MATERNAL NEWBORN
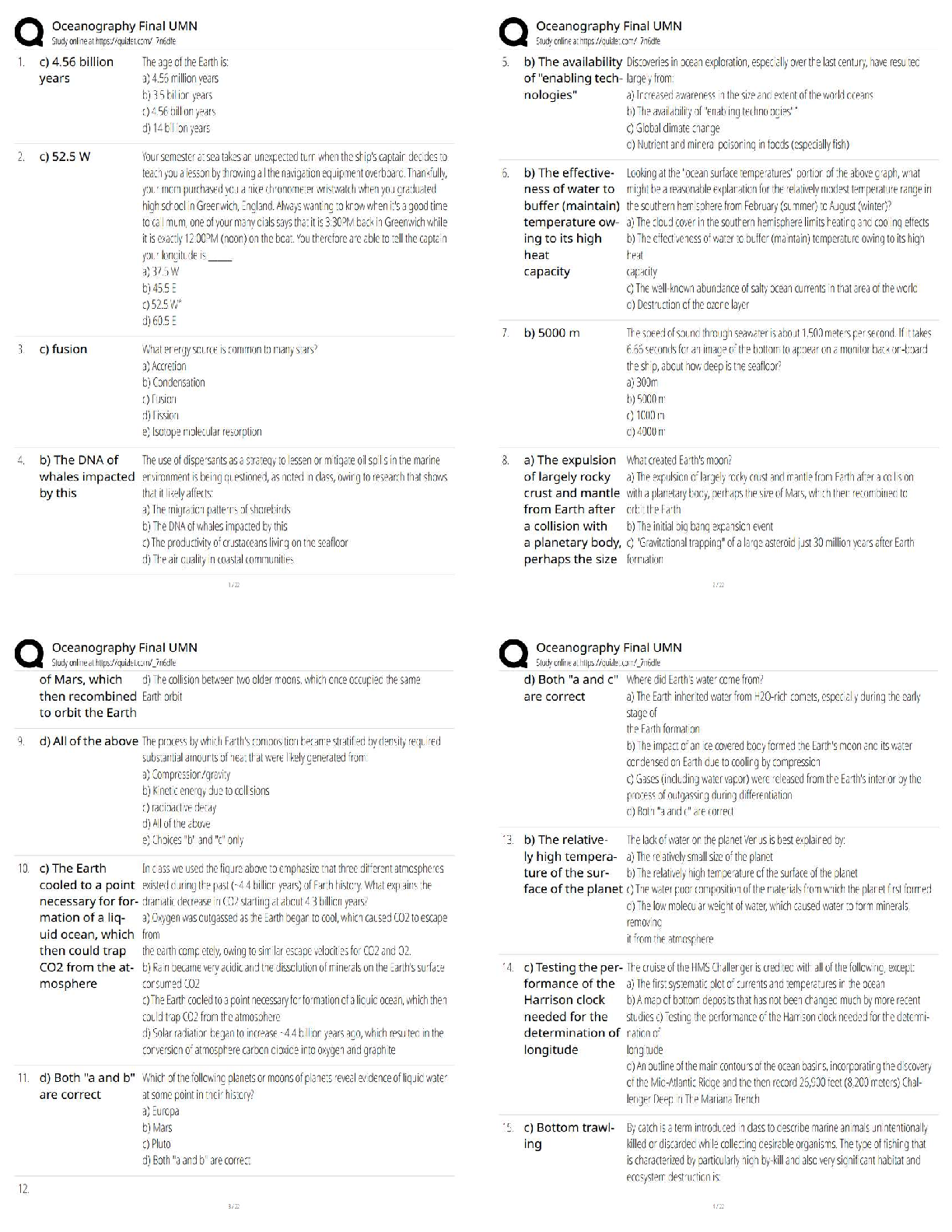
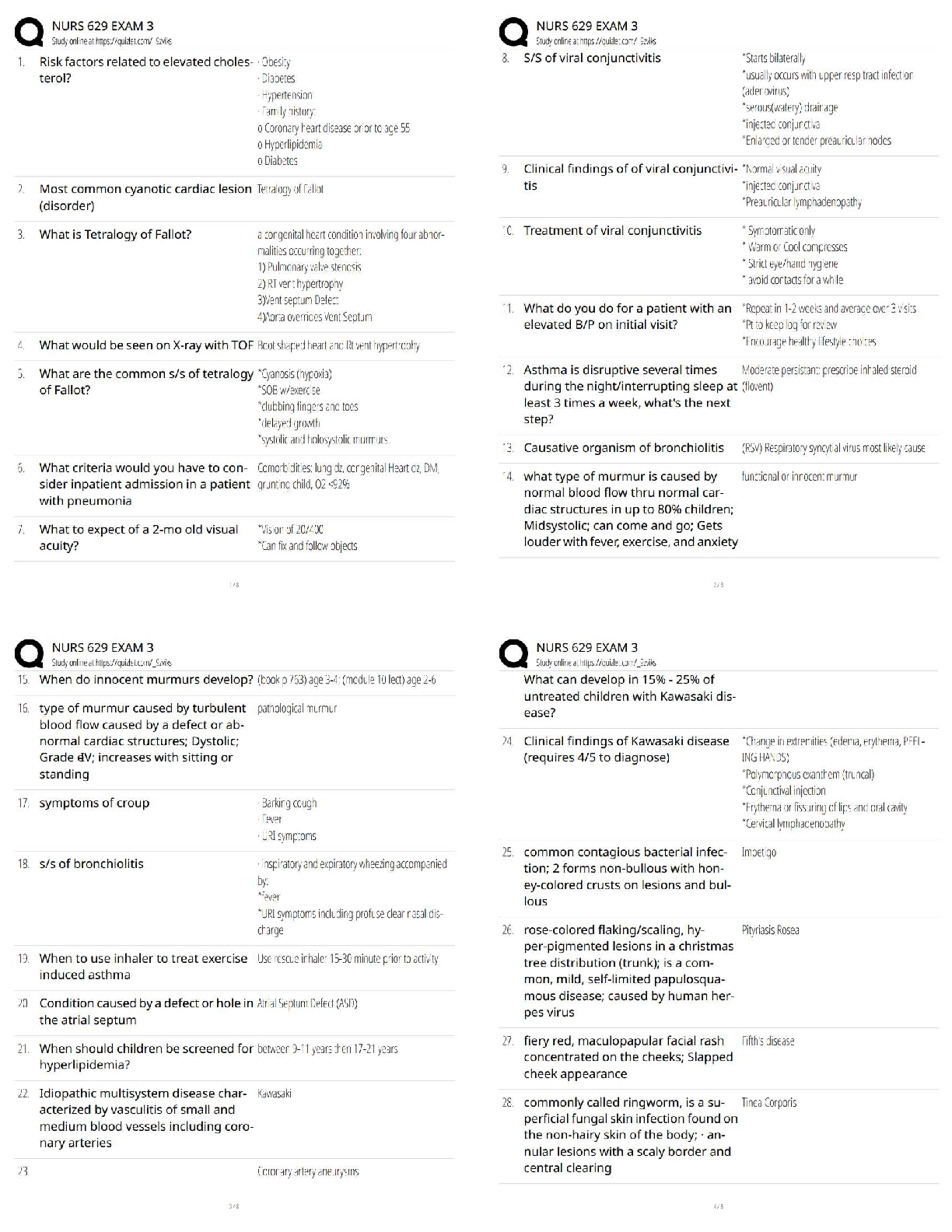
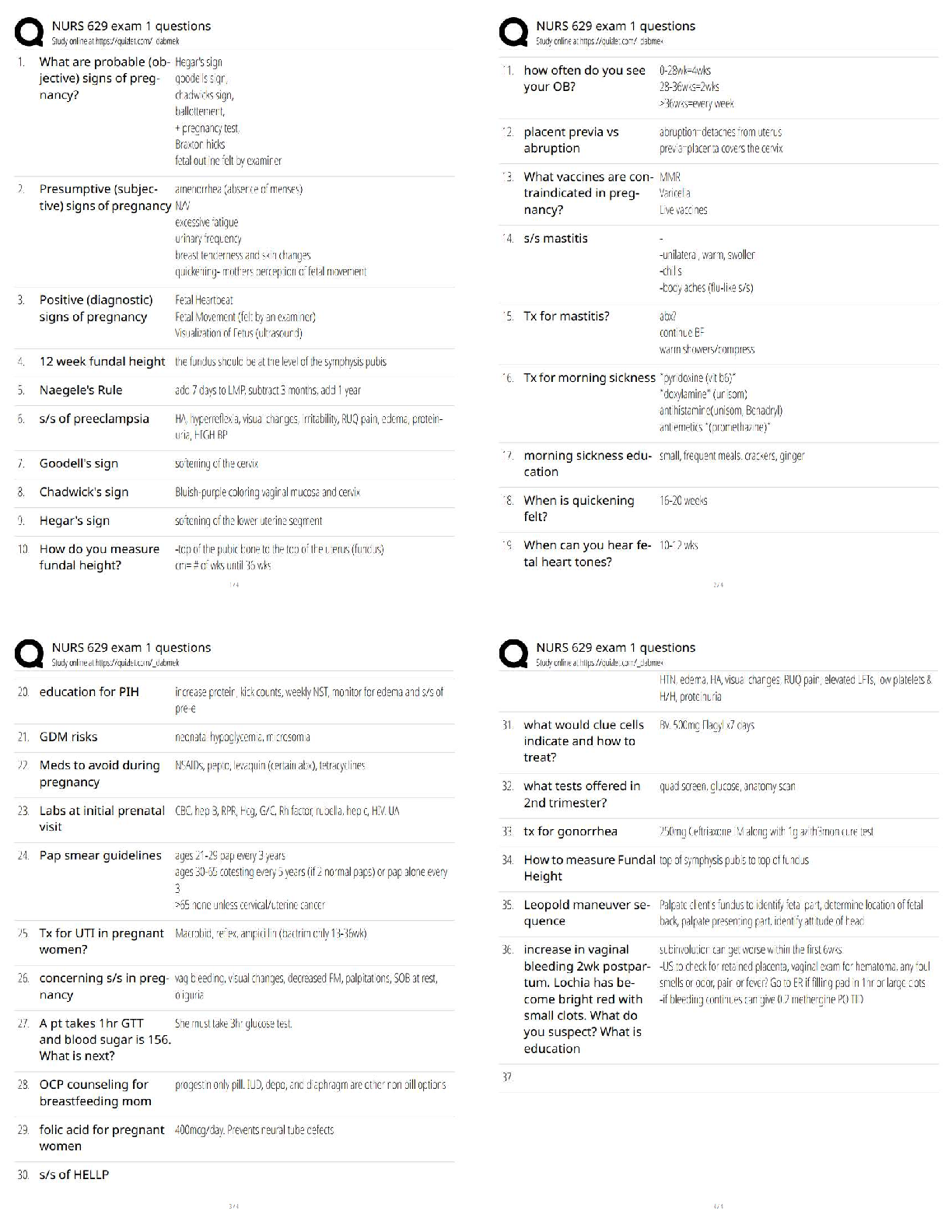
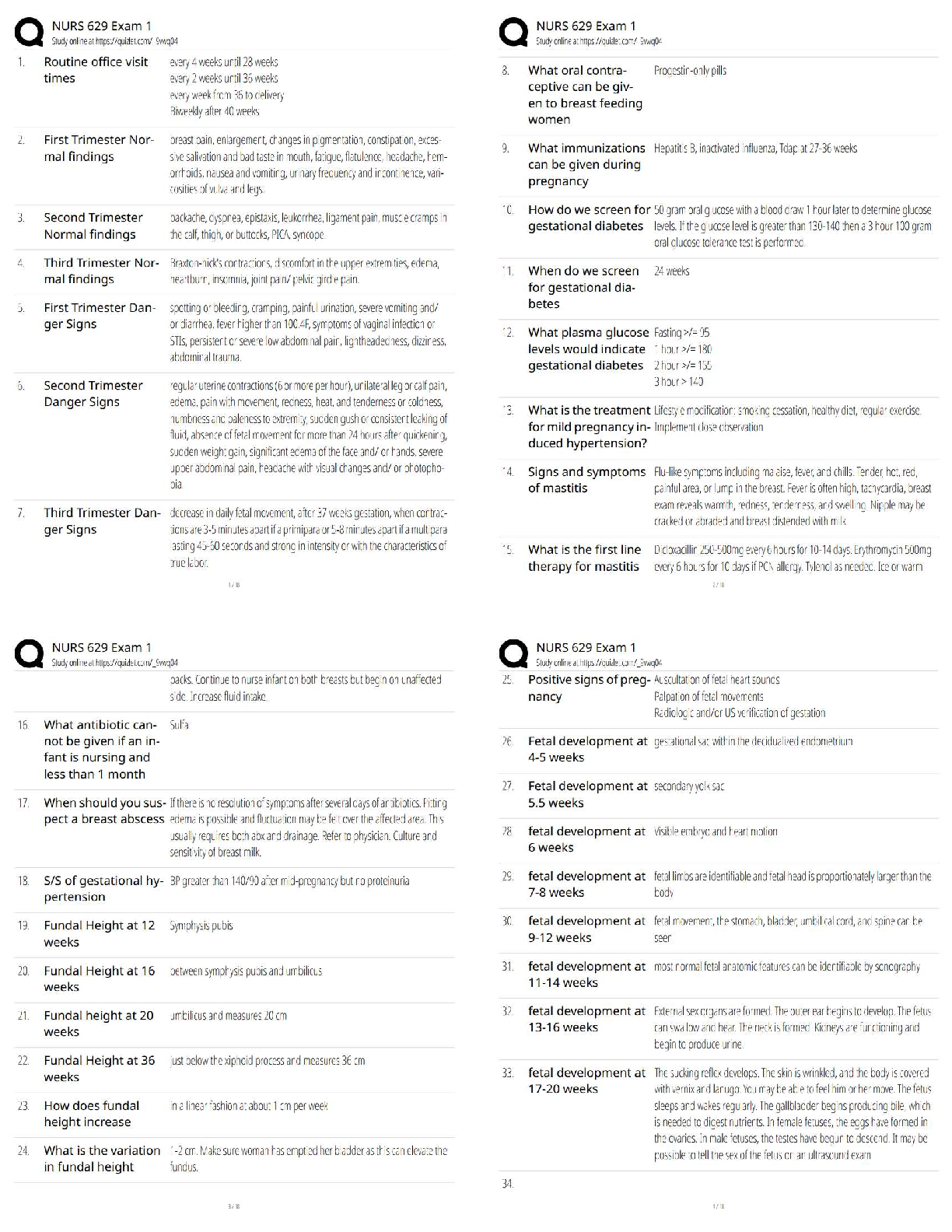
•Maternal metabolism, physical exertion, and delivery of the placenta can lead to a decreased blood glucose level.
•Physical and emotional stress can lead to an increased WBC count.
•Anxiety and i
...
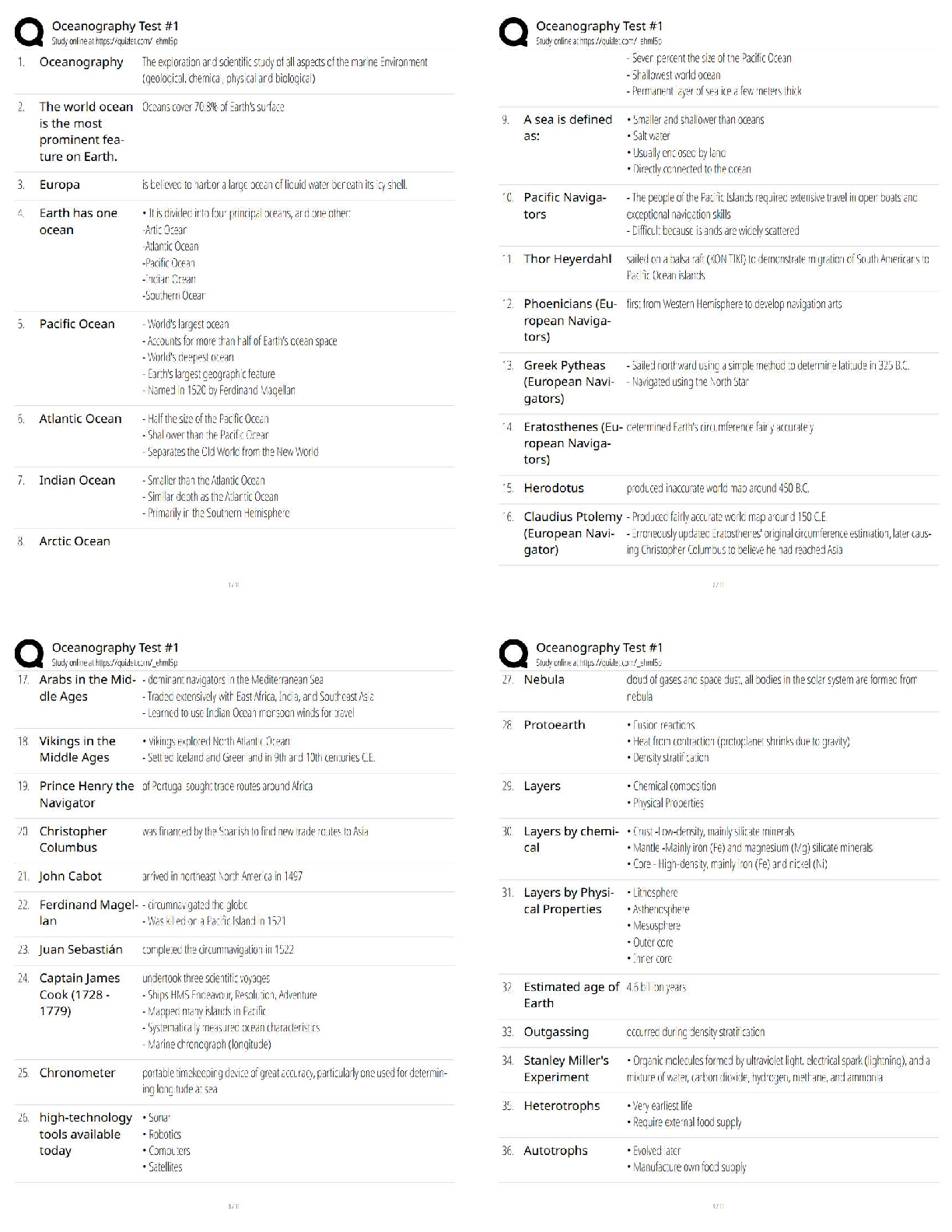
MATERNAL NEWBORN
•Maternal metabolism, physical exertion, and delivery of the placenta can lead to a decreased blood glucose level.
•Physical and emotional stress can lead to an increased WBC count.
•Anxiety and increased oxygen consumption from physical exertion during labor can lead to an
increased respiratory rate.
•Vascular changes can lead to an elevated temperature, flushed cheeks, and warm skin.
Newborn findings
•Generalized petechiae are pinpoint round spots that appear on the skin, which can indicate a clotting factor deficiency or infection. The nurse should report this finding to the provider immediately*.
•Transient circumoral cyanosis is bluish discoloration around the mouth of the newborn and is an expected finding that does not require reporting to the provider.
•Transient strabismus is a disorder in which the two eyes do not look in the same direction. This is an expected finding during the newborn period until 3 to 4 months of age and does not require reporting to the provider
•Caput succedaneum is swelling of the scalp of the newborn and is an expected finding following a vaginal birth. While it is important to assess and document, it does not require reporting to the
provider.
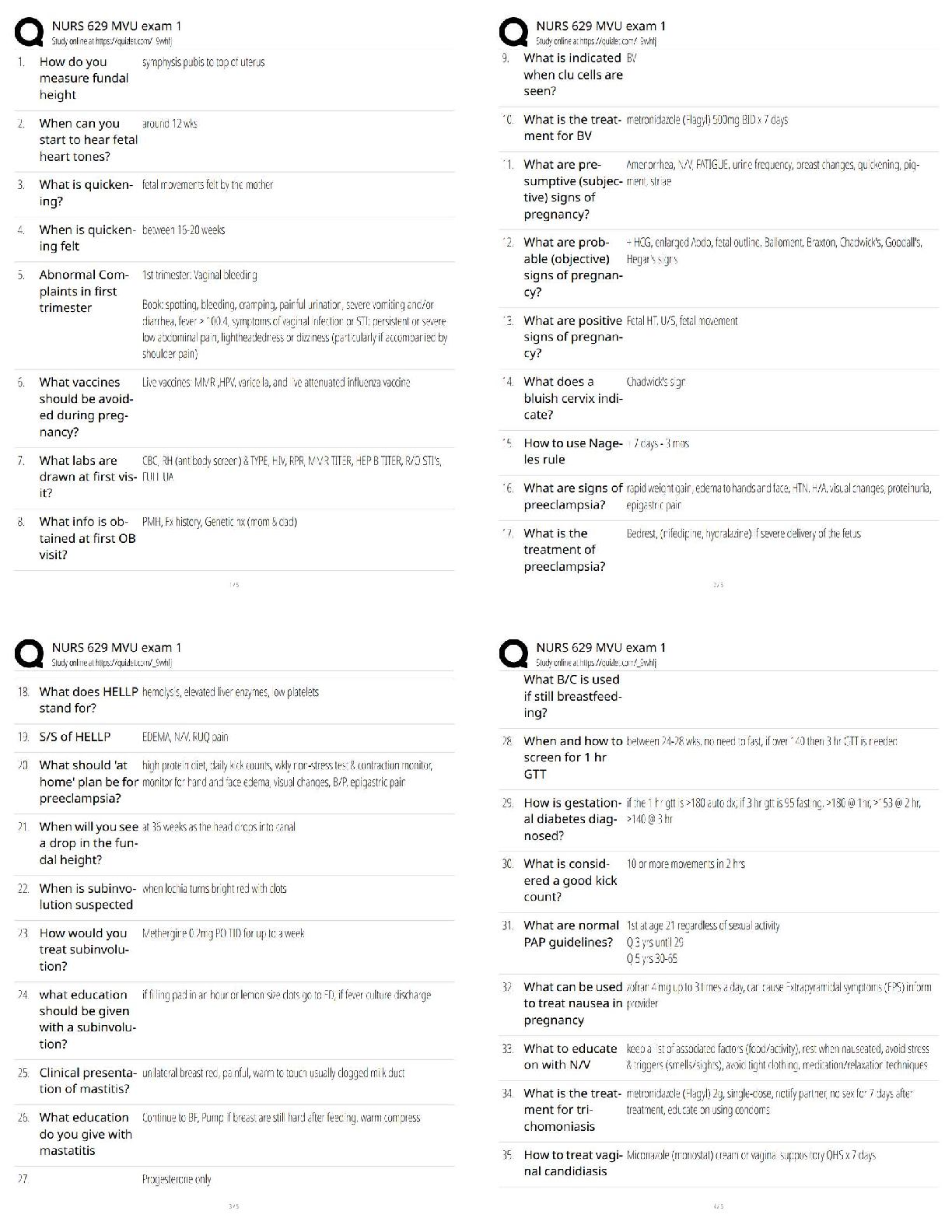
PHOTOTHERAPY
•The nurse should monitor intake and output because phototherapy can increase the rate of insensible water loss, which contributes to fluid loss and dehydration. The nurse should also monitor the newborn's fontanels. Hydration is achieved by breastfeeding or formula feeding the newborn.
•The nurse should avoid applying lotions and ointments to newborns who are receiving phototherapy because can cause burns.
Cardiac arrhythmia is a potential life-threatening adverse effect of nifedipine. Therefore, the client should report an irregular heartbeat to the provider.
[Show More]








.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)