cell > A-Level Question Paper > CELL BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW 1 FINAL (All)
CELL BIOLOGY EXAM REVIEW 1 FINAL
Document Content and Description Below
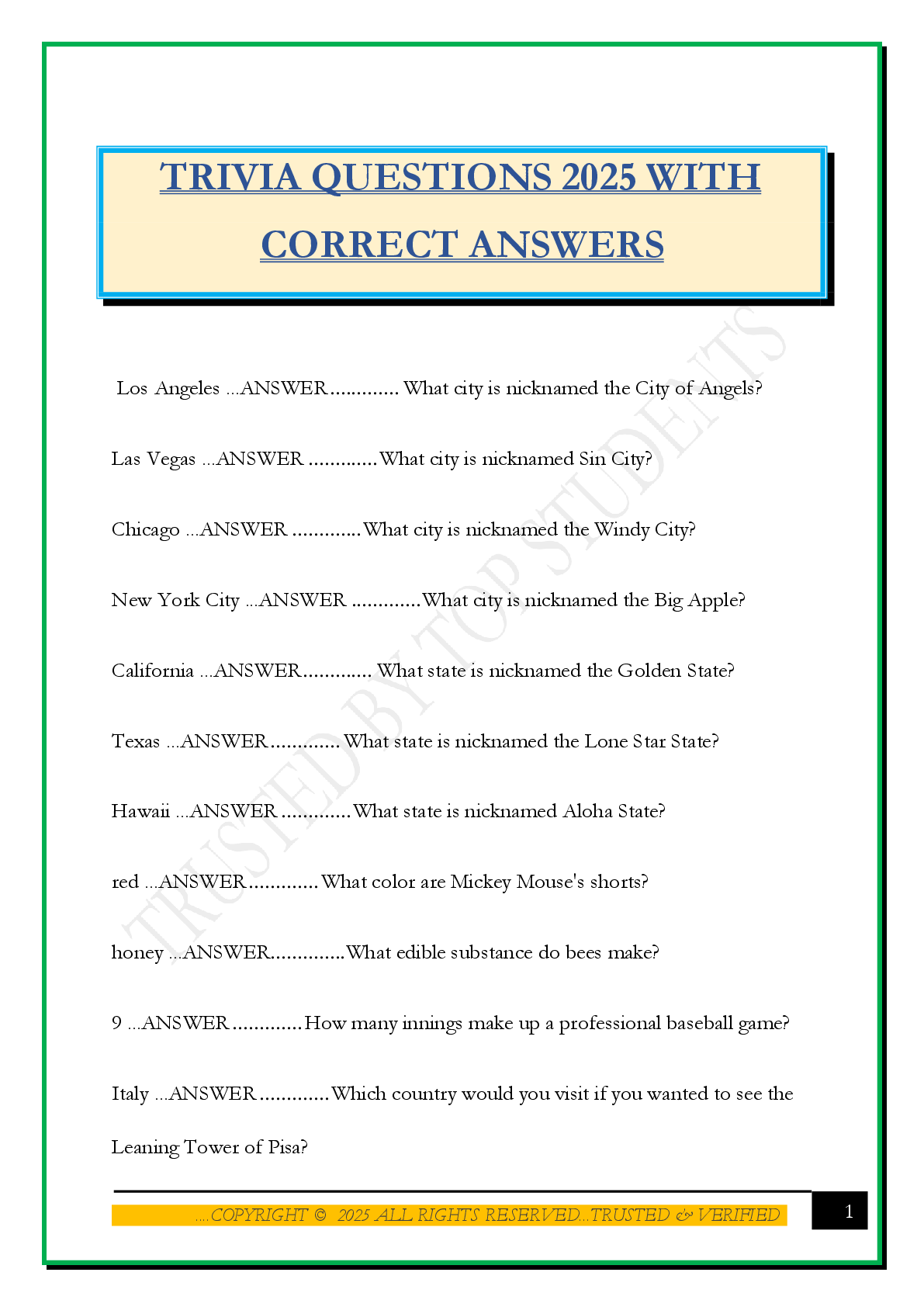
1. What is the Central Dogma? a. Flow of information: DNA -> RNA -> protein 2. What isspecialization? a. =Differentiation: which genes are expressed determine cell fate and function 3. What is the ... cell theory? a. Cells arise from existing cells; spontaneous generation does not occur 4. Describe confocal microscopy a. Machine scans a laser beam across the image at a specific depth (optical section) 5. Compare Transmission Electron Microscopy and Scanning Electron Microscopy a. TEM: Electrons going through specimen; need very thin specimen (thinner than hair) b. SEM: Looking at surface detail; electrons aimed back and forth across specimen. Collect e- that bounce off 6. Prokaryotic Eukaryotic No organelles Distinct organelles DNA not organized in nucleus Double membrane-bound nucleus Single celled; Two domains: Bacteria and Archaea Both single and multicellular organisms 7. Cell Organelles and their functions a. Mitochondria: Provide energy for the cell – synthesis of ATP through cellular respiration b. Chloroplasts: Responsible for photosynthesis in Eukaryotic cells(plants, algae) i. Chlorophyll -> absorb sunlight -> drive ATP synthesis c. Cytosol = cytoplasm: membrane bound structures and cytoskeleton d. Endoplasmic reticulum: Synthesis of most cell-membrane components and secreted proteins; some protein modifications e. Golgi apparatus: Further protein modification; sorting, directing of materialsfor transport within a cell; packaging for secretion f. Lysosomes: Site of intracellular digestion g. Peroxisomes: Production of H2O2, catalase (lipid metabolism and detoxification) h. Cytoskeleton: Controlsinternal organization – structure, movement i. Microfilaments: contraction, movement; ~5 nm diameter ii. Microtubules: vesicle transport, separation of chromatids; ~25 nm diameter iii. Intermediate filaments: mechanical strength; ~8-10 nm diameter 8. What is a model organism and what are some examples? a. Representative organismsthat are amenable to study b. Ex: E. coli, Drosphilia (fruit fly), M. musculus (mouse), Arabidopsis 9. What does it mean for genes to be homologous? a. The genes have a common ancestry [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 01, 2024
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 01, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
41