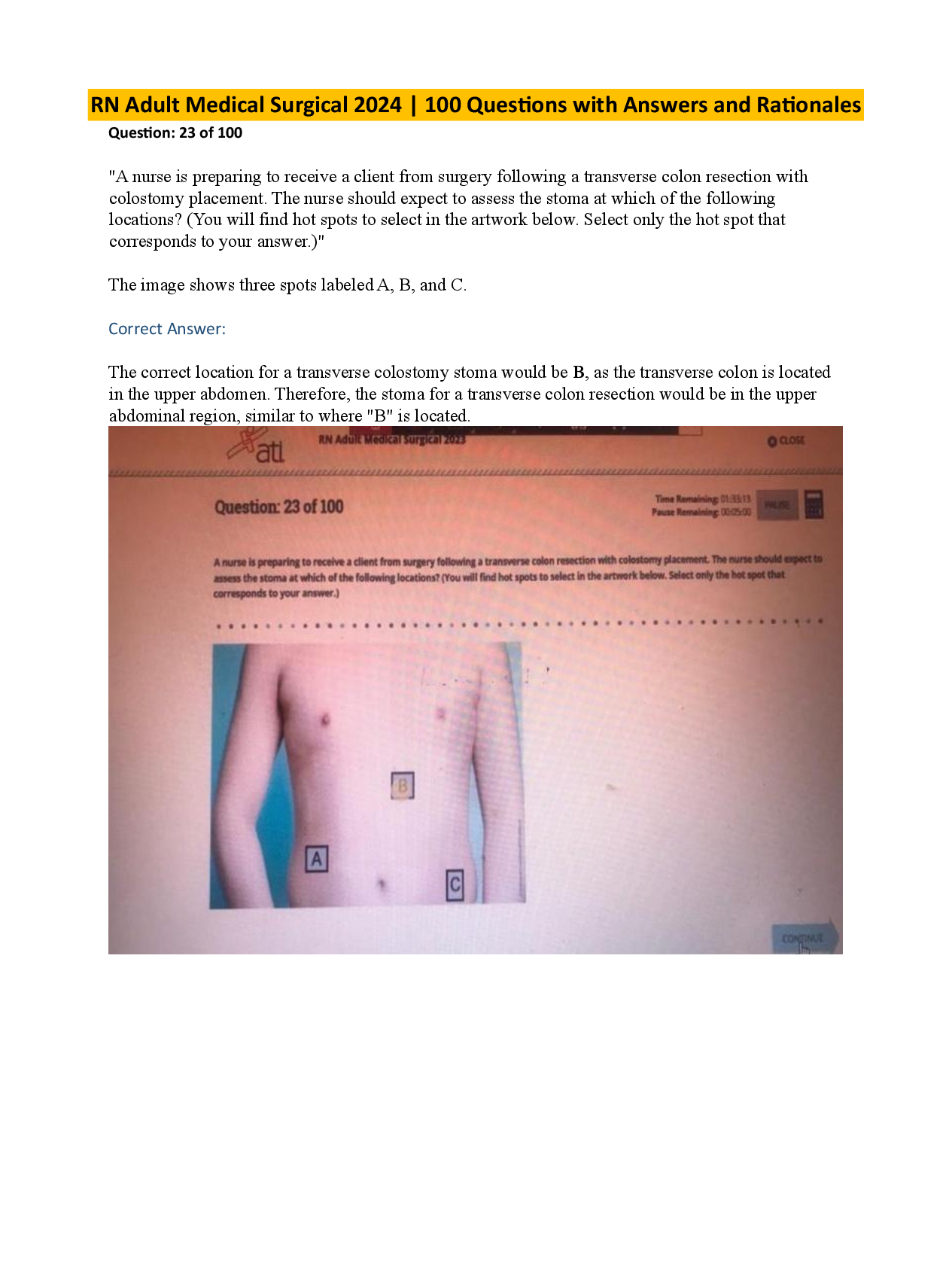
Adventis FMC Level 1 Exam Complete Solutions | Already Passed| Verified
Document Content and Description Below
financial statement communicates what? - ✔✔- financial condition - results of operations - various other activities of an organization how board of directors use financial data... - ✔✔- hol ... d management accountable - make board-level decisions about corporate strategy how company management uses financial data... - ✔✔- measure performance - make strategic, operating and financial decisions how creditors use financial data... - ✔✔- measure creditworthiness - liquidity - bankruptcy risk how investors use financial data... - ✔✔make decisions on buying/selling equity investments how acquirers use financial data... - ✔✔- determine valuation - make investment decisionshow regulators use financial data... - ✔✔determine whether company is operating according to regulations/law what does the income statement present? - ✔✔results of operations over a period of time what is the purpose of the income statement? - ✔✔to show whether the company made or lost money during the period reported what does the income statement indicate? - ✔✔how revenues are translated into net income through subtracting expenses revenue (sales) - ✔✔amount charged for the delivery of goods or services cost of sales (cogs) - ✔✔- direct cost of producing revenue - Ex: raw materials, direct wages, etc. gross profit - ✔✔- revenue - cogs - indicates how efficiently labor and materials are used in the production process operating expenses - ✔✔- all other expenses required to run a business - Ex: management salaries, marketing, travel, etc. operating income (EBIT) - ✔✔- revenue - cogs - operating expenses- indicates a company's earning power from ongoing operations non-operating expenses - ✔✔- expenses not related to regular business of the company - Ex: interest expense, restructuring expense, etc. corporate taxes - ✔✔local and federal income taxes the company incurs net income (net earnings) - ✔✔- revenue - cogs - operating expenses - non-operating expenses - taxes - indicates increase in shareholders' value resulting from operations what does the balance sheet show? - ✔✔an organization's financial position at a particular point in time what does the balance sheet disclose? - ✔✔- the resources an organization controls (assets) - the claims on those resources (liabilities and equity) what is the basic accounting equation? - ✔✔assets = liabilities + equity what is the basic accounting equation a foundation for? - ✔✔the double entry bookkeeping system what is the double entry bookkeeping system? - ✔✔there is a credit for every debit what does the accrual accounting method measure? - ✔✔the performance of a company regardless of when cash transaction occurcash - ✔✔current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately accounts receivable - ✔✔amount owed to an organization from the sale of a good or service fixed assets - ✔✔- value of assets and property that can't be easily converted to cash - has a useful life of greater than 1 year - Ex: PPE accounts payable - ✔✔amount owed to an organization's vendors debt - ✔✔amount of obligations owed to creditors equity - ✔✔cumulative shareholder investment + cumulative net income what is working capital a measure of? - ✔✔- a company's efficiency - short term financial health working capital equation - ✔✔non-cash current assets - non-debt current liabilities what does a positive or negative working capital indicate? - ✔✔whether it's a source or use of cashwhat can happen if a company's non-cash current assets < non-debt current liabilities? - ✔✔may run into challenges repaying creditors and suppliers in the short run non-cash current assets - ✔✔- non-cash assets expected to be turned into cash within one year - Ex: accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid expenses, other assets non-debt current liabilities - ✔✔- all obligations besides short-term debt that are due within one year - Ex: accounts payable, accrued liabilities, other obligations what is a less expensive form of capital? - ✔✔debt because it's less risky what types of claims to debt owners have? - ✔✔priority claims on company's assets if company goes bankrupt what is a more expensive form of capital? - ✔✔equity because equity holders aren't guaranteed to get their investment back if the company goes bankrupt what requires a higher rate of return, debt or equity? - ✔✔equity net debt - ✔✔total debt - cash what is net debt primarily used in? - ✔✔credit analysis because creditors assume that the company's cash balance could be applied to debt repayment in the event of a liquidity crunch or bankruptcywhat does the cash flow statement show? - ✔✔- how much cash is generated or lost during a period of time - how changes in the balance sheet and net income affect cash what does the cash flow statement reconcile? - ✔✔net income to change in cash what is the cash flow statement useful for in determining - ✔✔- a company's viability; it's ability to pay bills - liquidity cash from operating activities - ✔✔- cash generated by a company's normal business operations - Ex: net earnings, depreciation and amortization, change in working capital cash from investing activities - ✔✔- acquisition and disposal of long-term investments (PPE and M&A) - Ex: capital expenditures, acquisitions cash from financing activities - ✔✔- cash flow between organization and its owners and creditors - Ex: debt/equity issuances (change in debt), dividends, share repurchases beginning cash balance - ✔✔ending cash balance for previous period of time change in cash - ✔✔sum of cash from operating, investing, and financing activitiesending cash balance - ✔✔sum of beginning cash balance and change in cash depreciation and amortization - ✔✔method of allocating the cost of an asset over its useful life for both accounting and tax purposes how is depreciation and amortization shown on the income statement? - ✔✔as an expense why doesn't depreciation and amortization represent a decrease in cash? - ✔✔it doesn't represent a decrease in cash because cash only leaves the company during the initial purchase of the asset (CapEx) what does depreciation and amortization represent in terms of cash on the cash flow statement? - ✔✔a source of cash capital expenditures (CapEx) - ✔✔funds used by a company to purchase/upgrade physical assets (PPE) what does CapEx represent in terms of cash on the cash flow statement? - ✔✔a use of cash what does a decrease in working capital represent? - ✔✔a source of cash what does an increase in working capital represent? - ✔✔a use of cash share repurchase - ✔✔re-acquisition of an organization's own stock2 paths for share repurchases - ✔✔1. organization retires the stock 2. keep them as treasury stock what happens to the ownership percentage and portion of earnings for shareholders when shares are repurchased? - ✔✔they increase what are share repurchases a form of? - ✔✔returning capital to shareholders irregularly as opposed to a regular dividend program dividends - ✔✔distribution of cash how are dividends most often derived? - ✔✔from a dividend per share amount as directed by the board of directors what is the difference between share repurchases and dividends? - ✔✔- dividends don't affect ownership percentages - represent a pure check to shareholders what are sticky dividends? - ✔✔companies choose to have a dividend program where dividends are constantly distributed to shareholders how can removing a sticky dividend program affect the company? - ✔✔it can show signs of trouble for the companychange in debt - ✔✔represents any debt issuances or repayments EBITDA - ✔✔- gives an indication of a company's current operational profitability - one of most commonly used metrics why is EBITDA widely used when assessing the performance of a company? - ✔✔it allows for comparison of profitability between companies in a wide range of industries what does EBITDA exclude? - ✔✔- affects from different forms of financing - different political and tax jurisdictions - different rules surrounding depreciation and amortization free cash flow - ✔✔- see what cash is available for distribution to creditors and shareholders - ONE OF MORE IMPORTANT METRICS TO USE FOR VALUATION free cash flow equation - ✔✔cash flow from operations - CapEx financial ratios - ✔✔useful indicators of a firm's performance and financial situation what is the starting point for financial ratios? - ✔✔past ratios in order to forecast into the future how can financial ratios be expressed? - ✔✔- decimal - percentage- multiple (x) liquidity ratios - ✔✔indicate a company's ability to meet its short-term financial obligations who cares about liquidity ratios? - ✔✔those extending short-term credit such as banks 2 liquidity ratios - ✔✔1. current ratio 2. cash ratio current ratio - ✔✔indicates whether a company's short-term assets are readily available to pay off short-term liabilities current ratio formula - ✔✔current assets / current liabilities normal current ratio - ✔✔between 1.50-3.00 cash ratio - ✔✔indicates a company's ability to use cash to pay of its current liabilities cash ratio formula - ✔✔cash / current liabilities normal cash ratio - ✔✔between 0.20-1.00 efficiency ratios - ✔✔indicate how effectively a company utilizes its assets2 efficiency ratios - ✔✔1. days receivable 2. asset turnover days receivable ratio - ✔✔average number of days an invoice is in accounts receivable before collection days receivable ratio formula - ✔✔accounts receivable / revenue X 365 days receivable ratio of 60 means... - ✔✔company's invoices on average are paid down in 60 days asset turnover ratio - ✔✔- amount of revenues generated per dollar of assets - measures company's efficiency in turning assets into revenue asset turnover ratio formula - ✔✔revenue / assets asset turnover ratio of 2.5 means... - ✔✔for every dollar of assets, a company earns $2.5 of revenue profitability ratios - ✔✔profits made by company relative to its assets, equity, or revenue (metrics) what do profitability ratio metrics tell us? - ✔✔1. outperformance vs peers 2. opportunities for improvementgross margin ratio - ✔✔relative to revenue, indicates how efficiently labor and supplies are used in production process gross margin ratio formula - ✔✔gross profit / revenue what does a gross margin ratio of 35% mean... - ✔✔for every one dollar of revenue, $0.35 is converted into gross profit operating margin ratio - ✔✔relative to revenue, indicates a company's earning power from ongoing operations operating margin ratio formula - ✔✔operating income / revenue operating margin ratio of 15% means... - ✔✔for every $1 of revenue, $0.15 is converted to operating profit net margin ratio - ✔✔relative to revenue, indicates the increase in shareholders' equity from earnings net margin ratio formula - ✔✔net income / revenue net margin ratio of 10% means... - ✔✔for every $1 of revenue, $0.10 us converted to net income return on equity ratio - ✔✔measures profits earned for each dollar invested in a company's equi [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 4 out of 16 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 18, 2024
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 18, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
21