NUR 397 Pancreatitis/Pancreatic Disorders Exam | Answered with Rationales
Document Content and Description Below
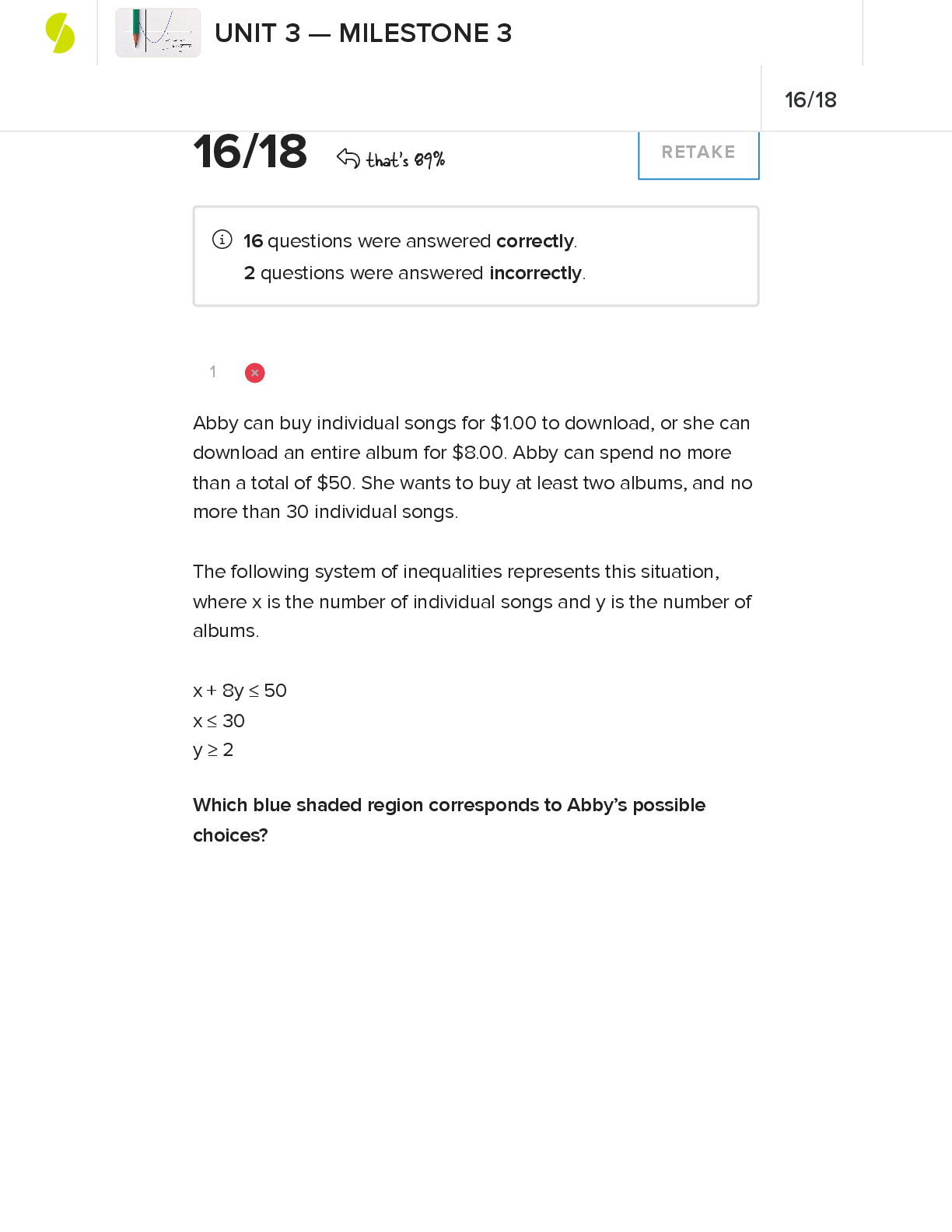
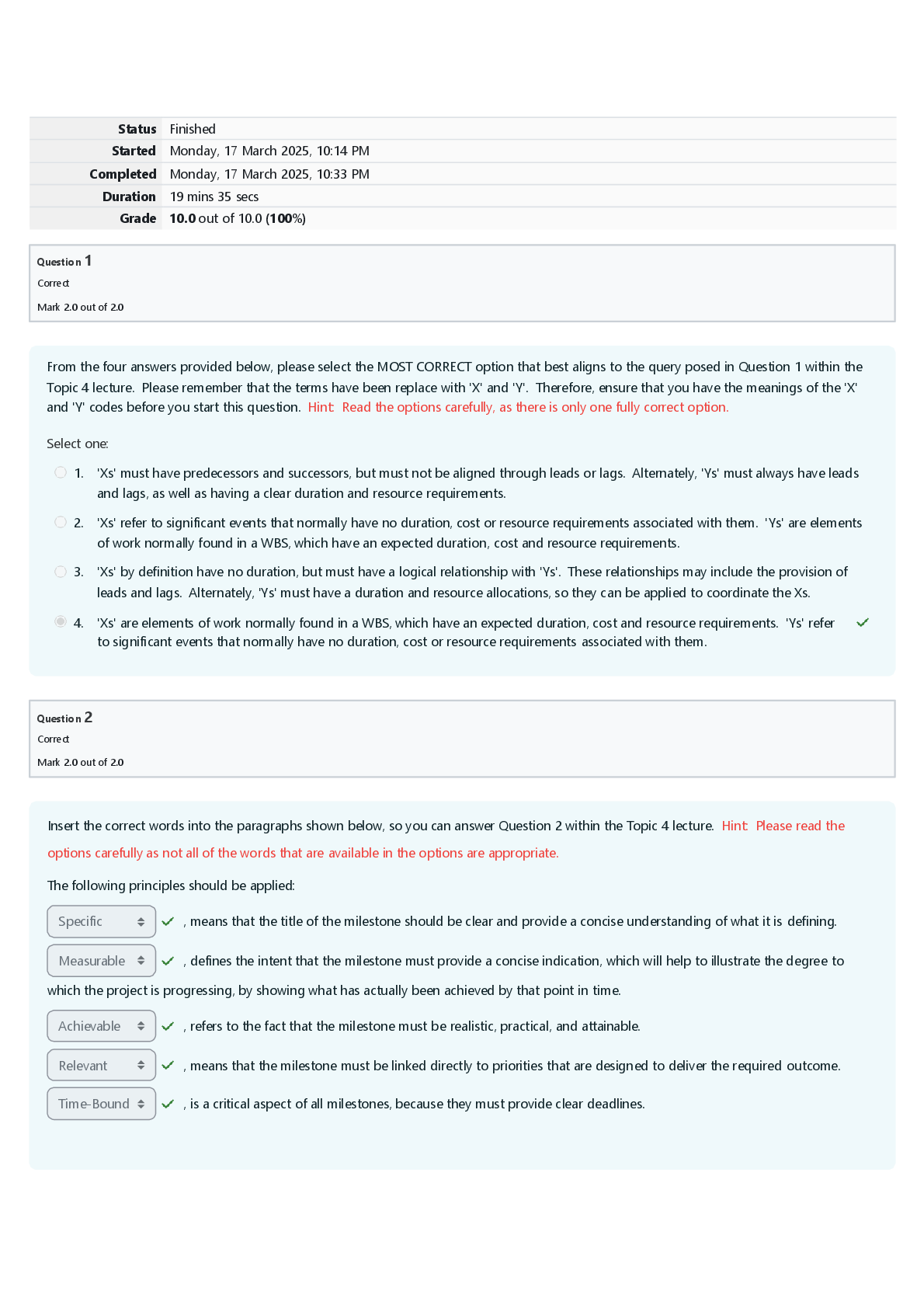
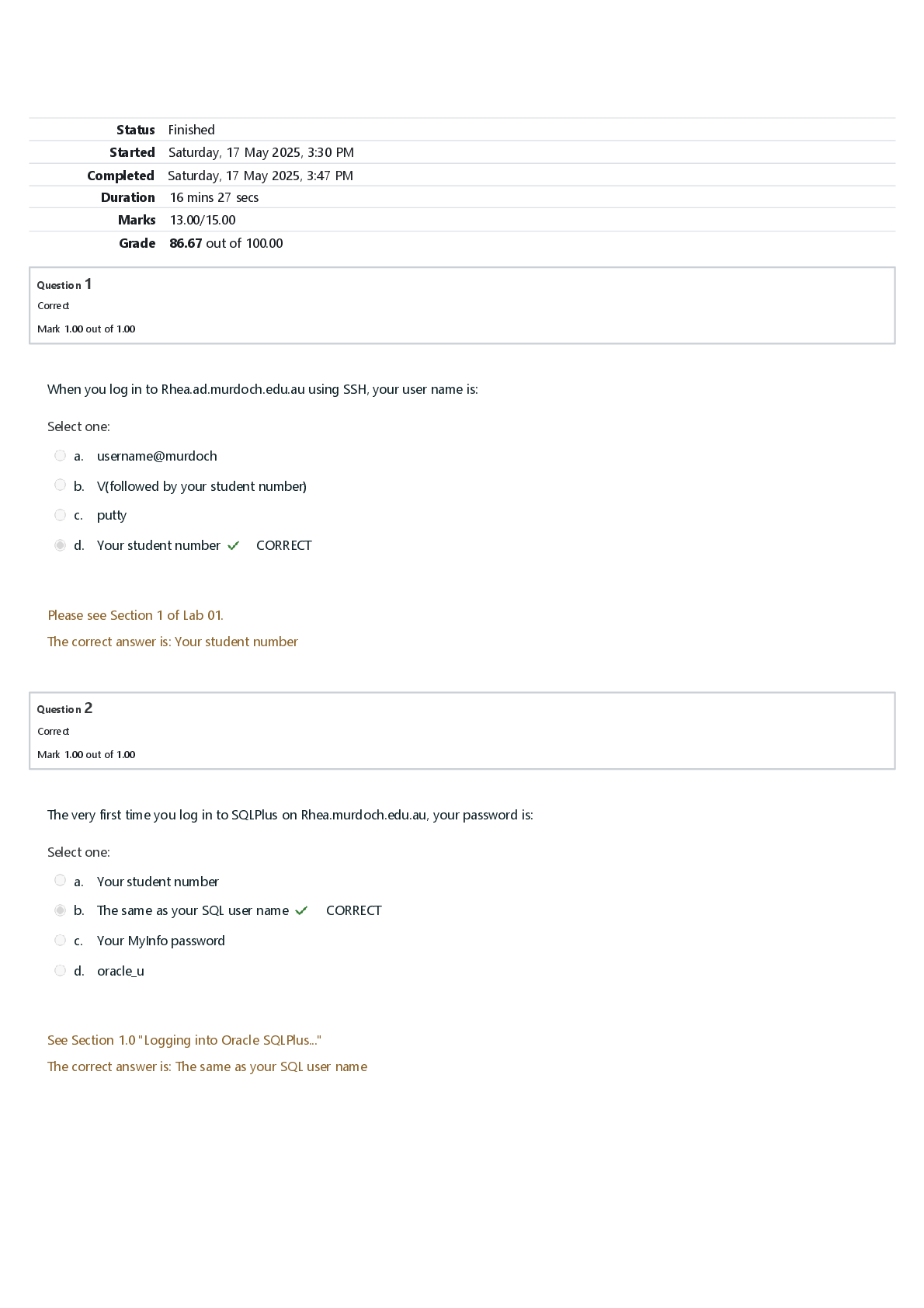
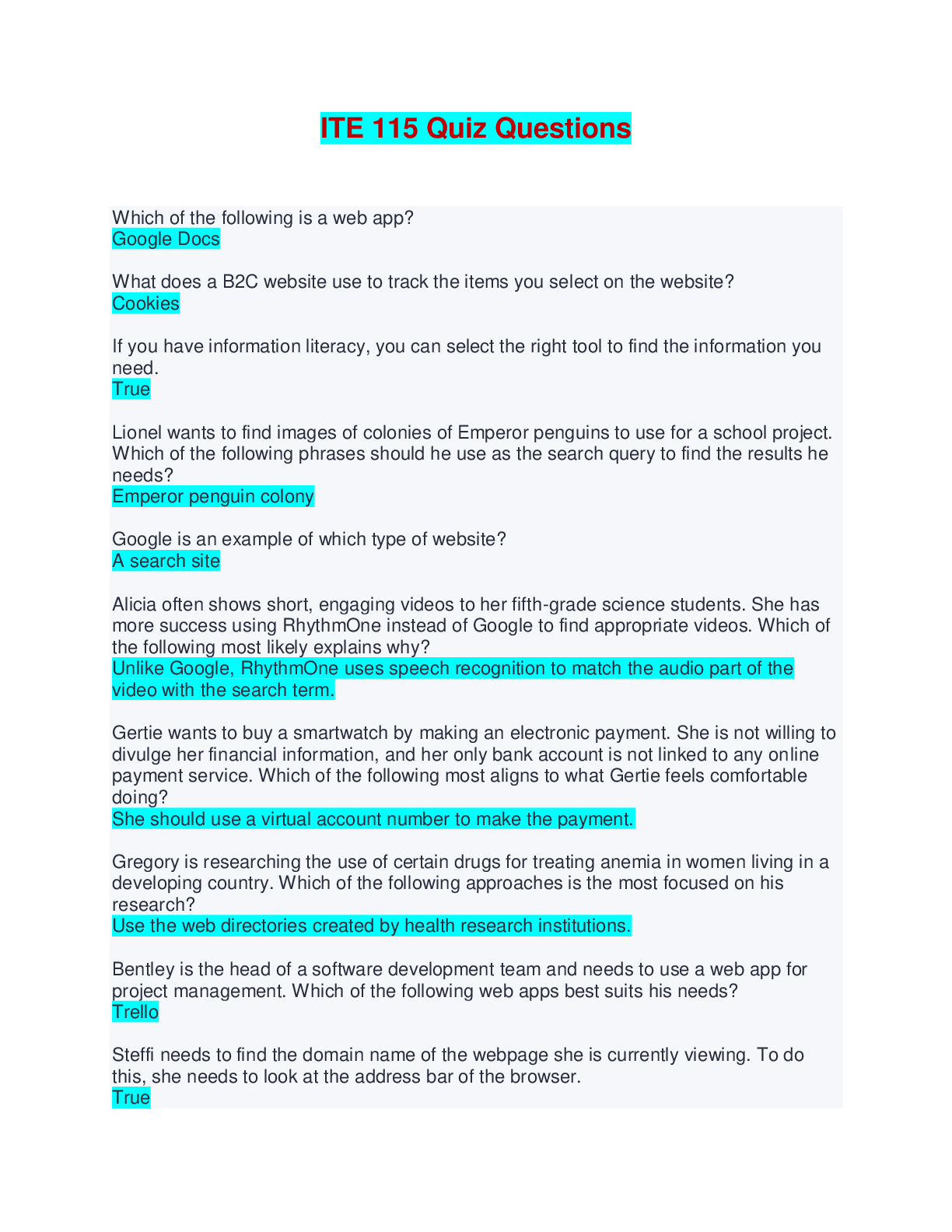
NUR 397 Pancreatitis/Pancreatic Disorders Exam | Answered with Rationales The nurse is caring for a patient who has been admitted multiple times for pancreatitis. The patient has inflammation and f... ibrosis of the tissue and diminished pancreatic function. Which assessment finding is priority for this patient? alcohol consumption Rationale The patient who undergoes a microdiskectomy typically can return home the same day. The patient who undergoes a traditional open laminectomy typically can return home 48 hours after the procedure, will have a drain in place after the procedure, and will need to wear special stockings after the procedure The nurse is providing teaching about pancreatic enzyme replacement to a patient diagnosed with chronic pancreatitis. Which statement by the patient indicates the need for further teaching? I will take the pancreatic enzyme half an hour before meals. Which scan will provide the most reliable diagnosis of acute pancreatitis? contrast enhanced CT Rationale Contrast-enhanced CT provides more reliable images and diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. A chest x-ray will show elevation but is not diagnostic. An abdominal ultrasound is not helpful to view the whole pancreas. An ERCP is better for diagnosing pancreatic stones, not acute pancreatitis. A patient reports severe mid-epigastric pain radiating to the left flank and back. The nurse notes generalized jaundice and a gray-blue discoloration of the patient's abdomen and periumbilical area. The nurse suspects which cause of acute pain in this patient? pancreatitis Rationale Patients with acute pancreatitis will have severe mid-epigastric pain that radiates to the left side and back and may have generalized jaundice and a gray-blue discoloration caused by pancreatic enzyme leakage into the cutaneous tissue. Biliary colic and cholecystitis will present with right-sided abdominal pain. Patients with gastroenteritis will have generalized discomfort. A patient is diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. Which test is a sensitive indicator of biliary obstruction in this disorder? serum alanine aminotransferase Rationale Serum alanine aminotransferase is a sensitive indicator of biliary obstruction in acute pancreatitis. A threefold or greater rise in concentration indicates that the diagnosis of acute biliary pancreatitis is valid. Serum bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, and serum amylase are diagnostic tests prescribed for a patient with acute pancreatitis but do not reflect biliary obstruction. Which enzyme is involved in enzymatic fat necrosis of the endocrine and exocrine cells of the pancreas? Lipase Rationale The lipase enzyme is involved in enzymatic fat necrosis of both the endocrine and exocrine cells of the pancreas. Trypsin activates elastase, which dissolves the elastic fibers of the blood vessels and ducts. Kallikrein releases vasoactive peptides, bradykinin, and a plasma kinin known as kallidin. Which symptom of chronic pancreatitis also occurs with acute pancreatitis? abdominal pain Rationale Abdominal pain occurs with both types of pancreatitis, though pain intensity does vary between the two. Ascites, loss of exocrine function, and protein malabsorption occur only with chronic pancreatitis. Which assessment finding would the nurse monitor to evaluate the effectiveness of pancreatic enzyme therapy? Consistency and number of stools. Rationale If the pancreatic enzymes are effective, the patient should have less frequent, less fatty stools. Blood glucose monitoring is performed when patients receive total parenteral nutrition. Urine output does not indicate effectiveness of pancreatic enzyme therapy. Monitoring weight is necessary for patients who have fat and protein malabsorption. Which enzyme is responsible for the release of vasoactive peptides, bradykinin, and a plasma kinin? Kallikrein Rationale Kallikrein releases vasoactive peptides, bradykinin, and a plasma kinin known as kallidin. These substances cause vasodilation and increased vascular permeability, compounding the hemorrhagic process. Lipase enzyme is involved in enzymatic fat necrosis. Trypsin activates elastase, which dissolves elastic fibers of the blood vessels and ducts. Which condition is the primary risk factor for chronic calcifying pancreatitis? alcoholism Rationale Alcoholism is the primary risk factor for chronic calcifying pancreatitis. Cholecystitis is a risk factor for chronic obstructive pancreatitis. Metabolic disturbances and viral infection are risk factors for acute pancreatitis, not chronic calcifying pancreatitis. Which complication is common for a patient with pancreatic cancer to develop? venous emboli Rationale The patient with pancreatic cancer is at a higher risk for developing venous emboli. This occurs because necrotic products of the pancreatic tumor have thromboplastic properties which, in turn, cause a hypercoagulable state. Decreased mobility and extensive surgical manipulation are also responsible for this infection. Dyspepsia (indigestion) and eructation (belching) are not common complications associated with pancreatic cancer. In the health record of a patient newly diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, which clue would the nurse consider a risk factor? smoking Rationale Cigarette smoking is a major risk factor for the development of pancreatic cancer. Hepatitis can cause liver cancer. Malnutrition can weaken the immune system. A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk for heart disease. The nurse is caring for a patient with acute pancreatitis. The patient is reporting shortness of breath and orthopnea. The patient's vital signs are blood pressure 140/80, pulse 110, O2 90% on room air, and temperature 99.8*F. Which complication does the nurse suspect? pleural effusion The nurse is caring for a patient diagnosed with acute pancreatitis who has had increased pain and guarding along with these vital signs: blood pressure 108/60 mm Hg, pulse 125 beats/min, temperature of 103.8°F (39.8°C), and an oxygen (O 2) saturation of 95% on 2 L via nasal cannula. The nurse suspects the patient has a pancreatic abscess. After contacting the health care provider, the nurse would perform which intervention first? prepare the patient for pancreatic drainage Rationale Pancreatic drainage needs to be performed as soon as possible to prevent sepsis. Reassessing vital signs should be done after the patient is prepared for drainage. Placing the patient in a supine position is not indicated. After ensuring everything is in order for the health care provider, acetaminophen may be administered, but it is not the priority. The patient presents to the ED with severe abdominal pain. The nurse is reviewing the patient's laboratory results. Which laboratory finding would prompt the nurse to suspect a diagnosis of acute pancreatitis? (select all that apply) increased serum amylase decreased serum calcium increased alanine aminotransferase A patient who has acute pancreatitis is prescribed famotidine. The nurse explains that this drug is given for which purpose? To decrease gastric acid secretion that often occurs with pancreatitis. The nurse is caring for a patient recently diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus who has had an episode of acute pancreatitis. The patient asks the nurse how he developed diabetes when the disease does not run in the family. Which response by the nurse is best? Type 1 diabetes can occur when the pancreas is destroyed by disease. As part of the pathophysiologic process during acute pancreatitis proteolysis results in which effect? Thrombosis and gangrene of the pancreas. Which condition is indicated by an elevate serum lipase level? pancreatic cell injury Which dietary suggestion is indicated for a patient who is in the healing phase after acute pancreatitis? (select all that apply) bland foods low-fat foods small, frequent meals A patient with history of chronic pancreatitis presents with the left upper quadrant pain, fever, and a palpable mass. A diagnosis of pancreatic abscess is made. Which intervention is most likely to promote a positive patient outcome? Placement of a percutaneous drain in the pancreatic abscess. Rationale Patients who have a pancreatic abscess will appear ill, have an elevated temperature, and have a high risk for fatality without aggressive treatment. Drainage via the percutaneous drainage method or laparoscopy should be performed as soon as possible to prevent sepsis. An ultrasound does not distinguish between an abscess and a pseudocyst, so it is not helpful in this scenario. Antibiotics are indicated, but antibiotic therapy alone does not resolve the abscess. Blood cultures should be obtained to identify the infectious organism, rather than serum electrolytes and a complete blood count. The patient recently diagnosed with acute pancreatitis reports severe pain despite IV narcotic pain medication. Into which position would the nurse assist the patient to help decrease pain? side lying Rationale The side-lying position may decrease the abdominal pain of pancreatitis. Prone, supine, and high-Fowler positions are not indicated to decrease pain in pancreatitis. The nurse is assessing a patient a patient the ED. Which assessment finding would prompt the nurse to suspect a pancreatic pseudocyst? (select all that apply) Jaundice palpable epigastric mass epigastric pain radiating to the back Rationale Patients with a pancreatic pseudocyst often have jaundice, a palpable epigastric mass, and epigastric pain that radiates to the back. Steatorrhea and odynophagia are not common findings of a pancreatic pseudocyst. Which medication is administered to a patient with acute pancreatitis to decrease gastric acid secretion? (select all that apply) Ranitidine pantoprazole Rationale Ranitidine is a histamine receptor antagonist, and pantoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor. Both medications help decrease gastric acid secretion. Imipenem and ciprofloxacin are antibiotics. Meperidine is an opiate analgesic. When performing an abdominal assessment on a patient diagnosed with pancreatitis, the nurse notes gray-blue discoloration around the periumbilical area, a dull sound on percussion, and normal bowel sounds. Which action by the nurse is priority? Document the findings. Rationale A blue discoloration around the periumbilical area is a normal finding in a patient with acute pancreatitis. A dull sound on percussion may be caused from pancreatic ascites. The findings should be documented. The patient does not need to go to the operating room. The health care provider does not need to be contacted immediately. Checking the hemoglobin and hematocrit level is not indicated. A patient with chronic pancreatitis has developed a pseudocyst that has not resolved after 8 weeks, and the health care provider plans a percutaneous drainage procedure. The patient asks the nurse why this is necessary as it does not seem to be causing problems. Which complication does the nurse explain the procedure will prevent? hemorrhage Rationale Pseudocysts may resolve spontaneously or may rupture and cause hemorrhage. Those that have not resolved after 6 to 8 weeks should be drained. The patient would have symptoms of infection, such as fever and malaise, if abscess or infection were present. Steatorrhea (fatty stool) is not a complication of pseudocyst. Which nursing assessment is priority for a patient with severe acute pancreatitis? Perfusion and other signs of shock. The nurse is reviewing the laboratory results for a patient with acute pancreatitis. Which finding does the nurse expect to find in the report? (select all that apply) Decrease in albumin level. Increase in serum glucose level. Increase in BUN. Rationale Acute pancreatitis occurs because of a premature activation of excessive pancreatic enzymes, which destroy ductal tissue and pancreatic cells. It results in autodigestion and fibrosis of the pancreas. In acute pancreatitis, the albumin level is decreased because fluid shifts into the peritoneal cavity. This occurs as a result of the inflammatory process in the pancreas. The serum glucose level is elevated because of the pancreatic injury. The BUN is increased because of dehydration. The platelet count is decreased because of inflammation of the biliary tract, including the spleen. Triglycerides are increased because of changes in fat metabolism. The nurse is preparing to administer the prescribed does of pancrelipase to a patient with chronic pancreatitis. Which pancreatic enzyme makes up this medication? (select all that apply) Lipase amylase protease Rationale Pancrelipase provides the enzymes that the body is unable to produce because of chronic pancreatitis. It is a combination of the enzymes lipase, amylase, and protease in different concentrations. It does not contain trypsin and elastase. Which symptom presents in a patient with acute pancreatitis and indicates complications? (select all that apply) Jaundice darkened urine clay colored stools Rationale Acute pancreatitis occurs because of an inflammation of the pancreas. The enzymes released by the pancreas cause autolysis of the pancreatic tissue. Jaundice, darkened urine, and clay-colored stools indicate complications of acute pancreatitis. Jaundice occurs because of an obstruction in the biliary tract, where bile cannot be absorbed into the GI tract. Bile salts accumulate in the skin, causing a yellowish discoloration. An increase in serum bilirubin because of the biliary obstruction causes darkened urine. Stools become clay-colored because of an obstruction in the biliary tract. Vertigo and depression are not symptoms of acute pancreatitis. Which factor increases the risk for developing pancreatic cancer? (select all that apply) Cirrhosis smoking chronic pancreatitis Rationale Pancreatic cancer is an abnormal growth in the pancreas. Cirrhosis, cigarette smoking, and chronic pancreatitis cause chronic irritation of the pancreatic tissue, increasing the risk for pancreatic cancer. Aging and vitamin deficiencies are not risk factors associated with pancreatic cancer. The nurse is caring for a patient with chronic pancreatitis. Which assessment finding is related to this disease process? (select all that apply) Jaundice Polydipsia Polyphagia Rationale Rationale Jaundice, polydipsia, and polyphagia are manifestations observed in chronic pancreatitis. Jaundice occurs because of chronic inflammation in the biliary tract; bile cannot drain into the small intestines. Excessive thirst (polydipsia) and an increased appetite (polyphagia) occur because the patient has chronic organ dysfunction and develops diabetes mellitus (of which both symptoms are common). Diarrhea is not a symptom of chronic pancreatitis. Weight loss occurs in chronic pancreatitis. Which possible complication of chronic pancreatitis presents as a painful, palpable mass in the left upper quadrant? abscess or pseudocyst A patient has been placed on enzyme replacement for treatment of chronic pancreatitis. In teaching the patient about this therapy, the nurse advises the patient not to mix enzyme preparations with foods containing which element? protein Which diet does the health care provider prescribe for a patient during the healing phase of acute pancreatitis? (select all that apply) high protein low fat meal high carbohydrates A patient with chronic pancreatitis has edema of the feet, legs, and hands. This is a sign of which problem associated with chronic pancreatitis? protein malabsorption The nurse suspects that a patient may have acute pancreatitis as evidence by which group of laboratory results? elevated lipase elevated WBC count elevated glucose A patient who has had acute mid-epigastric pain for 3 days has elevated glucose, bilirubin, serum lipase, and a threefold increase in alanine aminotransferase. The serum amylase is normal. Which possible cause for this patient's pain does the nurse suspect? It may be caused by acute biliary pancreatitis. [Show More]
Last updated: 8 months ago
Preview 4 out of 16 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 17, 2024
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 17, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
19