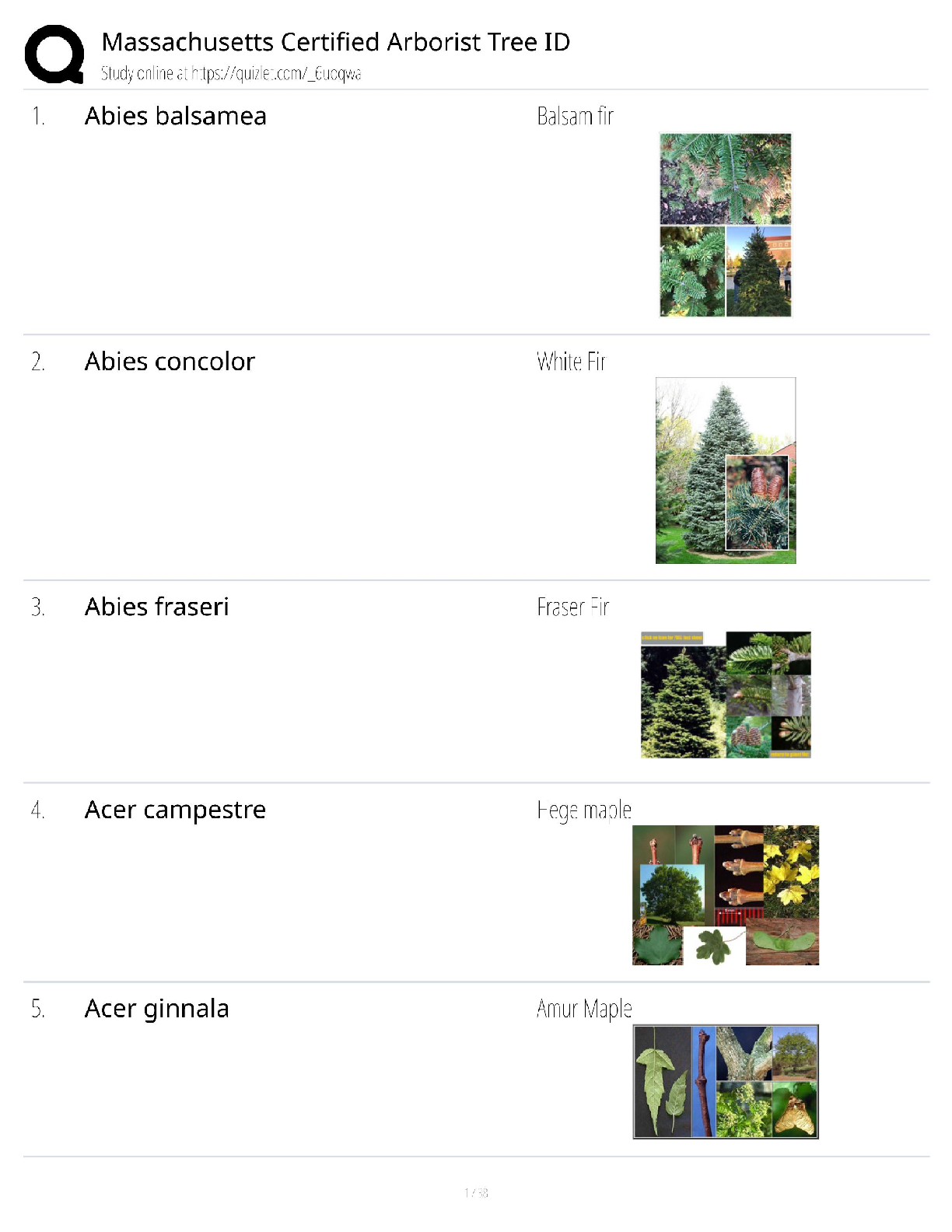
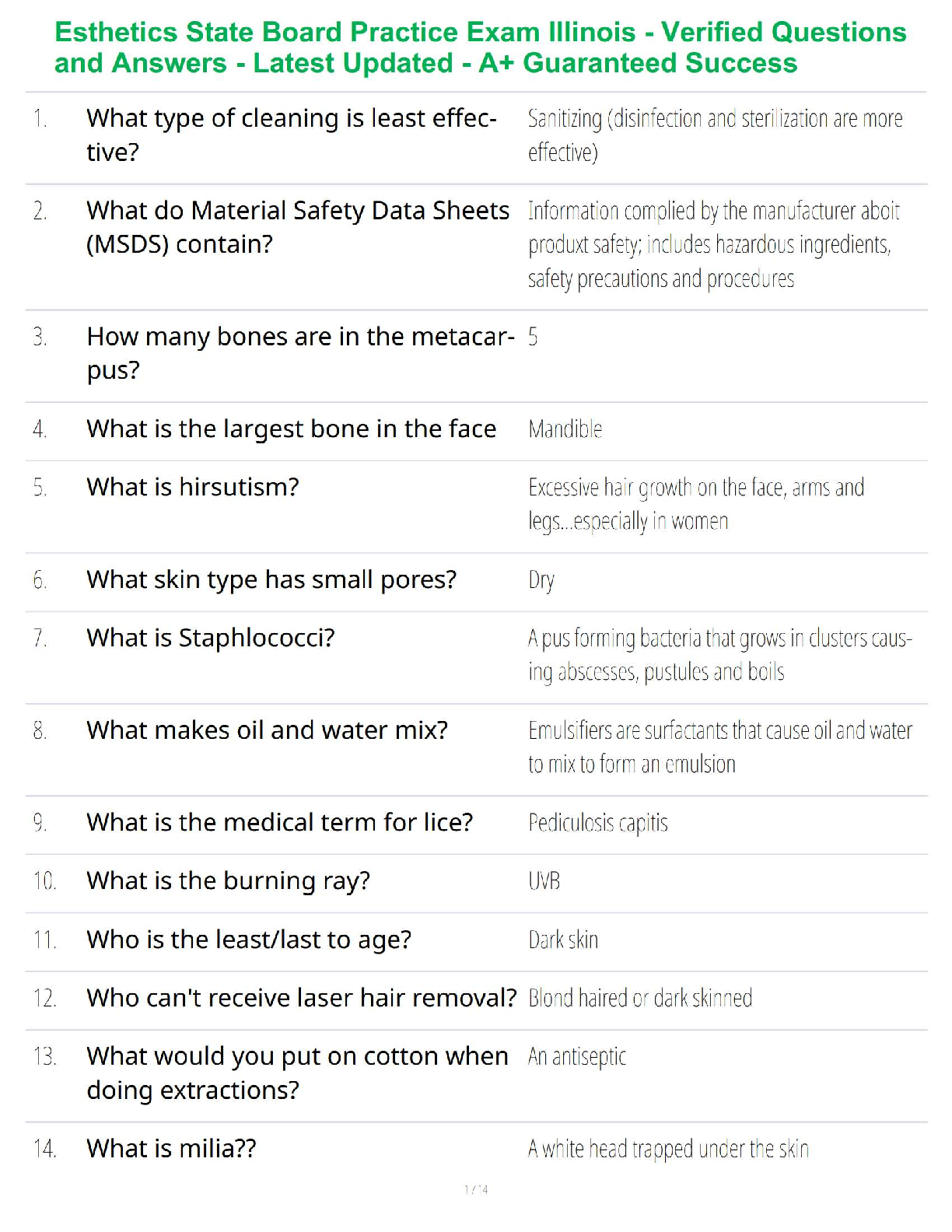
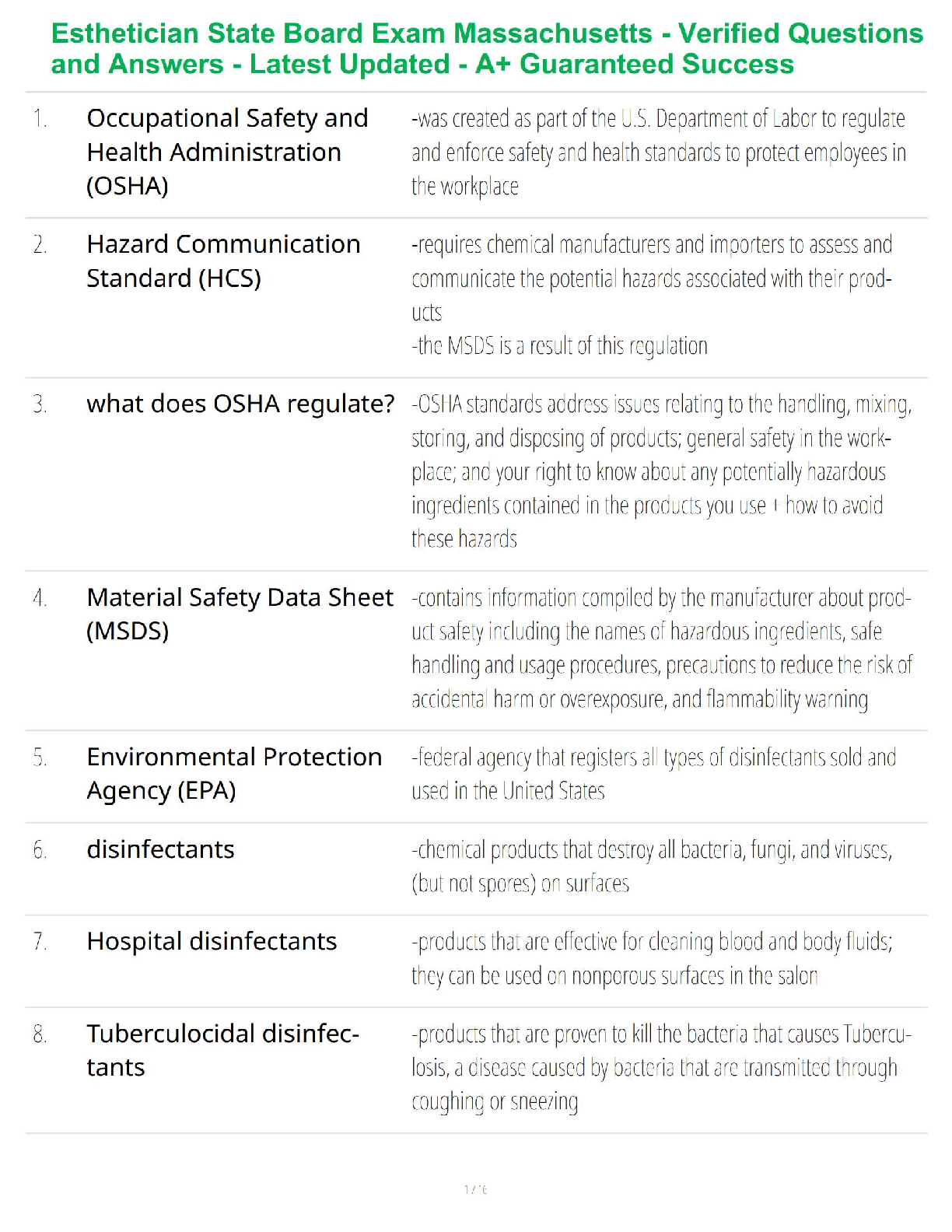
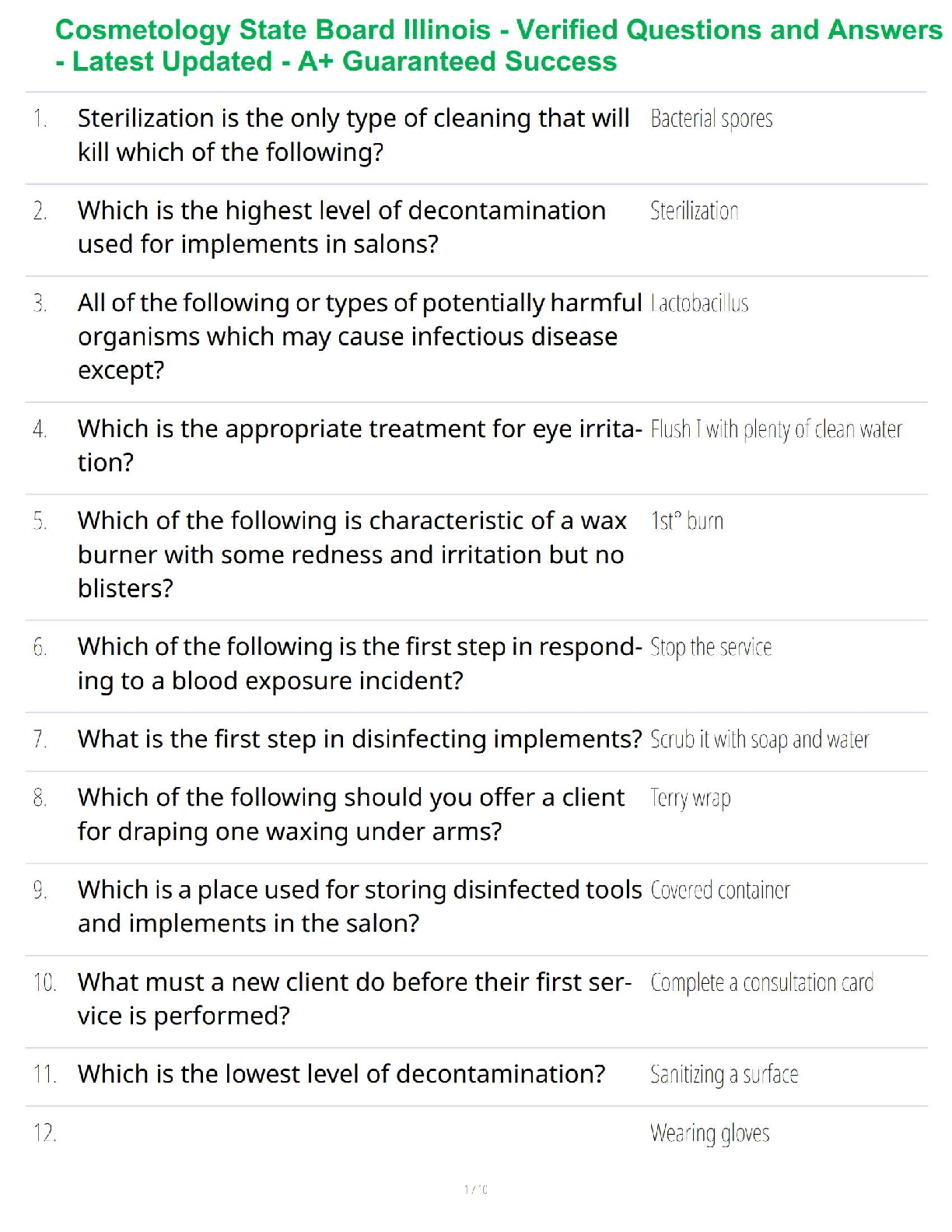
.png)
C100 WGU Module 2 Already Passed
$ 7

BIOS 242 TEST BANKweek_8_final
$ 8.5

Anterior Hip Anatomy - FINAL (1).
$ 8.5

N212 GERO EXAM 2 HIGHLIGHTABLE MOMENTS. A+ RATED STUDY GUIDE
$ 17
.png)
Hesibonus - Practice Problems Hesi Practice Problems Hesi HESI Saunders (Psych101)
$ 14.5

American Military University GEOG 101 Week 6 quiz (New)
$ 13
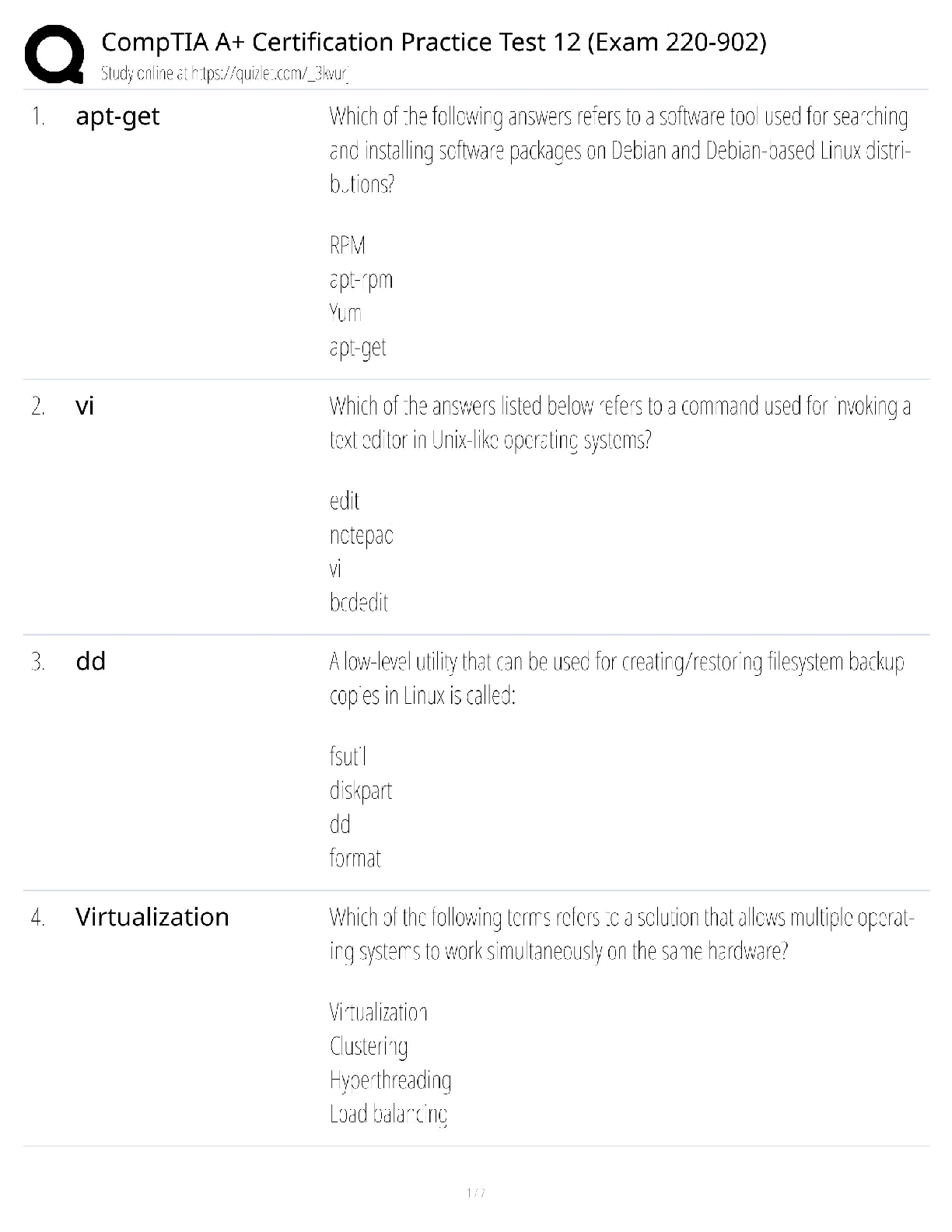
CompTIA A+ 220-902 Practice Test 12 (2023) / 90 Legacy Exam Questions / Windows & Security Focus
$ 4.5

Test Bank Chapter 7 Cash and Receivables.
$ 15

Makes Me Wanna Holler Essay
$ 7
.png)
NRNP 6566 WEEK 1-5 Knowledge check key concepts. 2022 update
$ 16.5

Pharmacology Exit HESI 2021 DOCS
$ 11.5

Focused Note Chest Pain - Brian Foster| Latest Update (Verified )
$ 10

NURS 6501 Advanced Pathophysiology Midterm Exam Latest 2021
$ 13
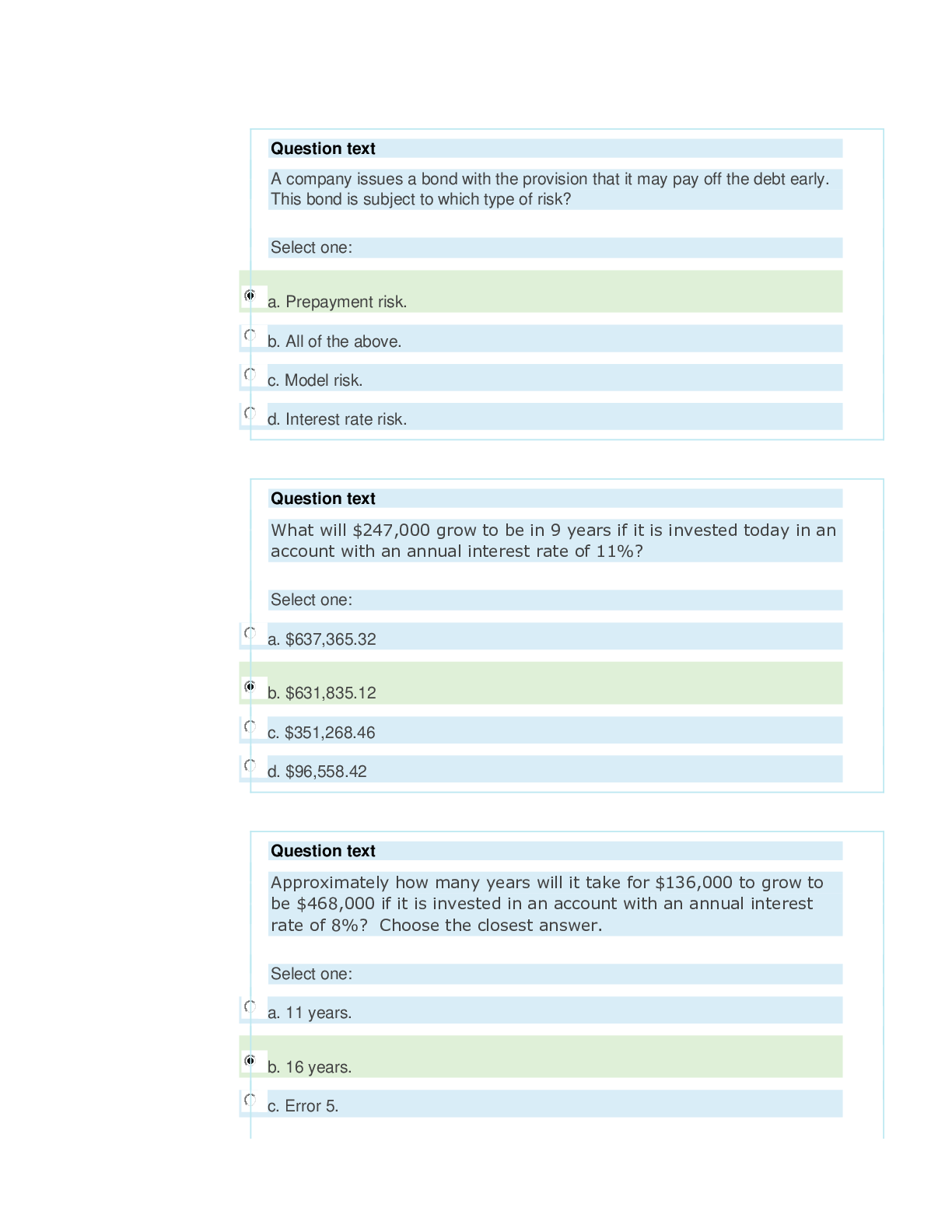
FNAN522 Module 2 Homework Questions And Answers (Latest Update)
$ 12
.png)
Corporate Finance, 3e (Berk/DeMarzo) Chapter 10 Capital Markets and the Pricing of Risk. TEST BANK. (Answers Explained).
$ 13

ATI Comprehensive Remediation_latest 2020 complete A+ guide.
$ 10

PALS Version A Questions And Answers Latest Update/ Download To get A
$ 11

IHUMAN COMPREHENSIVE CASE STUDY. WEEK 9. IHUMAN CASE STUDY. WEEK #9, REASON FOR ENCOUNTER: HAND PAIN. WITH A SOAP NOTE AT THE END. EXAM STUDY GUIDE. GRADED A+. LATEST UPDATE.
$ 15
NR 599 Week 5 Discussion Complete Latest Version
$ 12
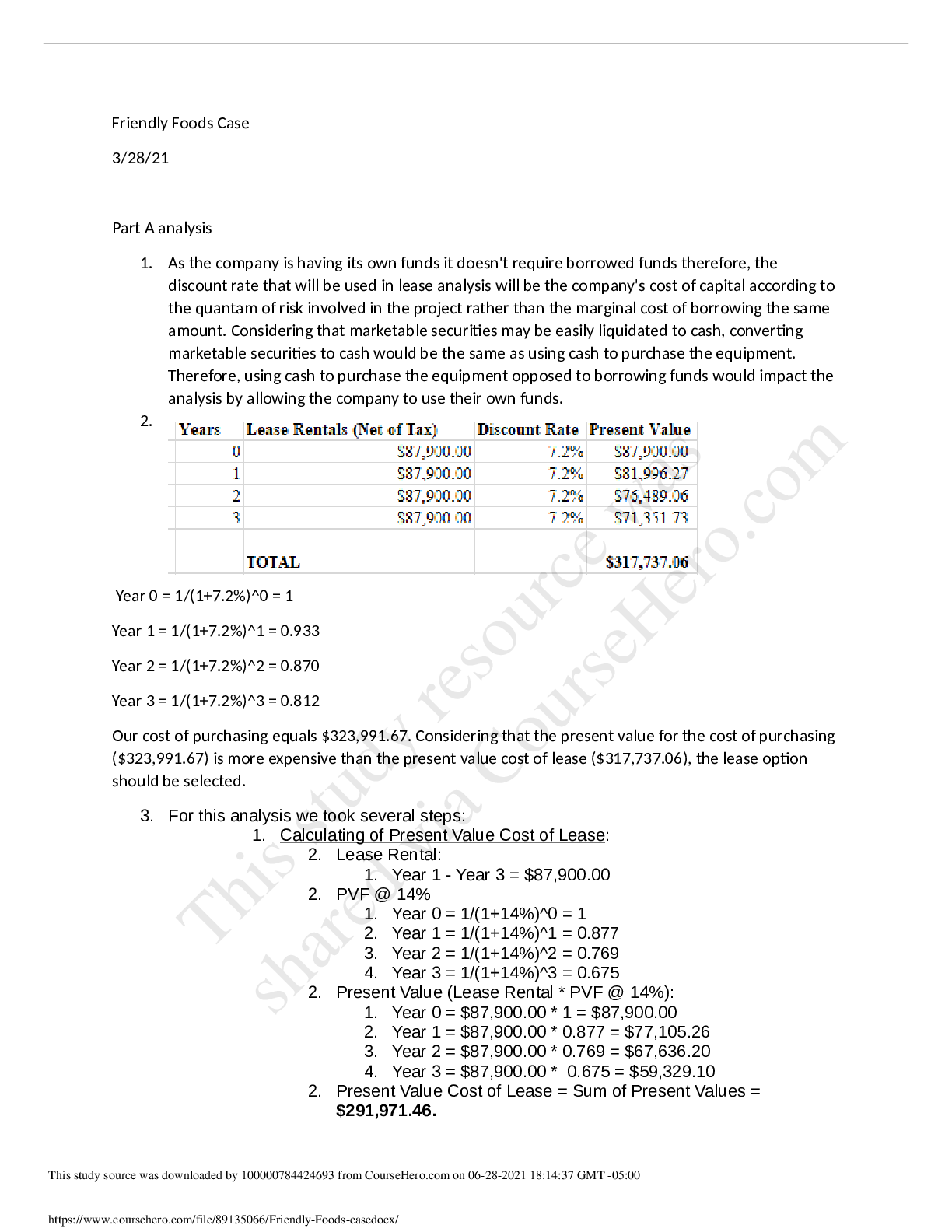
Georgia College & State UniversityFINC 5131Friendly Foods case
$ 11

ATI Proctored Nutrition Exam: Complete Guide (2026 Updated)














.png)