Telemetry with pictures 25 Questions with Verified Answers,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
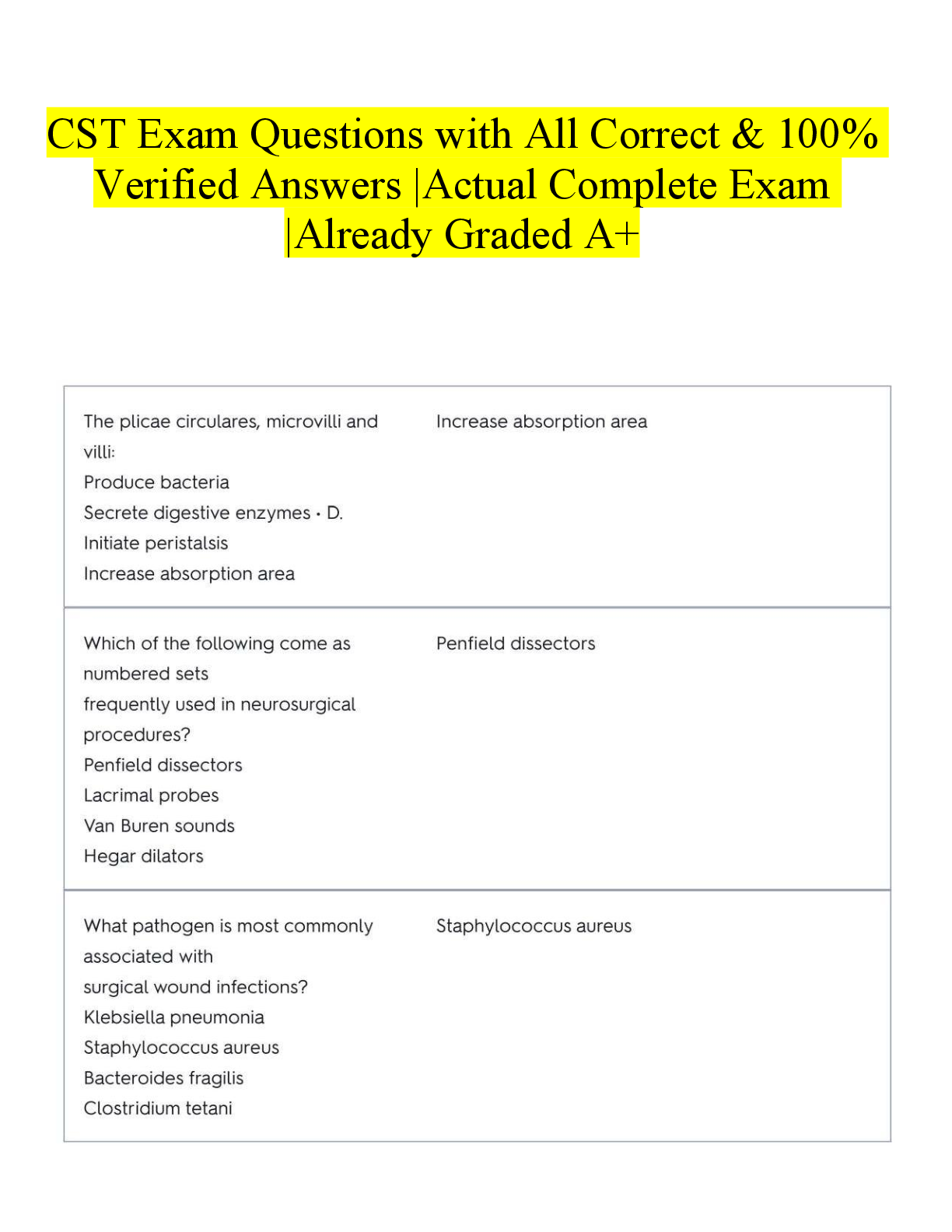
Telemetry with pictures 25 Questions with Verified Answers normal sinus rhythm - CORRECT ANSWER - normal intervals - rate 60-100 - walks out sinus bradycardia - CORRECT ANSWER - SA node in con ... trol - rate <60 - normal intervals - walks out - treat with atropine IV push sinus tachycardia - CORRECT ANSWER - SA node in control - rate >100 - normal intervals - walks out - treat with vagal maneuvers, BBs, or CCBs atrial fibrillation - CORRECT ANSWER - SA node not in control - random ectopic foci cells firing in atria - rate determined by AV node - rate often high (RVR) up to 180s - does not walk out - no definable P wave - normal QRS from AV node - treat with amiodarone or cardizem - treat with cardioversion and shock on R wave - treat with anticoagulants atrial flutter - CORRECT ANSWER - SA node not in control - one random ectopic foci cell firing in atria - rate determined by AV node - saw tooth pattern - does not walk out - easily definable P wave - same treatment as a fib supraventricular tachycardia - CORRECT ANSWER - SA node not in control - one cell rapidly firing - AV node determines rate - QRS narrow or wide - may look like sinus tach - treat with adenosine (reset drug), BBs, or CCBs junctional rhythm - CORRECT ANSWER - AV node in control - rate 40-60 - inverted or no P wave - walks out - treat with atropine to increase HR or an external pacemaker through femoral artery accelerated junctional rhythm - CORRECT ANSWER - AV node in control and fires spontaneously - no P wave - faster than normal - rate >60 - walks out - treat with external pacemaker first degree heart block - CORRECT ANSWER - slow electrical conduction through atria - PR interval >0.20 (up to 0.24) - QRS and QT intervals normal - rate can be slow or normal - no symptoms or treatment second degree heart block type 1 - CORRECT ANSWER - slow conduction between SA and AV node - PR gets progressively longer until a QRS is dropped - longer, longer till they drop that's how you know it's a Wenckebach - P with no QRS second degree heart block type 2 - CORRECT ANSWER - slow conduction between SA and AV node - PR prolonged but remains consistent until a QRS is dropped - same, same, drop - 2 normal heart beats, then a QRS drop - leads to 3rd degree heart block - treat with atropine third degree heart block - CORRECT ANSWER - no longer rhythmic - no relationship with SA and AV node - P wave buried into QRS but both walk out - HR low in 20-30s - only treatment is a permanent pacemaker - medical emergency bundle branch block - CORRECT ANSWER - delayed conduction in ventricle instead of atria - wide QRS complex - can be left or right - common in elderly - don't treat, just monitor premature atrial contraction - CORRECT ANSWER - SA node fires prematurely - looks like an early beat premature ventricular contraction - CORRECT ANSWER - an ectopic foci in the ventricle fires, causing contraction - looks like QRS without a P wave - can be from one or many cells (unifocal or multifocal) - treat with BBs or CCBs - can be caused from potassium imbalances, HTN, drugs, caffeine, stress, hypoxia, or MI bigeminy - CORRECT ANSWER - a pattern of PVCs - PVCs every second beat - poor perfusion because PVCs don't push good amount of blood out - beat, PVC, beat, PVC trigeminy - CORRECT ANSWER - PVCs occurring every third beat - still not a good beat atrial pacemaker - CORRECT ANSWER - pacemaker working as the SA node - spike before a P wave ventricular pacemaker - CORRECT ANSWER - pacemaker working as the AV node - line before QRS complex - P wave can be present atrioventricular pacemaker - CORRECT ANSWER - pacemaker works as both the SA and AV nodes - looks like a line before P and QRS waves ventricular tachycardia - CORRECT ANSWER - neither SA node or AV node are controlling heart - one ectopic foci firing in ventricles - looks like constant PVCs - a run of 3 or more PVCs - treat Hs and Ts - if pulse, treat with amiodarone - if no pulse, CPR or defibrillation or epinephrine or vasopressin ventricular fibrillation - CORRECT ANSWER - SA and AV node not in control - multiple ectopic foci firing in ventricle - treat with CPR or defibrillation in the first 2-3 minutes or epinephrine, vasopressin, or amiodarone torsades - CORRECT ANSWER - specific form of VTACH but twists and looks like a combination of VTACH and VFIB - can lead to VFIB - does not look uniform - treat with magnesium asystole - CORRECT ANSWER - flatline - no electrical activity - treat with CPR or epinephrine pulseless electrical activity - CORRECT ANSWER - heart not actually pumping - leftover electricity in heart makes it look like a beat, but no pulse - can look junctional [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

Telemetry Exam ( 33 Sets) Questions with Verified Answers,100% CORRECT
Telemetry Exam 68 Questions with Verified Answers,Telemetry Exam 39 Questions with Verified Answers,Cardiac- Telemetry Exam 72 Questions with Verified Answers,Telemetry Exam 60 Questions with Verified...
By securegrades 2 years ago
$30
34
Reviews( 0 )
$7.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 08, 2023
Number of pages
6
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 08, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
90