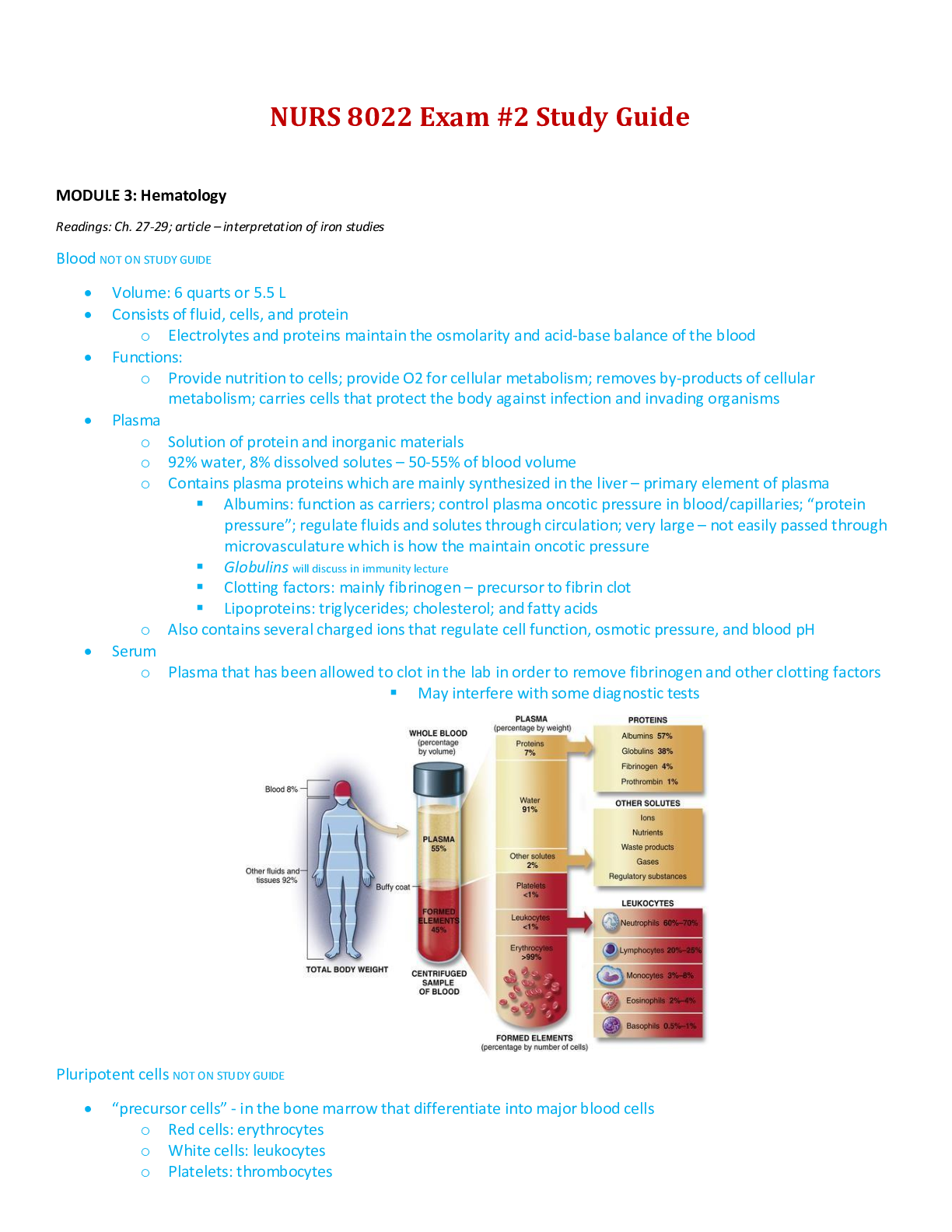
NURS 8022 Advanced Pathophysiology Exam #2 Study Guide MODULE 3: Hematology Readings: Ch. 27-29; article – interpretation of iron studies Blood NOT ON STUDY GUIDE • Volume: 6 quarts or 5.5 L • Consists of fluid, cells, and protein o Electrolytes and proteins maintain the osmolarity and acid-base balance of the blood • Functions: o Provide nutrition to cells; provide O2 for cellular metabolism; removes by-products of cellular metabolism; carries cells that protect the body against infection and invading organisms • Plasma o Solution of protein and inorganic materials o 92% water, 8% dissolved solutes – 50-55% of blood volume o Contains plasma proteins which are mainly synthesized in the liver – primary element of plasma ▪ Albumins: function as carriers; control plasma oncotic pressure in blood/capillaries; “protein pressure”; regulate fluids and solutes through circulation; very large – not easily passed through microvasculature which is how the maintain oncotic pressure ▪ Globulins will discuss in immunity lecture ▪ Clotting factors: mainly fibrinogen – precursor to fibrin clot ▪ Lipoproteins: triglycerides; cholesterol; and fatty acids o Also contains several charged ions that regulate cell function, osmotic pressure, and blood pH • Serum o Plasma that has been allowed to clot in the lab in order to remove fibrinogen and other clotting factors ▪ May interfere with some diagnostic tests Pluripotent cells NOT ON STUDY GUIDE • “precursor cells” - in the bone marrow that differentiate into major blood cells o Red cells: erythrocytes o White cells: leukocytes o Platelets: thrombocytes • Erythrocytes o Most abundant cells of the blood o Responsible for tissue oxygenation o Contain hemoglobin; carry gases and electrolytes o Have limited life span – 120-day life cycle ▪ No mitotic division ▪ Can be removed from circulation by spleen and replaced with new o Biconcavity: function/efficient shape that allows gas diffusion and ability to change shape o Reversible deformity: enables torpedo shape to squeeze through microcirculation & return to normal • Leukocytes o Defend the body against infection and remove debris (dead and damaged cells) o Classified by structure and function ▪ Granulocytes and agranulocytes – will discuss in immune lecture • Thrombocytes o 150,000-400,000/mm3 = normal o Irregularly shaped cytoplasmic fragments; formed by fragmentation of megakaryocytes o Essential for blood coagulation and the control of bleeding o Incapable of mitotic division – no nucleus or DNA; limited life span – 5-9 days & removed by spleen o Granules are proinflammatory – released when there is vessel injury – ATP, ADP, calcium, serotonin, histamine o Produced in bone marrow – stored in spleen – slowly released Lymphoid Organs NOT ON STUDY GUIDE • Sites of residence, proliferation, differentiation, and function of lymphocytes and mononuclear phagocytes • Link to hematologic and immune systems • Primary lymphoid organs: o Thymus, bone marrow • Secondary lymphoid organs: spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils, peyer patches of the small intestine • Spleen o Largest secondary lymphoid organ o Functions: fetal hematopoiesis, filters and cleanses the blood, mounts an immune response to bloodborne microorganisms, serves as a blood reservoir • Lymph nodes o Site of the development or activity of lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages o Structurally part of lymphatic system o Functionally part of the immune and hematologic systems Understand the basic physiology of hematopoiesis, erythropoiesis, and what erythropoietin is and what it does • Hematopoiesis: process of blood cell production in adult bone marrow or the liver and/or spleen of the fetus o Two stages ▪ Mitosis (proliferation) ▪ Maturation (differentiation) o Act on pluripotent cells o Bone marrow: “myeloid tissue” - primary site of hematopoietic stem cells ▪ Red marrow (produces RBCs) yellow marrow (does not produce RBCs) ▪ Active bone marrow sites: pelvic bones, vertebrae, cranium, mandible, sternum, ribs, humerus, femur o Process ▪ STEM CELL POOL contains: hematopoietic stem cell – progenitor cell ▪ BONE MARROW POOL contains:
[Show More]