NURS 6512 Week 7 Quiz, Recent complete Solutions Explained, All answers correct.
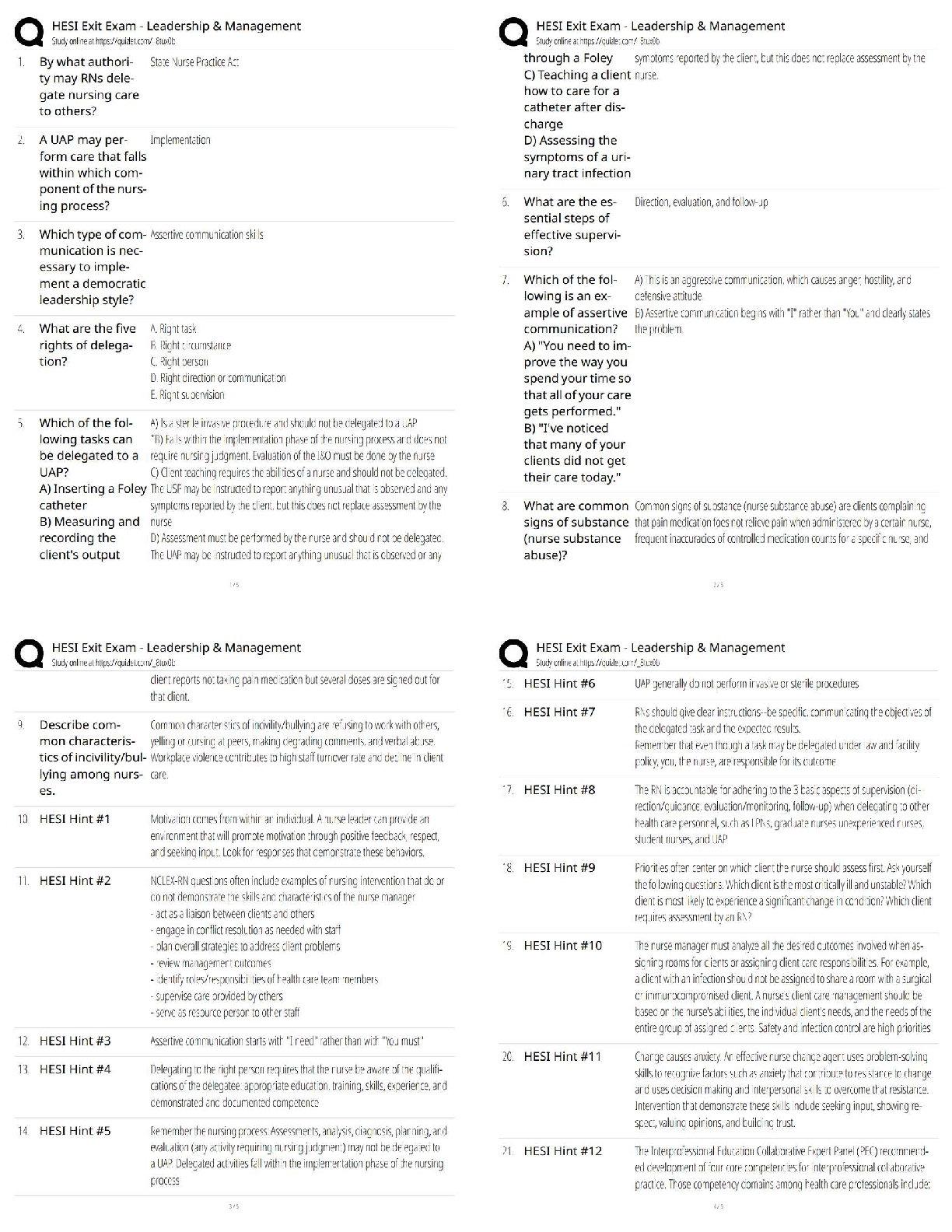
Document Content and Description Below
NURS 6512 week 7 quiz
•
• Question 1
Costovertebral angle tenderness should be assessed whenever you suspect the pa-tient may have:
• Question 2
In older adults, over
...
flow fecal incontinence is commonly due to:
• Question 3
• Question 4
Auscultation of borborygmi is associated with:
• Question 5
When auscultating the abdomen, which finding would indicate collateral circulation between the portal and systemic venous systems?
• Question 6
Conversion of fat-soluble wastes to water-soluble material for renal excretion is a function of the:
• Question 7
The major function of the large intestine is:
• Question 8
Which structure is located in the hypogastric region of the abdomen?
• Question 9
A 45-year-old man relates a several-week history of severe intermittent abdominal burning sensations. He relates that the pain is relieved with small amounts of food. Before starting the physical examination, you review his laboratory work, anticipat-ing a(n):
• Question 10
Percussion at the right midclavicular line, below the umbilicus, and continuing up-ward is the correct technique for locating the:
• Question 11
Baby Joe is 6 months old. He has abdominal distention and vomiting and is incon-solable. A sausage-shaped mass is palpable in his right upper quadrant. Joe s lower quadrant feels empty, and a positive Dance sign is noted in his record. Which one of the following conditions is consistent with Baby Joe s symptoms?
• Question 12
Mrs. G. is 7 months pregnant and states that she has developed a problem with con-stipation. She eats a well-balanced diet and is usually regular. You should explain that constipation is common during pregnancy due to changes in the colorectal are-as, such as:
• Question 13
A 51-year-old woman calls with complaints of weight loss and constipation. She re-ports enlarged hemorrhoids and rectal bleeding. You advise her to:
• Question 14
When examining a patient with tense abdominal musculature, a helpful technique is to have the patient:
• Question 15
The Joint Commission (TJC, formerly The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations [JCAHO]) requires that:
• Question 16
A 5-year-old is complaining of nondescriptive "belly pain." Your next action should be to ask him to:
• Question 17
Body language that leads you to suspect the person is in pain is:
• Question 18
Mr. Green is a 68-year-old patient who has complained of pain. As the health care provider, you have decided to use a pain scale for documentation of the patient's pain. The value of the use of scales for patients to rate their pain intensity is that:
• Question 19
Your trauma patient has no auscultated breath sounds in the right lung field. You can hear ade-quate sounds in the left side. A likely cause of this abnormality could be that the patient:
• Question 20
Clear or amber drainage from the nose or ears of a blunt trauma patient may indicate:
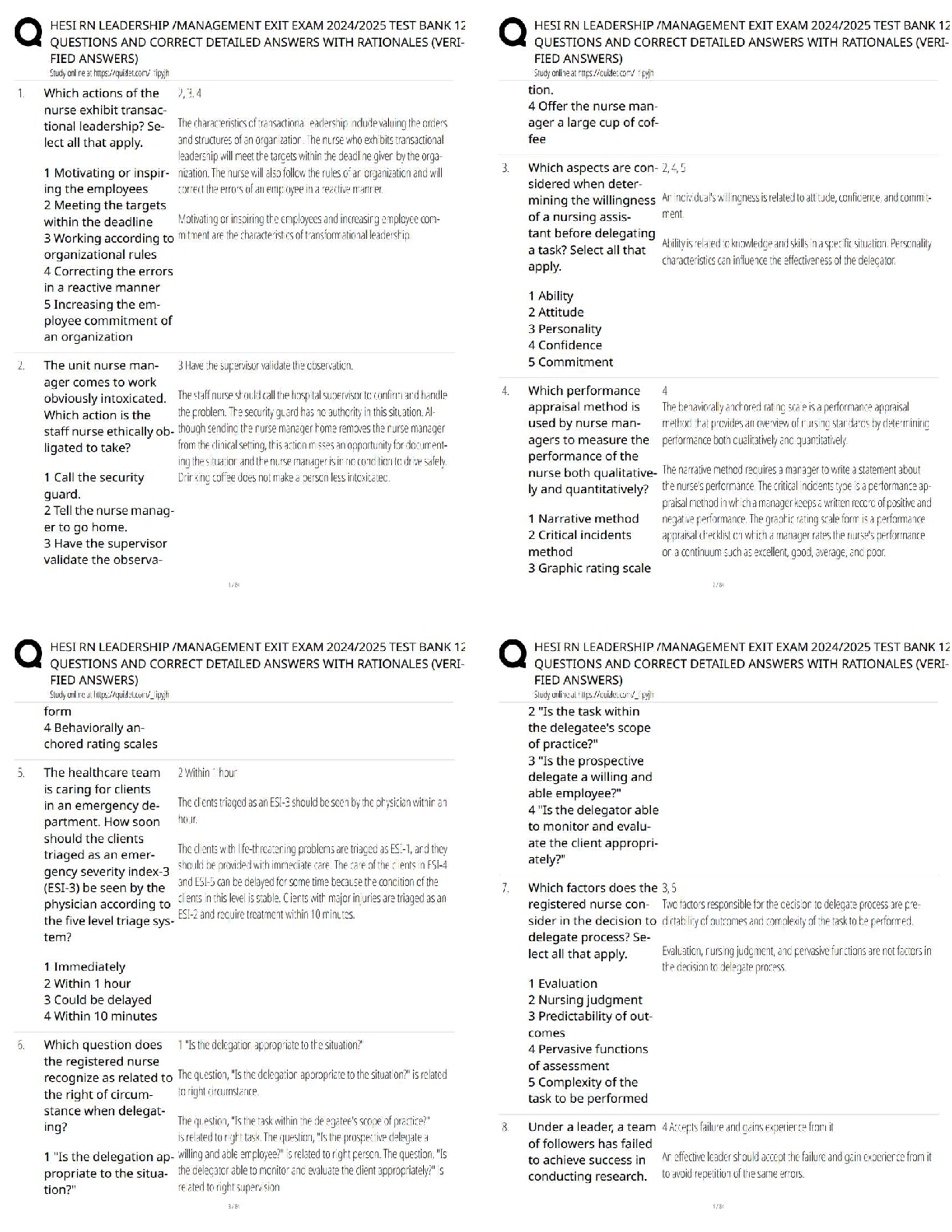
Chapter 17: Abdomen
Test Bank—Medical
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and forms a protective cover for many abdominal structures is the
a. peritoneum.
b. mediastinum.
c. linea alba.
d. mesentery.
e. pleura.
2. What part of the small intestine forms a C-shaped curve around the head of the pancreas?
a. Duodenum
b. Ileum
c. Jejunum
d. Falciform ligament
e. Pylorus
3. Peristalsis of intestinal contents is under the control of
a. cognitive processes.
b. gravity.
c. the autonomic nervous system.
d. the fluid content of the stomach.
e. cerebellum.
4. The esophagus travels a route from
a. anterior to the trachea through the mediastinal cavity.
b. lateral to the trachea through the diaphragm.
c. left of the trachea through the peritoneum.
d. the anterior trachea through the cardiac orifice.
e. behind the trachea through the mediastinal cavity.
5. Which organ is part of the alimentary tract?
a. Pancreas
b. Stomach
c. Gallbladder
d. Liver
e. Spleen
6. The superior most part of the stomach is the
a. body.
b. fundus.
c. pylorus.
d. cardiac orifice.
e. pyloric orifice.
7. Which of the following is true regarding the stomach?
a. It lies in the lower abdominal cavity.
b. It secretes gastric lipase that serves to digest protein.
c. Very little absorption takes place in the stomach.
d. The stomach produces most of the body’s bile.
e. Pancreatic enzymes directly enter the stomach.
8. The appendix is an extension of the
a. ileum.
b. cecum.
c. ascending colon.
d. transverse colon.
e. descending colon.
9. When palpating the abdomen, you should note whether the liver is enlarged in the
a. left upper quadrant.
b. midepigastric region.
c. periumbilical area.
d. right upper quadrant.
e. right lower quadrant.
10. One major function of the liver is to
a. secrete pepsin.
b. emulsify fats.
c. store glycogen.
d. absorb bile.
e. produce insulin.
11. The majority of nutrient absorption takes place in the
a. stomach.
b. small intestine.
c. cecum.
d. transverse colon.
e. descending colon.
12. The major function of the large intestine is
a. water absorption.
b. food digestion.
c. carbohydrate absorption.
d. mucous absorption.
e. glycogen breakdown.
13. Conversion of fat-soluble wastes to water-soluble material for renal excretion is a function of the
a. spleen.
b. kidney.
c. liver.
d. pancreas.
e. gallbladder.
14. Contraction of the gallbladder propels bile into the
a. stomach.
b. duodenum.
c. jejunum.
d. ileum.
e. cecum.
15. Which abdominal organs also produce hormones and function as endocrine glands?
a. Kidney and liver
b. Liver and gallbladder
c. Stomach and spleen
d. Gallbladder and pancreas
e. Pancreas and kidney
16. Which organ(s) are located in the retroperitoneal space?
a. Kidneys
b. Lungs
c. Spleen
d. Gallbladder
e. Liver
17. Mrs. G is 7 months’ pregnant and states that she has developed a problem with constipation. She eats a well-balanced diet and is usually regular. You should explain that constipation is common during pregnancy because of changes in the colorectal areas, such as
a. decreased movement through the colon and increased water absorption from stool.
b. increased movement through the colon and increased salt taken from foods.
c. looser anal sphincter and less nutrients taken from foods.
d. tighter anal sphincter and less iron eliminated in the stool.
e. increased absorption of nutrients and water in the colon.
18. The most pronounced functional change of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in older adults is
a. decreased hydrochloric acid production.
b. increased motility.
c. decreased bile absorption.
d. decreased motility.
e. increased saliva secretion.
19. The family history of a patient with diarrhea and abdominal pain should include inquiry about cystic fibrosis because it
a. only affects the GI tract.
b. is one cause of malabsorption syndrome.
c. is a curable condition with medical intervention.
d. is the most frequent cause of diarrhea in general practice.
e. is a common genetic disorder.
20. Infants born weighing less than 1500 g are at higher risk for
a. hepatitis A.
b. necrotizing enterocolitis.
c. urinary urgency.
d. cystic fibrosis.
e. pancreatitis.
21. Inspection of the abdomen should begin with the patient supine and the examiner
a. seated on the patient’s right side.
b. standing at the foot of the table.
c. standing at the patient’s left.
d. walking around the table.
e. seated on the patient’s left side.
22. Before performing an abdominal examination, the examiner should
a. ascertain the patient’s HIV status.
b. have the patient empty his or her bladder.
c. don double gloves.
d. completely disrobe the patient.
e. uncover only the painful areas of the abdomen.
23. Which structure is located in the hypogastric region of the abdomen?
a. Bladder
b. Cecum
c. Gallbladder
d. Stomach
e. Liver
24. When examining a patient with tense abdominal musculature, a helpful technique is to have the patient
a. hold his or her breath.
b. sit upright.
c. flex his or her knees.
d. raise his or her head off the pillow.
e. fully extend the legs.
25. You ask the patient to raise the head and shoulders while lying in a supine position. A midline abdominal ridge rises. You chart this observation as a(n)
a. small inguinal hernia.
b. large epigastric hernia.
c. abdominal lipoma.
d. diastasis recti.
e. incisional hernia.
26. What condition is associated with striae that remain purplish?
a. Cushing disease
b. Diastasis recti
c. Liver cirrhosis
d. Recent pregnancy
e. Intraabdominal bleeding
27. Visible intestinal peristalsis may indicate
a. normal digestion.
b. intestinal obstruction.
c. increased pulse pressure of aorta.
d. aortic aneurysm.
e. paralytic ileus.
28. After thorough inspection of the abdomen, the next assessment step is to
a. percuss.
b. palpate nonpainful areas.
c. auscultate.
d. perform a rectal examination.
e. palpate painful areas.
29. Auscultation of borborygmi is associated with
a. gastroenteritis.
b. peritonitis.
c. satiety.
d. paralytic ileus.
e. stenotic arteries.
30. Peritonitis often produces bowel sounds that are
a. decreased.
b. increased.
c. high pitched.
d. absent.
e. accentuated.
31. A patient is complaining of abdominal pain, nausea with vomiting, malaise, and a low-grade fever attributed to eating some “bad food” 4 hours ago. The abdomen is soft and rounded, with hypoactive bowel sounds after 5 minutes of auscultation to each quadrant. Which assessment finding is inconsistent with gastroenteritis?
a. Malaise
b. Low-grade fever
c. Hypoactive bowel sounds
d. Soft, rounded abdomen
e. Abdominal pain
32. An examiner can recognize a friction rub in the liver by a sound that is
a. clicking, gurgling, and irregular.
b. high pitched and associated with respirations.
c. loud, prolonged, and gurgling.
d. soft, low-pitched, and continuous.
e. low pitched, tinkling, and unrelated to respirations.
33. To correctly document absent bowel sounds, one must listen continuously for
a. 30 seconds.
b. 1 minute.
c. 3 minutes.
d. 5 minutes.
e. 10 minutes.
34. Percussion at the right midclavicular line, below the umbilicus, and continuing upward is the correct technique for locating the
a. descending aorta.
b. lower liver border.
c. medial border of the spleen.
d. upper right kidney ridge.
e. stomach.
35. When auscultating the abdomen, which finding would indicate collateral circulation between the portal and systemic venous systems?
a. Arterial bruit
b. Gastric rumbling
c. Renal hyperresonance
d. Borborygmi
e. Venous hum
36. Percussion of the abdomen begins with establishing
a. liver dullness.
b. spleen dullness.
c. gastric bubble tympany.
d. overall dullness and tympany in all quadrants.
e. bladder fullness.
37. To assess for liver enlargement in an obese person, you should
a. use the hook method.
b. test for cutaneous hypersensitivity.
c. auscultate using the scratch technique.
d. attempt palpation during deep exhalation.
e. have the patient lean over at the waist.
38. An umbilical assessment in the newborn that is of concern is
a. a thick cord.
b. an umbilical hernia.
c. one umbilical artery and two veins.
d. pulsations superior to the umbilicus.
e. visible nondistended superficial veins.
39. Failure to pass a meconium stool in the first 24 hours after birth along with abdominal distention is often the first sign of
a. Meckel diverticulum.
b. cystic fibrosis.
c. biliary atresia.
d. hydramnios.
e. Wilms tumor.
40. When palpating the aorta, a prominent lateral pulsation suggests
a. aortic aneurysm.
b. normal pulsation.
c. renal artery fistula.
d. vena cava varicosity.
e. coarctation.
41. A patient presents with symptoms that lead you to suspect acute appendicitis. Which assessment finding is least likely to be associated with this condition early in its course?
a. Positive psoas sign
b. Positive McBurney sign
c. History of periumbilical pain
d. Rebound tenderness
e. Obturator muscle test
42. When using the bimanual technique for palpating the abdomen, you should
a. push down with the bottom hand and the other atop.
b. push down with the top hand and the other atop.
c. place hands side by side and push equally.
d. place one hand anteriorly and the other posteriorly squeezing the hands together.
e. make a fist with the top hand and strike the bottom hand.
43. A 23-year-old man comes to the urgent care clinic with intense left flank and lower left quadrant pain. One patient response to history of present illness questions that further supports a tentative diagnosis of renal calculi is
a. “My urine has been bright yellow.”
b. “I have had fever and chills for 2 days.”
c. “I also have a headache and neck ache.”
d. “My left testicle and shoulder hurt as well.”
e. “I have had flatulence and foul-smelling urine.”
44. Flatulence, diarrhea, dysuria, and tenderness with abdominal palpation are findings most associated with
a. peptic ulcer disease.
b. pancreatitis.
c. ruptured ovarian cyst.
d. splenic rupture.
e. diverticulitis.
45. A 45-year-old man relates a several-week history of severe intermittent abdominal burning sensations. He relates that the pain is relieved with small amounts of food. Before starting the physical examination, you review his laboratory work, anticipating a(n)
a. elevated white blood cell count.
b. decreased potassium level.
c. positive Helicobacter pylori result.
d. increased urine specific gravity.
e. folate deficiency.
46. A 51-year-old woman calls with concerns of weight loss and constipation. She reports enlarged hemorrhoids and rectal bleeding. You advise her to
a. use topical over-the-counter hemorrhoid treatment for 1 week.
b. exercise and eat more fiber.
c. come to the laboratory for a stool guaiac test.
d. eat six small meals a day.
e. go to the emergency department for a barium enema.
47. Patients presenting with ascites, jaundice, cutaneous spider veins, and nonpalpable liver exhibit signs of
a. cholecystitis.
b. pancreatitis.
c. inflammatory bowel disease.
d. diverticulitis.
e. cirrhosis.
48. A patient presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The patient sustained blunt trauma to the abdomen and complains of pain in the upper left quadrant that radiates to the left shoulder. What organ is most likely injured?
a. Gallbladder
b. Liver
c. Spleen
d. Stomach
e. Colon
49. Costovertebral angle tenderness should be assessed whenever you suspect the patient may have
a. cholecystitis.
b. pancreatitis.
c. pyelonephritis.
d. ulcerative colitis.
e. intussusception.
50. Imaging studies reveal that a patient has dilation of the renal pelvis from an obstruction in the ureter. What condition will be documented in this patient’s health record?
a. Glomerulonephritis
b. Hydronephrosis
c. Pyelonephritis
d. Renal abscess
e. Renal artery emboli
51. The most common congenital anomaly of the gastrointestinal tract is
a. biliary atresia.
b. meconium ileus.
c. intussusception.
d. Meckel diverticulum.
e. pyloric stenosis.
52. Baby Joe is 6 months old. He has abdominal distention and vomiting and is inconsolable. A sausage-shaped mass is palpable in his right upper quadrant. Joe’s lower quadrant feels empty, and a positive Dance sign is noted in his record. Which one of the following conditions is consistent with Baby Joe’s symptoms?
a. Intussusception
b. Kidney stones
c. Meconium ileus
d. Pyloric stenosis
e. Necrotizing enterocolitis
53. A mother brings her 2-year-old child for you to assess. The mother feels a lump whenever she fastens the child’s diaper. Nephroblastoma is likely for this child when your physical examination of the abdomen reveals a(n)
a. fixed mass palpated in the hypogastric area.
b. tender, midline abdominal mass.
c. olive-sized mass of the right upper quadrant.
d. nontender, slightly moveable, flank mass.
e. sausage-shaped mass in the left upper quadrant.
54. A 1-month-old boy has been vomiting for 2 weeks. How is this symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and pyloric stenosis further differentiated in this child’s assessment?
a. Vomiting becomes projectile with GERD.
b. The infant has regurgitation with pyloric stenosis.
c. An olive-sized mass of the right upper quadrant (RUQ) occurs with GERD.
d. Normal stools are expected with pyloric stenosis.
e. The fontanel becomes sunken with pyloric stenosis.
55. Urinary incontinence that occurs from the inability to hold urine when the stimulus to urinate is perceived is called _____ incontinence.
a. paralytic
b. urge
c. overflow
d. functional
e. stress
56. In older adults, overflow fecal incontinence is commonly caused by
a. malabsorption.
b. parasitic diarrhea.
c. Meckel diverticulum.
d. fistula formation.
e. fecal impaction.
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages

.png)

.png)