Hypoxia
decreased tissue oxygenation
oxygen 2 to 4 L/min via NC or up to 40% via venture mask to achieve and O2sat of at least 95%.
Hypoxemia- low levels of oxygen in the blood.
Oxygen therapy is prescribe
...
Hypoxia
decreased tissue oxygenation
oxygen 2 to 4 L/min via NC or up to 40% via venture mask to achieve and O2sat of at least 95%.
Hypoxemia- low levels of oxygen in the blood.
Oxygen therapy is prescribed at the lowest liter flow need to managed hypoxemia
Why do we need oxygen?
Relieves hypoxemia
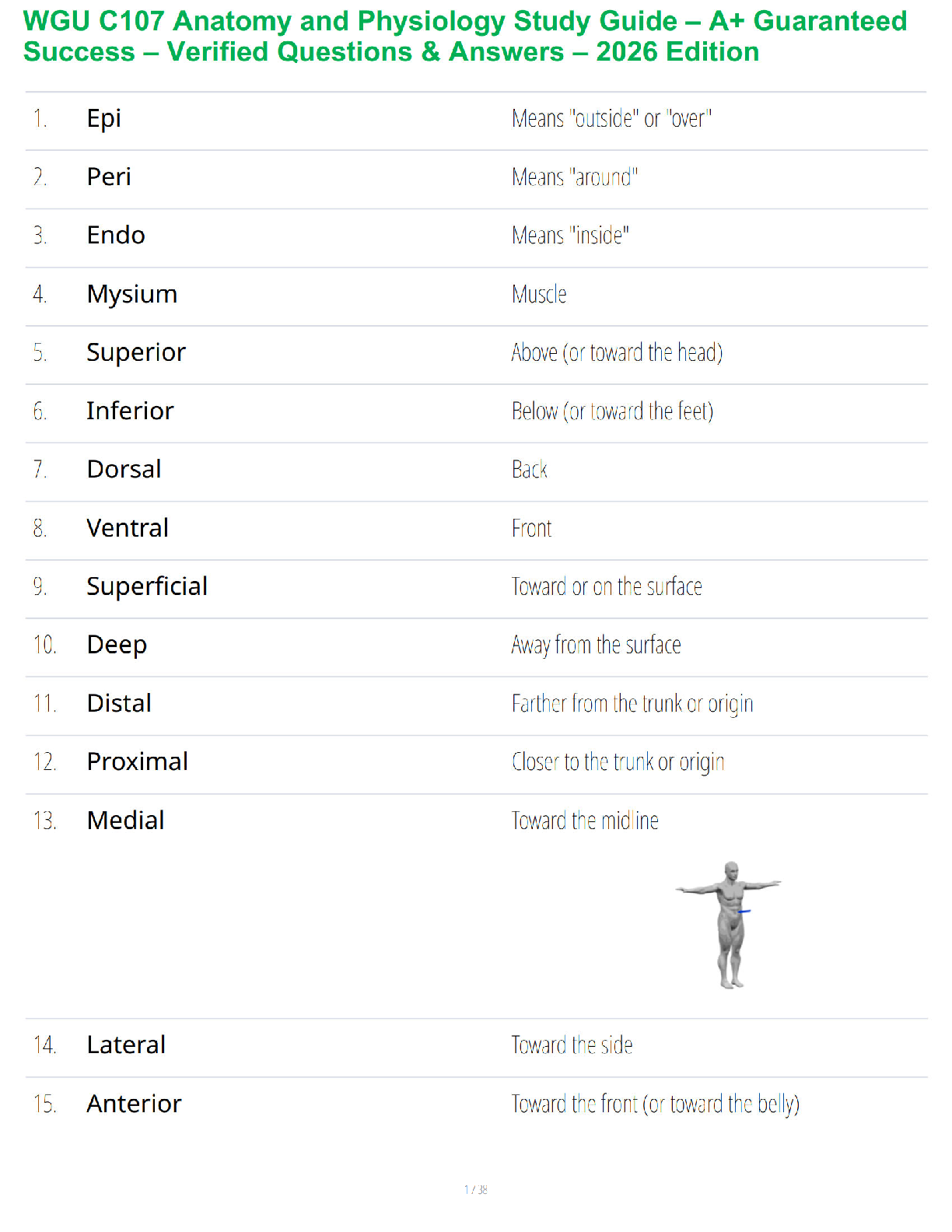
Essential for life & function of cells/tissues.
The best measure to determine the need for oxygen therapy and evaluate its effects.
Hazards and Complications of Oxygen therapy
Combustion
Candles and cigarettes should not be used in a room during oxygen therapy
Oxygen-Induced Hypoventilation
Hypercarbia- retention of Co2.
Co2 narcosis- loss of sensitivity to high levels of Co2.
Absorptive Atelectasis
Nitrogen in the air maintains patient airway and alveoli. Making 79% of room air, Nitrogen prevents alveolar collapse.
Drying of the Mucous membranes
Oxygen flow rates is higher than 4L/min, humidifier is needed to prevent damage to tissue integrity.
Low Flow Systems:
Does not provide enough flow to meet total oxygen and air volume.
1. Nasal Cannula:
Flow rates is 1 to 6/min.
Oxygen concentrations of 24% (at 1L/min) to 44% (at 6L/min).
1. Simple Facemasks
Delivers oxygen up to 40% to 60% for short-term oxygen therapy or in an emergency.
2. Partial Rebreather Mask
Provides 60% to 75% with a flow rates of 6 to 11/min.
3. Nonrebreather Mask:
Provides the highest oxygen level of the low-flow systems and can deliver FIo2 greater than 90%.
HIGH FLOW OXYGEN DELIVERY SYSTEMS:
Delivers an accurate oxygen level when properly fitted with oxygen concentrations from 24% to 100% at 8 to 15L/min.
NONINVASIVE POSITIVE-PRESSURE VENTILATION (NPPV)
Uses positive pressure to keep alveoli open, improve gas exchange without airway intubation.
CPAP or Continuous positive airway pressure
Delivers a set of positive airway pressure throughout each cycle of inhalation and exhalation.
Priority collaborative problems for patient with tracheostomy:
1. Decreased Gas exchange
Pneumothorax (air trapping in the chest cavity)
Can develop during the tracheotomy procedure if the chest cavity is entered.
TRACHEOSTOMY TUBES:
Tubes are available is sizes and made of plastics or metal. Most tubes are disposable
They have cuff and inner cannula.
CARE ISSUES FOR PATIENT WITH TRACHEOSTOMY
Preventing tissue damage
-Tissue damage can occur at the point where the inflated cuff presses against the tracheal mucosa
Ensuring Air warming and Humidification
Tracheostomy tube bypasses nose & mouth, which normally humidify, warm, & filter air
PROVIDING TRACHEOSTOMY CARE:
It is performed whether or not the patient can clear secretions.
Providing Bronchial and Oral Hygiene:
Bronchial hygiene promotes a patent airway and prevents infection.
Ensuring Nutrition
Swallowing can be a major problem for patients with trach. tube.
Respiratory changes when aging:
Heredity and lifetime exposure to environmental pollutants
Most common cause of chronic respiratory distress is smoking Calculating Pack- years
Multiply the number of packs of cigarettes smoked per day x by the number of years th e ACTION ALERT: Teach adults using drugs for nicotine replacement therapy that smoking while taking these drugs greatly increases circulating nicotine levels and the risk for heart attack. Cough- sign of a lung disease.
Ask pt how long the cough has been, any blood. Does it produce sputum, dry, tickling or hacking?
Diagnostic Assessments:
1. Bronchoscopy- insertion of the tube in the airways as fas as the secondary bronchi to view airway structures and obtain sample tissues.
Pre-op procedure:
Stress the importance of not moving, coughing or deep breathing during the procedure to avoid puncture of the pleura or lung.
Lung Biopsy
to obtain tissue for histologic analysis, culture or cytologic examination. *The first priorities after head and neck surgery are airway maintenance and gas exchange^
Airway Maintenance and Gas Exchange
Wound flap and reconstructive tissue care
Tissue “flaps” may be use to close the wound and improve appearance. Assesment:
*Priority action when caring for patient with facial trauma is airway assessment for gas exchange Interventions:
Anticipate the need for emergency intubation, tracheotomy or cricothyroidotomy.
Teach patient to cut the wires if vomiting occurs to maintain gas exchange.
*Instruct patient to keep wire cutters with him at all times to prevent aspiration if vomiting occurs.
4. Lab/s Diagnostic
• The Most accurate and rapid test for TB is the fully automated nucleic acid Remind patient that the disease is usually no longer contagious after drugs have been taken for 2 - 3 consecutively. But he or she must continue with the prescribed drugs for 6 months or longer as prescribed. Physical Assessments:
Acute episode attacks, common symptoms are an audible wheeze and increased RR.
When inflammation occurs, coughing may increase.
Interventions: Responding Bind to stimulate the beta2 adrenergic receptors in the same way epi and norephinerine do. This do increase smooth muscles to relax.
Drug Alert- LABAs should never be prescribed as the only drug therapy for asthma are not to be used during an acute asthma attack or bronchospasm. Teach the patient to use these control drugs daily as prescribed, even when no symptoms are present and to use a SABA to relieve acute symptoms. Any patient using thse drugs must be monitored. Burkholderia Cepacia is a serious bacterial infection of patients with CF. They are usually resistant too antibiotic therapy CHEST TRAUMA
Few types of chest trauma require thoracotomy. Pulmonary embolism
particulate matter (solid, liquid, air) that enters venous circulation and lodges in the pulmonary vessels
Prevention of Pulmonary Embolism THE PATIENT AFTER PULMONARY EMBOLISM
[Show More]






 Test prep.png)
















.png)