*NURSING > EXAM PROCTORED > Maternal ATI Questions and Answers Rationales,100% CORRECT (All)
Maternal ATI Questions and Answers Rationales,100% CORRECT
Document Content and Description Below
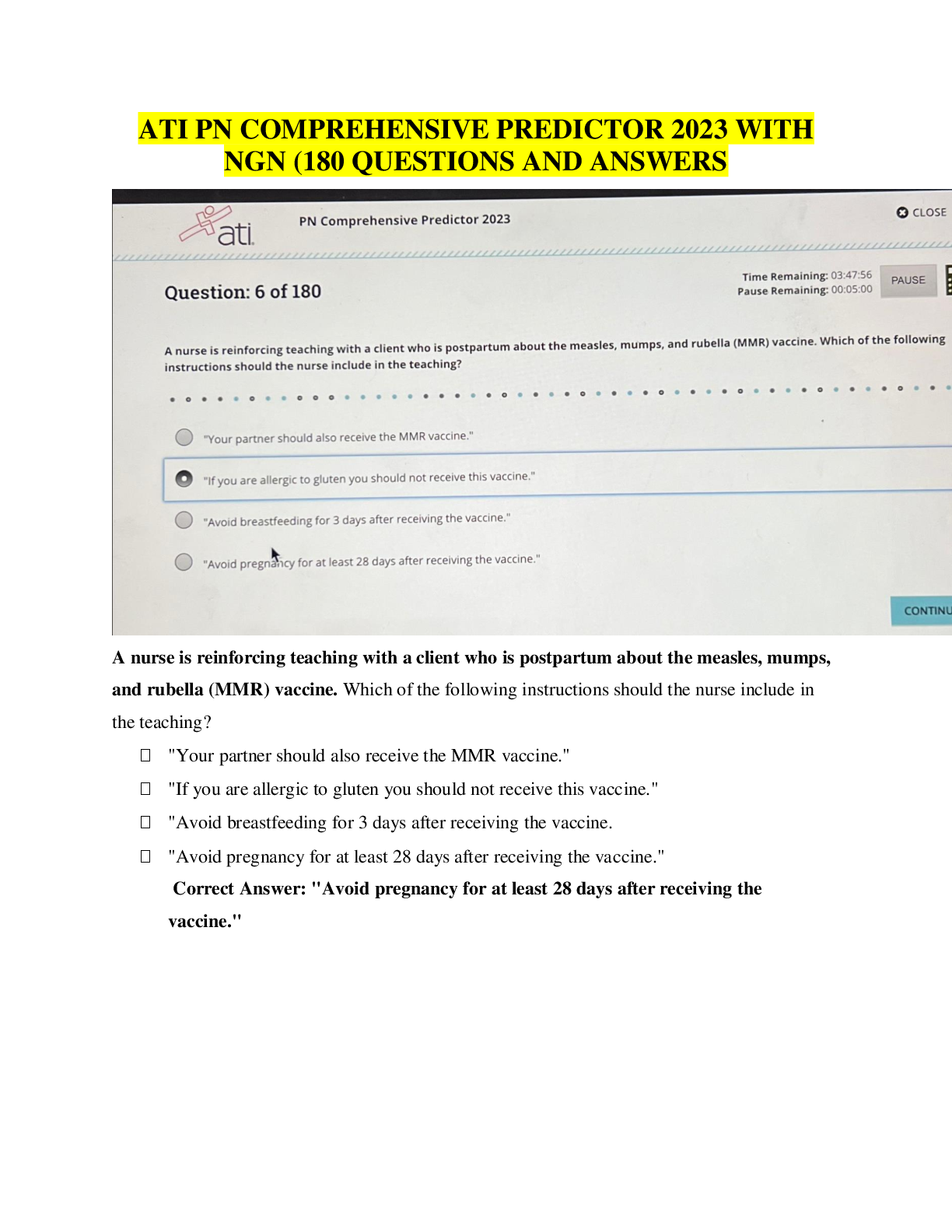
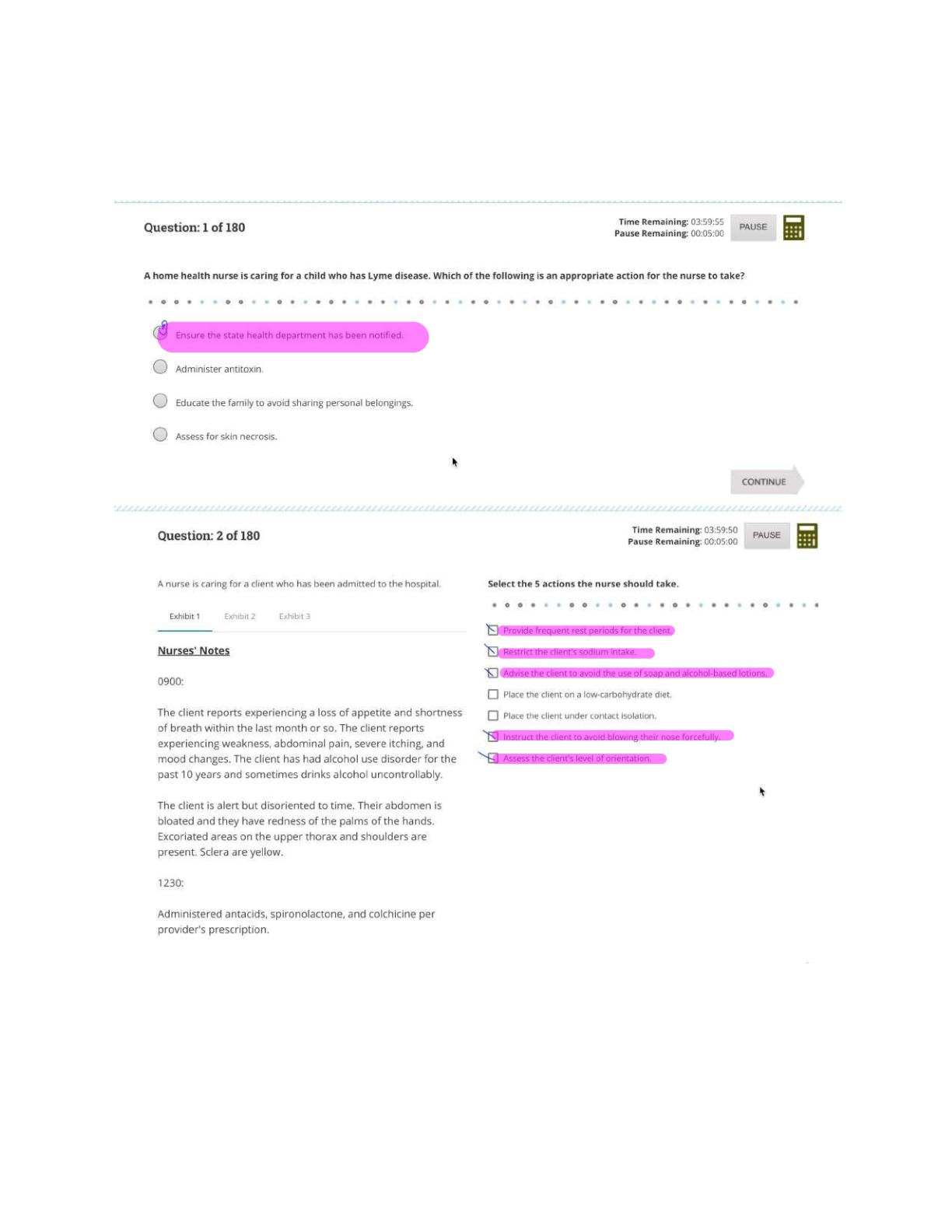
Maternal ATI Questions and Answers Rationales Maternal Newborn: Misoprostol: Stimulate uterine contractions for a client who is undergoing labor induction. Methylergonovine: Stimulate uterin ... e contractions for a client who is experiencing postpartum hemorrhage. Betamethasone: A glucocorticoid > stimulate fetal lung maturity > prevent respiratory depression. Poractant alfa: Synthetic lung surfactant > preterm newborn who is experiencing respiratory distress. Human chorionic gonadotropin: Secreted by the placenta and promotes the excretion of progesterone and estrogen. This hormone is the basis of pregnancy testing. Progesterone is a hormone critical to pregnancy. The female ovaries produce estrogen whether a woman is pregnant or not. Human somatomammotropin: Placental hormone Chadwick’s sign: Bluish discoloration in the cervix, vagina, and vulva that occurs at 6 to 8 weeks. This is a probable sign of pregnancy. After the client’s first pregnancy, this discoloration can remain, making it of little value as an indicator in subsequent pregnancies. A positive pregnancy test: Is a probable sign of pregnancy. A client can also have a positive pregnancy test due to menopause, choriocarcinoma, and hydratidiform mole. Palpable fetal movements: Positive sign of pregnancy. Quickening: The client’s report of fetal movement, is a presumptive sign of pregnancy. Amenorrhea: Lack of menstrual period; presumptive sign of pregnancy. A client can have amenorrhea due to stress, endocrine disorders, and significant weight loss. Oligohydramnios: Volume of amniotic fluid less than 300 mL during the third trimester of pregnancy and occurs when there is a renal system dysfunction or obstructive uropathy. Absence of fetal kidneys will cause oligohydramnios. Expected Findings in Abdominal Trauma; Experiencing uterine contractions due to abdominal trauma. Increase in the client’s heart rate during pregnancy. The heart rate will further increase in response to trauma or blood loss. Increased respiratory rate in response to trauma or blood loss. SHOULD NOT expect client to experience seizures secondary to abdominal trauma. Hydatidiform Mole: Increased urinary output due to the increase in maternal blood volume and pressure of the uterus on the maternal bladder. Expect the client’s temp. to be within the expected reference ranage because hydatidiform mole does not lead to hypothermia. SHOULD NOT expect to hear fetal heart tones because a viable embryo or fetus is not present. A hydatidiform mole, or a molar pregnancy, is a benign proliferative growth of the chorionic villi, which gives rise to multiple cysts. The products of conception transform into a large number of edematous, fluid-filled vesicles. As cells slough off the uterine wall, vaginal discharge is usually dark brown and can contain grapelike clusters. Mild gestation diabetes mellitus: Minimum acceptable urine output in an adult client: 30 mL/hr. > 480mL urine output in 24 hrs. > progression of hypertension, which requires immediate intervention! BP: 140/90 mm Hg +2 edema is an expected finding for a client who is 35 wks. gestation and has gestational hypertension. +1 protein in the urine is an expected finding for a client who has gestational hypertension. HIV: The nurse should inform the client that taking prescription antiviral medication every day decreases the risk of transmission of HIV to her newborn. Instruct the client that she can continue to have sexual intercourse during pregnancy as long as a condom is used. The client and her newborn will only require standard precautions after delivery. Tell the client that she can transmit HIV through breast milk. > Bottle feed her newborn. 8 Weeks Gestation: A client who is pregnant can have nausea upon awakening due to changes in hormone levels. A client who is pregnant can have an increase in vaginal discharge due to the cervix becoming hyperstimulated from an increase in hormones. A client who is pregnant should report experiencing blurred or double vision as these could be a manifestation of gestational hypertension or pre-eclampsia. A client who is pregnant can experience leg cramps while sleeping due to the compression of the pelvic nerves by the enlarged uterus. A nurse is caring for a client who is in the latent phase of labor and is receiving oxytocin via continuous IV infusion. The nurse notes that the client is having contractions every 2 min which last 100 to 110 seconds and that the fetal heart rate (FHR) is reassuring. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? • Nurse should not decrease the rate of maintenance IV fluid because this will not alleviate the uterine tachysystole. • Nurse should DECREASE the dose of oxytocin by half because the client is experiencing uterine tachysystole. • Nurse should not administer terbutaline 0.25 mg subcutaneously to the client because this is an unnecessary intervention that will not address uterine tachysystole. o The nurse should administer terbutaline if the FHR is non-reassuring. • Nurse should not administer oxygen to the client because this is an unnecessary intervention that will not address uterine tachysystole. o The nurse should administer oxygen if the FHR is non-reassuring. Meconium staining of the amniotic fluid: • Ensure that all supplies and equipment needed for resuscitation of the newborn are readily available for every delivery. • Endotracheal suctioning is recommended in cases of meconium staining only if the newborn has poor respiratory effort, decreased muscle tone, and bradycardia after delivery. • The nurse should know that routine suctioning of the newborn’s mouth and nose while the head is on the maternal perineum is no longer recommended. • Do not need to prepare the client for an emergency cesarean due to meconium-stained amniotic fluid. • No ultrasound Placenta Previa & Bleeding: • When a client has a placenta previa, the placenta implants in the lower part of the uterus and obstructs the cervical os (the opening of the vagina). The nurse should clarify this prescription because any manipulation can cause tearing of the placenta and increased bleeding. • Should obtain a blood sample for laboratory testing to identify baseline information regarding the client’s circulatory status. • Should perform continuous external fetal monitoring to provide ongoing assessment of the fetus. • Should initiate IV access with a large-bore IV catheter to ensure the client can receive blood and fluids if necessary. A nurse is caring for a client who is 37 weeks of gestation and is undergoing a nonstress test. The FHR is 130/min without accelerations for the past 10 min. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? • The nurse should use a vibroacoustic stimulator on the client’s abdomen to elicit fetal activity because the fetus is most likely sleeping. Fetal movement should cause accelerations in the FHR. • The external fetal monitor is recording the FHR. • Should have an internal fetal scalp electrode during labor to monitor FHR. • A nonstress test to be nonreactive = after 40 min of continuous monitoring without accelerations in the FHR despite vibroacoustic stimulation. A nurse is reviewing laboratory results for a client who is 37 weeks of gestation. The nurse notes that the client is rubella non-immune, positive for group A beta-hemolytic streptococci, and has a blood type of O negative. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? • Client has Rh-negative blood and should have received Rho(D) immune globin at 28 weeks of gestation and should receive it again within 72 hr. if the client’s newborn is Rh-positive. • The client is not immune to rubella and should receive this immunization after delivery. • The client will receive IV antibiotic therapy during labor to prevent transmission of group B beta-hemolytic streptococcus to the newborn. Polyhydramnios: • Polyhydramnios is the presence of excessive amniotic fluid surrounding the unborn fetus. Gastrointestinal malformations and neurologic disorders are expected findings for a fetus experiencing the effects of polyhydramnios. • An excess amount of amniotic fluid will result in a fundal height greater than expected for gestational age. • An excess amount of amniotic fluid will result in an increase in weight gain. Oligohydramnios: Gestational diabetes > Decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus. Magnesium Sulfate: Pre-eclampsia • Generalized pruritus can be a manifestation of an allergic reaction to magnesium sulfate. • Should tell the client that she will feel sedated while the magnesium sulfate is infusing. • Expect the BP to decrease while the magnesium sulfate is infusing. • Expect the feeling of warmth all over her body while the magnesium is infusing. Latent Phase: Low Back Pain • Provide counter pressure to the sacral area with a palm or a firm object, such as tennis ball, during contractions. Counterpressure lifts the fetal head way from the sacral nerves which decreases pain. • Should not place the client supine during labor because this will increase her back pain. • Use of hydrotherapy during the latent phase of labor can prolong the labor process. Instruct the client to pant during contractions to prevent pushing or bearing down before the cervix is completely dilated during the TRANSITION PHASE OF LABOR. Initiate hydrotherapy when the client is in the ACTIVE PHASE of labor, or approximately 5 cm (2 in) dilated. 12-week gestation: • Swelling of the face > Indicate a hypertensive disorder of preeclampsia. Nausea and vomiting are expected during the first trimester. Only should report this if she is unable to ingest adequate caloric intake. White vaginal discharge is an expected finding during pregnancy resulting from high levels of estrogen. Only report this finding if the discharge becomes foul-smelling or changes color. Urine frequency is an expected finding during pregnancy due to the enlarging fetus. Only report this if she has dysuria or fever. Abdominal Ultrasound: • Tell the client that a full bladder helps to lift the gravid uterus out of the pelvis during the examination. > Ensure that the client has a full bladder to obtain the most accurate image of the fetus. • Should not experience uterine cramping during an abdominal ultrasound. Nonstress test > After 26 weeks of gestation to determine fetal-well-being. Transvaginal ultrasound: Measure cervical length in the 2nd and 3rd trimester to assess for preterm labor. Mild Placental Abruption: • Expect the client who has a mild placental abruption to have minimal dark red vaginal bleeding. • Expect > Urine output within the expected reference range • Expect > Platelet count within the expected reference range • Expect > Reassuring FHR Late decelerations: • Non-reassuring FHR pattern resulting from fetal hypoxemia due to insufficient placental perfusion. Reposition the client, initiate oxygen, and increase the infusion rate of IV fluid to enhance placental perfusion. Fetal head compression: Early decelerations Umbilical cord compression: Variable decelerations Fetal ventricular septal defect: Abnormal opening between the right and left ventricles of the fetus’s heart. Magnesium sulfate: Severe pre-eclampsia • Urine output of 20 ml/hr> inadequate renal perfusion > increasing the risk of magnesium sulfate toxicity. A decrease in urine output can also indicate a decrease in renal perfusion secondary to a worsening of the client’s pre-eclampsia. • Expect: Elevated BP > Report BP greater than 160/110 mmHg • Expect: Respiratory rate within the expected range o RR less than 12/min > Magnesium toxicity • Expect deep tendon reflexes within the expected reference range o Magnesium sulfate toxicity causes a loss of deep tendon reflexes! A nurse is teaching a client who is 13 weeks of gestation about the treatment of incompetent cervix with cervical cerclage. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? • Cervical cerclage prevents premature opening of the cervix during pregnancy. The client should immediately go to a facility for evaluation if she experiences any manifestations of labor while the cerclage is in place. If the client experiences preterm uterine contractions she might require tocolytic therapy. • Client should not resume sexual intercourse until the provider gives approval at a postoperative visit. • Future pregnancies are not contraindicated for a client who has a cerclage, although the provider will likely place a cerclage for each subsequent pregnancy. • Expect spotting for 1 to 2 days after cerclage placement. The client should not have bright red bleeding while the cerclage is in place. The client should immediately go for evaluation if she experiences bright red blood. Labor: Moderate bright red vaginal bleeding • The nurse should obtain samples of the client’s blood for baseline testing for hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. • SHOULD NOT perform a vaginal examination on a client who is experiencing vaginal bleeding. A vaginal examination can lead to a hemorrhage if the client has placenta previa. • Client should be on a strict pelvic rest because she is experiencing bright red vaginal bleeding. • SHOULD NOT perform a vaginal examination on a client who is experiencing vaginal bleeding. A spiral electrode can be placed only when the client’s membranes are ruptured, the cervix is sufficiently dilated, and placenta previa is ruled out because it can lead to hemorrhage. No Fetal Movement for 24 hr.: • Presence of a FHR is a reassuring manifestation of fetal well-being. The nurse should auscultate for the FHR using a doppler device or an external fetal monitor. • Lack of fetal movement for 24 hours is not an expected finding Have the client drink orange juice > appropriate action to stimulate a sleeping fetus Daily weight> Is the most accurate assessment to determine a client’s fluid and electrolyte status. Warning signs of complications: • Vaginal bleeding can be an abnormal finding during pregnancy that might indicate a complication such as placental abruption, placenta previa, or preterm labor. Mild constipation is an expected finding in pregnancy due to the slowing of intestinal motility secondary to the increase in circulating progesterone and compression of the intestines by the enlarged uterus. Nasal congestion is an expected finding during pregnancy due to the swelling of mucus membranes secondary to increased circulating estrogen. The client should feel the fetus move at least 3 times per hour. 10 movements in 1 hr> is an expected finding. Uterine fibroid: • Can increase the risk for postpartum hemorrhage due to the increase in blood supply to the uterus, which supports the fibroid. • Uterine fibroid tumors are more than likely to grow during pregnancy in response to the increase in circulating estrogen. • The size and location of the fibroid will determine the safest method for delivery. If the client has a small fibroid that is not near the cervical os, she can have a vaginal delivery. • The client will undergo serial ultrasound examinations during pregnancy to monitor the fibroid. The provider will not surgically remove the fibroid during pregnancy due to the risk for fetal injury, death, and maternal hemorrhage. Constipation: • Encourage the client to participate in moderate physical activity, such as walking or swimming, every day. This activity increases intestinal peristalsis, which will help alleviate constipation. • The nurse should not instruct the client to stop taking her prescribed prenatal vitamin because this could cause harm to the fetus. • The client should not consume mineral oil to treat constipation during pregnancy because it can lead to severe cramping, diarrhea, fluid loss, and preterm contractions. • The nurse should not recommend for the client to include a daily intake of red meat because it is high in iron and contributes to constipation. Maternal Newborn: 2 Phototherapy: Bilirubin • The nurse should monitor the lamp’s energy throughout the therapy to ensure the newborn is receiving the appropriate amount to be effective. • The nurse should provide breast milk or infant formula to maintain the newborn’s hydration, which promotes the excretion of bilirubin in the stool. o Supplemental feedings of glucose or plain water can INCREASE circulation to the liver and impede bilirubin excretion. • The nurse should apply eye patches, so the light does not damage the newborn’s eyes. The nurse should remove the patches during feedings to observe the eyes and clean them. The parents can make direct eye contact with the newborn during this time. • The nurse should avoid applying any type of topical substance to the newborn’s skin because these substances can absorb heat and cause burns. A nurse is assessing a 4-hour-old newborn who is to breastfeed and notes hands and feet that are cool and slightly blue. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? • Exposure to a cool environment causes vasoconstriction, which results in cool extremities with a bluish discoloration. Placing the newborn skin-to-skin with his mother helps stabilize his temperature and promotes bonding. • Blue lips and mucus membranes can indicate central cyanosis and respiratory distress, which might require supplemental oxygen. • The nurse should not give the newborn glucose water between feedings because this can cause the newborn to become full and not suck enough to ensure adequate milk production. • Temporal and intraauricular thermometers are not effective tools to measure a newborn’s temperature. The nurse should use an axillary thermometer. Newborn: Immediately following delivery • ANSWER: The greatest risk to the newborn is cold stress, which increases the need for oxygen and glucose. Placing the newborn directly on the client’s chest will help maintain the newborn’s temperature.!! • The newborn is at risk for ophthalmia neonatorum and the nurse should administer erythromycin ophthalmic ointment within the first 2 hr of life. • The newborn is at risk for coagulation deficits and the nurse should administer vitamin K within the first 2 hr of life. • The nurse should perform a detailed physical assessment of the newborn to detect birth anomalies or injuries within 12 to 18 hr. Newborn: Home safety • The newborn should always sleep on his back to prevent sudden infant death syndrome. • The parent should never tie any type of string around the newborn’s neck due to the risk of strangulation. • The parents should not place the newborn’s crib close to a heat source due to the risk of the crib linen catching on fire. • The parents should always place the newborn in an approved car seat whenever driving with the newborn. Infant carriers are not approved safety seats for motor vehicles. A nurse is assessing a newborn 1 min after birth and notes a HR of 136/min, respiratory rate of 36/min, well flexed extremities, responding to stimuli with a cry, and blue hands and feet. Which of the following is the Apgar score the nurse should assign to the newborn? • The nurse should use the Apgar scoring system to perform a quick assessment of the newborn at 1 min and 5 min after birth. The nurse should assign a score of 0, 1, or 2 to each of five categories. The nurse should assign a score of 2 for a heart rate greater than 100/min; a score of 2 for a good, strong cry, which shows normal respiratory effort; a score of 2 for well flexed extremities, which shows expected normal muscle tone; a score of 2 for responding to stimulation with a cry, cough, or sneeze; and a score of 1 for blue hands and feet, known as acrocyanosis. A nurse is assessing a client who is 14 hr. postpartum and has a third-degree perineal laceration. The client’s temp. is 37.8 C (100F), and her fundus is firm and slightly deviated to the right. The client reports a gush of blood when she ambulates and no bowel movement since delivery. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? • When the client’s fundus is deviated to the right or left it can indicate that her bladder is full. The nurse should assist the client to empty her bladder to prevent uterine atony and excessive lochia. • The nurse does not need to massage the client's fundus because it is firm and the gush of blood when ambulating is expected due to blood pooling in the vagina when the client is lying in bed. • The nurse should not administer rectal suppositories and enemas to clients who have third- and fourth-degree lacerations due to the risk of injury to the suture line. • Dehydration can cause a client who is postpartum to have a temperature up to 38° C (100.4° F) during the first 24 hr following delivery. A nurse is assessing a 12-hr old newborn and notes a respiratory rate of 44/min with shallow respirations and periods of apnea lasting up to 10 secs. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? • The nurse should continue routine monitoring because the newborn’s assessments findings indicate he is adapting to extrauterine life. • The nurse should place the newborn in a side lying position or supine to promote sleep and decrease the risk of respiratory distress. • Manifestations of abnormal breathing patterns, which can indicate a need for supplemental oxygen, include tachypnea, nasal retractions, stridor, and gasping. • The nurse should expect short periods of apnea for a 12-hour-old newborn and should not perform chest percussion. Cesarean section: Intestinal gas pain • Walking can help stimulate peristalsis, which will promote expulsion of gas. • Splinting the incision with a pillow will assist with incisional pain relief but will not assist with relieving discomfort from gas pains. • Drinking carbonated beverages can cause the client to ingest air and increase gas production. • Drinking fluids through a straw can cause the client to ingest air and increase gas production. Premature: 30 Weeks gestation • Newborns who are premature have abundant lanugo, fine hair, especially over their back. A full-term newborn typically has minimal lanugo present only on the shoulders, pinnas, and forehead. • Newborns who are premature demonstrate hypotonia and a relaxed posture. Full-term newborns demonstrate moderate flexion of the arms and legs. • Newborns who are premature have abundant vernix caseosa, a thick whitish substance, covering and protecting their skin in utero. Post-mature newborns are likely to have dry, parchment-like skin. • Newborns who are premature have few heel creases. Full-term newborns have heel creases that cover most of the bottom of the feet. Report to provider: Newborn 1 hr. after birth • If the newborn has jaundice within the first 24 hr of life, this can indicate a potential pathological process such as hemolytic disease. Pathologic jaundice can result in high levels of bilirubin that can cause damage to the neonatal brain. • A blood glucose level of 60 mg/dL is within the expected reference range for a newborn. The nurse should treat the newborn for hypoglycemia when blood glucose levels are below 40 to 50 mg/dL. • The nurse should expect a newborn to have acrocyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the hands and feet. • A respiratory rate of 50/min is within the expected reference range for a newborn. Bottle feeding: • The parents should run tap water for 2 min and then boil it for 1 to 2 min before mixing it with the formula to decrease the risk of contamination. • The parents should not dilute ready-to-feed formula because the newborn will get full before consuming the appropriate amount of calories and nutrients. • The parents should only keep unused prepared formula for 48 hr to decrease the risk of contamination. • The parents should always hold the bottle when feeding the newborn to prevent aspiration and the development of caries. IV infusion of oxytocin after vaginal birth: Effectiveness of the medication • Oxytocin is a smooth muscle relaxant that causes contraction of the uterus. The nurse should palpate the uterine fundus to determine consistency or tone to determine if the medication is effective. • The nurse should monitor the client’s blood pressure to identify hypertension, which is an adverse effect of oxytocin. • The nurse should monitor the client’s pulse rate to identify cardiac dysrhythmias, which are adverse effects of oxytocin. • The nurse should monitor the client’s urinary output to identify water intoxication, which is an adverse effect of oxytocin. Premature: NICU> Actions to promote development • Positioning the naked newborn on the parent’s bare chest can decrease stress in the parent and the newborn. This action can help maintain thermal stability, raise oxygen saturations, increase feeding strength, and promote breastfeeding. • The nurse should assess the newborn to determine how well she will tolerate feedings and gradually make changes. Rapidly advancing feedings can lead to fluid retention, hyponatremia, vomiting, diarrhea, and apnea. • Newborn's need uninterrupted periods of sleep to promote self-regulation. Light and sounds are adverse stimuli, which can increase stress in a newborn who is premature. • Nonnutritive sucking can decrease oxygen use and energy, which can lead to decreased restlessness. Oxytocin promotes uterine contractions. A large fetus and multifetal gestation can lead to over-stretching of the uterus and prevent uterine contractions. Risk for Uterine Atony: • Magnesium sulfate is a smooth muscle relaxant and can prevent adequate contraction of the uterus. • After birth, clients can experience a decreased urge to void due to birth-induced trauma, increased bladder capacity, and anesthetics, which can result in a distended bladder. The distended bladder displaces the uterus and can prevent adequate contraction of the uterus. • Prolonged labor can stretch out the musculature of the uterus and cause fatigue, which prevents the uterus from contracting. Congenital hip dysplasia: • A newborn who has congenital hip dysplasia can have limited abduction because the head of the femur might have slipped out of the acetabulum. • Newborns who have congenital hip dysplasia will have asymmetrical gluteal folds. • Newborns have legs that are shorter than the arms. Reflexes: • To elicit the tonic neck reflex, the nurse should quickly and gently turn the newborn's head to one side when he is sleeping or falling asleep. The newborn’s arm and leg should extend outward to the same side that the nurse turned his head while the opposite arm and leg flex. This reflex persists for about 3 to 4 months. • To elicit the rooting reflex, the nurse should touch the newborn’s lip, cheek, or corner of the mouth. The newborn should turn toward that side and open his mouth. This reflex usually persists for 3 to 4 months but can last for 1 year. • To elicit the Babinski reflex, the nurse should stroke the bottom of the newborn’s foot upward along the lateral edge, then along the ball of the foot with a finger. The newborn’s toes should hyperextend while the big toe dorsiflexes. This reflex persists for about 1 year. • To elicit the Moro reflex, the nurse should hold the newborn in a semi-sitting position and allow the trunk and head to fall backward about 2.5 cm (1 in). The newborn should abduct and extend his arms symmetrically, and the fingers should fan out and form a "C" with the thumb and forefinger. This reflex is the strongest during the first 8 weeks and usually disappears in about 4 to 5 months. 39 Weeks of Gestation: • A newborn who is born at 39 weeks of gestation is full-term and should have a symmetric rib cage. • A newborn who is born at 39 weeks of gestation is full-term and should have normal, smooth skin with good turgor and the presence of subcutaneous fat pockets. A postmature newborn, greater than 42 weeks of gestation, will have dry, cracked skin with a wrinkled appearance. • A newborn who is born at 39 weeks of gestation is full-term and should have little to no vernix present at birth. • Lanugo is a fine, downy hair that is abundant in newborns who are preterm. Newborns who are born at full-term typically have sparse lanugo, which is only present on the shoulders, pinna, and forehead. A caput succedaneum is present at birth and extends across suture lines. It is edema of the scalp and will resolve in 3 to 4 days. This discoloration is a cephalhematoma, resulting from a collection of blood between the skull and periosteum, that will resolve within 2 to 6 weeks. • Egg-shaped, edematous, bluish discoloration that does not cross the suture line Vacuum-assisted birth: Cervical laceration • The nurse should monitor for bright red bleeding as a slow trickle, oozing or outright bleeding,and a firm fundus to identify a cervical laceration. The nurse should monitor for a report of increasing pain and pressure in the perineal area to identify a vulvar hematoma. The nurse should monitor for excessive vaginal bleeding in the presence of a flaccid uterus to identify that the blood is coming from the uterus. The most common cause of this occurrence is a full bladder or retained placental fragments. When the nurse massages the uterus, it will contract and help move pooled blood in the uterus to the vaginal opening. Postpartum: Cardiac disease • The nurse should weigh the client daily to monitor for fluid overload. • A client who has cardiac disease should follow a high-fiber diet to prevent straining with bowel movements because the pushing effort (Valsalva maneuver) can result in cardiac stress. • The nurse should initiate bedrest with the head of the bed elevated to promote rest and decrease the client’s oxygen consumption. • The nurse should monitor the client’s intake and output because blood flow to and from the heart increases for at least the first 24 hr after delivery. This physiological change places the client who has cardiac disease at high risk for cardiac decompensation and fluid overload. Does not want to breastfeed her newborn: • The nurse should instruct the client to place ice packs on her breasts using a 15 min on and 45 min off schedule, to decrease swelling of the breast tissue as the body produces milk. • The client should drink 2 to 3 L of fluid per day to promote normal bowel function. • The client should drink 2 to 3 L of fluid per day to promote normal bowel function. • The client should wear a well-fitting, supportive bra to provide comfort as the breasts fill with milk. Medications to administer within 1 to 2 hr. of delivery: • Every newborn born in the United States should receive erythromycin ophthalmic ointment to prevent gonorrheal or chlamydial infections that the newborn can contract during birth. • The nurse should administer naloxone, an opioid antagonist, if the newborn has respiratory depression. Respiratory depression can occur if the mother received opioid pain medications shortly before the birth of the newborn. • Newborns who are premature receive poractant alpha, a surfactant replacement, to prevent and treat respiratory distress syndrome. • The newborn should receive the rotavirus immunization at 2 and 4 months of age. A nurse is assisting a client who is 4 hr. postpartum to get out of bed for the first time. The client becomes frightened when she has a gush of dark red blood from her vagina. Which of the following statements should the nurse make? • In the early postpartum period, lochia will pool in the vagina when the client is lying in bed and will flow out of the vagina when the client stands up. After the initial gush, the bleeding will slow down to a trickle of bright red lochia. • If the client has a damaged blood vessel, blood will spurt out of the vagina and the flow will not slow down. • If the client has retained placental fragments, she will have excessive vaginal bleeding that does not stop. This increased lochia will be present regardless of the client’s position. • The client’s lochial flow will steadily decrease during the postpartum period. Breastfeeding: • Cluster feeding is an expected finding for newborns who are breastfeeding. The mother should follow her newborn's cues and feed her 8 to 12 times per day. • If the mother is experiencing pain during breastfeeding soon after the newborn starts sucking, she might not be holding the newborn correctly or the newborn may not be latching on correctly. The nurse should teach the client appropriate breastfeeding techniques. • The newborn’s demand for milk will influence the mother’s milk production. As the newborn removes milk from the breast, the mother will produce more milk. Mothers who are breastfeeding should drink only to satisfy thirst. • The client should eat a healthy, well-balanced diet of nutrient-dense foods with adequate amounts of calcium, minerals, and fat-soluble vitamins. The client is not required to eat specific foods. Magnesium Sulfate: • The nurse should have calcium gluconate available to give to a client who is receiving magnesium sulfate by continuous IV infusion in case of magnesium sulfate toxicity. The nurse should monitor the client for a respiratory rate less than or equal to 12/min, muscle weakness, and depressed deep-tendon reflexes. • The nurse should have protamine sulfate available to give to a client who is receiving heparin in case of hemorrhage. • The nurse should have atropine available to give to a client who is receiving medications that can lead to asystole or sinus bradycardia, such as beta adrenergic blockers. • The nurse should have naloxone available to give to a client who is receiving opioid medication in case of respiratory depression. Medications to promote uterine contractions: • The nurse should administer methylergonovine, an ergot alkaloid, which promotes uterine contractions. • The nurse should administer nifedipine, a smooth muscle relaxant, to a client who is experiencing preterm labor. • The nurse should administer terbutaline, a smooth muscle relaxant, to a client who is experiencing preterm labor. • The nurse should administer magnesium sulfate to a client who has preeclampsia to lower blood pressure and minimize the risk of seizures. Rubella Immunization • A client who receives a rubella immunization should not conceive for at least 1 month after receiving the rubella immunization to prevent injury to the fetus. • A client should have a rubella titer check with each pregnancy to determine if she is still immune. • The client can continue to breastfeed her newborn because the live attenuated virus does not pass into breast milk. • A client who is pregnant should not receive the rubella immunization because it is a live virus and can cause a rubella infection, which can cause miscarriage, congenital anomalies, or death of the fetus. Circumsion: • Allowing the newborn to suck on a pacifier is an effective form of nonpharmacological pain management. • The parents should apply the diaper loosely to prevent pressure and injury over the circumcision area. • The yellow exudate that forms over the glans penis is part of the healing process and should not be removed. This usually continues for 2 to 3 days. • The parents should not use prepackaged commercial wipes due to the alcohol content, which can delay healing and cause pain. The parents should use warm water to clean the penis gently. Maternal Newborn Final A nurse is assessing a client on the first postpartum day. Findings include fundus firm and one fingerbreath above and to the right of the umbilicus, moderate rubra with small clots, temperature 37.3 (99.2), and pulse rate 52/min. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? • Because the muscles supporting the uterus have been stretched during pregnancy, the fundus is easily displaced when the bladder is full. The fundus should be found firm at midline. A deviated, firm fundus indicates a full bladder. The nurse should assist the client to void. • The nurse should massage the fundus when it is boggy. • A slight maternal temperature increase is commonly seen in the first 6 to 10 days postpartum. A pulse of 52/min is within the expected reference range. • The client’s fundus is firm with moderate lochia rubra. Administering an oxytocic agent is not an appropriate intervention. Oxytocic agents are given for clients who have increased lochia rubra or a boggy fundus to promote uterine contractions. Naloxone: • The nurse should administer naloxone to reverse respiratory depression due to acute narcotic toxicity, which can result from IV narcotics administration during labor. • The use of naloxone in the newborn who has been exposed to narcotics during pregnancy could result in immediate withdrawal symptoms. • Naloxone has no effect on hyaline membrane disease. • Naloxone has no effect on meconium aspiration respiratory distress. Oxytocin: Induction of Labor • Clients who receive anesthesia before the active phase of labor usually find the progression of their labor to slow. The medication depresses the central nervous system. Therefore, it will take longer for the cervix to dilate and efface. • Epidural anesthesia will cause the maternal blood pressure to decrease because of central nervous system depression. • An epidural will be most effective when the client is in active labor, where there will be uterine contractions occurring at least every 3 to 5 min that last between 40 and 70 seconds, and contractions will be moderately strong in intensity. • An adverse effect of epidural anesthesia is maternal hypotension, which can cause bradycardia in the fetus. This adverse effect has nothing to do with the timing of the epidural and is usually prevented by administering a bolus of 500 mL of an IV fluid prior to the insertion of the epidural catheter. Pregnant: Nausea and Vomiting • Morning sickness is caused by the buildup of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the mother’s system. Dry foods eaten before rising in the morning tend to reduce the risk of nausea in clients who are pregnant. • The nurse should teach the client to decrease fluid intake with meals to prevent overdistention of the stomach, which will help reduce the risk of nausea and vomiting. • The nurse should teach the client to avoid brushing her teeth immediately after meals to decrease nausea and vomiting. • The nurse should teach the client to eat foods served at cool temperatures. Rh(D) Immune Globulin: • The nurse should administer Rh(D) Immune Globulin to a client who is pregnant and has Rh-negative blood at 28 weeks of gestation. Rh(D) Immune Globulin consists of passive antibodies against the Rh factor, which will destroy any fetal RBCs in the maternal circulation and block maternal antibody production. • The nurse should administer Rh(D) Immune Globulin to a client who is pregnant and has Rh-negative blood to prevent maternal antibody production. The nurse should administer Rh(D) Immune Globulin postpartum to a client who is Rh negative and has an Rh positive newborn. • The nurse should administer Rh(D) Immune Globulin following a mismatched blood transfusion. Magnesium sulfate toxicity: Newborn • Magnesium sulfate can cause respiratory and neuromuscular depression in the newborn. The nurse should monitor the newborn for clinical manifestations of respiratory depression. A premature newborn can experience jaundice, but it is related to prematurity A preterm newborn can have difficulty with thermoregulation due to immature temperature control mechanisms. A premature newborn can experience hypoglycemia, but it is due to prematurity. Narcotic use disorder: Contraindication for the care of the newborn • This newborn needs a quiet, calm environment with minimal stimulation to promote rest and reduce stress. A stimulating environment can trigger irritability and hyperactive behaviors. • Tight swaddling of the newborn discourages hyperactivity and provides comfort. Additionally, it reduces self-stimulation behaviors and protects the newborn’s skin from abrasions. • The newborn who is exposed to narcotics often has an uncoordinated suck and swallow, predisposing the newborn to aspiration. Small, frequent feedings provide adequate caloric intake and reduce the risk of aspiration. • Maternal-newborn bonding is an important part of the newborn’s care. The client’s drug use, as well as the newborn’s hyperactive behavior, often interferes with establishment of the maternal-newborn relationship. A nurse is caring for a client who is in labor. A vaginal examination reveals the following information: 2 cm, 50%, +1, Right occiput anterior (ROA). Based on this information, which of the following fetal positions should the nurse document in the medical record? • ROA describes the relationship of the presenting part of the fetus to the client’s pelvis. In this case, the occipital bone is the presenting part and is located anteriorly in the client’s right side. Based on the presentation of the fetus, the position is vertex. • The transverse position indicates that the fetus is lying horizontally in the pelvis and is presenting with its shoulder. • The breech position indicates that the fetus is upright in the uterus and is presenting with the buttocks or feet. • Mentum indicates that the fetus has fully extended its head and is presenting with its chin. Intrauterine device (IUD) contraception: Contraindication • An IUD is a small plastic or copper device placed inside the uterus that changes the uterine environment to prevent pregnancy. An IUD is contraindicated for women who have menorrhagia, severe dysmenorrhea, or history of ectopic pregnancy. • An IUD is an appropriate method of contraception for women who have hypertension. It is a good alternative to the estrogen-based oral contraceptive that cannot be taken by women who have hypertension. • A history of multiple gestations is not a contraindication for an IUD. • An IUD is an appropriate method of contraception for women who have a history of thromboembolic disease because the IUD is not associated with clotting problems. The IUD is a good alternative to oral contraceptives, which are contraindicated for women who have a history of thromboembolic disease. Active Labor: • Prior to administering an analgesic during active labor, the nurse must know how many centimeters the cervix is dilated. If administered too close to the time of delivery, the analgesic could cause respiratory depression in the newborn. • Monitoring the fetal heart rate every hour is not frequent enough. Even for low-risk clients, most facility protocols require monitoring fetal heart rate every 15 to 30 min while the client is in the first stage of labor and every 5 to 15 min in the second stage (as long as the fetal heart rate has reassuring characteristics). High-risk clients require more frequent monitoring. • Inserting an indwelling urinary catheter is not necessary under normal circumstances. The nurse needs to assess for bladder fullness, especially if the client has had epidural anesthesia. If the client is unable to void, a straight catheter will suffice in most instances. • Raising side rails is not usually required during labor unless clients have been medicated. Many clients in labor prefer to walk to help the progress of their labor. Raising four side rails can be considered a restraint. Trichomoniasis: Prescription for metronidazole • Trichomonas vaginalis is the organism that causes the sexually transmitted infection trichomoniasis. Both men and women can be infected with trichomoniasis. Clinical findings include yellowish to greenish, frothy, mucopurulent, copious discharge with an unpleasant odor, as well as itching, burning, or redness of the vulva and vagina. Trichomoniasis can be treated easily with metronidazole. However, for the treatment to work, it is important to make sure both sexual partners receive treatment to prevent reinfection. Instruct the client to use condoms during sexual intercourse while being treated. • Trichomoniasis can be easily treated and cured with metronidazole. However, for the treatment to work, it is important to instruct the client to avoid sexual intercourse while being treated or to use a condom. • Treatment of the male partner is done without a culture if his female partner has trichomoniasis. • The nurse should teach the client that both men and women can be infected with trichomoniasis. Unless both partners are treated, the male will likely reinfect the female. Hypoglycemia: • Large for gestational age (LGA) newborns are those newborns whose weight is at or above the 90th percentile. One of the most common etiologies of LGA newborns is a mother who is diabetic. LGA newborns, especially those born to mothers who have diabetes, are at increased risk for hypoglycemia. Other newborns at risk for hypoglycemia are small for gestational age (SGA) newborns (those below the 10th percentile), premature newborns, and newborns who have perinatal hypoxia. • A newborn who has pathologic jaundice has hyperbilirubinemia that can lead to acute bilirubin encephalopathy. • The newborn who has fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) will exhibit respiratory manifestations such as tachypnea, nasal flaring, and chest retractions. Neurologic manifestations of FAS include irritability, tremors, and incessant crying. Gastrointestinal manifestations of FAS include uncoordinated sucking swallowing reflex, incessant hunger, and vomiting. • A newborn who is Rh-positive, born to a mother who is Rh-negative, will have jaundice as a result of hyperbilirubinemia and the breakdown of RBCs. This is also called erythroblastosis fetalis. Postpartum Bleeding • The primary cause of early postpartum bleeding is uterine atony manifested by a relaxed, boggy uterus. Thus, the greatest risk for the client is hemorrhage. The nurse should massage the client’s fundus first. • A full bladder can cause uterine atony. • Administering carboprost is an appropriate action for the nurse to take to manage postpartum hemorrhage. Late decelerations: • Late decelerations indicate that the client is experiencing uteroplacental insufficiency. The client might be experiencing pressure on the inferior vena cava, which decreases the oxygen to the placenta and thus to the fetus. Turning the client onto her left side will relieve the pressure and facilitate better blood flow to the placenta, thereby increasing the fetal oxygen supply. Contraindication for oxytocin: • The use of oxytocin is contraindicated for clients who have an active genital herpes infection. The newborn can acquire the infection as they pass through the birth canal. Therefore, a cesarean birth is recommended for clients who have an active genital herpes infection. Intrauterine growth restriction is an indication for the use of oxytocin to induce labor. When the client is at or near term with prolonged rupture of membranes, oxytocin induction is indicated. Induction of labor with oxytocin is suggested in postterm pregnancies. Neonatal abstinence syndrome: • A newborn who has neonatal abstinence syndrome usually exhibits clinical findings of hyperactivity within the central nervous system (CNS). Exaggerated reflexes are indicative of CNS irritability. • A newborn who has neonatal abstinence syndrome usually exhibits clinical findings of hyperactivity within the central nervous system (CNS). • Newborns who have neonatal abstinence syndrome often experience respiratory distress manifested by respirations greater than 60/min. Contractions: • A contraction interval is how often a uterine contraction occurs. The nurse will measure the interval from the beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction. A contraction lasting 60 seconds with a relaxation period of 3 min is equivalent to contractions every 4 min. Ectopic pregnancy: • An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants in tissue outside of the uterus and the placenta and fetus begin to develop there. The most common site is within a fallopian tube, but ectopic pregnancies can occasionally occur in the ovary or the abdomen. Most cases are a result of scarring caused by a previous tubal infection or tubal surgery. Therefore, PID places the client at risk for an ectopic pregnancy. Jaundice: Jaundice in the first 24 hr of life is pathologic. The nurse should notify the provider and obtain a stat prescription for a bilirubin level. The nurse should give phytonadione soon after birth for prevention and treatment of hemorrhagic disease in the newborn. A bagged urine specimen is indicated for suspected or known maternal drug use during pregnancy. Active genital herpes simplex virus: type 2 • Whenever possible, the cesarean birth should be scheduled prior to the onset of labor or rupture of membranes to reduce the risk of neonatal transmission of herpes. • The client who has active herpes should receive a prescription for acyclovir. Metronidazole should be prescribed for bacterial vaginosis. • The cesarean birth should be planned prior to the rupture of membranes. If rupture of membranes occurs, an emergency cesarean birth should be done as soon as possible, but every attempt should be made to prevent this situation. • Erythromycin provides prophylaxis against ophthalmia neonatorum. It is given to prevent gonorrhea and chlamydia infections in the newborn. Naloxone: • By blocking the effects of narcotics on the CNS, naloxone prevents CNS and respiratory depression in the newborn following delivery. • Naloxone blocks the depressant effects of narcotics on the CNS rather than stimulating the CNS. • Naloxone lessens rather than accentuates the effect the narcotics. Weight gain: • A weight gain of 25 to 35 lb is associated with good fetal outcome. A gain of 4 lb in the first trimester and 12 lb each for the second and third trimester is recommended. • A weight gain of 4 lb in the first trimester and 12 lb each for the second and third trimester is recommended. Epidural for Pain relief: Maternal hypotension is an adverse effect of epidural anesthesia. The nurse should administer an IV fluid bolus prior to the placement of epidural anesthesia in order to decrease the likelihood of this complication. Tachycardia is not an adverse effect of epidural anesthesia. It is an adverse effect of opioid agonist-antagonist analgesics, such as butorphanol tartrate. Respiratory depression is not an adverse effect of epidural anesthesia. It is a risk in clients receiving magnesium sulfate for pre-eclampsia or premature labor. Removal of hydatidiform mole: • Hydatidiform moles are uncontrolled growths in the uterus arising from placental or fetal tissue in early pregnancy. There is an increased incidence of choriocarcinoma associated with molar pregnancies. Pregnancy must be avoided for 1 year so the client can be closely monitored for manifestations of this condition. • A baseline human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level should be obtained following evacuation of the hydatidiform mole and then weekly until levels are normal for 3 consecutive weeks. Additional hCG levels should be obtained every 4 weeks for the next 6 to 12 months. • Although the exact cause of molar pregnancies is unknown, it is not believed to be genetic in origin. • Molar pregnancies tend to cause hypertension. However, this manifestation usually disappears once the abnormal products of conception are evacuated. The nurse should obtain a vaginal/anal group B streptococcus ß-hemolytic (GBS) culture at 35 to 37 weeks of gestation to screen for infection. Prophylactic antibiotics should be given during labor to the client who is positive for GBS. The nurse should obtain a maternal blood type and Rh factor at the first prenatal visit to determine if the client will need to receive Rh(D) Immune Globulin at 28 weeks of gestation. The nurse should obtain a rubella titer at the first prenatal visit to determine immunity to rubella. A client who is pregnant and does not have a titer to rubella must be taught to avoid exposure. The nurse should obtain a 1-hour glucose tolerance test at 24 to 28 weeks of gestation to screen for gestational diabetes. Terbutaline: Preterm • The primary action of terbutaline is to cause bronchodilation and relax smooth muscles. However, an adverse effect is tachycardia. If the pulse is greater than 130/min, the terbutaline needs to be held until the provider is notified. Phototherapy: Hyperbilirubinemia • Overexposure to the lights during treatment can cause damage to the newborn’s corneas. Therefore, the nurse should gently close the newborn’s eyes prior to applying the eye shield. • Lotion on the newborn’s skin can cause burns during phototherapy. Therefore, the nurse should not apply lotion to the newborn’s skin. • The purpose of phototherapy is to reduce the level of bilirubin in the newborn. The nurse should ensure that the newborn has as much skin exposed to the lights as possible. • The nurse should encourage frequent feedings throughout the treatment to prevent dehydration and to help promote excretion of bilirubin in the stools. Betamethasone: Lung maturity • Betamethasone causes hyperglycemia in the client, which predisposes the newborn to hypoglycemia in the first hours after delivery. It is important to assess the newborn’s blood glucose level within the first hour following birth and frequently thereafter until blood glucose levels are stable. Severe-iron deficiency anemia • The nurse should administer iron using the Z-track method to prevent staining of tissue. A 20-gauge needle is the correct size. • The nurse should administer the iron into the ventrogluteal muscle. Iron is never given in the deltoid, only the ventrogluteal muscle, as this is a larger muscle mass. This is the typical finding of vena cava syndrome, or hypotension that occurs in clients who are pregnant upon assuming a supine position. It is caused by compression of the inferior vena cava by the gravid uterus with a consequent reduction in venous return. A side lying position promotes uterine perfusion and fetoplacental oxygenation. A nonstress test is a noninvasive test to determine fetal well-being. Hypoglycemia is associated with dizziness. Nonstress test: The purpose of the test is to assess fetal well-being. The client should press the button on the handheld marker when she feels fetal movement. Oxytocin is used to induce contractions for an oxytocin challenge test. The client is encouraged to eat prior to the test in order for the fetus to be more active. When the fetus is asleep, the nurse often offers the client orange juice to stimulate the fetus. A nonstress test measures fetal heart rate (FHR) accelerations with normal movement. A fetal acceleration is a positive sign present when the FHR increases 15/min and lasts 15 seconds. In a nonreactive nonstress test, there are no accelerations. Absence of FHR accelerations suggests that the fetus might be going into distress. The fundal height should be approximately the same as the number of weeks of gestation, plus or minus 2 cm. Pre-eclampsia is the development of edema, elevated blood pressure, and proteinuria during pregnancy. Pre-eclampsia is the development of edema, elevated blood pressure, and proteinuria during pregnancy. Pre-eclampsia is a blood pressure reading of 140/90 mm Hg or greater, an increase of 30 mm Hg or more in systolic pressure or 15 mm Hg in diastolic over baseline on two occasions taken at least 6 hr apart. A blood pressure reading of 140/98 mm Hg is elevated and consistent with pre-eclampsia. Magnesium sulfate: Pre-eclampsia Urinary output is critical to the excretion of magnesium from the body. The nurse should discontinue the magnesium sulfate if the hourly output is less than 30 mL/hr. The acceptable range for fetal heart rate is 120 to 160/min. The acceptable range for respiratory rate is 16 to 20/min. Oxytocin: Induction of labor • When oxytocin is administered to an antepartum client, the fetal monitor must be used to continuously monitor the fetal heart rate and maternal contractions. Diaphragm: • The diaphragm is a flexible rubber cup that is filled with spermicide and is inserted over the cervix prior to intercourse. The diaphragm is a prescribed device fitted by the provider. It should be replaced every 2 years. • The diaphragm should remain in place at least 6 hr after intercourse. • The diaphragm should be cleaned with mild soap and water and dried gently. Alcohol can dry out the diaphragm and can weaken the rubber. This will lead to an ineffective rate of birth control. • The diaphragm should be rinsed with water and contraceptive jelly should be applied prior to placing the device into the vagina. Vaginal lubricants, mineral oil, and baby oil should not be used on the diaphragm, because they can weaken the rubber. Hypoglycemia: Jitters or poor suck Complication of oxygen therapy: • Oxygen therapy can cause retinopathy of prematurity, especially in preterm newborns. It is a disorder of retinal blood vessel development in the premature newborn. In newborns who develop retinopathy of prematurity, the vessels grow abnormally from the retina into the clear gel that fills the back of the eye. It can reduce vision or result in complete blindness. • Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC): a severe disease of premature newborns. In NEC, the lining of the intestinal wall dies and the tissue sloughs off. The cause for this disorder is unknown. Decreased blood flow to the bowel might keep the bowel from producing the normal protective mucus. Bacteria in the intestine also might be a causative factor. The nurse should plan to administer betamethasone IM, a glucocorticoid, to stimulate fetal lung maturity and thereby prevent respiratory depression. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 27 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 07, 2021
Number of pages
27
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 07, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
108