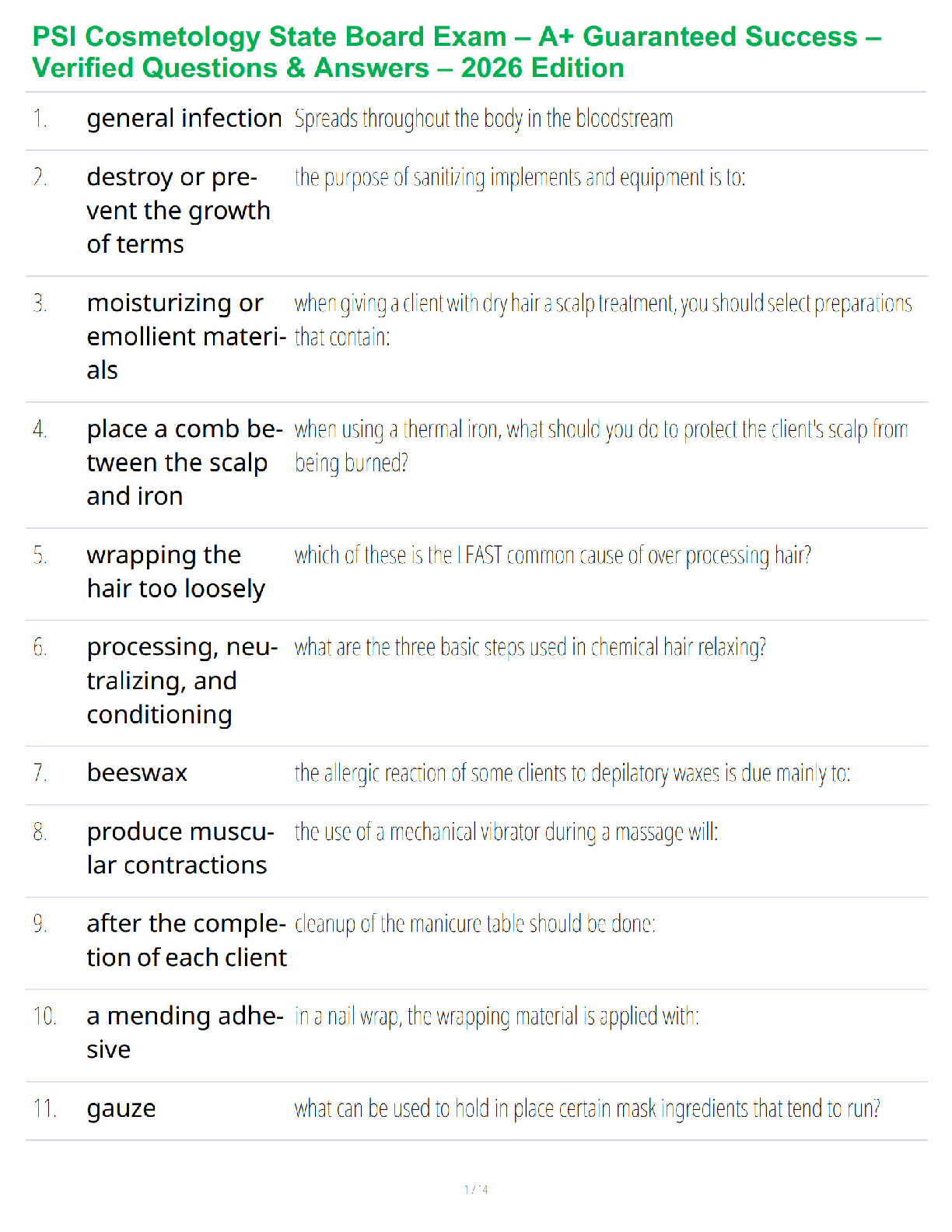
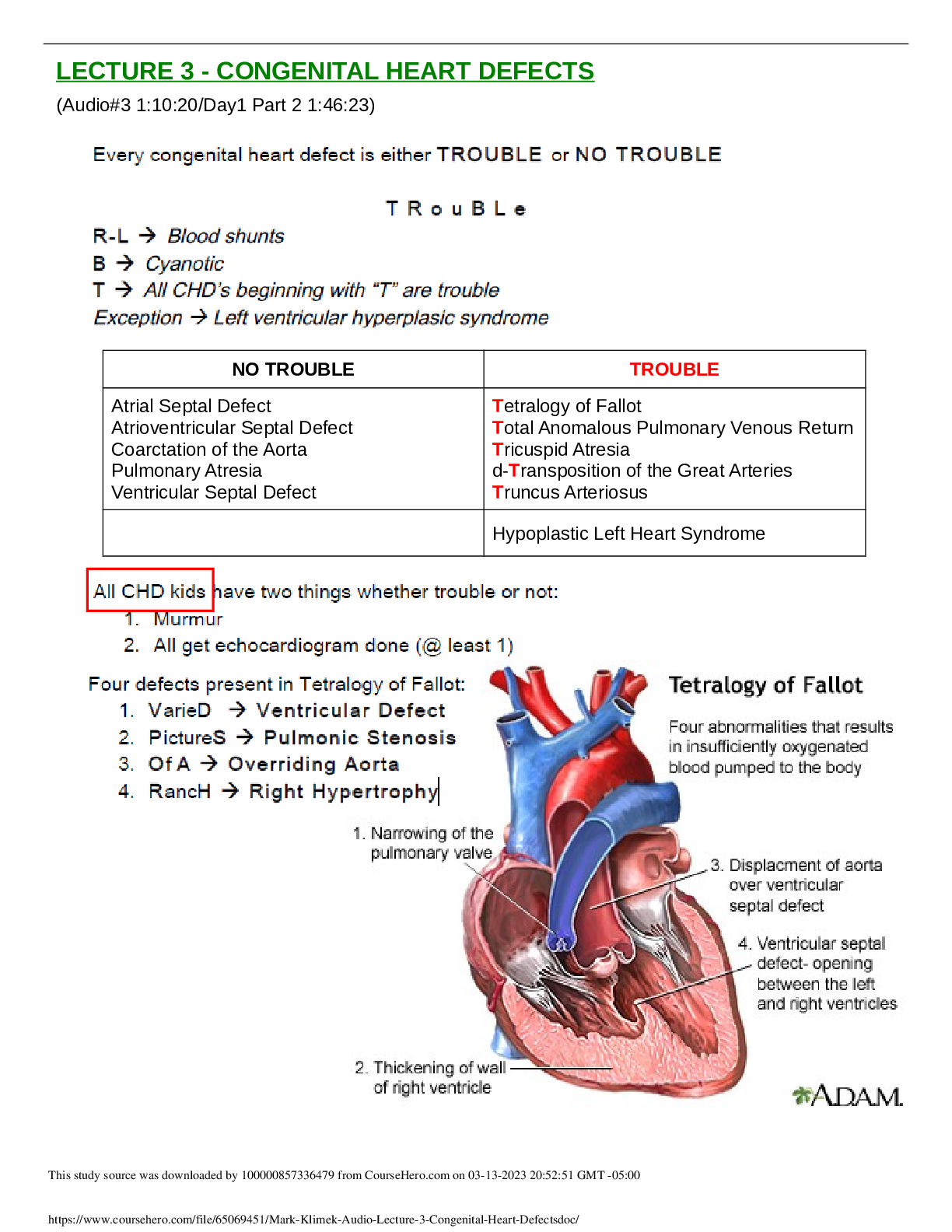
1. **For all anitibiotics/anti-infectives below – know class, nursing considerations/interventions, side/adverse effects, and client teaching plus detail as below…
3. fluroquinolones (Cipro) – what to avoid taking with
...
1. **For all anitibiotics/anti-infectives below – know class, nursing considerations/interventions, side/adverse effects, and client teaching plus detail as below…
3. fluroquinolones (Cipro) – what to avoid taking with it, client teaching 10. Side/adverse effects: nausea, vomiting, dysrhythmias, hepatotoxicity, *****Achilles tendon rupture esp if used with steroids. Cipro can cause tendinitis 16. macrolide (erythromycin) – know where mostly eliminated
17.
18. Azithromycin (Z-pak)
19.
20. Class: Anti-infectives; used for whooping cough (pertussis), streptococcus and mycoplasma pneumoniae, H. pylori (peptic ulcer disease); pregnancy category B.
32. tetracycline (Minocycline) - patient teaching
33.
34. Class: Broad spectrum Anti-infective; Pregnancy category D; used for Chalmydia, gram positive and negative organisms, H. pylori, acne.
44. ceftriaxione (Rocephin)/Cephalosporins – IM administration considerations
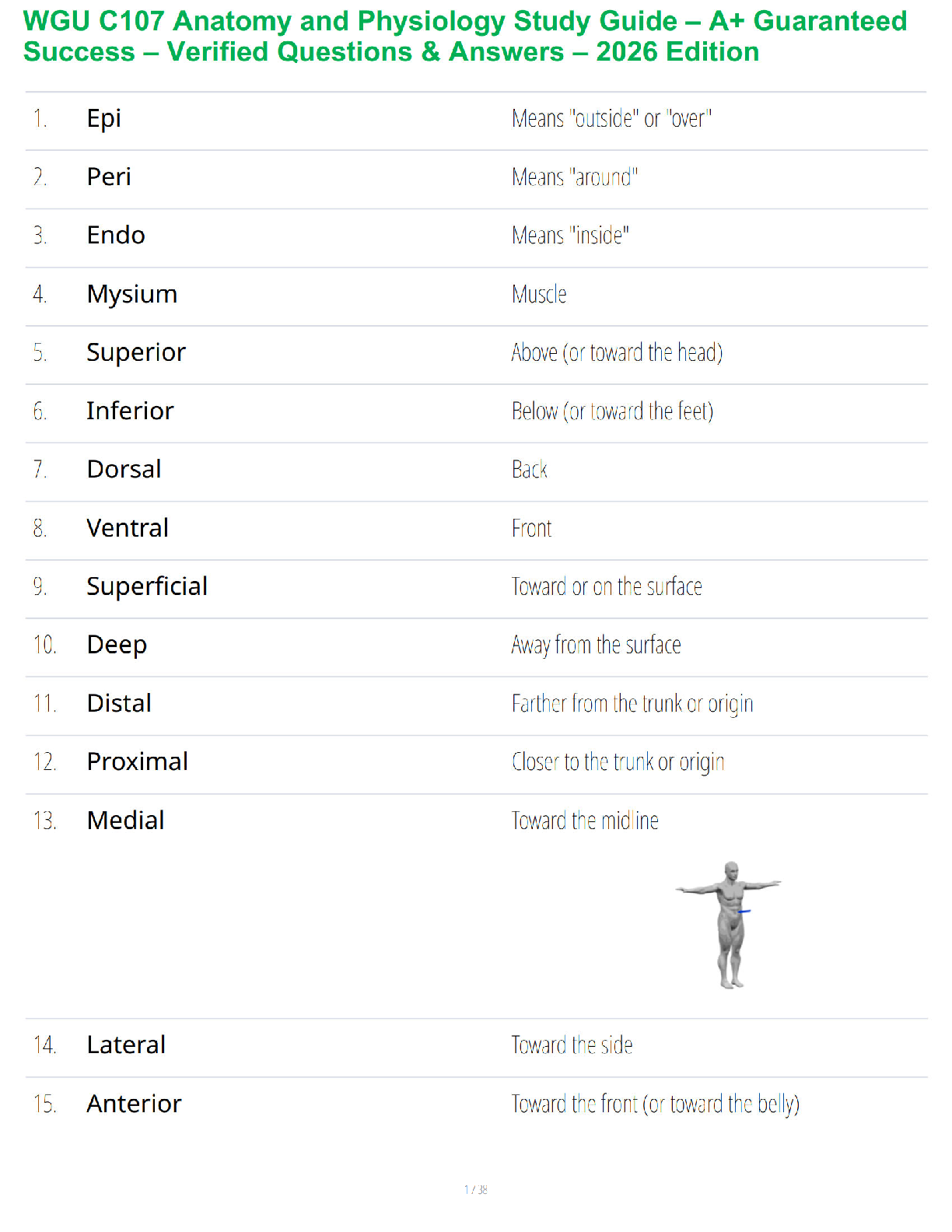
45. Keflex
46.
47. Class: anti-infective; pregnancy category B; similar pharmacologic properties as PCN.
60. sulfonamide (Bactrim)
61.
62. Class: anti-infective; pregnancy category C; used for RA, ulcerative colitis, generic name begins with “sulf” and end in “oxazole”
71. Vancomycin IV – nursing considerations/interventions for client receiving IV Vanco
72. ***Reserved for serious infections like MRSA, C-diff****
73. ****Benadryl can mask signs of ototoxicity
80. Flagyl – patient teaching
81.
82. ******Disulfiram like reaction if alcohol is consumed while on this 91. rifampin (Rifadin) – patient teaching
92. isoniazid (INH) – diet teaching for what vitamin and why
101. BCG for Tb Prevention – when contraindicated (hint: it’s a live vaccine)
102. This is a TB vaccine and is a live vaccine. Patients that are immunosuppressed or HIV CAN NOT get this vaccine.
112. Steroids/glucocorticosteroids (example :prednisone)– what conditions they are used for, what to watch for (what are clients at increased risk for) ; patient education; what analgesics to avoid with steroids
129. Desmopressin (Anti-diuretic hormone) – use, nursing considerations/interventions, side/adverse effects, pt. teaching, know normal sodium (Na) levels
135. Nursing considerations/interventions: monitor I&O, daily weights, assess for mental changes, poor skin turgor, monitor LOC changes due to water intoxication.
146. TSH levels – what do they mean about thyroid function if results are high or low 161. Hypothyroidism/hyperthyroidism – symptoms; what changes would you expect to see when hypothyroidism treated with levothyroxine (Synthroid) 165. Symptoms of hyperthyroidism: Intolerance to heat, fine straight hair, bulging eyes, tachycardia, weight loss, finger clubbing, enlarged thyroid, localized edema, muscle wasting. 167. Symptoms of thyroid storm/excessive thyroid medication levothyroxine (Synthroid) 175. Know signs and symptoms/types of allergic reactions and what to plan to administer based on symptoms/type of reaction 188. Use: anaphylaxis, seasonal allergies, skin and food allergies, medication allergies 194. disulfuram (Antabuse) like reaction - know what antibiotics we covered that this can happen with when taken with alcohol 202. Methotrexate (Trexall) – nursing considerations/interventions, side/adverse effects, client teaching, what to monitor for 215. cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan) – client teaching, adverse effects 228. Live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) – contraindications
229.
230. Patients with weakened immune systems, chronic diseases, immunosuppressed patients and the elderly can NOT receive these vaccines.
249. Hypoglycemia and hypergylcemia signs and symptoms
250.
251. *****Beta blockers can mask hypoglycemia******
252. Hypoglycemia is when your blood sugar is below 70.
263. glucatrol (Glipizide) – use/adverse effects - what to assess for
For all of the insulins below: know time of onset and peaks and what to assess for/nursing interventions for hypoglycemia
Nursing considerations/assessment for emergency contraception
Teach the patient that this is not a routine form of birth control. Explain that they need to begin a maintenance form of birth control. Emergency contraception should only be used in emergency situations. **You can still get STD’s so you have to take still use condoms**
Ask patient when intercourse happened because there is a small window time frame to use emergency contraception.
[Show More]












.png)